All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Delhi
(→Medical accomplishments, milestones) |
(→Why AIIMS is the best) |
||
| Line 243: | Line 243: | ||
= Why AIIMS is the best = | = Why AIIMS is the best = | ||
| + | ==Its edge, as in 2016== | ||
[http://indiatoday.intoday.in/story/all-india-institute-of-medical-sciences-delhi-top-institutes-india/1/704307.html Damayanti Dutta , All-India institute of excellence “India Today” 11/7/2016] | [http://indiatoday.intoday.in/story/all-india-institute-of-medical-sciences-delhi-top-institutes-india/1/704307.html Damayanti Dutta , All-India institute of excellence “India Today” 11/7/2016] | ||
[[File: Edge over others , India Today , July 11,2016 .jpg| Edge over others , India Today , July 11,2016 |frame|500px]] | [[File: Edge over others , India Today , July 11,2016 .jpg| Edge over others , India Today , July 11,2016 |frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|A ALL INDIA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES (AIIMS), DELHI | ||
| + | ALL INDIA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES (AIIMS), DELHI]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Institutions|A ALL INDIA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES (AIIMS), DELHI | ||
| + | ALL INDIA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES (AIIMS), DELHI]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ALL INDIA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES (AIIMS), DELHI | ||
| + | ALL INDIA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES (AIIMS), DELHI]] | ||
Revision as of 13:55, 3 October 2021
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
Background
Source:
1. The Times of India, Dec 27 2014
2. India Today
The All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi was established by the AIIMS Act of 1956. AIIMS was created to serve as a nucleus for nurturing excellence in all aspects of health care.The institute has comprehensive facilities for teaching, research and patient-care. Teaching and research are conducted in 42 disciplines.
For a long time, it remained the only medical institute of its kind in the country providing super-speciality care at an affordable cost. The act was amended in 2012 and six new AIIMS were established at other locations. The waiting period for surgery in various departments of AIIMS, Delhi shows the immense burden of patients on the institute. There is obviously no waiting period for emergency cases, but for some other cases it can stretch up to five years
Bone bank, cadaveric
1999-2017: only 24 donations
Just 24 donations at AIIMS bone bank in 18 years, May 22, 2017: The Times of India
One of India's first cadaveric bone banks started in 1999 in AIIMS remains a nonstarter. Officials say the bank has received just 24 cadaver donations in last 18 years.
More so, there has been no donation in the last two years. The donated bones can be used for replacing a lost segment of bone due to cancer, infection or injury . Also, it can be used to fill up cavities or holes left by major cancer surgeries, Dr Rajesh Malhotra, chief of AIIMS Trauma Centre and who had started the bank, said.
He said lack of knowledge coupled with misconceptions and religious sentiments are major reasons behind the failure of the programme.“Even after being set up in 1999, the first bone donation was not until 2001,“ he added.
People think that taking out bones will mutilate and disfigure the body and the limbs will dangle, the AIIMS doctor said, adding that it's not the case.
Once the bones are taken out, the body is reconstructed and the shape and structure of the limbs are restored by putting wooden sticks and stuffing it up with cotton and wool. Even knee caps are made with cotton and wool.
“So, after taking out the bones, which usually takes 10 minutes, we spend the next 30 minutes on stitching up the body so that aesthetically it looks good and the dignity of the donor is maintained.
“ All that the relatives of the deceased will be able to see is a stitch that is visible after surgery ,“ Malhotra explained. The cotton wool also absorbs any fluids oozing out and the body is not left in a puddle of blood after the procedure. Bones from cadavers have to be retrieved within 12 hours. If a body is refrigerated, then the time frame extends up to 38 hours. They are then tested for HIV , hepatitis or other infection.
If this procedure is followed and the bones then stored at -70 degrees Celsius, these can be preserved for around five years, Malhotra said.
Thousands of cancer and trauma patients need bone transplants in India every year, while only 35% of them get these. Bones can be donated by people even when they are alive, he said.
Disciplinary issues
2017/ Nurses take leave, Emergency shuts for 1st time
HIGHLIGHTS
Only around 400 senior staffers out of 5,400 nurses at the hospital reported for duty
AIIMS administration claimed that they had tried to persuade the nurses not go on mass leave
For the first time in the premier institution's history, emergency and OT services were completely shut down at AIIMS on Friday as nurses went on mass casual leave to press for increased allowances in the seventh pay commission.
Only around 400 senior staffers out of 5,400 nurses at the hospital reported for duty even as hundreds of critically-ill patients were denied admission in view of the staff crunch.
All planned surgeries and minor procedures had to be cancelled, officials said. More than 200 surgeries take place at the institute daily. "On Friday, only emergency cases could be taken up for surgery. We sought the help of senior paramedical staff and students for that," a senior doctor, who did not want to be quoted, said.
Friday's shutdown left many in tears."My uncle's condition is critical. But the gu ards are not allowing us to take him to the casualty ward. Where do we go now?" asked Nutan Verma, who had come from Tahirpur in east Delhi. Not a single patient was admitted to the casualty sections of AIIMS and its trauma centre. AIIMS's main casualty gets around 450 pa tients daily, many of them emergency cases requiring immediate medical attention.
Only those who got admission on Thursday were being treated by doctors. TOI found that the hospital staff utilised the opportunity to clean the main casualty .
At the trauma centre, which is the country's apex centre for emergency services and receives around 150 trauma patients daily , security guards had been deployed to tell patients to go elsewhere.
Initiatives
Video-Clinic For OPD
DurgeshNandan Jha, Avoid AIIMS rush, consult doc via web, Nov 14 2016 : The Times of India
Video-Clinic Facility For OPD
Getting a second opinion from specialists at AIIMS or seeking their suggestions on post-operative care is now just a click away.
Patients can log in to the institute's website and put a request for video consultation, a feature added recently to the online OPD consultation system. Officials told TOI that the dry run of AIIMS video clinic has been completed successfully. Specialists from 20 departments, including medicine, gastroenterology and cardiology, have consented to taking out a couple of hours daily for the job, they added.
Dr Deepak Agrawal, who heads the IT division, said that this consultation will not be valid for medico-legal purposes as it will be given without the physical presence of the patient.
“The AIIMS video clinic has been developed by Natio nal Informatics Centre. It allows uploading of discharge summary and investigation reports. We will be deputing nurses trained in IT to coordinate with the doctors for video calls in the time allotted for each patient,“ Agrawal added.
The video-clinic facility is expected to help reduce patient burden, apart from easing the hardship and financial impact suffered by patients travelling from other states for a second opinion or treatment without prior appointment.
On an average, doctors sa id, close to 10,000 patients visit AIIMS daily . Of this, 50% are follow-up cases and 40% come for a second opinion. Only 10% are new cases. “Today , majority of specialist doctors are concentrated in metro cities. The use of such technology can help reduce the gap of specialists in small cities and villages as even the local doctors can use it to treat local patients,“ said another doctor.
The waiting period for neurosurgery or cancer treatment is up to a year. Experts say that telemedicine and video clinic can be an additional help, but focus is needed to improving existing public health facilities.
Research
Low Body Mass Index among Indian women

An analysis of postmortems conducted at AIIMS on unclaimed bodies of women from 2006 to 2012 has revealed that most of bodies had low Body Mass Index (BMI), indicating malnutrition along with superimposed diseases.
Nearly one in every three woman suffered from acute pneumonia, which doctors pointed out could be linked to lack of shelter facility during winter months.
“Self-neglect, poor personal hygiene and lack of access to medical facilities may further exacerbate the morbidity and mortality due to pneumonia,“ stated the study published by AIIMS in the latest issue of National Medical Journal of India (NMJI).
It added that accidents were the second most common cause of death. Most women suffered haemorrhagic shock andor severe head injury in road traffic accident leading to their death.“One explanation for road accident deaths could be that most homeless people sleep near roads and hence they are prone to accidents,“ Dr Chittaranjan Behera, the lead author told TOI. He added that homicidal and suicidal causes accounted for 11% and 8% of all deaths, respectively.
“Most homeless women are vulnerable to physical as well as sexual abuse, which makes them more prone to homicides,“ the doctor said, adding they came across a 25-year-old pregnant woman who had been strangulated and left to die.
The doctors, in their report on unclaimed bodies of women published in NMJI, advocated for increased sensitivity to be shown towards the vulnerable section of society , apart from creating safe shelter homes.
“Mental distress caused by extreme poverty and physical andor sexual abuse may account for most instances of suicide,“ the journal said.
Activists said that while the number of night shelters for homeless has gone up, safety and security of women living there needs further improvement. “There were few toilets. In some cases, the shelters meant for men and women lay adjacent to each other,“ said an activist. He added that recently Delhi government has come up with plans to open mohalla clinics near the night shelters so that the habitants can seek medical care.
According to a 2010 survey, the NMJI study said that nearly 56,000 people are estimated to be homeless in Delhi. Women constitute a minor proportion of the homeless but represent a more vulnerable and often neglected section.
Medical accomplishments, milestones
Heart transplants, 1994-2016
A new first at AIIMS: 50th heart transplant, Nov 02 2016 : The Times of India
13 Surgeries Performed This Year, 5 In 2015
In a milestone surgery , the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) performed its 50th successful heart transplant -a first for any public hospital in the country -on Diwali eve this year.
The institute was the first to conduct heart transplant in India in 1994, but the rate of surgeries went down in the following years due to lack of donors.However, the hospital authorities said that it has improved significantly over the last two years.
In 2015, the hospital conducted five successful heart transplants and this year, as on October 31, the hospital has transplanted hearts in 13 patients suffering from endstage failure of the organ.
“Two heart transplants have been conducted in the past week. A 42-year-old man from Rohtak was operated upon on Diwali eve, while another patient suffering from heart failure underwent the life-saving procedure on October 25. The donors in both cases were road accident victims,“ said a senior official. “We told the Rohtak man, who used to work as a DTC driver earlier, that the transplant was his Diwali gift from AIIMS,“ said Dr Sandeep Seth, professor of cardiology at AIIMS.
He said that the donor, a 35-year-old woman, weighed nearly as much as the recipient and their blood groups also matched, so there was no hurdle in the transplant.
According to Dr Balram Airan, professor of cardiothoracic and vascular surgery , who was part of the team which had performed the country's first heart transplant at AIIMS on August 3, 1994, about 350 heart transplants have been performed in India. “Maximum transplants have taken place in private hospitals. It is good that government hospitals -like ours, where the surgery is nearly free of cost -are also conducting them frequently,“ he added.
“Better coordination among local administration and air and road traffic agencies have helped improve the rate of donations and transplants,“ said Dr M C Misra, AIIMS director.
According to the medical institute, nearly 50,000 people are in immediate need of heart transplants in the country . Dr Seth said the survival rate in heart transplant cases is maximum of 17 years after the surgery .
Bikini hip replacement surgery/ 2021
DurgeshNandan Jha, August 27, 2021: The Times of India

From: DurgeshNandan Jha, August 27, 2021: The Times of India
At least 20 patients, mostly women in their late 20s and 30s, have undergone hip replacement surgery at AIIMS using a modified technique in which the incision is made within the skin fold of the bikini line or the frontal groin crease. The surgery is often referred to as “bikini hip replacement surgery”.
Dr Rajesh Malhotra, professor and head of orthopaedics at AIIMS, told TOI that unlike the conventional approach for conducting hip replacement, which leaves behind a noticeable scar, the modified technique is done in a manner that few can tell surgery has been done even if the patient wears a bikini.
“Very few centres in the world do this surgery. It’s challenging and takes longer than usual, but we decided to adopt it to help young women who are hesitant to undergo the procedure for fear of the residual scar,” added Malhotra. There are three main approaches for a hip replacement surgery. In the posterior approach, the surgeon makes an incision on the back of the hip joint and cuts the gluteus maximus muscle to remove the damaged joint and replaces it with artificial parts. In the anterolateral approach, the incision is made on the outer side of the thigh. In the anterior approach, a vertical incision is made on the front of the hip to replace the joints without cutting or splitting the muscles.
The bikini surgery is a modified version of the anterior approach where the surgeons make a horizontal incision along the bikini line to ensure minimal scar. Further, special cosmetic stitches are used to minimise the noticeability of the scar.
Malhotra said the operation through the bikini incision, which is only 6-8cm in width, was more challenging than the other approaches because the field of vision and operation was less. “It needs a lot of experience and the right selection of patients to succeed,” he added.
AIIMS conducted the first such surgery last year. Till date, 20 surgeries have been performed. Nine patients suffered from avascular necrosis of the head of the femur, six patients had a history of damage to the hip joints due to rheumatoid arthritis, two others suffered from arthritis caused due to lupus and bone damage due to tuberculosis, and one patient developed avascular necrosis of the hip and extreme pain post-Covid. Most of the patients were young women.
A mini-review on the psychology of scars published in the journal Psychiatria Danubina in 2018 stated that scarring may be skin deep, but psychological impact went deeper. “The evidence is decisive; the presence of scars can result in clear markers of mental disturbance in patients with associated symptoms of depression, anger, anxiety and post-traumatic stress. A scar creates physical, emotional and psychological marks. Identity is called into question and individuals must integrate the scar with their sense of self to achieve psychological acceptance. This process causes a change of behaviour and reduced functioning, socially and psychologically, driven by the fear of being singled out. Hiding the scars relieves maladaptive behaviour and often leads to a return to normal functioning.”
Patients
2012-15: Statistics
The Times of India, Dec 07 2015
Records show 10 patients die at AIIMS daily More than 10 patients die daily on an average at the country's premier All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), according to data provided by the health ministry . As many as 4,432 patients were reported to have died in 2012-13, 4,302 in 2013-14, 4,467 in 2014-15 and 2,802 deaths were registered at the institute till October 2015.
Health ministry officials said that the institute is catering to a large number of patients from across the country on a daily basis, who are often referred to the hospital at critical stages. AIIMS attends to more than 8,000 patients every day in its OPDs and around 400 people in the hospital's casualty wing everyday.
The maximum number of deaths were reported from departments like gastroentrology where 536, 448, 403 and 223 people died in 2012-13, 2013-14, 2014-15 and 2015-16 respectively and the Jai Prakash Narayan Trauma Center which registered 631, 624, 544 and 472 deaths during the same period.
“A large number of critical and serious patients with multiple comorbidities get admitted for treat ment at AIIMS. The institute has created high dependency units (HDUs) in several wards in a bid to reduce the mortality rate,“ said a senior official at the ministry.
He said that keeping in view the admission rate of critical patients at AIIMS, the government has approved additional 85 HDU beds and 106 ICU beds in the last three years.
The official added that in order to keep with the increasing patient load, the government has also taken steps to augment tertiary care facilities, including setting up of new AIIMSlike institutions, strengthening super specialities and setting up of the State Cancer Institutes and Tertiary Cancer Care Centers in government medical colleges.
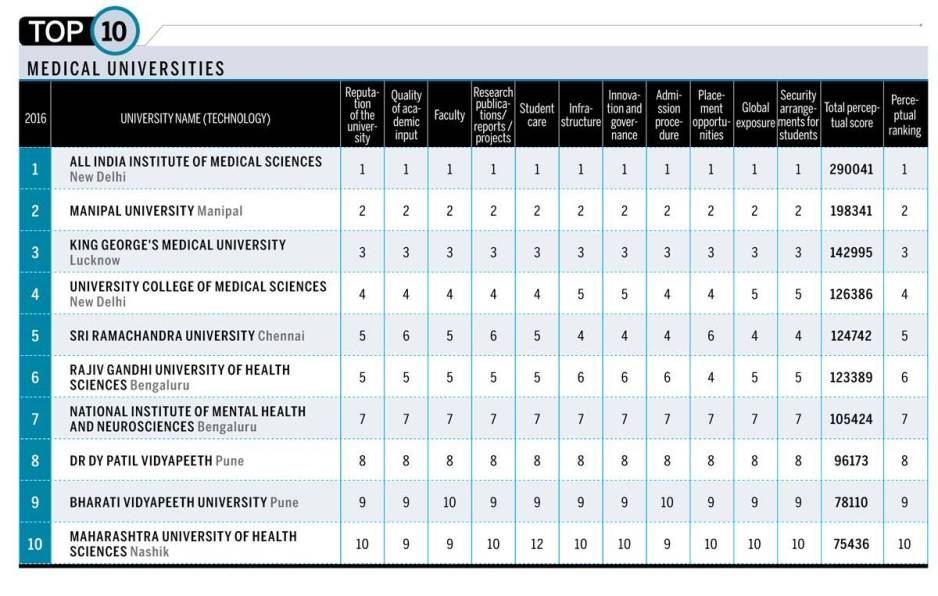
Ranking among Medical Colleges
2015: 1st
In 2015, the All India Institute of Medical Sciences was rated the No.1 college in the category Medical Colleges in the rankings released by India Today.
2016
Damyanti Dutta , All-India institute of excellence “India Today” 11/7/2016
Robotic technology
Spine surgeries
DurgeshNandan Jha , Sep 22, 2019: The Times of India
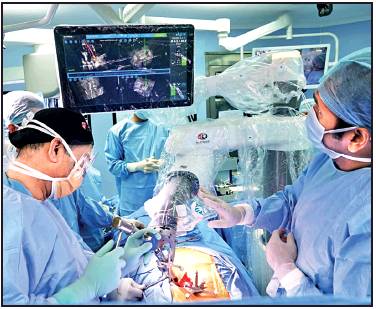
From: DurgeshNandan Jha , Sep 22, 2019: The Times of India
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) has acquired the latest robotic technology with inbuilt navigation and intraoperative imaging system for spine surgeries.
Dr Rajesh Malhotra, professor and head of orthopaedics at the hospital, told TOI that this would help reduce the risk of damage to surrounding tissues and nerves — a rare but known complication of the surgery to fix problems involving the spine. “This integrated technology for spine surgery is available at very few centres in the world. We have spent more than Rs 20 crore to set it up at AIIMS. Poor patients requiring complex surgeries will be able to avail it for free,” he said.
Dr Malhotra said a 45-yearold woman from West Bengal, suffering from spondylolisthesis — displacement of the lowest of the lumbar spine’s five vertebrae L5-S1 — is the first patient to have undergone spine surgery using the new technology at AIIMS. “She is doing fine. We plan to discharge her soon,” the doctor said.
According to Dr Bhavuk Garg, spine surgeon at AIIMS, surgery using the new technology is done in multiple steps. First, the imaging of the area to be operated is done using the o-arm2 — an intraoperative imaging system — and the surgeon plans how to put the screws and rods to fix the spine. Then, the image is fed into the robot, which shows the path to put the screws and rods accurately.
“Conventionally, such surgeries involve repeat Xray that leads to the patient being exposed to higher dosage of radiation. But in this case, imaging is done only once and the robotic system guides the doctor to put the screws and rods — needed to fix the spine — in the exact position on a real-time basis. This reduces the risk of intraoperative complications significantly,” Dr Garg said.
For the patients, surgery using robotic technology means smaller incision, less bleeding, reduced risk of complications and faster recovery. The doctors said spinal fixation using special screws is required for most patients suffering from spinal instability due to fracture, injury, tubercular infection and shift in spine because of ageing, among other factors. If the screw is malpositioned, there is risk of damage to the nerves, paralysis, and the screws can get loose and even migrate, they added.
Bhim Rao Institute Rotary Cancer Hospital (IRCH)
2017: Reeling Under Patient Load
DurgeshNandan Jha, ’Cancer Centre Reeling Under Patient Load’, Jan 14 2017, The Times of India
Waiting time for chemo session at AIIMS: `Infinite’
The number of cancer patients admitted every year: 36,000. The number of beds available for chemotherapy: 36. While not every cancer patient admitted would require chemotherapy , the disparity explains why the wait for a chemo session could be “infinite“ at AIIMS which houses one of India's top cancer centres, the Bhim Rao Institute Rotary Cancer Hospital (IRCH).
A recent review conducted by the institute says the cancer centre is crumbling under the load of patients since their numbers have only grown while infrastructure has not. The AIIMS report says patients seeking one to two week-long chemotherapy have to wait “infinitely“ for their turn. Those undergoing three-week-long chemotherapy often miss their dates due to unavailability of beds. The crisis does not end here. The IRCH does not have a dedicated MRI facility so patients have to queue up with the rest at AIIMS. So they could end up waiting up to a year or more for the crucial diagnostic test. Should surgery be in order, they could be waiting for one to three months.
More than 1.33 lakh cancer patients visit AIIMS every year and around 36,000 are admitted. The institute is now pin ning its hopes on the Na tional Cancer Institute (NCI) coming up at Jhajjar.“There is no space left for expansion of infrastructure at IRCH and hence they are working overtime to complete the 710-bedded cancer facility in Jhajjar to handle the constantly increasing patient burden,“ said V Sriniwas, deputy director (administration), told TOI. “NCI is projected to handle 5.19 lakh patients on OPD basis and 1.41 lakh indoor patients annually once it is fully operational.“
IRCH began functioning in 1983-84 with 35 beds on two floors. At present, it has 182 beds, of which only six are ICU beds, say doctors. “There are 30 beds for chemotherapy on daycare basis,“ Sriniwas added, explaining the “infinitely long“ waiting for chemotherapy . IRCH has only three functional operation theatres and two PET CT scan machines. Cancer patients from across the country come to Delhi for treatment but, health experts point out, barring AIIMS and the newly opened Delhi State Cancer Institute (DSCI), no public sector hospital has an efficient cancer facility. “Poor people cannot afford private treatment for a disease like cancer which can cost anywhere between Rs 5 lakh and Rs 40 lakh,“ said an oncologist.
Top officials said NCI, which will be run by AIIMS, will have 25 OTs and a reasonable number of PET CT and MRI machines. “The 710-bedded cancer facility in Jhajjar is projected to handle 5.19 lakh patients on OPD basis and 1.41 lakh indoor patients annually once it is fully operational. It will be headed by Dr G K Rath,“ Sriniwas said.
India requires at least 1,300 radiotherapy units but has only around 750, said Dr P K Julka, medical oncologist at Max Super Specialty Hospital, Saket. Most of the machines, he added, are in the private sector hospitals. Delhi has around a dozen radiotherapy units, of which four are in government-run hospitals -AIIMS, Safdarjung, Lok Nayak and DSCI. Safdarjung Hospital, sources said, does not have a simulator or treatment planning system (TPS) for precise administration of dosage and has been using Cobalt-60 machines for radiotherapy services when most hospitals have switched to newer technologies such as linear accelerators.
Oncologists say that infrastructure for cancer treatment needs to be scaled up rapidly . “In 1977, when I worked at Lok Nayak Hospital, it had one Cobalt 60 machine. That hasn't changed in 38 years although the number of patients has multiplied,“ said an oncologist.
Why AIIMS is the best
Its edge, as in 2016
Damayanti Dutta , All-India institute of excellence “India Today” 11/7/2016