Cancer, treatment and research: India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
Breast cancer
Oestrogen receptor-positive (ER+)
Factor behind treatment failure uncovered/ 2025
Eshan Kalyanikar, February 13, 2025: The Times of India
Mumbai : After a decade of research, Indian scientists have used whole genome sequencing to uncover a key factor behind treatment failure in about 25% of patients with estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer, the most common subtypeof the disease.
India records more than 2 lakh breast cancer cases each year, with ER+ cases accounting for 50% to 60% of them. These tumours contain estro- gen receptors — proteins that bind to the hormone estrogen —which fuel cancer growth.
Patients with ER+ breast cancer are placed on hormone therapy for up to 10 years, using drugs like Tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors. These medications work by blocking the pathway that allows estrogen to bind to its receptor, effectively slowing or stopping tumour progression.
While this treatment has proven effective for many, some patients either do not respond leading to progression or relapse. The study helps explain why, identifying the culprits: three genetic mutations found in the tumour. One (PIK3CA) drives cancer growth, another (ESR1) makes it resistant to hormone therapy, and the third (TP53) weakens the tumour’s ability to repair itself, allowing it to grow unchecked. Professor Partha Majumdar, a renowned human geneticist and statistician from the Indian Statistical Institute in Kolkata and a key collaborator in the research, said resistance to treatment was traditionally attributed to mutations in ESR1 alone. However, the study shows that ESR1 mutates alongside either PIK3CA or TP53 in order to develop resistance.
The findings could have far-reaching implications, potentially improving survival rates for thousands of women undergoing treatment for ER+ breast cancer. “When patients saw others being cured while they faced a relapse, they often asked why the same treatment failed for them. We had no clear answer — until now,” said Tata Memorial Hospital director Dr Sudip Gupta. “This research brings us closer to identifying highrisk patients early and tailoring their treatment accordingly,” he added.
The full impact of these findings remains a question for the future, dependent on government funding for clinical trials that will shape potential treatment interventions. In diagnostics, doctors can now turn to targeted sequencing — focusing on three specific genes — rather than whole genome sequencing used for the study as it generates an immense dataset of four billion characters.
Preparedness
In India and the world/ 2018
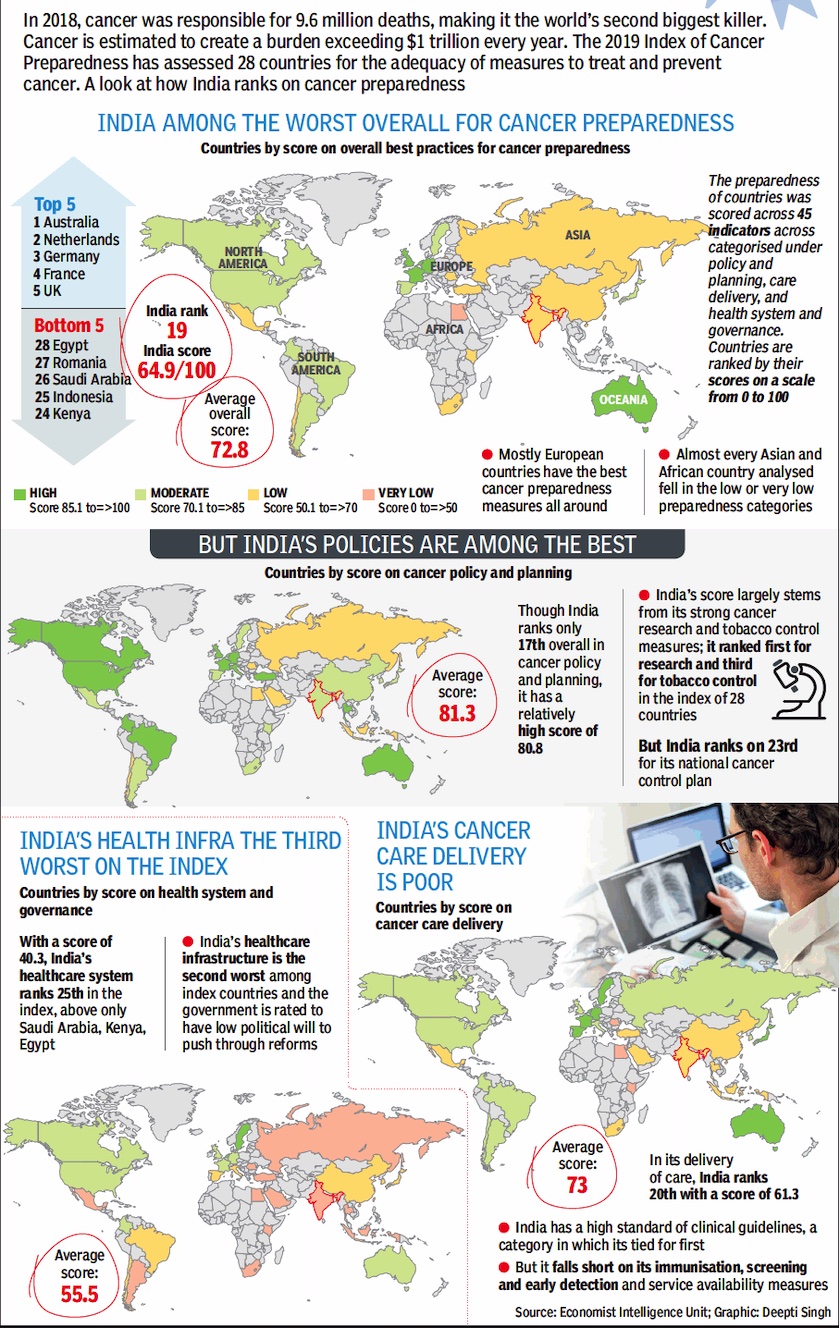
From: April 20, 2019: The Times of India
See graphic :
Cancer preparedness in India and the world/ 2018
Research
2019/ JNCASR model helps study bone marrow, blood disorders
Chethan Kumar, April 13, 2019: The Times of India
A group of Indian researchers has created a mouse model to study bone marrow and blood disorders that could aid in finding a cure for blood cancer (leukaemia).
The team, led by Maneesha S Inamdar at Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR), has published its findings in ‘Blood’, a journal of the American Society of Haematology.
Inamdar, whose lab has discovered a stem cell protein called asrij (blood in Sanskrit), has found it plays a key role in preventing myelo-proliferative disease — a condition characterised by excessive production of mature blood cells.
Producing new blood cells is a lifelong activity. Given the sheer number of cells, they are prone to mutation which then becomes cancerous.
90% cancers caused by p53 mutation
Now, 90% of solid cancers are known to be caused by the mutation of p53, a protein that regulates cells production. In case of blood cancer, only 11% of the cancer was seen to be caused by p53 mutation. “Despite no significant mutation of p53, we found levels of asrij were low, causing uncontrolled production of new cells,” Inamdar told TOI.
Saloni Sinha, first author of the paper, said asrij protects p53, a cancer-preventing protein also known as the ‘Guardian of the Genome’. “Without asrij, p53 is destroyed and blood stem cells proliferate and become cancerous. It is known that mutations in p53 lead to cancer. However, scientists have been puzzled about how some cancers develop without a mutation in p53. Our work explains how this can happen,” Saloni said.
Will lead to new diagnostics
Inamdar said this could pave the way to new diagnostics and lead to the cure. To study how asrij works, the team designed a mouse that is engineered to mark the asrij gene for deletion. This was done in collaboration with the RIKEN CDB, Kobe, Japan and the National Centre for Biological Sciences, Bengaluru.
The Inamdar laboratory then deleted the marked region and showed that deleting one or both copies of the gene has no apparent effect, which was perplexing. Based on their earlier work, they predicted the mice are likely to develop blood cancer.
“Detailed experiments, including bone marrow transplants in mice, showed the mutants had too many blood stem cells, an enlarged spleen and developed severe myeloproliferative disease as they aged, just like human patients. The study could potentially revolutionise research seeking to find the origin and clinical progression of blood and other cancers. It will also lead to a search for drug treatments for a wide range of diseases affected by asrij and p53, including cancers and neuro-degenerative disorders,” said Inamdar.
CAR-T cells
Oct 23, 2022: The Times of India
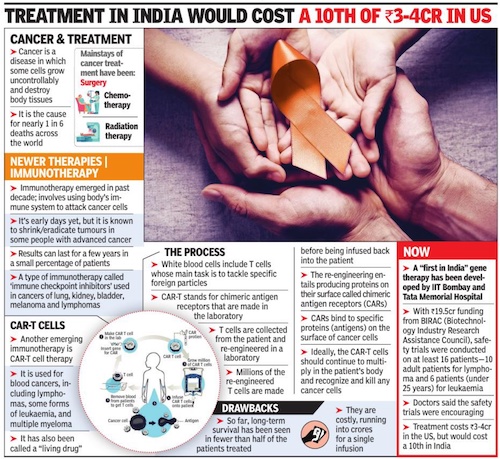
From: Oct 23, 2022: The Times of India
The safety trials for India’s first indigenously made CAR-T cells are a joint effort between IIT-Bombay and Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai (the first patient was infused on June 6, 2021). This made-in-India therapy’s price tag will be a 10th of its cost in the US, said IIT-B scientist Rahul Purwar who is driving the project.
Last month, the group announced “encouraging” results of the Phase 1 trial for 10 patients with lymphoma. Last week, (Surg Cdr) Gaurav Narula from TMC announced similar results for the safety trial for six patients of leukemia at a medical conference in Kochi. “For a group of patients who had no known options, these were very encouraging results and in line with published data ofother CAR-T products in other parts of the world,” said Narula. Each of these patients had received three to five lines of therapy, including previous stem cell transplant, but in vain.
TMC deputy director Navin Khattry said although “it’s early days yet” with CAR-T cells, the Indian product has proved to be safe. “We found it has low toxicity as compared to the western CAR-T cells. For instance, 33% of the western patients develop some level of neurological toxicity, but this wasn’t seen in our patients. Moreover, none of our patients developed cytokine storms (when the body’s immune system responds too aggressively to infection),” said Khattry.
Another eight-year-old boy who underwent CAR-T infusion over six months back is also cancer-free at the moment. Only one of the six patients didn’t have any response to CAR-T cells. Another patient, who responded well initially, passed away 16 months later after undergoing abone marrow transplant.
Doctors hope the 8-yearold girl and other patients in the future have the same response as American youngster Emily Whitehead, who was the first patient in the world to undergo CAR-T cell therapy 10 years back. She didn’t need any therapy thereafter and has been cancer free since 2012.
According to the girl’s father, doctors first collected his daughter’s blood through a special process for collecting white blood cells.
Thereafter, her T cells were gathered from white blood cells and “trasduced” with a viral vector (tools used to deliver genetic material into cells). “This is done in order to get the T Cells to express certain antibody,” said Dr Narula.
These modified T Cells were then multiplied in the high-tech laboratory at IIT Bombay. A battery of tests was done to check for toxicity before it was given as a single infusion to the patient. “We were in ACTREC for 30 days and came back to Igatpuri,” said the father. She has go back for a checkup in early November.
As for the IIB-TMC team, it is preparing for the second phase of the clinical trial in which 50 patients will be given CAR-T cells. Purwar, who has since set up ImmunoACT Laboratory, said, “We are also working on gene therapy for various other cancers, including solid tumours,'” he said, adding that the goal is to make gene therapy affordable to many more Indians.
Homegrown CAR-T cells ‘cure’ 8-yr-old’s leukemia
Mumbai : Three months ago, an eight-year-old girl’s parents were told she had only a few more weeks to live as her leukemia had relapsed. Doctors at Tata Memorial Hospital, where she was under treatment since 2020, however, offered them an option: A homegrown version of a gene therapy that had shown promise in at least 50% of the patients it was used for in the West.
Her father, a driver in a village near Igatpuri, said there was no reason to turn down the new therapy as her condition was “bad” at that time. “CAR-T saved her,” he told TOI. When the family visitedACTREC, Tata Memorial Centre’s research block in Kharghar earlier in the week, doctors told them no cancer cells could be detected in the girl’s blood. “She is eating normally for the first time in two years,” he added. CAR-T cells are a new form of immunotherapy, itself a fledgling branch of cancertreatment. It entails re-engineering the body's T immune cells with some genetic material so that they selectively target cancer cells for destruction. The 8-year-old got the treatment as part of the safety trials for India’s first indigenously made CAR-T cells.
Spread of cancer: prevention
2024 research by Tata Memorial Centre
Malathy Iyer, Feb 27, 2024: The Times of India

From: Malathy Iyer, Feb 27, 2024: The Times of India
Mumbai docs find way to curb risk of cancer spread
Mumbai : Doctors at Tata Memorial Centre say they’ve discovered a mechanism for cancer metastasis and developed nutraceutical therapy to minimise its risk. As per their decade-long research published in reputed journals, dying cancer cells release ‘chromosome fragments’ (chromatin), which, at times, fuse with healthy cells and cause new tumours, reports Malathy Iyer.
Anutraceutical is a food or food product that provides health benefits beyond basic nutrition, often due to its added bioactive compounds or medicinal properties.
Study reveals chemo, radiotherapy hazards
Although many patients are cured of cancer, our study uncovered a potential risk involved in current cancer treatment practices,” said Dr Indraneel Mittra, who led the research. While chemotherapy and radiotherapy kill primary tumour cells, they cause the dying cancer cells to release chromatins — called cfChPs — which could enter healthy cells elsewhere in the body through blood and “cause cancer there”, he said. Further tests on cfChPs revealed that a nutraceutical made from copper and a plant (grapes or berries) could neturalise them and reduce the risk of metastasis, said former TMC director Dr Rajendra Badwe, who was present at the press conference. TMC has tied up with a nutraceutical manufacturer to make the medicine — which could be prescribed as supportive treatment along with chemotherapy — available in June.
Cancer metastasis has been a topic of intrigue for centuries. “How does cancer spread? There are cases where the cancerous tumour has been removed with treatment, yet the patient dies,” said Dr Mittra. His team injected human breast cancer cells into mice. “We first treated the tumour that developed in the mice, biopsied the brain and found cfChPs of human cancer cells there,” said Dr Mittra. They conducted various research rounds using surgery, chemotherapy and radiation and found similar results. One arm of the study injected tumour-hit mice with the nutraceutical. “The brain biopsy of these mice revealed lower levels of CfChPs,” he said.
In the last few years, the doctors started studying the effect of the nutraceutical — called R-Cu as it is a combination of grape-extract resveratrol and copper — on humans. In a few patients with oral, blood, stomach and brain cancer, the doctors added R-Cu to the standard treatment with encouraging results.
“We used it in 20 blood cancer patients who developed painful ulcers in their mouths and oesophagus after bone marrow transplant,” said TMC deputy director Dr Navin Khattry. Patients who received R-Cu had fewer ulcers. Similar findings among stomach cancer patients were published in an indexed journal, Medical Oncology in November 2022,he said.
Oral cancer surgeon Dr Pankaj Chaturvedi, who tested the medicine in oral cancer patients, said, “Our findings conclude that relatively inexpensive nutraceuticals may be used as adjuncts to chemotherapy to reduce its toxicity.”
The doctors said their findings have important implications for cancer treatment policies. First, clinicians need to consider cfChPs as a potential cause of metastatic cancer spread, rather than metastasis being caused by migrating cancer cells. “Secondly, cancer treatment protocols may need to include agents that deactivate or destroy cfChPs,” said Dr Badwe.
Therapies
IIT-B’s immunotherapy using CAR T-cells
Yogita Rao, Dec 12, 2019 Times of India
In a breakthrough in research, IIT-Bombay scientists have developed technology to leverage a patient’s immune system to cure cancer. Such immunotherapy using CAR T-cells, a treatment for cancer, which costs Rs 3-4 crore in US, can be made available for Rs 15 lakh, if the technology is developed in the country.
Researchers made use of gene and cell therapies to reengineer immune cells to attack and kill cancer cells in the body. The treatment is less painful than surgery, chemotherapy or radiation, and is known to lower chances of a relapse. The therapy, which seems promising in the treatment of cancer, especially leukaemia, is currently not available in India. With the growing burden of cancer in the country, success in even a fraction of the patients using the technique will be remarkable, experts said.
Prof Rahul Purwar and his team of scientists from the institute’s Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering have conducted laboratory tests and hope to start clinical trials in collaboration with Dr Gaurav Narula from Tata Memorial Hospital next year, after getting permission from Drug Controller General of India.
T-cells (a type of white blood cell), an integral part of the immune system, can identify tumours and destroy them. But in advanced stages, the cancer cells adapt to the presence of T-cells and remain undetected. In the new approach in immunotherapy, called CAR (chimeric antigen receptors) T-cell therapy, the T-cell’s ability to detect and kill cancer cells is restored. CARs are protein that assist Tcells to recognise and attach to protein or antigen, present on cancer cells. These proteins help destroy cancer cells.
Treatment
Patients’ expenses in 2019
DurgeshNandan Jha, April 20, 2019: The Times of India
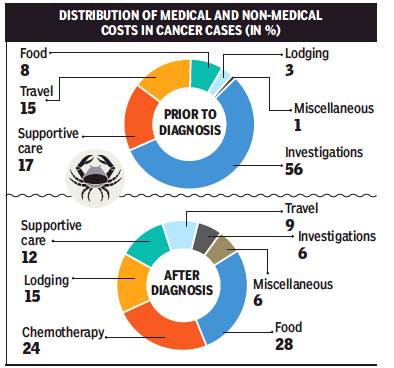
From: DurgeshNandan Jha, April 20, 2019: The Times of India
When it comes to the dreaded ‘C’, even the poorest of the families spend over Rs 50,000 towards treatment of their wards at public hospitals where consultation, surgery and key medicines are provided for free. This was revealed in a cost-analysis published in the journal, Psycho-Oncology.
Researchers from Australia’s McGill University, University of Sydney, University of Toronto and George Institute for Global Health, in partnership with CanKids, an NGO, interviewed 11 families of children being treated for cancer at AIIMS and Safdarjung Hospital.
Over half of the families’ primary income was generated from an unskilled-worker wage, and at least one parent per family was illiterate or had no formal schooling. Eight families were from outside the National Capital Region, according to the research paper.
In 14 weeks, a fortnight prior to the diagnosis and 12 weeks after the diagnosis of cancer, the families said they had spent Rs 51,644, on average. A maximum 53% of the money was spent on non-medical categories and 47% on medical needs.
Non-medical cost included travel, lodging, food and miscellaneous expenses. Medical cost involved chemotherapy, supportive care, surgery, radiation, investigations and transfusions. “The mean cost two weeks prior to the diagnosis was Rs 7,621 with 73% costs on medical and 27% on non-medical categories. The mean cost for 12 weeks following the diagnosis was Rs 44,023 with 42% on medical and 58% on non-medical categories,” the cost-analysis stated.
The researchers say, collectively, these costs are substantial, impose a catastrophic burden and impact employment, schooling and housing. “The study did not include the expenditures borne by the government in providing physician/nursing expertise, medications and investigations,” they added.
The researchers have called for hospital service providers to review their policies, procedures and service agreements to limit the financial burden imposed on families by encompassing a reasonable charge, consider families’ cost in the design of services, and ensure that provisions are in place to lower the economic burden.
A recent research published in the journal PlosOne found that out-of-pocket expenditure on cancer treatment was among the highest for any ailment.
The PlosOne research, conducted by experts from DU’s Institute of Economic Growth, which evaluated costs for all kinds of cancer, not just those involving children, said treatment for 40% of cancer hospitalisation cases is financed mainly through borrowings, sale of assets and contributions from friends and relatives.
The researchers suggested universal cancer care insurance, combined with existing accident and life insurance policies, for the poorer sections in India, in addition to policies to improve cancer survivorship through effective prevention and early detection.