Banking, India: I

This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
History
1720
The Times of India, Aug 22 2016



The Times of India
India's first joint stock bank was established in 1720 in Mumbai. This was followed by the setting up of a similar bank in Kolkata in 1770 and, later, in many other cities. Because of the growing need for modern banking services, of uniform currency to streamline foreign trade and to manage the remittances of British Army personnel and civil servants, three Presidency Banks were established in Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai. Apart from normal banking, these banks could also issue currency until 1861.During the same period, there was a significant increase in privately-owned commercial banks and, by 1913, there were 56 commercial banks operating in India. The First World War and the Great Depression exposed the flaws of banking in India as many banks failed and the need for a cent ral bank to ensure regulatory safeguards was felt.
1969: Nationalisation and political misuse
The Times of India, April 10, 2016
Banks will remain political fiefdoms till privatized
Public sector banks are losing huge sums and running up gargantuan bad debts. Defaulters like Vijay Mallya, once politically powerful, are fleeing abroad. India's banking crisis is fundamentally political, not financial.
The left, predictably, blames wicked busi nessmen, saying the banking system has become a fiefdom of big business. Rubbish! The banks were indeed fiefdoms of big business before 1969. Then Indira Gandhi nationalized them to make them the fiefdoms of politicians. That's the root of today's crisis.
Indira and her socialist acolytes claimed bank nationalization was essential for the state to capture the commanding heights of the economy , and channel bank lending to top social priorities.Actually , she could have ordered private banks to lend to favoured sectors (as is done today) without nationalization.
Her real aim was to control all big finance, emasculating the businessmen and maharajas leading the Swatantra Party , the main opposition party after the 1967 election. She nullified the treaties Sardar Patel had signed with the princes to persuade them to accede to India in 1947. She abolished their privy purses and made them taxable, bankrupting them.
She raised income-tax rates to 97.75%, added a wealth tax of 3.5%, nationalized several other industries, and made it clear to businessmen that dissenters would be crushed. The ploy succeeded. The Swatantra Party collapsed, and businessmen crawled.
However, the poverty ratio did not fall at all after 1947 till 1983. Meanwhile, the population doubled, so the absolute number of poor doubled. That terrible human cost exposes the fraudulent intent and outcome of Indira's Garibi Hatao policies, spearheaded by bank nationalization.
Did nationalization spur lending to “the people“? As Orwell said, in socialism all are equal, but some are more equal than others. Most equal of all was Sanjay Gandhi, Indira's son, who sought unending loans for his dud car project. Anyone opposing Sanjay -including R K Hazari, deputy RBI governor, and R K Talwar, chairman of the State Bank of India -got marching orders. After that, bank chiefs obediently followed orders (official or unofficial) from top politicians. That's the genesis of today's bank misgovernance and losses. The economy has grown 50 times since, so the misgovernance and losses have risen too. But in essence, Vijay Mallya is simply a new avatar of Sanjay Gandhi.
After Talwar's travails, pre-nationalization financial discipline was quickly destroyed. Loans were given to dud businesses and dud social projects (like loan melas to woo political vote banks). How many defaulters did nationalized banks remove from control of their businesses? Virtually none, since they had all bought political protection. Regional rural banks (RRBs) did indeed penetrate the countryside, a social plus. But they lost vast sums and had to be merged with the big banks.
By the early 1980s, the bad loans of banks exceeded their equity capital. Technically , they were bankrupt. But given government ownership, that was not even news. After all, public sector behemoths had always lost huge sums, and been replenished indefinitely by the taxpayer.
By the 1980s, nationalized banks were okaying highly inflated project costs that enabled promoters to skim off the excess. Banks “evergreened“ bad loans (renewing them indefinitely) instead of admitting they were unpayable, taking over the assets of borrowers and auctioning them. Unpaid and unpayable dues were listed as “receivables“. And all receivables, believe it or not, were classified as “income“, even though nothing was coming in.
Banking doyen Narayan Vaghul told me at the time that most bank profits were fictional, since they were based on receivables that were never received. On this fictional income the banks declared profits, and even paid corporate tax. And those that had no cash borrowed money to pay the taxes! That sad farce has continued ever since, in greater or lesser measure. Politicians have continued phoning bank managers.And at budget time finance ministers announce a host of schemes to be financed by the banks, a political diktat.
Governments have the right to lay down lending priorities.But bank funds are actually the resources of citizen savers, not the government. So, politicians should not force banks to hold loan melas for vote banks, or go easy on favoured borrowers.
Modi has brought in reforms aiming to provide more honest, independent bank chiefs and boards. This may improve matters.But the process is hardly foolproof, and can be reversed by a future government.
Private-sector banks (like ICICI Bank) have also been hit by bad loans in problem sectors like infrastructure and metals. But they avoided the worst loan proposals that nationalized banks happily accepted, with disastrous results. The private banks lent on commercial principles, not political orders. Probably bank privatization alone can ensure commercial discipline in future. But no political party wants that.
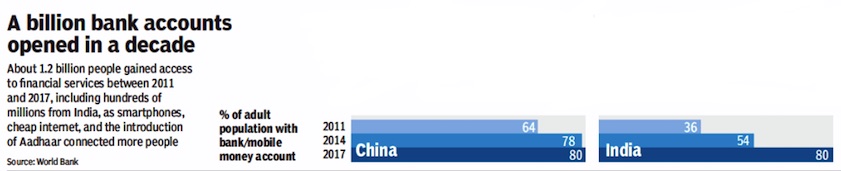
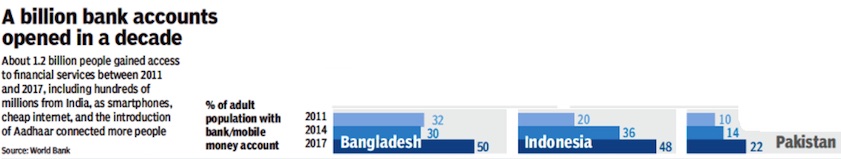
Accounts, number of/ population covered
2011> 2017
From: April 24, 2018: The Times of India
From: April 24, 2018: The Times of India
See graphics:
Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia and Pakistan: the percentage of the adult population with bank/ mobile bank accounts. In 2011, 2014 and 2017 (Part-I)
Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia and Pakistan: the percentage of the adult population with bank/ mobile bank accounts. In 2011, 2014 and 2017 (Part-II)
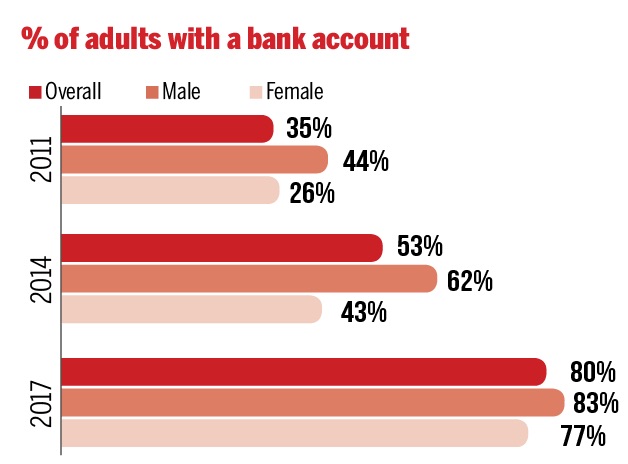
India has 2nd largest unbanked population
June 13, 2018: The Times of India
From: June 13, 2018: The Times of India
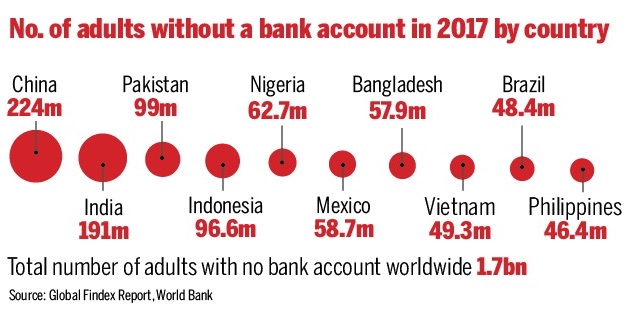
From: June 13, 2018: The Times of India
While India is quite proud about adding more individuals into the formal banking system -- the number of adults with bank accounts grew from 53% in 2014 to 80% in 2017 -- it is not enough. As many as 191 million Indian adults are still without a bank account. The figure places the country next only to China.
Bangladesh, China, India, Pakistan vis-à-vis the world/ 2017

i) The number of unbanked adults, and
ii) The percentage of unbanked population,
As in 2017
From: June 15, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Bangladesh, China, India, Pakistan vis-à-vis the world:
i) The number of unbanked adults, and
ii) The percentage of unbanked population,
As in 2017
State-wise contribution to banking business: 2018?
See graphic
The leading states’ contribution to the banking business in India, presumably as in 2018
Additional Tier 1 (AT1) bonds
The basics, as in 2020 March
All you want to know about AT1 bonds, March 10, 2020: The Times of India
What are AT1 bonds?
Additional Tier 1 bonds, also called AT1in market parlance, are a kind of perpetual bonds without any expiry date that banks are allowed to issue to meet their longterm capital requirement. That’s why these bonds are treated as quasi-equity instruments under the law. RBI is the regulator for these bonds.
Do these bonds pay interest?
Yes. AT1 bonds are like any other bonds issued by banks and companies, which pay a fixed rate of interest at regular interval. Usually, these bonds pay a slightly higher rate of interest compared to similar, non-perpetual bonds. However, the issuing bank has no obligation to pay back the principal to investors.
Are these bonds traded in the market?
Yes. These bonds are listed and traded on the exchanges. So if an AT1 bond holder needs money, he can sell it in the market.
How are AT1 bonds redeemed?
Investors can not return these bonds to the issuing bank and get the money. This means there is no put option available to its holders. However, the issuing banks have the option to recall AT1 bonds issued by them (termed call option). They can go for a call option five years after these are issued and then every year at a pre-announced period. This way the issuing banks can give an exit option to AT1 bond holders.
At present, what’s the total value of AT1 bonds in the market?
According to a report by rating agency ICRA, nearly Rs 94,000 crore worth of AT1 bonds are currently issued by various banks. Of this, Rs 55,000 crore is from PSU banks, while the balance Rs 39,000 crore is by private lenders.
Administrative costs levied on customers
2015-18: Charges For ATM Withdrawals, low minimum Balance
PSU banks collected ₹10k cr from you in 3 and a half yrs, December 22, 2018: The Times of India

From: PSU banks collected ₹10k cr from you in 3 and a half yrs, December 22, 2018: The Times of India
Charged For ATM Withdrawals, Not Maintaining Min Balance
State-run banks have collected over Rs 10,000 crore from those who did not maintain minimum balance in their savings accounts and from charges levied on ATM withdrawals beyond the free transactions in the last nearly three and a half years, data submitted in Parliament showed.
According to a written reply to a Parliament question, the low monthly average balance was charged by SBI till 2012 but it stopped doing so till March 31, 2016 while other banks, including private banks, were charging as approved by their boards. SBI reintroduced the charge from April 1, 2017.
The minimum balance requirements were subsequently reduced from October 1, 2017. There is no minimum balance requirement for basic savings bank deposit accounts and Jan-Dhan accounts.
Apart from the over Rs 10,000 crore collected by staterun banks during the threeand-a-half-year period, private banks would also have collected a hefty amount. Data for private banks was not included in the numbers provided in the Parliament question.
The details emerged in a reply by the finance ministry to a question posed by Lok Sabha MP Dibyendu Adhikari on Tuesday. The ministry said the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had permitted banks to fix charges on various services rendered by them, as approved by their boards. The banks are to ensure that the charges are reasonable and not out of line with the average cost of providing these services.
It also said, according to the RBI’s directions, a minimum of three free transactions at any other bank’s ATM at six metros — Mumbai, New Delhi, Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru and Hyderabad — and a minimum of five free ATM transactions at a bank’s own ATM at any other location is permitted during a month.
“Beyond this minimum number of free ATM transactions, banks have their boardapproved policy on charges from customers on ATM transactions subject to a cap of Rs 20 per transaction,” the ministry said in its reply.
The ministry also said public sector banks had informed that they do not have any plans to shut down their ATMs. This was in response to the question on whether the government proposes to withdraw 50% of total ATM services in the country by March 2019.
Administrative measures, initiatives, issues
RBI’s asset quality review under Raghuram Rajan: 2015
The Times of India, June 19, 2016

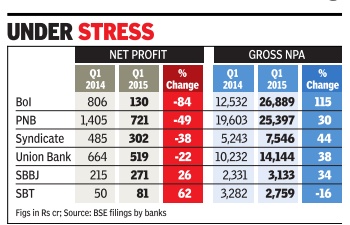
A few years down the line several of the current bank chiefs would probably remember Raghuram Rajan for one thing eating into their annual bonuses. ICICI Bank has already announced that its top management won't receive performance bonus for 201516. PSU bank chiefs too are expected to miss the annual pay-out as soaring bad debts have hit the financial performance of lenders.
Just when data showed promise of the economy stabilising, the RBI started what's come to be known as asset quality review, a term that most bankers dread.While annual inspection of banks was the norm, RBI has now opted to ask banks to classify several loans as non-performing assets (NPA), which in normal course would have been treated as “standard“.
Classifying a loan as an NPA or a sub-standard asset means that banks have to set aside more funds to cover for potential losses due to nonpayment of dues. The result is for everyone to see: NPAs of Indian banks shot up to a little under Rs 6 lakh crore as each lender was handed a list of companies where funds had to be set aside, called provisioning in banking parlance. Even loans which were restructured were to be monitored strictly and funds set aside for a year.
As a result, against cumulative profits of close to Rs 31,000 crore in 2014-15, state-run lenders ran up losses of almost Rs 18,000 crore as bank after bank reported record losses. Some of the large private banks, such as ICICI Bank, man aged to stay profitable but saw a steep decline in profit.
But the hit is not just for banks, it also impacts India Inc. Companies that get the NPA tag would be choked of funding, a move that will impact economic revival as these entities would be unable to add more capacity to their factories.
Banks can't refuse faded, scribbled notes: RBI
Banks can't refuse scribbled notes, says RBI circular, April 29, 2017: The Times of India
The RBI has said banks cannot refuse to accept faded notes or those with scribbles. The central bank said such banknotes had to be treated as “soiled notes“ and dealt with according to the RBI's “clean note policy“.
The circular to banks was sent by the RBI after it received complaints that many branches were not accepting banknotes, specifically of 500 and 2,000 denominations, with anything written on them or those either smudged with colour or faded due to washing.
Bank branches have been rejecting such notes following rumours in social media that such notes were not acceptable.
The RBI drew attention to its December 2013 statement, issued in response to rumours that from 2017 onwards banks would not accept notes with anything written on them. The RBI had then stated that it had not issued any such instruction. The central bank clarified that its instructions on scribbling on notes was a directive for staffers not to write on banknotes. This was after the RBI had observed that bank officials themselves were in the habit of writing on banknotes, which went against the central bank's clean note policy.
The RBI has sought cooperation from all members of public, institutions and others in keeping banknotes clean by not scribbling on them.
Bank Board Bureau/ 2016
The Hindu, February 29, 2016
Prime Minister Narendra Modi approved the setting up of the Bank Board Bureau with former Comptroller and Auditor-General of India Vinod Rai as its first Chairman.
The Bureau is mandated to play a critical role in reforming the troubled public sector banks by recommending appointments to leadership positions and boards in those banks and advise them on ways to raise funds and how to go ahead with mergers and acquisitions.
“With a view to improve the governance of public sector banks, the government had decided to set up an autonomous Bank Board Bureau. The bureau will recommend for selection the heads of public sector banks and financial institutions and help banks in developing strategies and capital raising plans,” the government said in a release.
The bureau was announced in August 2015 as part of the seven-point Indradhanush plan to revamp these banks. It will constantly engage with the boards of all 22 public sector banks to formulate appropriate strategies for their growth and development.
The bureau, led by Mr Rai, will select the heads of public sector banks (even from the private sector, if need be) and aid them in formulating strategies to raise additional capital. It will select and appoint non-executive chairmen and non-official directors.
The non-performing assets of public sector banks are estimated at almost Rs. 4 lakh crore, and they need to raise capital of Rs. 2.4 lakh crore by 2018 to conform to Basel-III capital requirement norms, according to the government.
While some questions have been raised on Mr. Rai's appointment as a CAG cannot hold a government office post-retirement, former senior civil servants say the role is advisory in nature and a part-time position. The government release said the appointments have been made for a period of two years.
The bureau will have three ex-officio members and three expert members, in addition to the Chairman.
2016/ Selection process of Managing Directors of public-sector banks
The Indian Express, May 30, 2016
George Mathew
The Bank Board Bureau (BBB), set up by the government in February 2016, has kicked off the selection process of managing directors and CEOs of public sector banks.
The body has conducted its maiden interviews for appointments of MDs & CEOs at three state-run banks and met as many 10 candidates who are currently serving as executive directors in various PSU banks, according to sources. One of the interviewees was earlier shunted out by the government from a large PSU bank in connection with a dubious loan to Atlas group, a Gulf-based jewellery chain.
2018/ Asset Quality Review
The RBI has included several top business groups in the ongoing asset quality review which, based on the replies of the banks, could lead to bankruptcy proceedings in many cases.
The regulator has already sent letters to banks to gauge the level of action by lenders to clean up the banking system, said a banking source. Each bank is expected to clarify the position separately. “This could be the second major asset quality review after former RBI Governor Raghuram Rajan kicked off the first review in 2015,” said an official of a nationalised bank.
The RBI has included several top business groups in the ongoing asset quality review which, based on the replies of the banks, could lead to bankruptcy proceedings in many cases. Most of these accounts have already been declared as non-performing assets (NPAs) by banks. The RBI did not respond to emailed queries.
The RBI had initially sent a list of 12 defaulters for resolution under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC). Out of this, 11 accounts are in various stages of resolution at different benches of the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT). Bankers are expecting over 50 per cent recovery from these accounts.
The regulator subsequently sent another list of 28 stressed accounts for resolution. However, banks don’t expect more than 25-30 per cent from these accounts. Some of these accounts were evergreened — or fresh loans disbursed to repay old loans — by banks to prevent them being classified as bad loans. The fresh exercise by the RBI comes at a time when gross non-performing assets in the banking system has risen to around Rs 10.3 lakh crore, or 11.2 per cent of advances compared with Rs 8 lakh crore, or 9.5 per cent of advances, as on March 31, 2017.
In FY18, the banking system reported a net loss of Rs 40,000 crore because of the sharp rise in NPAs and the resulting increase in provisioning costs. In the previous fiscal, as much as Rs 5 lakh crore of bank loans slipped into the NPAs category, taking the total slippages in the past three fiscals to Rs 13.6 lakh crore, Crisil has said.
In June, the RBI’s Financial Stability Report (FSR) warned that “the stress in the banking sector continues as gross NPA ratio rises further. Profitability of banks declined, partly reflecting increased provisioning”. RBI’s macro-stress tests indicated that under the baseline scenario of current macroeconomic outlook, gross NPA ratio of banks may rise from 11.6 per cent in March 2018 to 12.2 per cent by March 2019.
Nearly a dozen PSU banks are under the prompt corrective action (PCA) of the RBI.
2019: RBI removes BOI, BOM, OBC from PCA framework
RBI lifts lending restrictions on three public sector banks, February 1, 2019: The Times of India
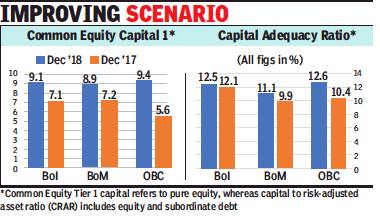
From: RBI lifts lending restrictions on three public sector banks, February 1, 2019: The Times of India
Bank of India, Bank of Maharashtra, OBC Exit PCA Framework
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has removed Bank of India, Bank of Maharashtra and Oriental Bank of Commerce from its prompt corrective action (PCA) framework — a watch list for weak banks that placed lending restrictions on them.
“The RBI’s decision to remove the three banks from the PCA framework is on expected lines, given the sizeable capital infusion in these three during December 2018,” said Anil Gupta, sector head (financial sector ratings) at Icra. “The balance of the budgeted capital can support the exit of one or two more banks from the PCA framework if the government allocates higher capital to some of these lenders, like Corporation Bank,” he added.
Responding to the RBI action, BoM MD & CEO A S Rajeev said that the recent capital infusion of Rs 4,498 crore helped the bank improve its capital adequacy ratio to 11.05%. At the same time, the bank reduced its non-performing assets (NPAs) by 50% year-on-year.
The decision is understood to have been taken following a meeting of the board for financial supervision on Thursday. The board, chaired by governor Shaktikanta Das, reviewed the performance of all the 11 banks on the PCA list.
According to Gupta, although the three banks have exited PCA, the question remains whether negative return on asset continues to remain a PCA criteria? Following the RBI announcement, finance secretary Rajeev Kumar said in a tweet that this was an outcome of the government’s ‘4R’ strategy — recognition of stressed loans as default, recapitalisation of banks, resolution of bad loans, and reform of public sector. “Banks need to be more responsible, adopt high underwriting and risk management standards to avoid recurrence,” Kumar added.
The RBI’s move comes two days after a review meeting of banks with interim finance minister Piyush Goyal. In the meeting, Goyal informed banks that if they maintained the trend of improvement in performance, they would exit the PCA soon.
2018/ Inter-Creditor Agreement
Sangita Mehta, July 11, 2018: The Economic Times
The Reserve Bank of India has started a review of over 200 stressed assets of top business groups in the banking system to assess the provisioning level and classification of assets.
Over the past few years, Indian banks have been forced by the Reserve Bank of India to recognise troubled assets on their books, but their resolution has remained a challenge. • Public sector, private sector and foreign banks signed an inter-creditor agreement to push for the speedy resolution of non-performing loans on their balance sheets.
• It is aimed at the resolution of loan accounts with a size of Rs 50 crore and above that are under the control of a group of lenders.
• It is a part of "Sashakt" plan approved by the government to address the problem of resolving bad loans.
As many as 56 lenders signed an inter-creditor agreement which will prohibit dissenting creditors from making an easy exit.
The agreement — based on a recommendation by the Sunil Mehta committee that looked into resolution of stressed assets — aims to deal with bad loans that banks must resolve before next month end under a February 12 RBI circular. Banks will have to refer unresolved loans to the bankruptcy court and they fear the asset value may erode if there are no buyers at bankruptcy court.
The agreement says if 66 per cent of lenders by value agree to a resolution plan, it would be binding on all lenders. The dissenting creditors will, however, have the option to sell their loans to other lenders at a discount of 15 per cent to the liquidation value, or buy the entire portfolio paying 125 per cent of the value agreed under the debt resolution plan by other lenders.
The agreement says each resolution plan would be submitted to an overseeing committee comprising experts from the banking industry. For dissenting creditors, the agreement says the “lead bank has the right, but not the obligation, to arrange the buyout of the loan facilities at a value that is equal to 85 per cent of the liquidation or the resolution value —whichever is lower.”
However, “if the lead bank does not arrange for a buyout, the dissenting lenders shall have the right, but not the obligation, to arrange for buyout of the facilities of all the other lenders at a value that is equal to 125 per cent of the liquidation value or the resolution value — whichever is higher.”
Dissenting creditors can also exit by selling their loans to any entity at a price mutually arrived at between the lender and buyer. The agreement has a standstill clause wherein all lenders are barred from enforcing any legal action against the borrower for recovery of dues. During the standstill period, lenders are barred from transferring or assigning their loans to anyone except a bank or finance company. But it is not clear if a loan can be sold to an asset reconstruction company during that period.
The standstill provision will be operative for 180 days from the reference date — the RBI had asked lenders to resolve their restructured loans within 180 days beginning March 1 or refer those to the bankruptcy court. However, the provision would not prevent lenders from acting against borrowers or directors for criminal offence. Lenders are in the process of getting this inter-creditor agreement approved by their boards.
Benefits:
• Such an agreement may persuade banks to embark more quickly on a resolution plan for stressed assets.
• It is an improvement over the earlier model, which replied solely on the joint lenders' forum to arrive at a consensus among creditors. It is, in fact, logical for joint lenders who want to avoid a deadlock to agree on the ground rules of debt resolution prior to lending to any borrower. But the obligation on the lead lender to come up with a time-bound resolution plan can have unintended consequences.
Challenges:
• The biggest obstacle to bad loan resolution is the absence of buyers who can purchase stressed assets from banks, and the unwillingness of banks to sell their loans at a deep discount to their face value. Unless the government can solve this problem, the bad loan problem is likely to remain unresolved for some time to come.
Alternative lending
2014-17
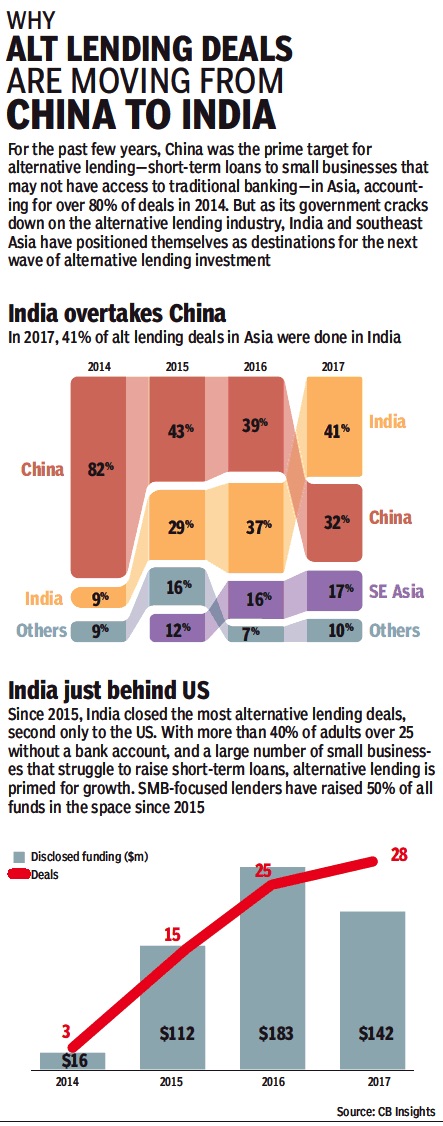
i) India overtakes China
ii) India just behind US
From: August 5, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic :
Alternative lending deals, 2014-17
i) India overtakes China
ii) India just behind US
CEOs’ turnover
2008-18
Govt banks see higher CEO churn than pvt sector peers, December 1, 2018: The Times of India

From: Govt banks see higher CEO churn than pvt sector peers, December 1, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
The turnover of the CEOs of selected public-sector and private banks, presumably as in 2008-18
PSU banks have a higher turnover of CEOs compared to their private sector peers. In the last decade, five PSU banks have had six CEOs, meaning that the average tenure has been less than two years. Analysts say such quick changes impact governance and the ability of a bank to take strategic long-term initiatives. Bank chiefs are also unwilling to take decisions on tricky issues and are happy to kick the can down the road.
CEOs’ salaries
2017

HIGHLIGHTS
SBI chief Arundhati Bhattacharya took home Rs 28.96 lakh in 2015-16.
In comparision, ICICI CEO Chanda Kochhar received a basic salary of Rs 2.66 crore in 2015-16.
Such high disparity in compensation impacts the motivation of public sector managers who have to fiercely compete with private sector peers.
SBI, one of the world's 50 largest banks, pays only a small fraction to its top management as compared to private sector players like ICICI Bank and HDFC Bank.
Former RBI governor Raghuram Rajan had flagged the low remuneration issue last August saying it makes difficult for state-owned banks to "attract top talent, especially a lateral entry".
SBI chairman Arundhati Bhattacharya took home Rs 28.96 lakh last fiscal, which is pittance when compared to remuneration of her counterparts in private banks receive, according to analysis of annual reports of various banks.
In comparison, ICICI Bank MD and CEO Chanda Kochhar received a basic salary of Rs 2.66 crore last fiscal besides Rs 2.2 crore performance bonus to be paid over the next few years. In addition, she received allowances and perquisites of over Rs 2.43 crore.
The total compensation received by Kochhar in FY17 stood at Rs 6.09 crore.
Similarly, Shikha Sharma, MD and CEO of Axis Bank, took home a basic salary of Rs 2.7 crore, and Rs 1.35 crore as variable pay, besides host of perks and allowances like Rs 90 lakh HRA.
Yes Bank MD and CEO Rana Kapoor, who also happens to be promoter of the bank, took home Rs 6.8 crore as salary in 2016-17.
HDFC Bank's managing director Aditya Puri saw his remuneration rise marginally to Rs 10 crore and exercised stock options worth over Rs 57 crore during the last fiscal.
Speaking about public sector banks at a banking conference in Mumbai, Rajan had said state-owned banks tended to overpay at the bottom but underpay their top executives.
He jokingly said he himself was underpaid and the disparity made it harder to attract talent from outside at the top level in public sector banks.
On the business front, SBI, after merger with its subsidiary banks, caters to 42.04 crore customers with a market share of 23.07 per cent and 21.16 per cent in deposits and advances, as opposed to 18.05 per cent and 17.02 per cent respectively, before the merger.
Punjab National Bank, the nearest rival of SBI among PSBs post merger, will have a market share of 5.96 per cent, and 7.04 per cent in deposits and advances.
Remuneration comprises various components, including basic salary, allowances and perquisite, PF, superannuation allowances, gratuity and performance bonus and payment of performance bonus is deferred over a multi-year period.
Not only such high disparity in compensation makes it difficult for the government to hire top managers laterally at public sector banks, as pointed out by Rajan, it also impacts the motivation of public sector managers who have to fiercely compete with their private sector peers.
2018
Highest-paid Indian banker Aditya Puri gets 4% pay cut, June 17, 2018: The Times of India

From: Highest-paid Indian banker Aditya Puri gets 4% pay cut, June 17, 2018: The Times of India
HDFC Bank CEO Aditya Puri, who has been the highest-paid Indian banker for years, has seen a small dip in overall remuneration to Rs 9.6 crore in FY18 from Rs 10 crore in FY17 despite the bank’s net profit rising 20% to Rs 17,487 crore.
The compensation could change if the central bank approves a higher performance bonus. According to information in the bank’s annual report, bonus for FY17 has not been paid out as it is pending RBI approval and therefore not disclosed. In FY17, he had received a performance bonus of Rs 92 lakh.
The ratio of Puri’s salary to that the median is 209:1. However, his salary has not increased in line with the 8.9% average percentage increase for key managerial personnel and non-managerial staff. Puri holds around 0.13% stake in the bank, which is worth about Rs 687 crore. Puri, who has led the bank for 24 years, is credited with creating the country’s most valuable financial institution, which is today worth nearly Rs 5.3 lakh crore.
Uday Kotak, founder and CEO of Kotak Bank, received compensation of Rs 2.92 crore in FY 18 (Rs 2.63cr last year), which is 48.44 times the median salary in the bank. However, despite the relatively modest salary, Kotak ranks 104 in the Bloomberg Billionaire Index with assets worth nearly Rs 76,000 crore because of his 29.75% holding in the bank.
Yes Bank CEO Rana Kapoor’s total remuneration for FY18 stood at Rs 5.35 crore compared to Rs 6.81 crore in FY17. This was despite the bank’s net profit rising nearly 27% to Rs 4,224 crore in FY18. His salary is 79 times the median salary in the bank. Kapoor’s individual shareholding in the bank is worth Rs 3,306 crore.
Shikha Sharma, MD & CEO of Axis Bank, has seen her salary dip marginally to Rs 2.90 crore from Rs 2.94 crore in the previous year. This does not include other perks such as HRA, deferred variable pay and company contribution to provident fund. Her remuneration is 77.6 times the median.
ICICI Bank is yet to publish its annual report for FY18. The bank’s CEO Chanda Kochhar received total remuneration of 5.54 crore in FY17 which was 112 times the median. As compared to the private sector, public sector bank chiefs receive modest salaries. For instance, the chairman of SBI, the country’s largest bank, received compensation of Rs 14.25 lakh for the second-half of FY18 after he took charge mid-year. However, analysts point out that public sector banks have a higher wage to income ratio because of higher entry level salaries and also because private sector banks score higher in terms of productivity.
Credit-deposit ratio
2016-17
February 3, 2018: The Times of India
See graphics:
1. State-wise deposit and credit of scheduled commercial banks, 2016-17-I
2. State-wise deposit and credit of scheduled commercial banks, 2016-17-II

From: February 3, 2018: The Times of India
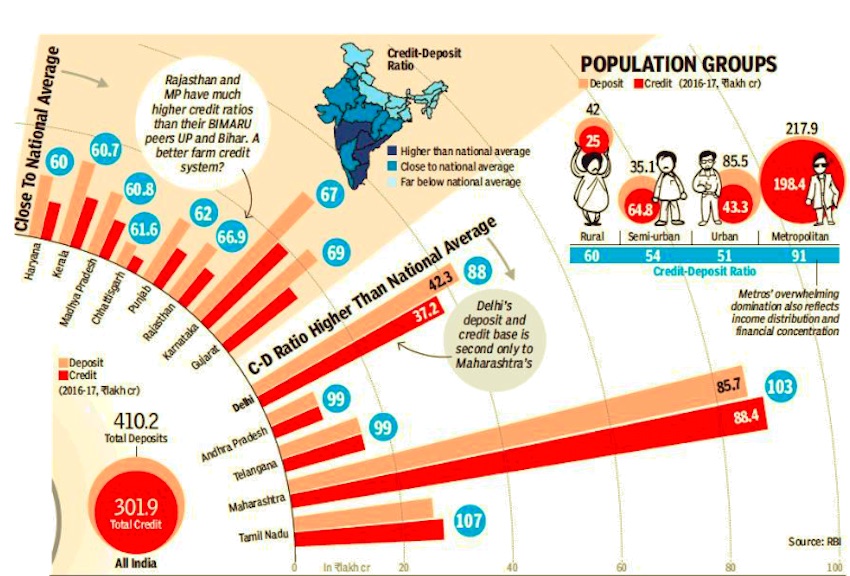
From: February 3, 2018: The Times of India
ARE BIHAR’S DEPOSITS FUNDING TAMIL NADU’S GROWTH?
Banks help convert people’s savings into investment, which in turn creates employment, income and assets. The process of conversion is called credit creation in which banks lend money to businessmen, farmers and consumers who need loans and are creditworthy. States with higher credit demand and more creditworthy people convert higher share of deposits into credit and have a high credit-deposit ratio. States with low credit-deposit ratios are those whose income, savings or both are higher than their investment needs — mostly the poor ones. India’s average credit-deposit ratio is 73.6
Credit growth
2000-16
`At 5.1%, credit growth slide reaching a point of no return', Jan 06 2017: The Times of India
Growth of bank credit fell to a multi-decade low of 5.1% for the fortnight ended December 23, as drying up of demand in the last two months of the year saw businesses cutting down on borrowing. Data released by RBI showed that as of December 23, bank lending to busines ses, individuals and the farm sector stood at Rs 73.48 lakh crore, an increase of 5.1% over the same period of last year.Going by readily available RBI data, this is the slowest rate of growth since 2000.
SBI chief economist Soumya Kanti Ghosh went further to say that credit growth was actually the lowest in over 60 years -since 1954-55 -when it had slowed to 1.7%. A slowdown to 5.1% in De cember seems to indi cate that credit growth is reaching a point of no return in this financial year.While there is marginal growth year-on-year, on a yearto-date basis (from April 2016) credit has declined in many sectors,“ said SBI chief economist Soumya Kanti Ghosh.Year-on-year credit growth in the previous fortnight ended December 9 was also a low 5.76%.
D K Joshi, chief economist at Crisil, the country's leading credit rating agency , attributed the drop in credit growth to the disruption caused by demonetisation. “Otherwise there was no reason for credit growth to fall. The economy was looking up, there was the pay commission hike, there were good rains, and some interest rate cuts were being passed on to borrowers, which would have created more demand for credit,“ he said.
The second half of the year is when banks advance the bulk of their loans. A slow down at this time will hurt growth targets, said economists. “Demonetisation has hurt activity across all corners of the economy . Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) data shows that both manufacturing and services have contracted in December. The PMI order-to-inventory ratio suggests that upcoming manufacturing activity will also remain weak. Input prices have been rising, but have not yet been passed on to final prices, suggesting that corporate margins have worsened,“ said Pranjul Bhandari, chief economist, HSBC India in a report.
According to Jefferies In dia, an investment bank, credit growth could slip to 6% in FY17. “Deleveraging of corporate balance sheets, halt in fresh capex, and increased access to corporate bond market have led to a negative growth in banks' credit to corporates.Given that 56% of bank loans and 88% of non-performing assets are with large borrowers, they hold the key to bank credit growth pick-up and asset quality improvement,“ the research firm said in a report.
RBI numbers show that corporate loans are shrinking.Since end-September bank loans have shrunk by Rs 1.72 lakh crore (2.3%). The sectors which saw a slowdown or drop in credit include infrastructure, food processing, chemical and chemical products, all engineering, textiles and basic metal and metal products.
Although very little fresh investment was taking place even before demonetisation, there was a consumption push. Crisil's Joshi expects consumption-led growth to return because of “some of the measures likely in the Budget, lower interest rates and if we have good rains. The next fiscal year will see a pick-up. But it will not happen in the January-March quarter.“
The silver lining appears to be the gains to the government from demonetisation.“We continue to expect the Income Disclosure Scheme II to net around Rs 1 lakh crore of tax. At the same time, we have cut our estimate of RBI dividend from black cash money not returned to banks to Rs 50,000 crore from Rs 95,000 crore earlier with the bulk (of demonetized currencies) depositedexchanged,“ said Bank of America Merrill Lynch in a report.
2000-2020

From: August 17, 2020: The Times of India
See graphic:
Credit and deposit growth in India, 2000-2020.
2017>2018: Consumer loan growth exceeds overall credit
Consumer loans beat overall credit, March 29, 2019: The Times of India
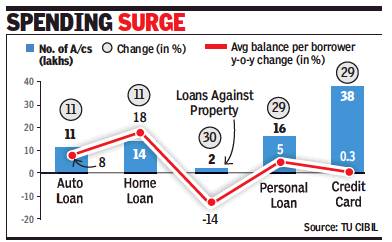
From: Consumer loans beat overall credit, March 29, 2019: The Times of India
Unsecured Loans Grow Twice As Fast As Total Borrowing
Unsecured personal loans, which are availed for consumption, have emerged the fastest growing segment in bank lending.
According to borrower data analysed by TransUnion CIBIL, loans outstanding under credit cards, personal and consumer durable loans grew
31.3% year-on-year as on December 2018. This is more than double the 15% year-on-year growth recorded by overall bank credit.
The TU CIBIL Industry Insights Report (IIR) shows consumer credit market continued to expand over the past year thanks to strong growth in these unsecured segments. As against this the secured lending category — loans against property (LAP), auto and housing — experienced more moderate total balance growth. But even these segments grew at a robust rate of 21.8%, 17.4% and 17.1%, respectively.
Also, while default rates remained relatively stable across most major consumer lending categories, loans against property have seen a 53-basis point rise in serious delinquencies. Auto loans have been an exception with serious delinquency rates dropping 116 basis points to 2.8%. Serious delinquency rates are measured as the percentage of loans that are overdue for 90 or more days.
“Consumer credit continues to be a key driver for the Indian economy. Although GDP growth has decelerated in recent quarters, the rate of overall consumer lending growth in India is still significantly higher than for most other major economies in the world,” said Yogendra Singh, vice-president of data science and analytics for TransUnion CIBIL. One reason for the sharp growth in this unsecured segment is the improved ability of lenders to provide loans for the non-salaried new-to-credit segment by using fresh data sources and analytical tools.
2015-18, Jan: high growth, though from low base (in 2018)
Mayur Shetty, Bank credit grows highest in 2 yrs, January 18, 2018: The Times of India

From: Mayur Shetty, Bank credit grows highest in 2 yrs, January 18, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic':
Bank credit growth rate (%), 2015- 2018, Jan
Outstanding bank credit has touched Rs 82.06 lakh crore, recording a yearon-year growth of 11.1% — the highest since February 2016. Bankers attribute the surge to a lower base following absence of credit offtake during demonetisation coupled with incipient recovery in demand for loans.
For the same period, nonfood credit growth has touched almost 12% — the highest since April 2015 — partly due to an increase in demonetisation. Non-food credit represents bank loans other than those advanced to Food Corporation of India for grain procurement.
Data released by the Reserve Bank of India showed that outstanding non-food bank credit stood at Rs 81.5 lakh crore, an increase of 11.96% over the last 12 months.
Compared to this, outstanding bank deposits of Rs 109.97 crore were up only 4.5% over the same period last year. The deposit growth rate was, however, higher than the preceding three fortnights.
According to SBI chief economist Soumya Kanti Ghosh, there are signs of a pickup in the economy.
“The latest IIP (index of industrial production) numbers confirm that few of the manufacturing sectors are pushing growth rate up. These are sugar, cement, steel, commercial vehicles, passenger vehicles and two-wheelers. Numbers suggest that some sectors are actually showing green shoots,” Ghosh pointed out.
“While some element of the base effect may be there, I believe that there is traction in terms of growth momentum. For instance, the SBI composite index shows that industrial production for December 2017 is also likely to come out strong,” said Ghosh.
Some bankers say that the surge in yields in end-December could have resulted in some corporates shifting to the loan market from money market instruments. In 2017, a large chunk of funding came from money market instruments like commercial paper and short-term bonds. The rise in bond yields is seen as a pointer to hardening interest rates.
Ghosh, however, rules out a rate hike by the central bank. “I don’t think that rate hike is an overarching feature. Economic growth is at an incipient stage and inflation is still under control,” he said.
2016-17: Lowest growth since 1953

From: Mayur Shetty, At 5.1%, FY17 bank credit growth lowest in over 60 yrs , April 15, 2017: The Times of India
Hit By Bad Loans, Sluggish Corporate Investments, DeMon
Growth in bank credit in FY17, at 5.1%, has turned out to be the slowest in over 60 years as state-owned banks burdened with bad loans struggled to find safe avenues to lend. The last time loans grew slower than this was in 1953-54 when bank credit growth had slowed down to 1.7%.
According to data released by the RBI, outstanding bank credit as on March 31, 2017 stood at Rs 78.82 lakh crore. A large part of the growth in lending has come in the last fortnight of the month when banks disbursed Rs 3.16 lakh crore. But even after this last-minute surge, loan growth for the whole year was 5.1% as against 10.3% last year.
Other than bad loans and corporate investment coming to a standstill, bank credit growth was also constrained by demonetisation. Between October and December 2016, bank credit contracted by 2.3% as against a 2.7% growth during the same period last year.
Besides bad loans, one of the biggest concerns for the RBI is managing the surplus liquidity with banks. While on the one hand banks are seeing lower credit growth, on the other their deposits continue to remain high, again thanks to demonetisation.
Banks have ended the year with an 11.8% growth in deposits, which now stand at more than Rs 108 lakh crore. Some bankers feel that the RBI is reluctant to intervene in the forex market as this would add to the surplus liquidity in the system.
According to a senior banker, of the total credit growth during the current fiscal, half has come from home loans and alarge part of the rest has been due to loans to the service sector. Most of the lenders are private banks and a few large private banks. Other than them, most public sector banks are likely to report flat credit growth for FY17.
One fallout of the slow down in credit is that banks will report a higher percentage of bad loans. Growth in credit helps to mask the level of bad loans. With bad loans at close to 10% of their total assets, many banks face a catch-22 situation. The RBI's prompt corrective action may make it difficult for banks to expand their balance sheet.The absence of fresh lending would, however, make it difficult for banks to generate revenues to clean up their books.
“With asset quality pressures, banks -especially the weaker public sector banks (PSBs) -have been reporting a continuous degrowth in their net interest income (NII) over the five consecutive quarters of Q3FY2016 to Q3FY2017, mainly on account of slower credit growth and reversal of interest income recognised on NPAs“ ratings agency ICRA said in a report.
Credit growth, sector-wise: 2016-17
Mayur Shetty, Home loans biggest driver of credit growth, May 2, 2017: The Times of India
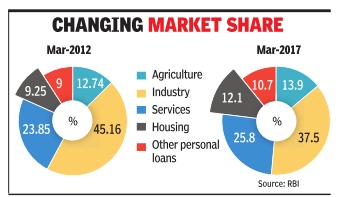
Grow 16% Over Five Years As Loans To Corp Slow To 6.7%
Over the last five years home loans have recorded the highest compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 16% and now account for over 12% of all bank credit.Overall credit to industry during the same period has slowed to single digits at 6.7% after a negative growth this year.Though the share of loans to industry in March 2017 were still hight at 37.5%.
According to data on sector credit released by the RBI, bank credit to industry as on March 31, 2017 stood at Rs 26.77 lakh crore which is 2% lower than outstanding bank credit of Rs 27.30 lakh crore as on end-March 2016. This has resulted in the slowest growth in bank credit in decades.
The main driver of bank credit in 2016-17 has been home loans which stood at Rs 8.60 lakh crore, 15% higher than Rs 7.46 lakh crore as on endMarch 2016. The share of housing which was 9.26% on March 2012 has been rising over the years. The last time bank credit to housing was in double digits was in 2009, when the government introduced special schemes to boost demand in the wake of the global financial crisis. “Between FY12-FY16 bank credit registered double digit growth, barring in FY15 when credit grew by 9%. However, growth in bank credit slowed to 5% in FY17. The slowdown has mainly been on account of banks stressed with bad loans, stagnant corporate investment environment and some migra tion to the debt market,“ said Madan Sabnavis, chief economist, CARE Ratings.
The slowdown in lending to industry is largely because of PSBs which have reduced their exposure to corporates.After home loans, credit card outstandings are the fastest growing segment which have grown at a CAGR of 20% over the last five years. However, they account for less than 1% of bank credit and are one of the smallest components of lending to the personal segment -smaller than education and auto loans.
December 22, 2017: Bank credit growth in double digits

From: Mayur Shetty, Bank credit growth hits double digits for first time since Sept ’16, January 6, 2018: The Times of India
Bank credit has grown in double digits for the first time since September 2016 driven by home loans and advances to traders and finance companies.
According to RBI data, the loan book of the banking sector stood at Rs 80,967 crore as on December 22, 2017 — an increase of 10.7% from the same period a year ago. The last time bank credit was above 10% was on September 30, 2016 when year-on-year advances grew 11.83%. A month later the government announced demonetisation which led to a prolonged slump in credit growth. For the whole of 2017, bank credit growth was only in single digits.
On the commercial end, Banks have been lending to trade and to non-banking finance companies. Besides shrinking demand for credit, demonetisation also brought down interest rates sharply. This resulted in large corporates replacing loans with borrowings by issuing debt. While lenders do invest in debt, these investments are not reflected in credit numbers. Besides banks, mutual funds have also invested a significant amount in corporate bonds.
The growth in the loan book of banks during the current fiscal (up to December 22) has been Rs 2,55,260 crore. In the same period last year, it was Rs 67,780 crore. Overall bank credit stood at Rs 80,967 crore as on December 22.
A break-up of the sectoral deployment of bank credit up to November-end shows that 40% of the incremental loans went to services sector, which included loans to trade and non-banking finance companies. Almost half (47%) of the incremental bank loans went to the personal segment. Loans to the housing segment grew at 13.1% with the homeloan books of banks growing by Rs 10,680 lakh crore to Rs 9,22,210 crore. The highest growth was recorded by credit card advances which rose 37% to Rs 63,700 crore.
Although bank credit to industry accounts for 36% of the total loan book, it is only 4.5% of the incremental credit. Overall credit to industry has grown by only 1%.
According to rating agency CARE, bank credit has grown faster this year leading to a strain on liquidity. “Credit growth to manufacturing and services for April-October are negative, while that to agriculture and personal loans segment is 7.7%. For the year, we expect growth in credit to match that of deposits, with thrust being on retail sector,” the rating agency said in a report.
Growth in aggregate bank deposits has slowed to 4% mainly due to the impact of demonetisation wearing off. With currency supply, improving most of these funds were withdrawn resulting in a drop in deposits growth. As on December 22, bank deposits stood at Rs 1,08,851 crore a decline of Rs 16,960 crore over the fortnight.
2017-18: individuals, not industry, drove growth

From: Sidhartha, IDBI to boost retail loans, raise ₹5k cr from non-core asset sale, May 7, 2018: The Times of India
Ailing IDBI Bank is looking to step up focus on housing, retail, farm and MSME loans and pare the size of its corporate loan book, with the management planning to raise Rs 5,000 crore through the sale of non-core assets as part of a revamped five-year strategy to be finalised by the state-run lender’s board.
The plan hinges on specialised branches and digital transactions — targeted to account for 80-85% share (of all transactions) over the next five years — with the management banking on the rapidly-depleting manpower to deliver results, sources told TOI. In recent months, large number of employees have left the bank due to uncertainty and no salary revision for several years. The new strategy has been prepared by Boston Consulting Group, which may get a fresh lease of life through a one-year extension in its contract that is estimated to cost over Rs 15 crore.
Since shedding its development financial institution tag nearly 15 years ago, IDBI has been a story of misses with several twists and turns and repeated failures to significantly scale up retail banking, a business that has moved from the public sector to private banks, which are seen as more efficient in delivering services. The retail loan book made up for 23% of the lender’s advances at the end of December, while the loans to industry accounted for nearly half the global loans of over Rs 2 lakh crore. Between March and December 2017, the retail loan portfolio grew 10% to Rs 47,000 crore, while agri- and MSME-loans remained flat. The sources said the agri-loan portfolio may be expanded from around Rs 17,000 crore to nearly Rs 45,000 crore in five years.
The bank is saddled with over a quarter of its loans turning into NPAs, and over the next five years the plan is to reduce the proportion of gross NPAs to 10% of advances. IDBI Bank sources, however, said a large part of this is depended on the bankruptcy cases filed against various companies. Of the 12 highprofile cases, none have been finalised yet as promoters and bidders have used multiple judicial tracks to hold up decisions even as the 270 resolution deadlines near in almost every case.
Last May, RBI invoked the provisions of prompt and corrective (used for so-called weak banks) against IDBI Bank due to worsening asset quality and negative return on assets. The action puts curbs on expanding the loan portfolio and forces managements to initiate action to put the bank back on track.
The five-year strategy has been in the making for a while and is expected to factor in the recent government instructions on running banks and sanctioning loans.
Since the change of management at IDBI Bank, which saw M K Jain take over as managing director, the public sector lender has focused on cutting costs and selling non-core assets, including real estate, which is also part of the plan charted out by the finance ministry.
2017-18: At 83%, consumer durables loans grew most
At 83%, consumer durables loans grow most in FY18, June 28, 2018: The Times of India

From: At 83%, consumer durables loans grow most in FY18, June 28, 2018: The Times of India
The number of borrowers with consumer durable loans grew 83% to 1.95 crore in the 12 months ended March 2018 — the fastest expansion rate among all retail loans, followed by credit cards (28%) and personal loans (27%). Bankers say that the increase in retail borrowers is due to the use of credit scoring and analytics, which has helped take retail loans to new-to-credit customers.
According to a TransUnion (TU) Cibil report, total outstanding retail advances as of March 2018 increased 25% from March 2017. The number of outstanding accounts increased by more than 32% over the same period. “The number of live accounts rose considerably across all major credit types over the past year. The average balance per borrower grew at more modest levels,” said TU Cibil vice-president (research and consulting) Yogendra Singh.
Lenders like HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank are using analytics to enable customers avail of pre-approved loans online. Non-bank lenders like Bajaj Finance have developed online systems that enable loans to be cleared at retail outlets within minutes. E-commerce companies are partnering lenders to offer goods on equated monthly instalments (EMIs). In many consumer durables, the manufacturers are providing interest subvention, enabling customers to buy on credit without interest cost.
There are currently nearly 9 crore retail loan accounts across various segments such as auto, consumer durables, home loans, personal loans, credit cards and loans against property. Many borrowers have multiple loans. TU Cibil’s analytics show that nearly 15 crore Indian consumers who are not currently borrowers can be eligible for retail credit.
Another positive development is that while lenders are seeking lower income borrowers, delinquency has not gone up. Delinquency rates — 90 or more days past due (DPD) — for major retail lending products declined or remained relatively stable over the year ended March 2018. The quality of auto loan portfolio improved with delinquency rates falling by 83 basis points (100bps = 1 percentage point) to 2.78% in the first quarter.
The rising share of retail loans has implications for lenders. Very few banks are geared to tap the potential in retail lending. As a result, non-banking finance companies (NBFCs) contribute a significant chunk of retail loans. According to a report by ratings agency ICRA, retail-focused NBFCs (or retail-NBFCs) — with an estimated portfolio size of Rs 7.5 lakh crore in FY18 — will require Rs 3.8-4 lakh crore fresh debt in FY19 to support 20% growth.
Much of the growth in consumer durable loans has been driven by issuing higher volumes of smaller ticket loans. Consequently, the average loan per consumer declined by 5.7% over the year ended March 2018 to Rs 10,382.
The number of live credit card accounts stood at 3.26 crore as of March 2018 — an increase of 28% over the same period last year. Outstanding balance on credit cards increased by 43% to Rs 75,100 crore during the same period. Over the past two years, and particularly following the demonetisation event in November 2016, the number of credit card accounts had increased by nearly 50%, while the number of consumers with a card account has expanded as well. Consumer usage of those credit cards has also increased. The average credit card balance per borrower rose 12% to Rs 35,495 as of March 2018. “It is anticipated that the trend of increasing adoption of digital transaction channels should continue to act as a tailwind for future card growth,” said TU Cibil in its report.Personal loans saw similar growth dynamics, with the number of live consumers increasing 27% to 1.2 crore in the year ended March 2018, while aggregate balances increased 49% to Rs 2.7 lakh crore.
While retail loans are growing, delinquencies in these accounts are not. The delinquency rate for consumer durable loans (after 90 days) declined by 43bps year-over-year to reach 0.89% at the end of Q1, while the delinquency rate for personal loans dropped 19bps over the year to 0.52%. The credit card 90+ day delinquency rate increased modestly — by 9bps — to 1.70% in March 2018 but remains essentially unchanged from the level two years prior in March 2016.
2018> 2019
March 1, 2019: The Times of India

From: March 1, 2019: The Times of India
See graphic:
Growth of credit, Jan 2018> Jan 2019
Non-food credit increased 13.1 percent in January 2019 compared to 9.5 percent in January 2018, RBI data shows. Services and retail segments were the driving force behind this double-digit growth. While the services sector grew a whopping 23.9%, personal loans too showed a double-digit growth. Industry, on the other hand, saw a mere 5% increase.
2018 Jun- 2020 Jul
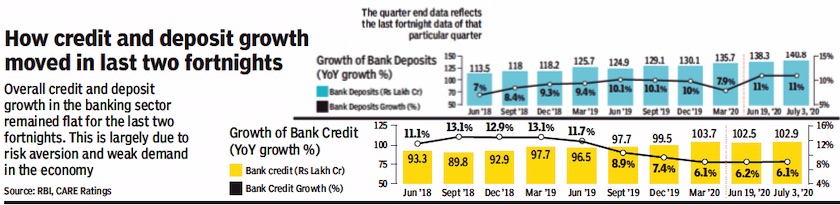
From: July 29, 2020: The Times of India
See graphic:
Credit and deposit growth in India, 2018 Jun- 2020 Jul
Deposits
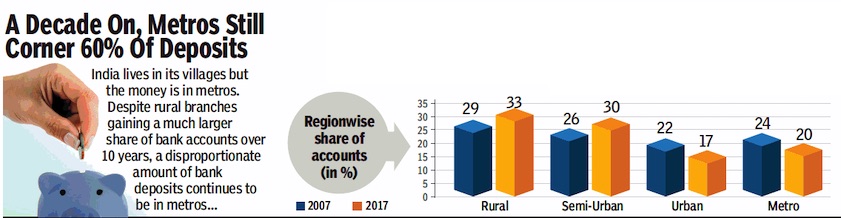
From: November 13, 2018: The Times of India

From: November 13, 2018: The Times of India
See graphics:
Region-wise share of accounts- the share of urban and rural areas, and metros- 2007 and 2017
Region-wise share of deposits- the share of urban and rural areas, and metros- 2007 and 2017
Share of households in FY16 deposits increases, govt's dips, December 27, 2016: The Times of India

Households contributed most to deposit growth in FY16, while deposits held by government agencies shrank according to data released by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on Monday . The latest numbers show that government and entities in the financial sector (banks in particular) brought down their deposits with other banks. However, individuals and corporate as increased their share of deposits.
Bank deposits in FY16 grew by 8.8%, or Rs 8.68 lakh crore, to Rs 98.41 lakh crore. Of this, growth in household deposits was 11%, or Rs 6.65 lakh crore.The overall deposit growth would have been higher but for 14% drop in state government deposits to Rs 3.82 lakh crore.Interbank deposits also fell 24.5% to Rs 2.71 lakh crore while corporate deposits jumped nearly 115% to Rs 10.65 lakh crore.
The RBI on Monday released the data on composition and institutional ownership pattern of deposits with sche Source: RBI duled commercial banks (SCBs) as on March 31, 2016. Households continue to own the majority of deposits with their share rising to 61.5% from 60.1% earlier. The government sector and the private corporate sector followed, contributing 12.8% and 10.8%, respectively. A majority (63.8%) of deposits were term deposits.
Dormant bank accounts
2018: ₹11,300cr lying unclaimed with 64 banks
Chethan Kumar, ₹11,300cr lying unclaimed with 64 banks, March 18, 2018: The Times of India
The largest amount — Rs 1,262 crore — is lying with the State Bank of India, Rs 1,250 crore with PNB, while all other nationalised banks together hold Rs 7,040 crore. All this money, howver, is just a fraction of the total deposits of over Rs 100 lakh crore handled by banks in India.
Former RBI chair professor at IIM-B Charan Singh says: “Most of these deposits would be cases of deceased account holders, or people with multiple bank accounts. It is unlikely that too much of it, or may be any of it, is benami or unaccounted money.”
Section 26 of Banking Regulation Act, 1949, mandates that banks submit a return of all accounts in India which have not been operated for 10 years to the RBI within 30 days after the close of each calendar year. But Section 26A says that it does not prevent a depositor or claimant from claiming the deposit or operating the account after the expiry of the period of 10 years and the banking company is liable to repay amount.
Money lying in dormant bank accounts is parked in the Depositor Education and Awareness Fund, which has been created under the provisions of the Banking Laws (Amendment) Act, 2012.
Among the private banks, RBI says that seven — Axis, DCB, HDFC, ICICI, IndusInd, Kotak Mahindra and YES Bank — have a total of Rs 824 crore in unclaimed deposits. Twelve other private banks together have Rs 592 crore, taking the total such money with private banks to Rs 1,416 crore.
Of all the private banks, ICICI Bank with Rs 476 crore and Kotak Mahindra Bank with Rs 151 crore have the highest unclaimed deposits.Comparatively, 25 foreign banks, whose operations are much smaller in size, account for Rs 332 crore in unclaimed deposits, with HSBC alone accounting for Rs 105 crore.
Foreign banks
2018: Companies turning to overseas lenders
Why Indian companies' dependence on foreign banks rising, December 18, 2018: The Times of India
India’s companies are growing more dependent on banks to raise offshore funds going into 2019 as the bond markets sputter and local-currency funding from domestic banks dries up.
Borrowers that are facing challenges in the credit market are finding solace in dollar-denominated loans, even as non-performing debt at local banks, volatility in the rupee and uncertainty over national elections next year add to pressure on financing costs.
The downfall of shadow lender IL&FS group has fueled concerns about default risks, making banks cautious and pushing up the cost some firms pay for loans at home. Companies are increasingly turning to overseas lenders, as distressed assets of about $210 billion at India’s banks limit their capacity to lend rupee funds.
“Many issuers are looking at offshore loans due to low liquidity in the rupee debt markets,” said Durgesh Tinaikar, head of corporate and institutional banking at Mizuho Bank India. “Borrowers find offshore loans easier to raise funds, even though pricing is largely on an upward trend, mainly for banks and non-banking finance companies, due to political uncertainty and risks for volatility in the rupee.”
Borrowing cost trends
The big picture is that loan costs are heading up for some borrowers, but had fallen so much earlier that they are still lower this year on average. Average margins on Indian five-year foreign-currency loans are 130 basis points more than London interbank offered rate in 2018, the lowest since 2005, according to Bloomberg-compiled data. In comparison, spreads over Treasuries for dollar bonds of local issuers have risen 109 basis points this year to 275, according to ICE BofAML index data.
Recent Examples
Some Indian companies are stomaching the recent uptick in loan rates. State Bank of India, the nation’s biggest lender, is paying a margin of 115 basis points over Libor for its new $500 million five-year loan, 10 basis points higher than its similar-tenor facility in 2017. Indian Oil Corp is offering 100 basis point margin on a $1.3 billion five-year loan, compared with 70 basis points on the refiner’s $300 million loan with the same tenor from a year ago.
Insights
“Some of the non-bank financial institutions and smaller banks in India have had some credit risk problems,” said John Corrin, global head of loan syndications at Australia and New Zealand Banking Group in Hong Kong. “Some of the companies are strong and will continue to have access to the foreign market, while others are less so and definitely will struggle to raise funds or will have to pay significantly more.” In the bond market, credit rating downgrades have weighed on sentiment toward some borrowers.
Foreign, private, PSU banks
2018, 19
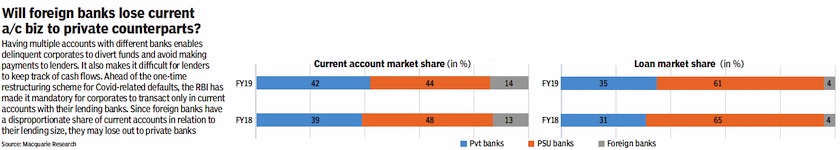
From: August 19, 2020: The Times of India
See graphic:
The Market share of Foreign, private, PSU banks in India in 2018, 19.
Mobile banking
Unified Payment System/ UPI
The Times of India, August 26, 2016
Mayur Shetty
The RBI has cleared a Unified Payment System a platform which links bank account numbers to virtual payment addresses (aliases). The UPI-enabled app in effect turns your smartphone into a bank and has come as a boost to a cashless economy .
Just as an ATM of one bank can be used to access accounts in all banks in the network, any UPI-enabled app can be used to log into one's accounts in other banks. Second, the interface overcomes one of the biggest pain points in sending money online -that of knowing 15-digit account numbers and an 11digit IFSC code (used to identify bank branches). Instead of account details, the receiver has to merely share an alias like xyz@axisbank. The UPI makes use of the existing Immediate Payment System (IMPS) which allows funds transfer using bank account number, an IFSC code and other credentials.
“Real-time sending and receiving money through a mobile application at such a scale on interoperable basis has not been attempted anywhere else in the world. The UPI app will be made available on Google Play Store by banks,“ NPCI managing director and CEO A P Hota said here on Thursday .
Twenty-one banks will go live over the next couple of days. But the country's largest bank, SBI, has expressed concerns and has kept it on hold until it gets more clarity from the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), the umbrella organisation for retail payment systems in India. Of the 21 banks, eight banks have gone live.
“Our app is still under development. We have raised some security concerns on the registration process and transactions being timed out. The NPCI has not yet come back.We will be ready by Septemberend. But the decision to join will depend on NPCI coming back to us with clarifications,“ said Manju Agarwal, deputy MD, SBI. HDFC Bank too is working on its application and expects to be ready in three weeks. ICICI Bank has announced that it will integrate its iMobile and Pockets app with UPI in the next few days. iMobile is for the bank's customers, while Pockets is an app with a prepaid instrument available to anyone who downloads it.
Kotak Mahindra Bank has decided to play it safe and provide a separate application for UPI. “We are in process of development and certification of UPI-enabled app. We will launch a new app which will be UPI-enabled in 4-6 weeks. “ said Deepak Sharma, chief digital officer, Kotak Mahindra Bank.
Bank Board Bureau/ 2016
The Hindu, February 29, 2016
Prime Minister Narendra Modi approved the setting up of the Bank Board Bureau with former Comptroller and Auditor-General of India Vinod Rai as its first Chairman.
The Bureau is mandated to play a critical role in reforming the troubled public sector banks by recommending appointments to leadership positions and boards in those banks and advise them on ways to raise funds and how to go ahead with mergers and acquisitions.
“With a view to improve the governance of public sector banks, the government had decided to set up an autonomous Bank Board Bureau. The bureau will recommend for selection the heads of public sector banks and financial institutions and help banks in developing strategies and capital raising plans,” the government said in a release.
The bureau was announced in August 2015 as part of the seven-point Indradhanush plan to revamp these banks. It will constantly engage with the boards of all 22 public sector banks to formulate appropriate strategies for their growth and development.
The bureau, led by Mr Rai, will select the heads of public sector banks (even from the private sector, if need be) and aid them in formulating strategies to raise additional capital. It will select and appoint non-executive chairmen and non-official directors.
The non-performing assets of public sector banks are estimated at almost Rs. 4 lakh crore, and they need to raise capital of Rs. 2.4 lakh crore by 2018 to conform to Basel-III capital requirement norms, according to the government.
While some questions have been raised on Mr. Rai's appointment as a CAG cannot hold a government office post-retirement, former senior civil servants say the role is advisory in nature and a part-time position. The government release said the appointments have been made for a period of two years.
The bureau will have three ex-officio members and three expert members, in addition to the Chairman.
Mobile banking transactions
The Economic Times, Mar 22, 2016
Mayur Shetty
Top 5 banks generate 92% of mobile banking value
Mobile banking penetration in India is concentrated among customers of five banks. According to data released by the Reserve Bank of India, the top five banks account for more than 92% of the entire value of mobile banking transactions in the country.
State Bank of India leads the pack with 36% market share, followed by ICICI Bank (21.5%), HDFC Bank (17.8%), Axis Bank (12.8%) and Kotak Bank (4.7%). These banks have managed to increase the number of mobile transactions by being proactive in development of mobile apps and making mobile banking feature-rich.
According to Deepak Sharma, head of digital banking at Kotak Mahindra Bank, his customers are leapfrogging to mobile banking directly from branch banking without using the browser. "Around 35% of our online banking customers are coming in from their mobile phones without having used net banking," he said. As against its market share of 1.4% of deposits, the bank has over 4.5% share of mobile banking. He said that online has already become the primary channel for most of the customers in the bank.
"Overall, 60% of fixed deposits have moved online. But if you look at only retail, nearly 80% of FDs are opened online," said Sharma. He added that it was largely bu sinesses that were obtaining fixed deposits in the branch.
"In terms of number of logins, mobile banking had overtaken net banking more than six months ago. Now mobile banking is ahead of net banking in terms of transactions as well," said Sharma. He said that the fastest growing segment is online recharge, which is driving transactions.
"We are now getting more and more categories online, like bill pay and IPO subscription. We are also seeing systematic investment plans (SIPs) gaining traction. We feel that any simple product that is easy to start, liquidate and monitor will pick up online," said Sharma.
In terms of volumes, the top five banks account for more than 85% of all mobile banking transactions. While the banks are the same as the toppers in transaction value, the rankings and consequent market shares vary slightly for volumes.State Bank of India again led the pack with a 38.5% market share, followed by ICICI Bank at 17.7%, Axis (15.3%), HDFC Bank (9.9%) and Kotak Bank (4.3%).
2018: UPI
The writer is the MD & CEO of NPCI

From: Dilip Asbe, UPI 2.0 can turn into a mega citizen-scale pay system, January 11, 2019: The Times of India
India capable of replicating China’s digital economy — better & faster
India enters 2019 on the cusp of a digital revolution, mainly due to major influencers. First, we have a regulator defining the landscape by innovation-led policies, fuelling new-age business models and maintaining security and risk management standards to highest levels. Second, we have a government that is focused on moving towards a digital or less-cash economy. Third, we have banks embracing technology to accelerate digital payments, proliferation of financial inclusion and superior customer services. And last, we have fin-tech innovators who are re-imagining solutions for our day-to-day problems and providing superior consumer experience for digital payments.
The Unified Payments Interface (UPI), the most advanced payment system in the world, was launched in 2016, designed on the principles of interoperability, consumer choice and forging partnerships between banks and fintechs, leveraging each other’s strengths. The RBI’s payment system division DPSS, under the governorship of Raghuram Rajan, played a key role in bringing banks together to promote this initiative. Support of the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) and leading lenders has been a critical factor in its success. In the second half of 2018, the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) launched UPI 2.0 with the support of regulatory teams under former RBI governor Urjit Patel and deputy governor B P Kanungo to incorporate path-breaking features.
Several milestones were achieved in domestic payments last year. India’s RuPay Card crossed 500 million and Bharat BillPay on-boarded over 100 billers in its ecosystem. The Aadhaar payments services, too, surpassed 100 million unique customers every month. After demonetisation, the UPI-based ‘Bharat Interface for Money’ (BHIM) app, launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has acted as a catalyst to nudge many third-party providers to launch the UPI app. We are
now seeing the results. Sticking to the design principle of “consumer choice”, there are now over 90 BHIM UPI apps provided by banks or thirdparty providers to customers of 130 banks.
The Supreme Court’s decision to limit the use of Aadhaar database was a setback. The fintech community is relying on the government to identify a solution to use Aadhaar systems based on voluntary sharing by the customer. The NPCI had to stop the e-NACH (National Automated Clearing House) using e-sign due to the SC judgment. However, we are working to create alternatives, but it may take time.
While it was a practice to look towards the latest trends in Silicon Valley in the US, with UPI, the West has turned to partner with India for innovation. Many global giants (Google, WhatsApp, Amazon, Samsung, Truecaller, Xiaomi, etc) and Indian unicorns (Paytm, PhonePe, Hike, etc) have joined the UPI bandwagon in collaboration with banks.
Unlike China that operates mobile payments mostly under two players in a closedloop manner, the RBI has been
clear from the start to set UPI as an interoperable system. When it comes to mobile payments and financial inclusion using Aadhaar, India has an edge due to innovation.
While there are multiple ways for making payments, the market is broadly divided into three parts — a) financial inclusion that covers the JAM trinity, i.e. Jan-Dhan, Aadhaar and mobile (additionally, it covers Direct Benefit Transfers, e-KYC, etc), b) mobile and internet payments powered by UPI, IMPS (Immediate Payment Service), net/mobile banking and interoperable QR codes, and c) card-based payments.
In the coming years, we will see a significant shift to a mobile-first strategy with consumers using functionalityrich and user-friendly apps for P2P (peer-to-peer) or P2M (peer-to-merchant) payments. The electronification of all kinds of C2G (citizen-to-government) payments is a big opportunity. I’m glad to see the efforts from all government divisions pushed by the ministry of electronics and information technology (MeitY) and the department of financial services (DFS).
If the growth momentum continues, we hope that the use of UPI will take the shape of citizen-scale payments system. Volumes may come down in the short term once firms go slow on promotional offers. However, the outlook is very strong for medium to long term. We have started an awareness campaign to protect customers from social frauds. But, more needs to be done. Now that diverse payment platforms are available to customers, our goal would be to drive adoption among the masses. We have the potential and capability to do what China has done to build its digital economy, better and faster. Startups/fintechs, in collaboration with banks, should build specific-use cases to drive adoption that will be the main attraction of 2019.
Frauds committed in banks
1992-2015

From: Mayur Shetty, ₹11k-cr PNB fraud will have a domino effect on banks, February 15, 2018: The Times of India
3 Banks Advanced ₹7,000Cr Against Fraudulent Guarantees
Punjab National Bank (PNB) has said that it faces a contingent liability in respect of letters of undertaking (LoUs) that have been fraudulently issued to Nirav Modi and Mehul Choksi groups. The bank wrote letters to all major lenders on Wednesday, informing them of the fraud. Banks, which have lent on the basis of the LoUs issued by PNB, have an exposure close to Rs 11,000 crore. LoUs are like a bank guarantee that undertake to pay lenders if borrowers default.
Bankers says dozens of lenders have provided loans against the LoUs issued by PNB. Initial investigations suggest that Allahabad Bank, Axis Bank and Union Bank had funded close to Rs 7,000 crore on the strength of the LoUs, with Allahabad Bank having the largest exposure. However, a major chunk of the loans were sold down. SBI and Bank of Mauritius are understood to have a secondary exposure.
In banking circles, these loans are treated more like interbank exposures as lenders have recourse to the bank issuing the guarantee. These loans are also traded by banks among themselves in the same manner that they trade bonds. For instance, Axis Bank, which has funded some of the imports through its overseas branch, has sold some of the loans to other banks.
With no assurance from PNB that it will honour the fraudulent guarantees, financing banks will find themselves stuck for payment. Bankers fear a legal stalemate as those who purchased loans in the secondary market will approach the financing banks. The lenders, in turn, will approach PNB to invoke the guarantee. PNB’s caution letter to banks stating the LoUs are fraudulent are seen as an indicator that the bank is trying to deny liability.
Some banks are saying that the RBI will have to intervene to break the likely stalemate. In banking frauds that took place in earlier years, defaults ballooned in excess of the funds siphoned off as accounts were frozen and claimants went to court.
Lenders say that the RBI will have to intervene to prevent such a stalemate from occurring again. Although PNB denies liability on the grounds that the transactions are fraudulent, lender banks claim that since the transactions have gone through the Swift messaging platform — which is the basis for settling trade deals globally — the contracts have to be honoured.
2013-16
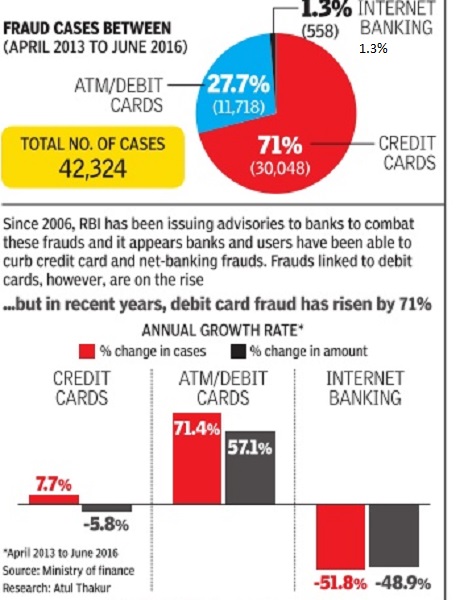
Out of over 40,000 cases of fraudulent use reported in 2013-16, more than 70% had to do with credit cards. Net banking accounted for only a miniscule 1.3% of the cases
The Times of India
See graphic:
Banking frauds, 2013-16
2012-17: 8,670 fraud cases, totalling ₹ 61,260 cr ($9.58 billion)
India's fraud problems extend far beyond PNB, shows RBI data, February 16, 2018: The Times of India
HIGHLIGHTS
RBI data shows state-run banks have reported 8,670 'loan fraud' cases totalling Rs 61,260 crore over the last five financial years
In India, loan frauds typically refer to cases where the borrower intentionally tries to deceive the lending bank and does not repay the loan
Investors may have been shocked when one of India's biggest banks disclosed a $1.77 billion fraud by a billionaire jeweller, but the central bank has recorded data that shows the problem runs far deeper and wider.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data, which a Reuters reporter obtained through a right-to-information request, shows state-run banks have reported 8,670 "loan fraud" cases totalling Rs 61,260 crore ($9.58 billion) over the last five financial years up to March 31, 2017.
In India, loan frauds typically refer to cases where the borrower intentionally tries to deceive the lending bank and does not repay the loan.
The figures expose the magnitude of the problem in a banking sector already under pressure after years of poor lending practices. Bad loans surged to a record peak of nearly $149 billion last year.
Bank loan frauds have steadily increased as well, reaching Rs 17,634 crore in the latest financial year from Rs 6,357 crore in 2012-13, according to the data, which doesn't include the PNB case.
Punjab National Bank, India's second-largest state lender, said on Wednesday two junior officers at a single branch had illegally steered $1.77 billion in fraudulent loans to companies, most of them controlled by billionaire jeweller Nirav Modi. It was India's biggest fraud ever.
"This might be the tip of the iceberg or the middle, and that is the worry," said Pratibha Jain, partner at law firm Nishith Desai Associates, who advises on bankruptcy cases.
"The fact is we don't know what else is out there."
BANK DISCLOSURES
The RBI did not immediately respond to a request for comment. But in June 2017 the central bank, in its Financial Stability Report, called frauds in banks and financial institutions "one of the emerging risks to the financial sector".
"In a number of large value frauds, serious gaps in credit underwriting standards were evident," the RBI said, adding that some of the gaps include lack of continuous monitoring of cash flows and cash profits, diversion of funds, double financing and general credit governance issues in banks.
The RBI has been commended for forcing Indian banks to fully disclose its bad loans, speed up their recovery, and stop hiding fraud cases as non-performing assets.
Yet to some critics, the RBI has, at the same time, been too guarded about publicly sharing data on loan defaults or fraudulent loans. This is partly due to legal constraints on disclosing individual cases and worries investors would pummel the affected banks, making loan recovery even harder.
In fact, the numbers of loan fraud cases across India could be even higher since they only include cases reported to the RBI, which involve only loans of Rs 1,00,000 or more.
In its right-to-information request, Reuters sought data from 20 of India's 21 state-run lenders and obtained 15 replies.
PNB topped the list with 389 cases totalling Rs 6,562 crore ($1.03 billion) over the last five financial years, in terms of the total amounts involved.
Reuters was unable to obtain a detailed breakdown on the exact nature and method of the loan frauds the banks reported to RBI over the last five financial years.
After PNB, Bank of Baroda had the highest amount of loan fraud reported, with Rs 4,473 crore from 389 cases and Bank of India ranked third, with loan frauds totalling Rs 4,050 crore from 231 cases over the same period, the data shows.
India's biggest lender, State Bank of India reported 1,069 loan fraud cases in the last five financial years but did not disclose the amount.
It was also unclear how much has been recovered by the banks over the years.
WHOLESALE REFORMS
The magnitude of the bad debt in India forced the government last year to bail out the sector by pledging to inject $32 billion over this financial year and next.
Yet analysts and credit rating agencies have long warned that solving the bad debt at India's banking sector needs to also involve wholesale reforms of the lending practices that led to the surge in bad loans.
Bankers have been blamed for steering funds to politically connected business tycoons, such as Vijay Mallya, without due diligence, or after being pressed by government officials to steer funds to sectors it wanted to promote, such as infrastructure.
Mallya stands accused in India of fraudulently palming off losses from his now defunct Kingfisher Airlines onto banks by taking out loans he had no intention of repaying, an allegation he denies.
Nirav Modi, the jeweller accused in the PNB fraud case, posed for pictures with Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi at the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, where he was part of India's delegation of corporate leaders.
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) has denied any link with Nirav Modi, who is not related to the prime minister.
2013-16: PS banks lost Rs 2,450 crore to frauds involving staff
HIGHLIGHTS
Southern states, including Maharashtra, has 49% (609) of all cases, but reported just 19% of the total money lost
In comparison, Rajasthan, which has just 3% of cases with employee involvement, accounts for 44% of money involved
Among other things that emerged in the aftermath of the massive Punjab National Bank (PNB) scam is the active role of employees of the Public Sector Banks (PSBs) in multiple frauds over the years. TOI has accessed Reserve Bank of India data that reveals the number of cases involving staff across various states and the amount of loss reported.
Overall, data from April 2013 to June 2016 shows that a total of Rs 2,450 crore was lost to 1,232 frauds of Rs 1 lakh and more where employees were involved. RBI is yet to classify state-wise data for subsequent quarters.
Of these, southern states, including Maharashtra, has 49% (609) of all cases, but account for just 19% (Rs 462 crore) of the total money lost to such crimes. In comparison, Rajasthan, which has just 3% (38) of cases with employee involvement, accounts for 44% (Rs 1,096 crore) of money involved.
Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Maharashtra have the most cases of staff involvement in frauds (in the same order) in the country while Rajasthan, Chandigarh, Delhi and West Bengal lost the most money, collectively accounting for 70% of all the money lost (in the same order).
The RBI mandates that “Cases of fraud involving Rs 1 lakh and above, committed by outsiders on their own and/or with the connivance of bank staff/officers must also be reported." But these cases do not account for smaller cases of employee fraud, which experts say also run into crores of rupees.
One bank manager who did not wished to be named, said: “One of the reasons you see more number of such cases in the South could be because there are more bank branches in these states which have more number of urban centres. However, that is no excuse to have high crime rate, especially involving staff.”
Analysing the data, one expert said that it is most likely that frauds in Rajasthan and other states that lost the most money, could all be related to advances, while those from the Southern states could be related to deposits.
“When money is being lent as loan, the exposure is generally higher, as opposed to deposit-related frauds which generally do not involve large amounts of money,” he explained. Multiple experts argue that lack of good practices, including allowing employees to work at the same section and branch for long periods, have been hurting PSBs.
The RBI says “that banks should follow the guidelines for reporting frauds such as unauthorised credit facilities extended by the lender for illegal gratification, negligence and cash shortages, cheating, forgery, et al to the state police authorities.”
It adds that while dealing with such cases, the banks should not merely be motivated by the necessity of recovering expeditiously the amount involved, but should also be motivated by public interest and the need for ensuring that the guilty persons do not go unpunished.
Frauds Over Rs 1 lakh Involving Staff & Money Lost:
|
State |
No. of cases |
% To Total Cases |
Amount Involved |
% To Total Loss |
|
Tamil Nadu |
170 |
14% |
Rs 83.09 cr |
3% |
|
Andhra Pradesh |
157 |
13% |
Rs 148.41 cr |
6% |
|
Karnataka |
125 |
10% |
Rs 89.34 cr |
4% |
|
Maharashtra |
107 |
9% |
Rs 110.43 cr |
4.5% |
|
Kerala |
50 |
4% |
Rs 30.53 cr |
1.2% |
|
Rajasthan |
38 |
3% |
Rs 1,096 cr |
45% |
|
Chandigarh |
3 |
0.02% |
Rs 253.44 cr |
10% |
|
Delhi |
37 |
3% |
Rs 188.22 cr |
8% |
|
West Bengal |
69 |
6% |
Rs 167 cr |
7% |
|
Overseas Branches |
9 |
0.7% |
Rs 41.6 cr |
1.7% |
|
21 Other States |
467 |
38% |
Rs 241.53 cr |
10% |
|
Total |
1,232 |
100% |
Rs 2450 cr |
100% |
2013-18/ over 23,000 cases of fraud committed- RBI
May 2, 2018: The Times of India
HIGHLIGHTS
A total of 5,152 cases of fraud, up from over 5,000 cases in 2016-17, were reported in banks from April, 2017, to March 1, 2018, the Reserve Bank said
In 2016-17, banks had reported 5,076 cases of fraud involving Rs 23,933 crore
Over 23,000 cases of fraud involving a whopping Rs 1 lakh crore have been reported in the past five years in various banks, according to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
A total of 5,152 cases of fraud, up from over 5,000 cases in 2016-17, were reported in banks from April, 2017, to March 1, 2018, it said in reply to an RTI query filed by this correspondent.
The highest ever amount of Rs 28,459 crore is said to have been involved in these cases of fraud reported from April, 2017, to March 1, 2018, the central bank said.
In 2016-17, banks had reported 5,076 cases of fraud involving Rs 23,933 crore.
From 2013 to March 1, 2018, as many as 23,866 cases of fraud, of Rs 1 lakh or above in each case, were reported. A total of Rs 1,00,718 crore was involved in all the cases put together, according to the RTI reply.
Giving the break-up, the RBI said 4,693 such cases (involving Rs 18,698 crore) and 4,639 cases (involving Rs 19,455 crore) were reported in 2015-16 and 2014-15 respectively.
In 2013-14, banks reported 4,306 cases of fraud, involving Rs 10,170 crore, the central bank said.
"The reported fraud cases are processed and action is taken according to the facts and circumstances of individual cases," the RBI said.
The data assumes significance as central investigating agencies such as the CBI and the ED are looking into various big-ticket fraud cases in banks involving industrialists and others.
Among the prominent ones is the over Rs 13,000-crore fraud in the Punjab National Bank (PNB) allegedly committed by diamantaire Nirav Modi and his uncle Mehul Choksi, the promoter of Gitanjali Gems.
The CBI had recently also booked top officials of two public sector banks, a former CMD of the IDBI Bank, former Aircel promoter C Sivasankaran, his son and companies controlled by him in connection with a Rs 600-crore loan fraud in the IDBI.
The CBI has named 15 bank officials who worked at senior levels at the IDBI in 2010 and 2014 when loans were sanctioned to the companies controlled by Sivasankaran in its FIR registered on a complaint from the Central Vigilance Commission.
Managing Director and CEO of Indian Bank Kishor Kharat (who was then MD and CEO of IDBI Bank) and his counterpart in Syndicate Bank Melwyn Rego (then Deputy Managing Director in IDBI Bank), along with then Chairman-cum- Managing Director of IDBI Bank M S Raghavan, have been named in the latest FIR filed by the CBI.
According to government data, the gross non-performing assets (NPAs) of all banks in the country, amounting to Rs 8,40,958 crore in December 2017, were led by industry loans followed by those in the services and agriculture sectors.
The highest amount of gross NPAs was for the country's largest lender, the State Bank of India, at Rs 2,01,560 crore.
Among the others, the NPA for PNB stood at Rs 55,200 crore and for IDBI Bank, Rs 44,542 crore. Bank of India had NPAs worth Rs 43,474 crore; Bank of Baroda, Rs 41,649 crore; Union Bank of India, Rs 38,047 crore; Canara Bank, Rs 37,794 crore and ICICI Bank, Rs 33,849 crore, according to data presented by Minister of State for Finance Shiv Pratap Shukla in the Lok Sabha on March 9.
2014- 20
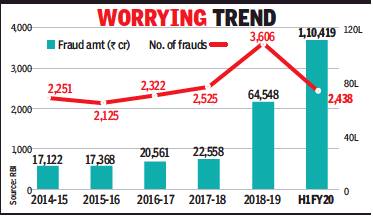
From: Mayur Shetty, June 22, 2020: The Times of India
See graphic:
Frauds in Indian banks, 2014- 20
2015-17: PSB staff punished for committing fraud
Chethan Kumar, February 18, 2018:The Times of India

From: Chethan Kumar, February 18, 2018:The Times of India
On an average, at least one banker is caught and punished for involvement in fraud every four hours, an analysis of data compiled by the Reserve Bank of India has revealed.
Between January 1, 2015 and March 31, 2017, as many as 5,200 officials of public sector banks have been punished for fraud.
“These employees have been convicted, awarded penalties, including dismissal from service,” the RBI document states. The central bank is in the process of compiling the data for such cases from April 2017.
While 1,538 officials of the State Bank of India faced action for fraud, putting the bank on top of the chart, Indian Overseas Bank and Central Bank of India occupy the second and third place with 449 and 406 insiders, respectively, being found guilty.
Between ’13 & ’16, all banks lost ₹66k cr to 17,504 frauds
BANK FRAUD
At Punjab National Bank (PNB), 184 officials were caught for fraudulent activities during the same period. The numbers assume significance as multiple agencies are now digging deeper to unearth insider role in the massive fraud at PNB.
Netrika Consulting managing director Sanjay Kaushik, whose clientele include banks, says that banks spent too much time looking outside their walls for frauds, and thus have ignored introducing networkwide risk frameworks.
Concerned, the RBI has been issuing circulars to banks about how to effectively report cases and also put in place mechanisms to prevent them. A July 2016 circular, the latest in a series, reads: “To compress the time taken in detection of fraud, a framework for handling loan frauds has been put in place.”
Bikash Gangadharan, a senior manager with a multinational bank, says: “...There should be multiple levels of authentication… But the Indian banking system is extremely hierarchical… If the manager says something must go through, nobody says that it must need a second review, which is a risky way of running things.”
While this set of data does not reveal the financial loss banks suffered due to employees committing fraud, separate data accessed from RBI for the period between April 1, 2013 and December 31, 2016 shows that all commercial banks, including private ones, lost Rs 66,066 crore to 17,504 frauds.
Of the total number of frauds, 2,084 cases saw the involvement of insiders, accounting to 12% of the cases. But the data does not say how much money was involved in the frauds committed by the employees.
“It is obvious that banks have not been able to identify and take proactive steps to mitigate known risks. This makes it hard to pinpoint who is involved. The top management is definitely at fault for failing to put in place a clear compliance strategy,” says Tobby Simon of Synergia Foundation, a multi-disciplinary thinktank.
Most of the foreign banks employ efficient frameworks for risk reporting that help in identifying the patterns. Risk frameworks have algorithms that pinpoint a particular threat.
Jatinder Pal Singh, who had worked with a multinational corporation bank’s IT risk management team for seven years, says that service providers such as IBM have even developed software that flag frauds.
2016-17/ 86% of all bank frauds, 99% of PNB’s, tied to loans
Chethan Kumar, February 22, 2018: The Times of India
From misuse of letters of credit, guarantee or undertakings to diversion and siphoning of funds, a variety of frauds linked to advances haunt the Indian banking system, indicating a lack of hygiene and risk frameworks.
While 86% of all frauds in India for 2016-17 are linked to advances, it was 99% at Punjab National Bank (PNB) which, experts say, points to collusion with insiders. Also, 26 banks reported that more than 97% of their frauds were advance-related, of which 15 peg it at 99% or more. Eight banks said such frauds account for 90%- 95% of frauds.
Data of the Reserve Bank of India show that of Rs 23,903 crore lost to fraud in 2016-17, 86% (Rs 20,561 crore) was lost to advance-related fraud. In PNB, of Rs 2,808 crore lost to fraud, Rs 2,788 crore (99.3%) was linked to advances.
28% increase in cases: While RBI is compiling figures for 2017-18, data for three years ending March 31, 2016 show that 67% of total frauds were linked to advances, indicating a 28% increase. In 2016-2017, banks lost Rs 22,743 crore to fraud, of which Rs 15,238 crore was linked to advances.
According to experts and bankers, advances-related frauds are due to breach of trust and contract, and involve misuse of letters of credit or guarantees, submission of forged or fake documents to avail of loans and mortgaging of assets that don’t exist or have been pledged elsewhere, among other things.
Bankers guilty of collusion:
Prof Charan Singh, RBI Chair Professor, IIM-B, says: “So long as there is money, the greed to obtain it in whichever way possible cannot be rid from the system. What government and banks can do is install systems that minimise such frauds. We need an overhauling, from period transfers of all employees in banks to making top management and directors liable, a complete cleansing of the system is needed.”
A working paper titled “Frauds in the Indian Banking Industry”, published by Prof Singh and associates, points out: “Big frauds aren’t so easy to commit and often result because bank officials collude with borrowers, and sometimes even with officials of third parties such as advocates or chartered accountants.”
It adds that third parties often get away as it is nearly impossible for banks to prove criminal intent due to various reasons, such as lack of understanding of legal matters, and lack of expertise and legal advice, and unwillingness to reveal sensitive data to courts/ public domain.
Netrika consulting managing director Sanjay Kaushik said such frauds indicate a larger systemic issue that needs addressing professionally, using globally-accepted tools and best practices, and mere troubleshooting after a scam has been unearthed won’t help.
“To mitigate risks, it’s imperative for the banking sector to move towards employing an independent party during the credit sanctioning process. It’s now critical to validate and verify claims made by individuals seeking loans. An independent audit must be conducted to verify if funds procured are being used for which they were intended,” said Rohit Karnatak, managing director, India, APAC & EMEA — Global Screening, Pinkerton (a corporate risk management services firm).
2017: CVC discussed jewellery firms’ irregularities with CBI, ED, PSU bank vigilance

From: Neeraj Chauhan, Told Banks, CBI Of Irregularities By Jewellery Cos, April 9, 2018: The Times of India
A year before the Rs 13,500 crore Nirav Modi-Mehul Choksi scam came to light, the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) had sounded an alarm over irregularities in the gems and jewellery sector.
On January 5, 2017, the commision met senior CBI and ED officials as well as the chief vigilance officers of 10 banks, including Punjab National Bank, to discuss serious irregularities in the accounts of some jewellery firms, particularly those of Jatin Mehta’s Winsome group, says CVC’s annual report for 2017. PNB, which was the lead bank in one of the loans given to Mehta as well, has been left grappling with the Modi-Choksi scam after the duo, in collusion with some bank officials, illegally renewed letters of undertaking. They left India with their families in the first week of January this year and a case was registered soon after. The CVC report puts the focus on PNB’s senior management’s lapses.
Bizman Mehta fled India after taking loans of ₹6,200cr
Chief vigilance commissioner K V Chowdary told TOI, “That meeting was called to discuss frauds committed on banks by Jatin Mehta of Winsome group.” It also discussed issues related to frauds by other jewellery firms, loopholes in the banking system, enquiry procedures by CVOs, borrowers’ accounts and gold import.
The Modi-Choksi fraud had not been discovered then but PNB was the lead bank in one of the loans given to Mehta as well. The bank reportedly had an exposure of Rs 1,658 crore with Mehta, who is now said to be living in St Kitts. In all, Mehta fled after taking loans of Rs 6,200 crore.
Senior government officials said that PNB, which was already a victim of fraud, should have checked its accounts relating to the sector more carefully and this might have put the focus on Modi and Choksi’s companies. “Had PNB done that, the two might have been held,” a CBI officer said.
The CVC had also advised the RBI as well as the department of financial services (DFS), which comes under the finance ministry, to issue an advisory to banks to ensure control over forex remittances purportedly for the purpose of imports and that banks should have specific standard operating procedures (SOPs).
The CVC report said it had been dealing with issues related to the core banking system, which was not updated by PNB officials in the case of loans given to Modi and Choksi, human resource management systems (HRMS) and projects of development of IT infrastructure in the banking sector.
Concerned with the problems, the CVC had recommended systematic improvements in the banking sector last year.
The commission had noticed irregularities in import transactions such as non-compliance of Know Your Customer/Anti-Money Laundering (KYC/AML) guidelines while opening of account, absence of due diligence on the Indian importer and the overseas supplier, violation of bank’s guidelines and breaching the limit of advance remittances several times which was exploited by borrowers.
The CVC observed while examining a case that KYC documents, proof of income and other documents submitted by the borrower were forged. The commission observed that “there is no uniformity in the banking sector” on the issue of appointment of outside agencies.
Hall of shame
SBI funds bomb-makers
The Times of India, Jun 20, 2016
Top bank in `Hall of Shame' for funding bomb-makers
SBI has been named in a “Hall of Shame“ list of 158 banking and financial institutions globally that have invested billions of dollars in companies making cluster bombs. SBI is the only Indian entity on the list, which includes JP Morgan, Barclays, Bank of America and Credit Suisse that invested over $28 billion in seven producers of cluster munitions between June 2012 and April 2016, according to Dutch campaign group PAX.PAX said the Convention on Cluster Munitions bans use, production of cluster munitions. This convention was signed by 94 countries. The maximum number of 74 banks are from the US, followed by China (29).
SBI has been included in the list because of its exposure to Orbital ATK, a USbased company specialising in space and rocket systems.
“SBI has made $87 million available to the companies on the red flag list since June 2012,“ PAX said. “ SBI always works in accordance with local laws and regulations,“ a bank spokesman said.
August 2017: SBI owes 27% of bad loans
SBI defaulters owe 27% of all PSU banks' bad loans, August 21, 2017: The Times of India

SBI accounts for over 27% of the total amount owed to public sector banks by wilful defaulters. As many as 1,762 wilful defaulters owed SBI Rs 25,104 crore as on March 31, putting pressure on its balance sheet. Punjab National Bank (PNB) is next on the list with 1,120 wilful defaulters having outstanding non-performing assets (NPAs), or bad loans, of Rs 12,278 crore.
Together, these two banks account for Rs 37,382 crore -or 40% -of the total outstanding loans of Rs 92,376 crore due to public sector banks by wilful defaulters, according to finance ministry data. This is more than 20% higher than Rs 76,685 crore at the end of the previous fiscal 2015-16.
At the same time, there has been close to 10% increase in the number of wilful defaulters on an annual basis. It increased to 8,915 at the end of March as against 8,167 in the previous fiscal. Out of 8,915 cases of wilful defaults, banks have filed FIR (first information report) in 1,914 cases with outstanding loans of Rs 32,484 crore.
During 2016-17, 27 public sector banks, including SBI and its five associates, had written off Rs 81,683 crore -the highest in the last five fiscals.
2015-17: PNB, UBI top list of officials prosecuted
Chethan Kumar, PNB, UBI top list of officials prosecuted, February 28, 2018: The Times of India

From: Chethan Kumar, PNB, UBI top list of officials prosecuted, February 28, 2018: The Times of India
Among 30 Who Faced Music, 5 Each Were From These 2
In yet another indication of systemic glitches dogging banks in India, Punjab National Bank (PNB), along with United Bank of India (UBI), has reported the highest number of officials prosecuted for corruption.
Between 2015 and 2017, the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) sanctioned the prosecution of 30 officials of 13 banks. Of the 30 people prosecuted, five (16%) each were from PNB and UBI.
State Bank of India (SBI), with four of its officials being prosecuted, is in third place. Overall, year-wise data shows that 2015 had the most number of sanctions (11), followed by 2017 (10). In 2016, prosecution of nine officials was cleared. All the cases against these 30 officials were registered under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988.
This is apart from all officials of public sector banks (PSBs) involved in various frauds (not referred to CVC) — which stands at 5,000 for the same period — who have either been convicted, dismissed or awarded penalties.
Looking at the three banks in this category — PNB, UBI and SBI — the last bank had the most number of officials involved in fraud (1,538), followed by PNB (184) and UBI (141). There are 24 other banks which together accounted for 3,137 officials, with some banks reporting more cases than PNB.
While the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been issuing various guidelines and circulars about prevention of corruption and reporting of fraud, experts say unless the top management is punished, the issue will continue to plague the banks.
“The punishment needs to be demonstrative and overarching. While there is no need to politicise and overreact, this is not something the country can ignore any longer,” Prof Charan Singh of IIM-B told TOI.
The CVC, which maintains that PSBs and the government are committed to a ‘zero tolerance’ approach to corruption, has given its sanction to several investigating agencies, including the CBI.
Home loans
2013-18: 2,700% growth
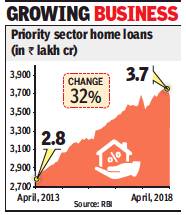
From: Mayur Shetty, Affordable home finance cos multiply Loan Book Grows 27X In Less Than 5 Years To ₹27,000Cr, June 6, 2018: The Times of India
Loans for affordable housing have seen sharp growth in less than five years. Home loans by affordable housing finance companies have grown from Rs 1,000 crore as of March 2013 to Rs 27,000 crore as of December 2017. This has led to an explosion in housing finance companies (HFCs) focusing on the small-ticket segment. As many as 26 HFCs have registered with the National Housing Bank — with self-constructed homes accounting for bulk of the loans.
There are 77 registered HFCs, of which 26 are focused exclusively on affordable housing. According to the ‘State of affordable housing 2018’ report by FSG Consulting, one of the drivers of growth in this segment was the credit-linked subsidy (CLS) under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) that provides an upfront reduction of up to Rs 2.67 lakh for a loan of Rs 6 lakh.
According to FSG MD Ashish Karamchandani, while the PMAY does bring down costs, it has little impact on affordability. Only after a customer has availed a loan, does he know that he will receive a subsidy, and hence he cannot factor it into his purchase decision. “If the subsidies under the credit-linked scheme are based on a sanctioned plan, it will increase the affordability allowing those with lower income to purchase houses,” he said.
Also, the PMAY is not reaching out to all the intended beneficiaries. “Many low-income households are excluded from the credit-linked subsidy benefits because of the location of their new homes. As a bulk of low-income housing is being constructed on the peripheries of around 4,500 urban areas notified for CLS, which come under the purview of gram panchayats, they are not eligible unless notified by state governments,” said Karamchandani. This is a big impediment as 60% of demand for affordable housing finance is for self-constructed properties, and these are largely happening on the outskirts of cities — in areas classified as rural.
There is also a problem in the incentive structure for HFCs. Under present norms, if the loan is below Rs 6 lakh, the HFC cannot charge a processing fee, and gets only a flat fee of Rs 3,000. HFCs are therefore not keen on seeing the home loan amount go down below Rs 6 lakh.
“One solution is to have geospatial coding on all places eligible for subsidy on the map, so as to enable the HFC confirm to the aspiring borrower that he is eligible,” said Karamchandani. Besides, taking a relook at the CLS for urban housing, Karamchandani says that there is a need to relook at the beneficiaryled construction (BLC) scheme, which provides for home improvement to enable upgrading slum housing.
Rates, 2014-18

From: Mayur Shetty, Your home loan’s got costlier. SBI, ICICI have upped rates, September 2, 2018: The Times of India
Unlikely To Raise Rates Again: HDFC
Bank borrowings which include home loans and other retail and business loans have become more expensive from September 1. The country’s largest publicsector lender State Bank of India and largest private lender ICICI Bank have increased by 20 and 15 basis points respectively their benchmark rate against which all home loans are priced.
The SBI has announced a uniform increase of 20 bps on its marginal cost of lending rates (MCLR) across different maturities. The oneyear MCLR, against which home loans are benchmarked, now stands at 8.45% as against 8.25% earlier. ICICI Bank has increased its sixmonth MCLR by 15 basis points from 8.35% to 8.5%. One basis point equals a hundredth of percentage point.
If the SBI continues to price home loans at the current spread above its benchmark rate, SBI’s best home loan rate will go up from 8.45% to 8.65%. This rate is available on loans to salaried borrowers, which include a woman as home owner, for up to Rs 30 lakh. This rate goes up to 8.80% for loans up to Rs 75 lakh and 8.9% for loans of Rs 75 lakh and above. In the case of ICICI Bank, the best home loan rate will go up from 8.7% to 8.85% if loans continue to be priced at a spread of 35 basis points over six-month MCLR.
Bankers say that there is a possibility that SBI, while increasing rates for existing borrowers, might offer new customer lower rates by narrowing the spread between the MCLR and lending rate. If this happens, ICICI Bank too is likely to revise its spread to remain competitive. SBI lending rate goes up by 5 basis points if the loan does not include a woman as borrower or co-borrower. Also self-employed borrowers have to pay 15 basis points more as compared to salaried. With this increase, SBI’s home loans are more expensive compared to HDFC, the country’s largest home loan company. HDFC had recently raised rates and is unlikely to do so soon. “We have not planned any increase in interest rate,” said Keki Mistry, vice chairman & CEO.
The hike has come ahead of the festival season — a time when lenders try to boost sales by announcing special loan deals. According to bankers, there is not much scope to hold on to rates because the cost of funds in the system is rising and the spread between the yield on the benchmark 10-year bond and home loan rates is at the lowest. Last week, yield on the 10-year bond shot up to cross 7.9% due to sudden pressure on the rupee in the foreign exchange market.
2018: City-wise

From: Rachel Chitra, Delhi has highest ticket size of ₹5cr in home loans, January 23, 2019: The Times of India
In the average ticket size of personal loans taken, Mumbai (Rs 2.79 lakh) was ahead of Bengaluru (Rs 2.66 lakh) and other metros, according to data from 1.6 million loan applications in 2018 with BankBazaar, one of the country’s biggest online financial services aggregators.
In home loans, Delhiites took the highest ticket sizes (Rs 5 crore), followed by Chennai (Rs 2.2 crore), Bengaluru (Rs 1.5 crore) and Mumbai (Rs 1.8 crore).
The highest personal loan ticket sizes however were in Bengaluru, at Rs 47 lakh, followed by Mumbai (Rs 40 lakh), Delhi (Rs 26 lakh) and Kolkata (Rs 30 lakh).
BankBazaar CEO Adhil Shetty said the large loans in Bengaluru were perhaps a reflection of larger disposable income and high-growth opportunities. He said the city also had more first-time salaried borrowers than other metros.
Since the data is of those who use the online mode, it is possible that in some of the other cities, a higher proportion of people chose offline modes and less transparent payment methods In car loans too, the top segment of Bengalureans took higher loans than their counterparts elsewhere, suggesting their preferance for flashy cars.
The highest car loan ticket sizes came from Bengaluru, at Rs 49.9 lakh, followed by Chennai at Rs 46.8 lakh, and Delhi at Rs 21.8 lakh.
Compared to their urban counterparts, borrowers from tier-2, and tier-3 cities restrict themselves to not spending above Rs 20 lakh for a car. Even when it came to average car loan size, rural and semi-urban borrowers were more conservative and borrowed only up to Rs 5.2 lakh, compared to their urban counterparts, who were willing to shell out Rs 5.7 lakh. The highest car purchase by a woman borrower in 2018 was at Rs 12.9 lakh.
In personal loans, Bankbazaar’s data shows that the average ticket size in metros was at Rs 2.6 lakh, lower when compared to Rs 2.8 lakh in nonmetros. “It’s possible that urban users have more choices such as credit card, and EMI options for consumer purchases on debit cards, and may not choose a personal loan as their first option,” said Shetty.
But this trend could only be an indicator of the buying pattern of younger, tech-savvy individuals. An SBI official said, “We get out biggest home loan and car loan requests from Mumbai. It’s possible that Mumbaikars prefer directly contacting their banker than going through a thirdparty aggregator.”
Interest rates
2013, 2018: Real Interest rates
October 26, 2018: The Times of India
The weakening rupee is reminiscent of the forex markets in 2013. But the Indian macro situation now is much better than it was five years ago, with one indication being the real policy rate (adjusted for inflation)…

From: October 26, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
2013, 2018- Real Interest rates in India, China and other major countries
2016: Real Interest rates
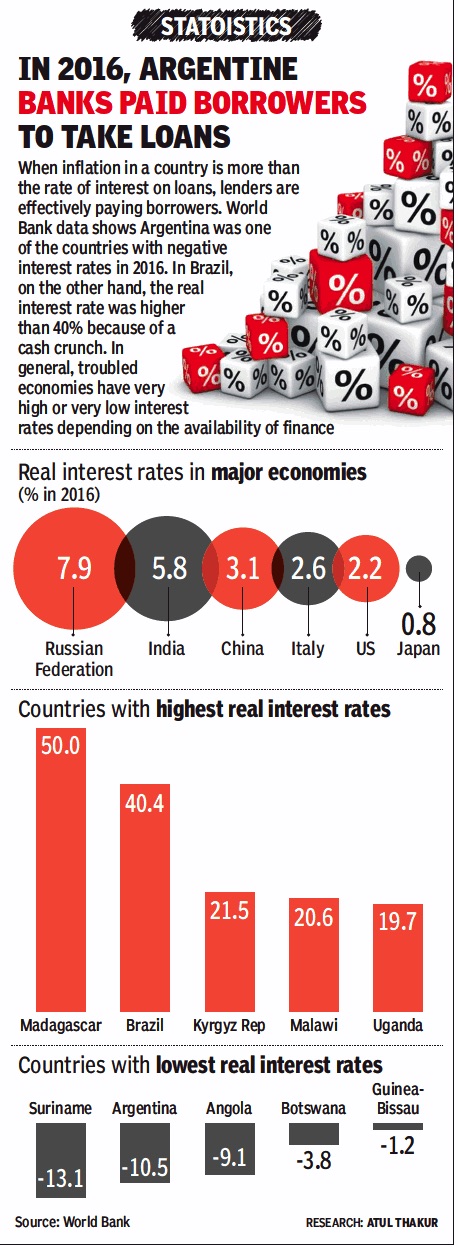
From: May 26, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
2016: Real Interest rates in India, China and other major countries
2018: Real rates in India among highest
December 22, 2018: The Times of India

From: December 22, 2018: The Times of India
RBI May Alter Stance To Neutral On Cheaper Oil
Real interest rates in India have been the highest across countries as well as over time as inflation has undershot targeted levels. According to ICICI Bank, the unexpected drop in international crude prices is likely to compel the RBI to change its stance from calibrated tightening to neutral.
“In India, we have been targeting inflation of 4% and the repo rate has accordingly been kept at two and half percentage points above this. But actual inflation has been much lower, resulting in high real rates,” said B Prasanna, head of markets at ICICI Bank. Real rates are the nominal rates adjusted for inflation, but they can be determined only for the past since inflation can be observed only in hindsight.
“Earlier, when the policy was targeting wholesale prices, there have been instances when real rates were negative despite repo rate being at 9% because of high inflation,” said Prasanna. He added that the present high real rates improve the attractiveness of Indian bonds.
Going forward, however, inflation is expected to firm up. ICICI Bank has forecast consumer price index (CPI) to average around 4% for the first half of FY20, but then pick up sharply in the second half. The key risks are a possible reversal in food prices and the government slipping on its fiscal deficit target.
The stress in the farm sector due to low food prices is expected to keep consumption demand in check. This will keep economic growth contained at 7.4% in FY20, which will be marginally better than the 7.2% forecast for FY19. This would be because the economy would have finished its transition to the goods & services tax (GST) regime, resulting in higher formalisation.
The biggest positive news in 2018, however, is the sharp fall in crude oil prices, which will result in balance of payments swinging to the positive. This, coupled with the likelihood of the US Federal Reserve pausing rate hikes, has turned out to be positive for the rupee, which has staged a smart recovery in recent weeks. “The fall in oil prices would also benefit high-yield current account deficit countries such as India and Indonesia,” said Prasanna.
Investment banking
Fees
2016-2020
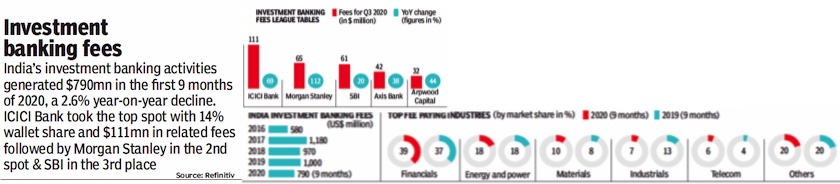
From: The Times of India
See graphic:
Investment banking fees in India, 2016-2020
Investments
Government securities/ G-Secs
See graphic:
i) The monthly average yield of 10-year-G-Secs, and
ii)the trading profits of Indian banks, from Q4 of 2015-16 to Dec 29 2017.

ii)the trading profits of Indian banks, from Q4 of 2015-16 to Dec 29 2017
From:January 9, 2018: The Times of India
Letters of undertaking
What is a letter of undertaking/ LoU
LoUs virtual DDs from one bank to another, February 18, 2018: The Times of India
What is a letter of undertaking (LoU)?
An LoU is a guarantee issued by one bank to another. In trade finance, an LoU is sent in the form of a message using SWIFT (earlier known as society for worldwide interbank financial telecommunication), a secure messaging platform. Think of it as moder n-day telex.
An instruction on money transfer sent through SWIFT is equivalent to a demand draft issued to the bank at the other end.
How did the recently unearthed fraud take place?
PNB employees fraudulently, in connivance with the accused, sent LoU messages over SWIFT favouring the Nirav Modi/Mehul Choksi group companies. For an overseas bank branch, an LoU message over SWIFT is a sufficient guarantee, on the basis of which it will provide funds to the beneficiary mentioned, as happened in this case.
What if PNB does not honour its guarantee?
The lender who has invoked the guarantee will have to classify PNB as a defaulter. The loan will have to be classified as a non-performing asset and provisions made out of the bank’s profits. The lending bank will legally pursue recovery with PNB. There is also a possibility that overseas lenders might not accept LoUs from PNB.
Who are the parties affected by the fraud?
PNB has said the fraudulent guarantees total around Rs 11,300 crore. Lenders have already started making claims on PNB, assuming that Nirav and Choksi are unlikely to repay. Some of the lenders have sold the loans to other banks. These secondary buyers can try their luck by pursuing a claim with either the selling bank or PNB, the original guarantor. If they feel they will get a quicker decision in the global markets, they may choose to pursue the seller overseas where the loan was sold to them.
What are the regulatory implications of a PNB default?
Since the buyer’s credit has been extended in overseas markets, the lenders might choose to pursue claims with PNB offshore. The local regulators are likely to get involved and pull up the branches of Indian banks.
2018: RBI bans letters of undertaking, letters of comfort
March 14, 2018: The Times of India

From: March 14, 2018: The Times of India
The Rs 12,700-crore fraud at Punjab National Bank has prompted the Reserve Bank of India to ban use of letters of undertaking (LoUs) and letters of comfort (LoCs). LoUs and LoCs are instruments issued by Indian banks to domestic importers to get forex from banks abroad at a cheaper rate.
The RBI issued the directive on Tuesday, about a month after it was discovered that Nirav Modi and Mehul Choksi had misused LoUs issued by PNB to defraud the bank of over $2 billion.
The ban could potentially push up the cost of imports by up to half a percentage point, besides putting foreign banks on an even keel with Indian banks in financing imports, bankers said.
LoU ban may hit cos with longer working capital cycle
This regulation will certainly help global banks that were earlier outpriced by Indian banks, to get back to financing genuine trade finance transactions of Indian corporates and support Indian imports, though withholding tax would add to the cost of the importers,” said Joiel Akilan, ED & chief representative-India of BBVA, one of Europe’s leading banks. The RBI directive is effective immediately. However, “letters of credit and bank guarantees for trade credits for imports into India may continue to be issued subject to compliance with” existing regulations, a notification from RBI said.
A ban on the use of LoUs and LoCs could inconvenience some Indian corporates that have a longer working capital cycle—meaning those companies which take several months to get back the money used in their business by selling their goods, compared to other companies that can recover their money in weeks.
Indian corporates use LoUs to make payments to those companies from which they buy goods to send to India. It is alleged that Modi and Choksi had used LoUs much beyond the limit they were eligible to and finally defaulted on the payments to PNB.
Loans
Prompt Corrective Action (PCA)
Impact on advances: 2017-20

From: April 14, 2020: The Times of India
See graphic:
The Impact of Prompt Corrective Action on advances: 2017-20
The top borrowers
Cities, 2018
Rachel Chitra, Bengalureans take most personal, car loans, January 23, 2019: The Times of India
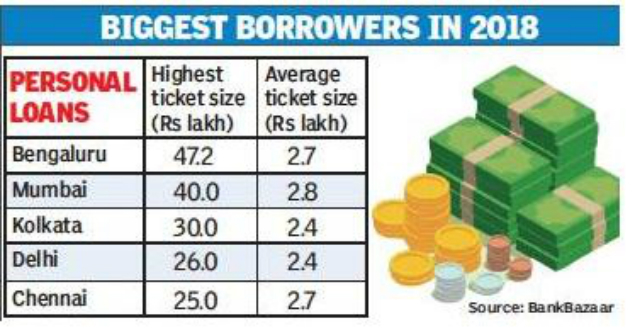
From: Rachel Chitra, Bengalureans take most personal, car loans, January 23, 2019: The Times of India
The highest personal loan ticket sizes are in Bengaluru, at Rs 47 lakh, followed by Mumbai (Rs 40 lakh), Delhi (Rs 26 lakh) and Kolkata (Rs 30 lakh), as per data from 1.6 million loan applications in 2018 with BankBazaar, one of India’s biggest online financial services aggregators.
In the average ticket size of personal loans taken, Mumbai (Rs 2.79 lakh) was ahead of Bengaluru (Rs 2.66 lakh) and Chennai, Delhi and Kolkata.
BankBazaar CEO Adhil Shetty said the high number of large loans in Bengaluru is, perhaps, a reflection of larger disposable income and high growth opportunities. He said the city has more first-time salaried borrowers than other metros.
The data is of those who use the online mode. It’s possible that in some of the other cities, a higher proportion of people choose offline modes.
In car loans too, the top segment of Bengalureans takes higher loans than their counterparts elsewhere, suggesting they go for more flashy cars. The highest loan ticket sizes came from Bengaluru, at Rs 49.9 lakh, followed by Chennai at Rs 46.8 lakh, and Delhi at Rs 21.8 lakh.
Highest car purchase by women borrower in 2018 was at Rs 12.9L
Compared to their urban counterparts, borrowers from tier-2 and tier-3 cities restrict themselves to not spending above Rs 20 lakh for a car. Even when it came to average car loan size, rural and semi-urban borrowers were more conservative and borrowed only up to Rs 5.2 lakh, compared to their urban counterparts, who were willing to shell out Rs 5.7 lakh.
The highest car purchase by a woman borrower in 2018 was at Rs 12.9 lakh. In personal loans, Bankbazaar data shows the average ticket size in metros was at Rs 2.6 lakh, lower when compared to Rs 2.8 lakh in non-metros.
“It’s possible urban users have more choices such as credit card, and EMI options for consumer purchases on debit cards, and may not choose a personal loan as their first option,” said Shetty.
In home loans, Delhiites took the highest ticket sizes (Rs 5 crore), followed by Chennai (Rs 2.2 crore), Bengaluru (Rs 1.5 crore) and Mumbai (Rs 1.8 crore).
But this trend could only be an indicator of the buying pattern of younger, tech-savvy individuals. An SBI official said, “We get biggest home loan and car loan requests from Mumbai. It’s possible Mumbaikars prefer directly contacting their banker than going through a third-party aggregator.”
The top lenders
2008-18
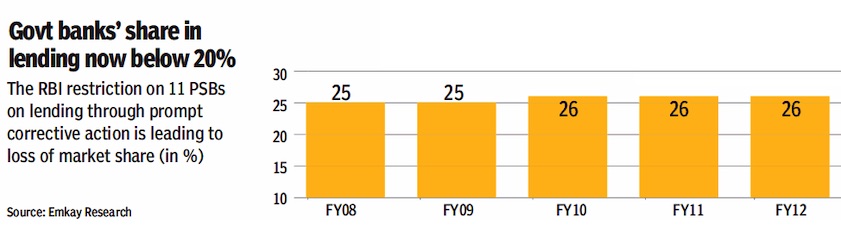
From: October 13, 2018: The Times of India

From: October 13, 2018: The Times of India
See graphics:
2008-12: PSB banks’ share in lending
2013-18: PSB banks’ share in lending
2017
SBI, ICICI Bank Are The First Two Lenders
The RBI added HDFC Bank to the list of systemically important banks, or banks that are considered too big to fail.The other banks on the list are the two largest lenders -SBI and ICICI Bank. Since 2015, the central bank has been identifying banks whose failure would impact the whole financial system.These banks are subject to more rigorous regulation and capital requirement.(The Times of India Sept 2017)
Loans to gems & jewellery cos

From: Sidhartha, February 19, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Outstanding bank loans to gems and jewellery, 2014-17
Gender-wise size of loans, 2018
Rachel Chitra, Loan sizes higher when women borrow, January 23, 2019: The Times of India

From: Rachel Chitra, Loan sizes higher when women borrow, January 23, 2019: The Times of India
The average ticket size of a home loan when women borrow is significantly higher (Rs 27 lakh) than when a man borrows (just under Rs 23 lakh), according to data from 1.6 million loan applications in 2018 on BankBazaar, one of India’s biggest online financial services aggregators.
BankBazaar CEO Adhil Shetty said the higher loan amount when a woman applies could indicate it’s a household with two incomes, unlike when a male applies, where he could be the only breadwinner. Banks also have special loan offers for women, with interest rates many basis points (100bps = 1 percentage point) lower than for men.
When it came to car-buying patterns, the data shows that when a woman is the primary loan applicant, they tend to steer away from big-ticket car purchases. Male borrowers borrowed up to Rs 49.9 lakh for a car, whereas the highest female car loan ticket size was Rs 12.9 lakh.
But in terms of the average car loan size taken by women, it’s significantly higher (Rs 5.5 lakh) than when men are the sole applicants (Rs 5.3 lakh). “Again, I think when women apply, they are an indicator of a double-income household,” said Shetty.
This trend of women boosting the household’s purchasing capacity could be seen across metros. The average ticket size of home loans in Delhi for women borrowers was Rs 28 lakh, compared to male borrowers at Rs 24.5 lakh. In Bengaluru, women borrowed Rs 37.9 lakh — higher than men at Rs 36.9 lakh, and in Chennai women borrowed Rs 34.8 lakh compared to men at Rs 30.1 lakh. However, the situation was the opposite in Mumbai, where men borrowed more in home loans at an average of Rs 32.8 lakh compared to women at Rs 29.7 lakh.
For personal loans, women seem to borrow less than men. The average ticket size for female applicants was Rs 2.7 lakh, compared to men who borrowed Rs 2.8 lakh.
Women seem to now have the firepower for globe-trotting just as much as men — women’s applications for travel credit cards grew 73%, slightly higher than male applications that increased 71.5%. In lifestyle credit cards too, applications from women grew at a 10.5% rate, compared to men at 8%.
Loans: Bad loans
5 business houses alone owe PSU banks Rs. 1.4 lakh crore
The Times of India, May 06 2016
Adani Group Has Debt Of Rs. 72,000 Crore'
Raising the issue of corporate loans in Rajya Sabha, JD(U) member Pavan Verma said the Adani group had a debt of Rs 72,000 crore -an amount equal to the total debt of farmers in the country. Verma said corporate houses owed about Rs 5 lakh crore to PSU banks and particularly referred to the Adani group, alleging that the company got “unimaginable“ favours. Raising the issue during zero hour, he contended that PSU banks were influenced to give loans to people who were not able to repay them.
“PSU banks are owed abo ut Rs 5 lakh crore by corporate houses and of this, roughly Rs 1.4 lakh crore are owed by just five companies, which include Lanco, GVK, Suzlon Energy , Hindustan Construction Company and a certain company called the Adani group and Adani Power,“ he said.
“I want a reply from the government, are they aware of this or are they not. And if they are aware, what are they doing in this matter. One company owes as much as all the farmers of India,“ he further said.
The amount owed by this group both in terms of its long-term and short-term debt was around Rs 72,000 crore, Verma said, claiming to be quoting from reports. He added that on Wednesday , it was mentioned that the entire amount owed by farmers as crop loans was Rs 72,000 crore.
“I don't know what is the relationship of this government with this business house. I don't even know if they know them, but the owner of this group (Gautam) Adani is seen everywhere the prime minister has gone, every country , China, the UK, the US, Europe, Japan,“ Verma said.
“This company has been given favours which are unimaginable. In Gujarat, their SEZ was approved in spite of the high court's strictures,“ he added.
When deputy chairman P J Kurien warned Verma against making allegations, the JD(U) member said, “I am giving you factual account. It is a high court judgment. It was left to the state government.The UPA government had not approved it and when this government came to power, it was approved.“
Verma said it did not matter if Adani group had the ability to pay this amount, but in the last 2-3 years, the company's net worth had gone up by 85%.
25% of Rs 8 lakh crore bad debt is from just 12 accounts
HIGHLIGHTS
Just 12 accounts responsible for 25% of all NPAs with banks
Lenders will be asked to initiate insolvency proceedings to recover the dues
The RBI today identified 12 accounts each having more than Rs 5,000 crore of outstanding loans and accounting for 25 per cent of total NPAs of banks for immediate referral for resolution under the bankruptcy law.
Without naming the defaulters, the Reserve Bank said the lenders will be asked to initiate insolvency proceedings to recover the dues. The banking sector is saddled with non-performing assets (NPAs) worth over Rs 8 lakh crore, of which Rs 6 lakh crore is with public sector banks (PSBs). The Internal Advisory Committee (IAC), the central bank said, has arrived at an objective, non-discretionary criterion for referring accounts for resolution under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC).
"In particular, the IAC recommended for IBC reference of all accounts with fund and non-fund based outstanding amount greater than Rs 5,000 crore, with 60 per cent or more classified as non-performing by banks as of March 31, 2016," the RBI said in a statement. The IAC noted that under the recommended criterion, 12 accounts with about 25 per cent of the current gross NPAs of the banking system would qualify for immediate reference under IBC, it said.
The apex bank, based on the recommendations of the IAC, will accordingly be issuing directions to banks to file for insolvency proceedings under the IBC in the identified accounts.
Such cases will be accorded priority by the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT).
2013-16: Loans held by ARCs

From: Govt may create ‘bad bank’ to take over PSBs’ NPAs, June 9, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Total loans held by asset reconstruction companies: 2013-16
2014: loans to coal sector…

… and scrapping of coal block allotments
Power sector bad loans may rise
Mumbai:
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
The Times of India Sep 25 2014
The Supreme Court verdict scrapping all but four coal block allotments has added to the bad loan headache of the banking industry .
Although bank exposure to coal mining sector is estimated to be below Rs 20,000 crore, the biggest fear is that coalfuelled power plants may stop producing power and default on loans. Bank exposure to power companies is around Rs 5.16 lakh crore and accounts for 9% of their loans. A large chunk of these depend on coal.
Shares of leading public sector banks dipped sharply on Monday over fears that their bad loans would rise following the Supreme Court order.
Bank of India and Canara Bank, which have large exposures to the power segment (relative to their loan book) fell 5.6% and 5%, respectively , to Rs 263 and Rs 358. Punjab National Bank, which is estimated to have the largest exposure to coal mining, fell 4.3% to Rs 927. The State Bank of India, one of the largest lenders to power in absolute terms, saw its share price fall 2.7% to Rs 2,487. Even without the coal block cancellation, several power projects and steel companies are under stress and are undergoing restructuring. Stoppage of fuel to these projects could tip them into the non-performing assets category , considering that imported coal is four times as expensive as domestic coal. Reacting to the SC order, SBI chairman Arundhati Bhattacharya said, “We believe that uncertainty is possibly the worst enemy of growth. We are glad that this is over with the SC verdict on coal blocks allocation. We now look forward for a quick plan of action for ensuring that coal supplies are not disrupted and, thereafter, a swift and transparent bidding process for reallocation.“
According to IDBI Bank chairman MS Raghavan, the bank has an exposure of close to Rs 2,000 core to the companies affected by the Supreme Court order. The bank is still assessing the impact of the verdict.
In the private sector, ICICI Bank has loans to power and steel companies that are dependent on coal supply . Earlier in an interview to TOI, Chanda Kochhar, MD & CEO of ICICI Bank, had said it was important to ensure that back-end projects that depend on coal keep producing. “The government has been talking about finding ways of reallocating coal. As long as coal is produced and power and steel plants get it, that ensures the viability of the power project; where it is allocated, who owns it and who mines it is not the primary thing. Banks had mainly extended assistance to either power or iron and steel projects,“ Kochhar had said. While deciding to cancel all but four coal blocks allotted since 1993, The Supreme Court brushed aside Coal Producers Association's (CPA) estimate that Rs 9 lakh crore linked to them would come to naught.
The CPA, through senior advocate K K Venugopal, had said that loans worth Rs 2.5 lakh advanced by banks and financial institutions would become non-performing assets. It had said that SBI has an exposure of up to Rs 78,263 crore.
Venugopal had said that apart from huge losses to other PSU banks like PNB and Union Bank, public sector entities like Rural Electricity Corporation and PFC would experi ence an even higher exposure than banks. The financial implication narrated by CPA covered many other aspects.“Huge investments up to about Rs 2.9 lakh crore have been made in 157 coal blocks as on December 2012, investments in the end-use plants have been made to the extent of about Rs 4 lakh crore, which employ 10 lakh people,“ CPA had said.
The CPA had warned of many other adverse effects -the country's dependence on coal as a primary source of fuel for up to 60% for power generation might result in inflationary trends; 28,000 mw of power capacity would be affected due to de-allocation; closure of coal mines would result in an estimated loss of Rs 4.4 lakh crore in terms of loss of royalty , cess, direct and indirect taxes; coal imports would go up even more in financial year 2016-17 to the extent of Rs 1.4 lakh crore.
A bench of Chief Justice R MLodha and Justices Madan B Lokur and Kurian Joseph cited arguments of attorney general Mukul Rohatgi to counter adverse economic fallout predicted by CPA. “It was submitted by the AG that all aspects, including the economic implications or fallout of the cancellation of coal block allotments and the possible adverse impact that it may have on other socio-economic factors, have been taken into consideration and it is only after that the affidavit has been filed by the Union of India,“ the bench said.
2018/ Loans to the power sector
‘RBI excess capital identified by panel may back power loans’, April 4, 2019: The Times of India
The Bimal Jalan committee has to submit its report on the appropriate level of reserves to be maintained by the RBI. According to a report by Bank of America Merrill Lynch, the panel will identify excess capital of $14 billion to $42 billion, which can be used to address stressed loans in power sector.
The Supreme Court quashed a circular from the RBI forcing banks to initiate insolvency proceedings against defaulting companies. This order has paved the way for restructuring of loans to the power sector. While this is a relief to both lenders and borrowers it does not address the issue. Lenders did not want to start insolvency proceedings as projects were under implementation and would not find takers.
According to BoAML, the finance ministry should be able to form a much-needed public sector asset reconstruction or asset management company that manages banks’ nonperforming assets (NPAs) in power with the Supreme Court ruling against the February 12 RBI circular, which had adopted a one-size-fits-all approach. This had also been proposed by RBI deputy governor Viral Acharya earlier.
“Our power analyst estimates that auctioning these power NPLs will need a haircut of 75%, that is $9 billion (Rs 63,000 crore) more. Banks can then transfer the $9 billion of cleaned-up power NPLs to the ARC/AMC. This can be done by either the government recapitalizing banks by an additional Rs 7,000 crore or it can deploy excess RBI economic capital set to be identified by the Jalan committee next week,” said Indranil Sen Gupta, India Economist with Bo-AML.
Priority sector more creditworthy than corporates/ 2016
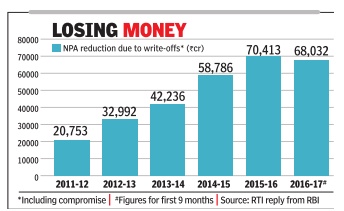
Priority sector loans, long seen as a socialist burden on banks, have turned out to be more credit worthy than advances to large corporates. During April-December 2016, banks had written off loans worth Rs 35,587 crore to large industries as against write-offs of Rs 32,445 crore of advances in the priority sector.
Also, banks could recover only Rs 16,717 crore from large industries who are in default as against Rs 25,070 crore from the priority sector.
An RBI response to a Right to Information (RTI) filing shows that inability to make timely recoveries from large businesses is forcing banks to take a huge hit on their earnings. Banks had written off Rs 68,032 crore of bad loans in the first nine months of FY17 -close to 97% of total write-offs in the whole of FY16. Given that the fourth quarter writeoffs in FY17 had been significant, the total write-offs in the last three years have crossed Rs 2 lakh crore.
CARE Ratings chief economist Madan Sabnavis said, “After the asset quality review norms were put in place by the RBI, bad loans and provisioning have risen steeply . As banks started realising a part of these bad lo ans cannot be recovered, they also started writing off more to clean their balance sheets.“ He added the situation is a result of bad lending decisions and governance issues among banks, which was supported by the “system“.
In the first nine months of FY2017, scheduled commercial banks (SCBs) wrote off Rs 35,587 core worth of loans to large industries, compared to Rs 6,628 crore written off by lenders to farm loans, Rs 8,106 crore toward MSME loans and Rs 17,711 crore wrote off to the other priority sectors.
A loan write-off does not mean that the borrower goes scot free as all recovery proceedings continue. A balance sheet write-off indicates that even if the borrower does not repay , the bank has set aside own funds to repay depositors. Similarly , the farm loan waiver announcement by state governments is not included in `write-offs' by banks. “The loan is always there in the books. They are just moved from sub-standard to standard when the government waives and makes good the loan outstanding. Only that amount of the agriculture loan is written off which is not made good by the government,“ said a senior public sector banker in charge of priority sector banking.
2017: Bad loans at record Rs 9.53 lakh crore
HIGHLIGHTS
Unpublished data show that bad loans in banks have reached a record Rs 9.53 lakh crore by end-June
The stressed loans have risen 5.8 per cent in last six months
Stressed loans as a percentage of total loans reached 12.6 per cent at end-June, the highest level in at least 15 years
The bad loans of banks hit a record Rs 9.53 lakh crore at the end of June, unpublished data shows, suggesting Asia's third-largest economy is no nearer to bringing its bad debt problems under control.
A review of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data obtained through Right To Information (RTI) applications show banks' total stressed loans - including non-performing and restructured or rolled over loans - rose 4.5 per cent in the six months to end-June. In the previous six months they had risen 5.8 per cent.
While banks remain the main source of funding for companies in India, the stubborn bad debt problem has eaten into bank profits and choked off new lending, especially to smaller firms, at a time when an economy that depends on them is stalling.
The GDP grew at its slowest pace in three years in April-June quarter - a concern for the government which faces elections in 2019 and has pledged to create millions of new jobs before then. Banks are having to take higher provisions to account for more defaulters being pushed into bankruptcy and margins are likely to be squeezed further by proposed new rules to encourage commercial banks to pass on central bank interest rate cuts.
To be sure, the bulk of India's bad loans are in the state banks and stem from lending to large conglomerates, especially in steel and infrastructure. But analysts say the rise in bad loans among small firms, and even retail borrowing, is worrying and will do little to encourage new loans to help fuel growth.
"On the corporate side, we think it's a recognition cycle which is nearing an end," said Alka Anbarasu, senior analyst at Moody's Investor Service, referring to more bad loans being recognised as such, as banks come under pressure from the RBI and other regulators. "But it's really those data points beyond corporate that are causing some worry."
Anbarasu forecast weak quarters ahead for banks before profitability picks up, and several senior bankers from public sector lenders - which account for more than two-thirds of Indian banking assets - agreed the months ahead would be strained.
Stressed loans as a percentage of total loans reached 12.6 per cent at end-June, according to the RBI data, the highest level in at least 15 years.
Higher provisions, weaker loans
Part of the issue for banks and the government is a strict provisioning regime: the RBI wants banks to provide for at least 50 per cent of the secured loans to companies taken to bankruptcy proceedings, and 100 per cent for the unsecured part.
A dozen of the biggest such cases account for nearly Rs 1.78 lakh crore, or a quarter of total non-performing assets.
For those companies, banks will need to provide Rs 18,000 crore on top of existing provisions, according to July estimates from India Ratings and Research, the local affiliate of Fitch Ratings. More than 20 other sizeable companies are at risk of being taken to bankruptcy court.
Bankers say these and other pressures - including rising government bond yields that forced banks to post mark-to-market losses - have added to the squeeze, and hit new loans.
According to RBI data, new loans grew at just about 5 percent in the year to March, the lowest growth rate in more than six decades. Several banks have already cut back their loan books to conserve capital.
"What are they (RBI) thinking while they're taking these steps all at the same time?" said a treasurer at a state-run bank, who didn't want to be named due to the sensitivity of the issue. "Do they want banks to wind up their businesses, or do they want to save the banks?"
Treasury income accounted for 22.7 per cent of banks' operating profits in the last financial year, doubling its share from a year earlier, India Ratings estimates.
"The almost zero treasury income will hit provisioning ability and, in turn, make it more difficult for weaker banks to give loans as capital becomes more scarce," said Soumyajit Niyogi, an associate director at the rating agency.
A senior policymaker, who requested anonymity as the discussions are not public, said the government would have to help to sufficiently capitalise the banks.
Fitch Ratings estimates Indian banks will need Rs 4.24 lakh crore of additional capital by March 2019 to meet Basel III global banking rules. Moody's expects the top 11 state lenders alone will need nearly Rs 98,000 crore. The government has just Rs 19,500 crore left in its budget for bank recapitalisation.
"We think capitalisation is the biggest challenge for the banks at the moment, given that earnings will remain subdued and will not support any capital generation," said Moody's Anbarasu.
2017-18: Wilful defaulters form 14% of PSB bad loans
Mayur Shetty, Wilful defaulters form 14% of PSB bad loans, January 8, 2018: The Times of India

From: Mayur Shetty, Wilful defaulters form 14% of PSB bad loans, January 8, 2018: The Times of India
With 53%, Vijaya Bank On Top Of RBI List
Around 14% of the bad loans in public sector banks (PSBs) are due to wilful defaulters. The total gross non-performing assets (NPAs) of 21 PSBs stood at Rs 7.33 lakh crore as on September 30, 2017. Of this, Rs 1.01 lakh crore of loans were termed as those in wilful default.
Wilful defaults have an element of malfeasance as it broadly means that the borrower has reneged on the agreement on usage of funds or has not paid despite having resources.
Recovery from such accounts are difficult because in many cases the money is siphoned off from the books of the defaulting company and most of them are being fought in courts. Some of the largest cases of wilful default are Kingfisher Airlines, Zoom Developers, Winsome Diamonds and Varun Industries.
Of the 9,025 cases of wilful defaults in PSU banks, lenders have filed cases against 8,423 for recovery of Rs 95,384 crore of NPAs. They have also filed 1,968 police complaints in cases of loan amounts totalling 31,807 crore. In 6,937 accounts, representing an outstanding of Rs 87,458 crore, banks have also initiated proceedings to attach and sell assets under the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act.
Data released by the RBI in response to a Parliament query shows that Vijaya Bank has the highest share of wilful defaulters in its books. The Bengaluru-based banks had NPAs worth Rs 6,649 crore as on September 30, 2017. Of this loans amounting to Rs 3,537 crore were on account of wilful defaults. Punjab National Bank has the highest share of wilful defaults in its books among the larger banks. Of its bad loans worth Rs 57,630 crore, 25% are on account of borrowers who have deliberately defaulted.
The implication for a business or promoter being declared a wilful defaulter is that they will never be able to get bank loans as long as they have the tag. For a lender, declaring a borrower as a wilful defaulter is a complicated process with senior bankers having to give a hearing to the borrower. In several cases, courts have ruled against the labelling of the borrower due to shortcomings in the process.
Among banks with small percentage of wilful defaulters among NPA accounts are Punjab & Sind Bank (4%), Bank of Maharashtra (5%) and Syndicate Bank (5.4%).
As on September 30, 2017, leading corporate houses accounted for approximately 77% of the total gross NPA from domestic operations for banks in India.
2017-18/ Bad loan write-offs by PSBs surge 140% over their losses
June 15, 2018: The Times of India
HIGHLIGHTS
This is a double whammy for the struggling PSBs as they had massive write-offs as well as huge losses in the last financial year
Till 2016-17, 21 state-owned banks made combined profit while in 2017-18, they posted a staggering loss of Rs 85,370 crore, as per the data
Public sector banks have written off bad loans worth a whopping Rs 1.20 lakh crore, an amount that is nearly one-and-a-half times more than their total losses posted in 2017-18, according to official data.
This is a double whammy for the struggling PSBs as they had massive write-offs as well as huge losses in the last financial year. This is for the first time in a decade that banks have made huge write-offs of bad loans along with booking of hefty losses. Till 2016-17, 21 state-owned banks made combined profit while in 2017-18, they posted a staggering loss of Rs 85,370 crore, as per the data.
During 2016-17, PSU banks wrote off non-performing assets (NPAs) worth Rs 81,683 crore as against combined net profit of Rs 473.72 crore.
SBI alone has written off bad loans of Rs 40,196 crore, nearly 25 per cent of the total write-offs during 2017-18. This was followed by Canara Bank (Rs 8,310 crore), Punjab National Bank (Rs 7,407 crore) and Bank of Baroda (Rs 4,948 crore).
As per the data provided by rating agency Icra, Indian Overseas Bank has written of NPAs worth Rs 10,307 crore, followed by Bank of India (Rs 9,093 crore), IDBI Bank (Rs 6,632 crore) and Allahabad Bank (Rs 3,648 crore). These banks along with 7 others come under Prompt Corrective Action framework of RBI.
As per the government data, banks' write-offs stood at Rs 34,409 crore in 2013-14. The figure has jumped nearly four-fold in five years. In 2014-15, the banks wrote off Rs 49,018 crore ; Rs 57,585 crore in 2015-16, Rs 81,683 crore in 2016-17 and hitting a record high of Rs 1.20 lakh crore (provisional) in 2017-18.
Write-off in banking parlance means that the bank has made 100 per cent provision from its earning against that account. Following this, NPA is no longer part of its balance sheet.
However, a write-off puts pressure on balance sheet of banks as it erodes operating profit.
Indian banking sector is grappling with mounting NPAs and host of scams and frauds. NPA in the banking sector stood at Rs 8.31 lakh crore as of December 2017.
Weak financials due to mounting bad loans have already pushed 11 banks, out of 21 , under the Prompt Corrective Action (PCA) framework of RBI.
The recent tight prudential norms released by RBI on February 12 have added to the NPA woes.
Interim Finance Minister Piyush Goyal has announced setting up of a committee to give recommendations in two weeks on formation of an Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) for faster resolution of stressed accounts.
The committee under Sunil Mehta, non-executive chairman of PNB, will make recommendations for the same.
The finance minister said the committee will consider whether such an arrangement will be good for the banking system and, if any such suggestion is advisable, it will also consider the modalities by which such an ARC should be set up.
How ‘haircuts’ help in dealing with bad loans
July 9, 2018: The Times of India

From: July 9, 2018: The Times of India
As the government looks to reel in the likes of Nirav Modi and Vijay Mallya, who have sought shelter on foreign shores after leaving behind huge outstanding loans in India, a panel has come up with recommendations to help state-run banks achieve faster resolution of their non-performing assets. A look at these bad loans and how deep the problem is...
How are haircuts a solution to the NPA crisis?
One reason private and foreign banks have a lower level of NPAs is they have the flexibility to cut their losses by selling off assets in a bad loan for whatever it is worth. In the case of public sector banks, selling a loan or a company for less than the outstanding loan was not feasible as it would trigger action by Central Vigilance Commission, Central Bureau of Investigation and Comptroller and Auditor General. It is only now that the bankruptcy code provides a framework for selling assets at a discount to the loan amount (taking a haircut).
What caused this pile-up?
Post global financial crisis, RBI and the gover nment relaxed lending nor ms to stimulate the economy and allowed banks to lend more to projects as part of a countercyclical measure. The government also allowed banks to ‘restructure’ project loans that were going into default by giving borrowers more time and more money. Loans of these troubled borrowers were classified as ‘restructured’ and not NPAs.
How much money would banks lose if they took haircuts on NPAs?
Losses reported by banks so far include the part-provisions made on existing NPAs. According to CLSA, the top-32 NPAs facing action under the bankruptcy code account for Rs 4 lakh crore or 45% of total NPAs. CLSA estimates the haircut on these loans are less than 60%. Banks must make provisions for at least half the loan amount in case of bankruptcy.
What is the NPA crisis?
NPAs or non-performing assets are loans for which borrowers are unable to meet repayment obligations. Ideally, these should be within 2% of total assets (loans) for banks. Bad loans beyond this level are difficult to manage as banks work with narrow margins and the interest spread they earn is not enough to make up for the losses from defaults. For public sector banks it has reached crisis level with gross NPAs at 14.6% — almost three times the level of 4.9% for private banks.
Why did NPAs blow out in FY18?
In 2017, the new insolvency law came into effect. It provided a resolution mechanism for bad loans, enabling companies to be sold. Earlier under Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Securities Interest Act, 2002, lenders could sell assets but not businesses as a whole. With a mechanism in place, RBI removed restructuring schemes, asking banks to come clean on bad loans. As a result, provisions rose to Rs 3.2 lakh crore in FY18 from Rs 2 lakh crore in FY17, surpassing operating profits of banks.
What are the haircuts that are talked about?
Under the Bankruptcy Code, borrowers unable to repay their dues face insolvency proceedings in the National Company Law Tribunal. Under the insolvency process, a resolution professional is appointed to invite bids for the bankrupt business. The difference between the best bid and the borrower’s total outstanding dues is the haircut.
CVC finds many flaws in sale of bad debt/ 2019
Sidhartha, March 18, 2019: The Times of India

From: Sidhartha, March 18, 2019: The Times of India
Review Points To Several Lapses In Deals, Govt Orders Scrutiny
In high season for sale of bad loans to asset reconstruction companies (ARCs), the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) has pointed to several irregularities in transactions involving non-performing loan accounts, prompting the government to initiate action against errant executives.
“Instances have come to the notice of the commission, wherein prudence has not been observed, while taking decision on sale of stressed asset to ARCs. Irregularities have been noticed in estimating the value of underlying securities (which) is much higher that the value at which the assets were sold to ARCs, post-sale realisation from assets, management fees and expenses charged by ARCs, etc,” the CVC said after an analysis of 302 cases of over Rs 50 crore from 2014-15 to 2017-18.
In at least 48 cases, assets were sold to ARCs below the realisable value of securities that the borrower had given as security at the time of availing of the loan. In several cases, banks were found to be fixing the reserve price without factoring in the accrued interest, resulting in banks having to take a deeper haircut, the CVC said in its report to the government. It also said that in case of companies that are sold as a “going concern”, the primary value of stocks and equipment were not factored in, while fixing the reserve price.
Similarly, in 55 cases, assets were sold within a year of the date of the account turning into a non-performing asset (NPA), without banks initiating recovery action under the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act.
In all, 22 irregularities and gaps in regulations have been pointed out by the vigilance body, prompting the government to swing into action.
The department of financial services has written to all staterun banks, asking them to analyse all accounts of over Rs 50 crore and initiate action after examining accountability of executives and lodge complaints with law enforcement agencies.
While bankers acknowledged that there may be instances of improper transactions, they said the latest advisory is prompting many lenders to go slow on asset sales — which typically peak at the year-end. Some of the bankers said this may result in several loans, which would have been sold, remaining on their balance sheets.
Loans and Defaulters
Wilful defaulters:38% rise, 2012- 2015
The Times of India, May 04 2016
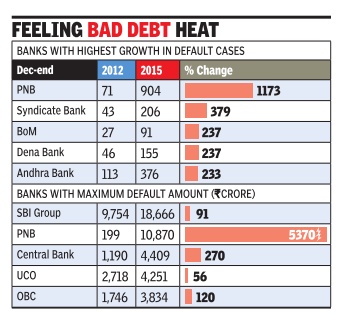
The number of wilful defaulters, who have not repaid their loans to public sector banks despite having the ability to do so, shot up by 38% to 7,686 at the end of December 2015, compared to 5,554 in December 2012, with lenders finally starting to issue the tag amid rising bad debt plaguing the Indian economy.
The amount involved in these cases has shot up 2.4 times to Rs 66,190 crore, compared to around Rs 27,750 crore three years ago, the government informed Parliament.
Bankers, however, war ned that some of the banks may still have kept a few firms and their promoters out of the net. “Banks have not done a complete exercise to identify all wilful defaulters in line with RBI guidelines,“ said Deepak Narang, a former executive director of United Bank of India. No one certifies that all the wilful defaulters have been identified. There has been an increase in recent years but not all accounts have been identified,“ Narang said.
He furnished the exam ples of Indian Overseas Bank and United Bank, where the numbers of such defaulters have come down. “How is that possible when the NPA in the system is rising and banks are reporting losses?“ RBI rules require banks to declare a borrower `wilful defaulter' if it has defaulted in repayment despite having the capacity to honour the obligation. Similarly , a defaulter who has diverted or siphoned off the funds, or has disposed off fixed assets or immovable property , can be given the tag.“The default to be categorised as wilful must be intentional, deliberate and calculated,“ the guidelines say .
Under pressure from RBI to act against defaulters, banks have begun to crack the whip only in recent months.As a result, lenders such as PNB have seen a massive spurt in the number of wilful defaulters -from 71 to 904 in three years (see graphic). In value terms too, PNB tops the list in terms of the growth rate with the amount involved jumping from Rs 199 crore at the end of December 2012 to almost Rs 11,000 crore at the end of 2015. Indian Bank and Andhra Bank (over 7times each).
SBI and its associates, which account for nearly a quarter of banking business, are at top of the pile in terms of amount involved but their share is around 28%, compared to 35% at the Dec-end of 2012, indicating that nationalised banks have only now begun to take exercise seriously .
2017: wilful defaulters owe ₹1 lakh cr+ to banks

How the debt has grown, 2008-2017
From: Atul Thakur, India’s wilful defaulters owe more than ₹1 lakh cr to banks, February 23, 2018: The Times of India
As on September 30, 2017, more than Rs 1 lakh crore was owed to banks by people or companies characterised as “wilful defaulters”, that is those who are unwilling to pay despite having the capacity to do so. TOI analysed more than 9,000 such accounts for which banks have filed lawsuits for recovery and found that the top 11 debtor groups, each with dues of over Rs 1,000 crore, together had over Rs 26,000 crore outstanding to the banks.
Analysis of the publicly available data for suit-filed accounts (wilful defaulters) of Rs 25 lakh and above shows that Jatin Mehta-promoted Winsome Diamonds & Jewellery Ltd and Forever Precious Jewellery & Diamonds Ltd owed close to Rs 5,500 crore to various banks. Mehta is reported to be now a citizen of St Kitts and Nevis, a tax haven with which India doesn’t have an extradition treaty.
Mehta’s companies are followed by Vijay Mallya’s Kingfisher Airlines, which has to pay back over Rs 3,000 crore under this head. The third in the list is REI Agro, a company owned by Sandip Jhunjhunwala, which, according to news reports, was once listed in London and Singapore stock exchanges and was co-sponsor of an IPL team. It owes Rs 2,730 crore.
Bad loans grew 4-fold to ₹1.1L cr during 2013-2017
Next in the list are the companies owned by Prabodh Kumar Tewari and his family members. The amount outstanding on Mahuaa Media, Pearl Studio Pvt Ltd, Century Communication and Pixion Media Pvt Ltd is Rs 2,416 crore.
The other companies that owe more than Rs 2,000 crore and are unwilling to pay despite having the means, according to the banks, are Zoom Developers Pvt Ltd promoted by Vijay Choudhary, Reid & Taylor (India) Limited & S Kumars Nationwide Limited, both promoted by Nitin Kasliwal, and media baron T Venkatram Reddy’s Deccan Chronicle Holdings Limited.
The data shows the alarming rate at which these bad loans are growing. In the past one year it has increased by about 27%. In the previous three years, it had increased by 38%, 67% and 35%, respectively.
Thus, between September 2013 and September 2017, the amount has quadrupled from Rs 28,417 crore to over Rs 1.1 lakh crore. While some of this would be due to interest being added each year, the quantum of the increase is too large to be entirely or even mainly due to that.
The RBI defines “wilful default” as defaults done despite the borrowers’ paying capacity. Money diverted for purposes other than the specific purpose of finance, or siphoned off and hence not available as assets to the borrower also qualifies as wilful default. Borrowers who have sold fixed assets that they provided as collateral to secure the loan without informing the bank also come under this category.
The cumulative total of more than 50 companies or groups each with over Rs 250 crore of wilful default works out to about Rs 48,000 crore. To put that in perspective, it is only slightly less than the government’s allocation of Rs 52,800 crore for health in the 2018-19 Budget.
Bank-wise analysis of data shows nationalised banks (excluding SBI and associates) constitute about 60% of this money. SBI and its associates account for one-fourth of the total. Private sector banks have also declared over Rs 14,000 crore as wilful defaults.
Defaults by gems, jewels companies, till 2017

From: Chethan Kumar, PNB lost four times more money than SBI did to jewel thieves, February 23, 2018: The Times of India
Highly cash-dependent traders in gems and diamonds have cost banks at least Rs 5,000 crore through 90 defaults, bank-wise and company-wise data on wilful defaulters compiled by the Federation of Bank of India Staff Unions (FBISU) shows.
The top loser is PNB, with just nine defaulters but a loss of Rs 1,790 crore — four times the amount SBI lost.
SBI reported the most number of wilful defaults(15) and lost Rs 410 crore (see table). PNB, incidentally, has lost the most among banks.
According to FBISU data, the total number of wilful defaulters is a little over 5,000, costing banks about Rs 49,000 crore, but the latest RBI data shows the numbers have jumped to 8,915 and Rs 92,376 crore, respectively. Of these wilful defaulters at the end of March 2017, PNB had the most (1,120), followed by SBI (997).
At least two bankers TOI spoke to said the exposure to gems and jewel companies must have also increased multifold. “Given that this data doesn’t include the recent PNB scam, the final number could point to one of the worst frauds the sector has seen,” one of them said.
Small and big loans have remained unpaid, while companies like Winsome, Beautiful Diamonds and Auro Gold Jewellery have defaulted with multiple banks. In some cases, banks are in the process of recovery, while in others investigations are pending.
Among the various means used to exploit banks is changing the names of companies and borrowing.
Data shows that Beautiful Diamonds was earlier called Splendour Gems, while Auro Gold Jewellery Private Limited later dropped the word “Private” from its name. Another firm, Ghanshyandas Gems and Jewels, later became “Ghanshyamdas”.
“The diamond trade is highly cash-dependent and the source of major money laundering. It may be conceivable that diamond merchants resorted to higher borrowing through Nostro accounts overseas to deal with the setbacks caused by constriction of the cash economy,” Tobby Simon of Synergia Foundation, a multidisciplinary think tank, said.
Experts, while pointing out how the total recapitalisation amount PNB received was about Rs 5,473 crore, pushing the bank’s net worth to Rs 20,000 crore, said that assuming the best scenario of recovery (of the Rs 11,300 crore) is 50%, the fraud has wiped out the entire money taxpayers had coughed up to recapitalise the bank.
Among other banks that suffered are Union Bank of India with nine defaults and Oriental Bank of Commerce with eight defaults.
Professor Charan Singh, former RBI chair professor at IIM-B, while calling for a complete overhaul of the banking system, cautioned against politicising the issue. “There’s a need to consider the sentiments of the public. Overreaction in the public domain can only deter depositors from banking, and bankers from lending.”
2018, March: The biggest defaulters

From: Mayur Shetty, Banks face triple whammy: Nirav, NPAs & rising yields, March 26, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
The biggest defaulters, as in March 2018
Riot defaulters exempt
The Times of India, May 03 2016
Defaults can't bar Guj riot-hit from special loans: HC
The Gujarat high court has held in a case that a bank cannot deny loan under special policy for 2002riot affected because the applicant had defaulted in payments earlier. The HC has asked the state government and Bank of India to extend loan to a 2002-riot affected trader from Bhavnagar, Usman Ghani Aadhiya, who had defaulted in an earlier loan from the same bank. The bank was refusing to pay him a fresh loan after riots on the ground of his earlier default.
Aadhiya had suffered damage of Rs 5.1lakh to his business in the riots and was thus entitled to a loan at 4% flat interest from a bank according to policy.The HC said it was not permissible for the bank to exclude him from extending the loan because he falls in the category of the riots affected.
Loan defaulters’ rights
The Times of India, Apr 18 2016
PREETI KULKARNI
Five rights loan defaulters should know of
If you have defaulted on loan repayment and the bank wants to repossess your assets, all is not lost
If you have defaulted on a loan, the rules do not give the lender a complete walko ver. Keep the following points in mind if you find yourself in such a situation.
Right to ample notice
A default does not strip you of your rights.Banks have to follow process and give you time to repay dues before repossessing your assets to realise the arrears. Typically, banks initiate such proceedings under the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Secu-rity Interests (Sarfaesi) Act. If the borrower's account is classified as a non-performing asset, where repayment is overdue by 90 days, the lender has to first issue a 60-day notice.
“If the borrower fails to repay within the notice period, the bank can go ahead with sale of assets. However, in order to sell, the bank has to serve another 30-day public notice mentioning the details of the sale,“ says banking and management consultant V.N.Kulkarni.
Right to ensure fair value
The lender starts the process of auctioning your property to recover dues if you fail to clear what you owe or respond during the 60-day notice period. However, before doing so, they will have to issue another notice specifying the fair value of the secured asset as assessed by the banks' valuers, along with details like reserve price, date and time of auction. “The borrower can object if the property is undervalued. He can justify his objection by conveying any better offer that he may have so that the bank can make a decision,“ says Kulkarni. In other words, you can look for prospective buyers on your own and introduce them to the lender if you think that the property can yield a better price.
Realise balance proceeds
Do not write off your asset mentally the moment it is repossessed. Keep track of the auc tion process. Lenders are required to refund any balance after recovering the dues, which s a real possibility given that property pric es can shoot up beyond the owed amount After recovering the dues and expenses of conducting the auction, the bank has to re und the remaining amount to the borrower as the money belongs to him,“ says Kulkarni
Right to be heard
During the notice period, you can make your representation to the authorised officer and put forth your objections to the repossession notice. “The officer has to reply within seven days, giving valid reasons if he rejects the representation and objections raised by the borrower,“ says Kulkarni.
Frauds below Rs 1L not to be reported to police: CVC
Don't report frauds below Rs 1L to police, CVC asks banks, The Times of India, Jun 17 2017
The Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) has asked public sector banks not to report frauds below Rs one lakh to local police, unless their staff is involved in such crimes. Earlier banks were mandated to report fraud of above Rs 10,000 and below Rs 1 lakh to police.
The decision was taken by the CVC in consultation with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), taking into account the practical difficulties faced by public sector banks in reporting such categories of cases.
It has been decided that only if staff of the bank is involved in the fraud cases of below Rs 1 lakh and above Rs 10,000, would such cases need to be reported or complaint filed with local police station by the bank branch concerned, the commission said in a directive to chiefs of all the banks.
The cases of frauds of upto Rs one lakh and not below Rs 10,000 are to be scrutinised by banks officials concerned for further necessary action, a senior CVC official said.
As of September 30, 2016, the Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) declared by various scheduled commercial banks stood at a whopping Rs 6,65,864 crore, according to an official data. The NPAs of the country's largest lender State Bank of India is Rs 97,356 crore, followed by Rs 54,640 crore of Punjab National Bank and Rs 44,040 crore of Bank of India, it said. Bank of Baroda has NPAs of Rs 35,467 crore, Canara Bank Rs 31,466 crore, Indian Overseas Bank Rs 31,073 crore, Union Bank of India Rs 27,891crore.
Loans: recovery of
'Lender can't seize vehicle without prior notice'
Dipak K Dash, 'Lender can't seize vehicle without prior notice', April 8, 2018: The Times of India
A finance company cannot forcibly take possession of a vehicle for non-payment of dues without sending a notice to the borrower, country's apex consumer commission has said.
The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCRDC) on Friday ordered a private finance company to pay Rs 80,000 to the borrower whose tractor was seized by the company in January, 2011 for alleged non-payment of dues.
Directing Shriram Transport Finance Company to refund the amount, which the borrower had paid to the company, with 9% interest within four weeks, single-member bench of M Sreesha said, "In my opinion, a seizure of the vehicle in such circumstances violating the principles of natural justice without giving an opportunity to the borrower to show his bona fides, amounts not only to unfair trade practice but also deficiency of service for which the financier is liable to compensate the complainant."
The NCDRC relied on the "vehicle repossession notice" by the company to the borrower, which showed that the notice was issued 10 days after the actual date of repossession of the tractor and the Commission observed that this "cannot be stated to be a notice prior to repossession which is in contravention of the principle of natural justice".
The case dates back to December 2009 when one Sakharam Sahu of Durg in Chhattisgarh had purchased the tractor with Rs 1 lakh loan after mortgaging his vehicle. Sahu needed to pay Rs 4,677 monthly instalment for 31 months. The finance company took possession of the vehicle on January 15 in 2011 as the borrower did not pay the instalment "despite repeated demands". The company had raised a demand of Rs 1.30 lakh. Sahu had submitted that he had repaid Rs 80,000 out of the total Rs 1 lakh loan and hence the company demanding Rs 1.30 lakh was "unjustified". The finance company took possession of the vehicle in January, 2011.
Aggrieved by the action, Sahu approached the district consumer forum, but did not get any relief. Though he later challenged the order in the state commission, it upheld the district forum's order. Finally, he challenged the state commission order in the NCDRC in 2014.
The NCDRC observed, "It is relevant to note that the notice is admittedly dated 25.01.2011, whereas in the body of the letter it is stated that the vehicle was taken into possession on 15.01.2011 at 2 pm. Viewed from any angle this repossession notice which dated 10 days after the actual date of repossession cannot be stated to be a notice prior to repossession which is in contravention to the principles of natural justice."
2018: RBI issues circular to treat defaulters as insolvent
April 3, 2019: The Times of India

From: April 3, 2019: The Times of India
The Feb 12 circular placed the RBI in a lonely corner — business houses were up in arms, banks were upset at having to make large-scale provisions and the govt was unhappy because several under-construction power projects faced the prospect of liquidation
WHAT IS THE CIRCULAR ABOUT?
On February 12, 2018, the RBI wrote to banks asking them to classify as a defaulter any company that fails to meet the payment deadline even by a day. The circular also forced banks to drag these companies to bankruptcy court if the defaults were not resolved in 180 days. The circular did away with various loan-restructuring schemes that aimed to give stressed borrowers more time to repay.
WHY WAS IT ISSUED?
The circular was issued after the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) came into force. Until the IBC laws were enacted, defaulters had the upper hand as banks could avoid making provisions towards non-performing assets (NPAs) by giving them more time and restructuring the loan. However, experience showed that restructuring only delayed and worsened the problem and the dues of these companies snowballed because of restructuring and all of them defaulted.
The RBI’s objective was to get banks to clean up their books by selling defaulting companies and not postponing the problem through restructuring.
WHAT’S THE IMPACT?
The circular resulted in banks classifying a larger chunk of their loans as NPAs. The first quarter of FY19 saw 21 PSU banks reporting a loss of Rs 16,600 crore as against a loss of Rs 307 crore a year earlier. Losses continued to rise for the second and third quarters. For public sector banks, gross NPAs hit 10.9% as of December 2018.
Most of the loans that were restructured in the earlier years turned into NPAs.
WHO OPPOSED IT?
The lead in the legal battle against this directive was taken by an association of power producers, representing projects with loans of over Rs 1.73 lakh crore. Of this, Rs 34,000 crore of defaults were because government departments did not make payments in time or due to policy changes. Later, other industries too became part of the suit with the RBI fighting a lone battle on the other side.
WHY DID THE SC STRIKE IT DOWN?
The apex court observed that the RBI had the power to give directives to banks to proceed against companies in the event of a default but cannot give directions in respect of debtors generally. While the argument was confined to RBI’s power to direct banks to initiate insolvency proceeding against debtors in general, the final order struck down the entire circular as ‘ultra vires’ (beyond one’s authority).
2019/ SC quashes the RBI circular

From: Amit Anand Choudhary & Dhananjay Mahapatra, SC quashes stringent RBI circular against defaulters, April 3, 2019: The Times of India

From: Amit Anand Choudhary & Dhananjay Mahapatra, SC quashes stringent RBI circular against defaulters, April 3, 2019: The Times of India
Debt-Laden Power Sector To Benefit Most
In a big setback to efforts for recovery of bad debts of companies owing Rs 2,000 crore or more to banks, the Supreme Court on Tuesday quashed the RBI’s February 12, 2018, circular, which directed banks to move against defaulters under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) on their failure to pay up within 180 days from March 1, 2018.
A bench comprising Justices R F Nariman and Vineet Saran also quashed all IBC proceedings initiated by banks under the RBI circular against defaulters.
Thus, the apex court turned the clock back to March 1, 2018, giving a huge relief to defaulters who owe Rs 2,000 crore or more to banks.
“All actions taken under the said circular, including action by which the Insolvency Code has been triggered, must fall along with the said circular,” it said.
However, this ruling will not affect initiation of IBC proceedings by banks against big defaulters taken before, or independent of, the RBI circular.
One such example is the IBC proceedings launched by a State Bank of India-led consortium against Essar Steel, which on culmination of proceedings is set to be taken over by Arcelor Mittal. Essar Steel had a debt of Rs 45,000 crore.
Writing the 84-page judgment, Justice Nariman accepted the main plea of senior advocate A M Singhvi, who appeared for the Association of Power Producers and argued that peculiarity of stress factors in each sector would not permit the RBI to bracket defaulting companies in different sectors for proceeding under IBC.
Singhvi’s arguments were adopted by other counsel who appeared for defaulting companies operating in varied sectors including telecom, steel, infrastructure, sports infrastructure, sugar, fertilisers and shipyards.
SC: Circular illegal due to lack of Central authorisation
Although the SC accepted senior advocate Rakesh Dwivedi’s arguments and upheld the constitutional validity of Section 35AA of the Banking Regulation Act, which empowers the Centre to exercise the power itself or authorise the RBI to direct banks to proceed against specific defaulters, it found the February 12 circular to be illegal as there was no such authorisation from the Centre to RBI to direct banks to proceed against defaulters by specifying a default limit and a 180-day period.
“The Banking Regulation Act specifies that the central government is either to exercise powers along with the RBI or by itself. The role assigned by Section 35AA, when it comes to initiating the insolvency resolution process under the Insolvency Code, is thus, important. Without authorisation of the central government, obviously, no such directions can be issued,” the bench said.
Referring to Section 35AA, the bench said, “It is clear that directions that can be issued by the RBI (to banks) under Section 35AA (with authorisation from Centre) can only be in respect of specific defaulters by specific debtors. This is also the understanding of the central government when it issued the notification on May 5, 2017, which authorised the RBI to issue such directions only in respect of ‘a default’ under the Code. Thus, any direction in respect of debtors generally, would be ultra vires (in violation of) Section 35AA.”
Justices Nariman and Saran also said the RBI circular “applies to banking and nonbanking institutions alike, as banking and non-banking institutions are often in a joint lenders’ forum which jointly lend sums of money to debtors. Such non-banking financial institutions are, therefore, inseparable from banking institutions insofar as the application of the RBI circular is concerned”.
Having clarified this, the bench said proceedings initiated by both banking and nonbanking financial institutions under the circular would have to be quashed along with the circular.
2018: PNB gets vigilance prize, Govt explains why
Govt explains why PNB got vigilance prize, March 9, 2018: The Times of India
The government informed the Rajya Sabha that the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) had conferred the ‘vigilance excellence award’ to chief vigilance officer (CVO) of Punjab National Bank (PNB) purely for best disposal rate of cases relating to disciplinary proceedings initiated in 2016.
Replying to a question, minister of state for personnel Jitendra Singh said the awards were conferred in 2017 for the first time under various categories to chief vigilance officers (CVOs), vigilance functionaries and management of six public sector banks for work done in 2016.
For the award in the category ‘timely completion of disciplinary proceedings’, Singh told the Elders, CVO of Punjab National Bank had the best disposal rate (92%) of vigilance complaints, among four eligible entries.
Disciplinary proceedings were finalised in 187 cases out of a total of 203 cases within the prescribed timeline of six months for major penalty and three months of minor penalty, he added. The vigilance award had raised eyebrows as it came in the wake of outbreak of the PNB scam involving jewellers Nirav Modi and Mehul Choksi.
Loans: Education loans
Education loan specialists grow faster
Mayur Shetty|Edu loans attract specialist lenders|Jul 12 2017: The Times of India (Delhi)
Edu loans attract specialist lenders
Mumbai
Pvt Players Positive On Growing Biz Education loans advanced by banks have grown by a measly 2.7% in FY17--half as much as the average growth rate of all loans.But that's only half the story .Specialist lenders are growing rapidly and private players are looking at this segment. Education loan specialists like HDFC Credila and Avanse have seen growth rates ranging from 40% to 70% in disbursements even as new age lenders like InCred Finance are eyeing the sector. Ajay Bohora, co-founder and CEO of HDFC Credila, says it's clear there is great demand. The shift in government focus to primary schooling has resulted in private in stitutions filling the gap in tertiary education. Secondly , in India and globally , cost of attendance (fees and other expenses) for tertiary education has been rising faster than inflation which is taking it out of reach of the middle class. HDFC Credila has disbursed Rs 1,300 crore of loans in FY17, which is slightly lower than the Rs 1,800 crore increase in the education loan portfolio of banks.
Bankers say they have pulled back from education loans because bad loans are high(7-8%). This is particularly true for the sub-Rs 4 lakh category where banks do not demand any security.
According to a senior PSU bank official, the reasons for the defaults are two-fold. One, engineering and management institutions have mushroomed but the quality of education has not been up to the mark. Two, many students relocate after graduation and their loans turn into NPAs.
“A lot of education loans are probably camouflaged as personal loans or loans against property ,“ said Prashant Bhonsle who heads the education loan vertical at InCred Finance. According to Bhonsle, students are rushed for time and at many banks it is faster to get a personal loan or a loan against property .The downside is that the interest paid cannot be claimed as deduction under Section 80E of the I-T Act. Also, repayment of such loans begins immediately , unlike education loans where there is a repay ment holiday . Also, education loans have tenures ranging from one to 12 years depending on course duration.
According to Rajnish Kumar, MD, State Bank of India, the outlook for education loans has improved with the government introducing a credit guarantee scheme for borrowings up to Rs 7.5 lakh in 2015. “The recovery problems that we faced in the south are now behind us and we will be growing the portfolio,“ said Kumar.
The ground reality is that unsecured education loans are a viable business only in segments where employment is certain. As a result, only those who qualify for top management or engineering institutes can expect to cover fees through bank financing without collateral. For others, a loan above Rs 7 lakh would invariably require property as collateral from parents.
Private lenders are positive as they have the skills and they can be selective.“Appraising a loan application is not easy because there are over 700 universities in India--some, like the University of Pune, have over 600 affiliated colleges, with each having 20-30 courses--and for credit assessment it's important to know the employment opportunities for each course,“ said Bohora.
It is not just finance companies, even lenders like Axis Bank, which was earlier a small player in education loans, has now created a new vertical for this product and is planning to grow. “We have grown 100%, although on a small base, and we see potential in this business,“ said Rajiv Anand, head of retail at Axis Bank. However, the bank is focusing on higher education in premier institutions like IIMs where both employment opportunities and fees are high. “The advantage for us is that we have good banking relationships with several trusts and educational institutions which makes it easier to partner with them for education loans,“ said Anand.
2017: Defaults highest in govt designed education loans
Mayur Shetty, Defaults highest in govt-designed education loans, Aug 30, 2017: The Times of India
The government-designed education loan scheme, which accounted for half of all education loans five years ago, now amounts to only a fifth. The scheme provides for loans up to Rs 4 lakh without collateral.
Banks are withdrawing from this segment, which is seeing the highest level of defaults. A study by TransUnion Cibil shows that defaults in education loans are lowest (below 1%) on big ticket loans of over Rs 15 lakh, which are typically taken for post-graduate MBA programmes in reputed institutes.
TOI had earlier reported how lenders were shifting focus on high-value loans as defaults in the sub-Rs 4 lakh category rose. The reasons cited by banks are now borne out by the data released by Cibil, which shows that the industry has experienced a default ratio of 8.1% on loans below Rs 4 lakh. Incidentally, most of these smaller-ticket education loans were disbursed by public sector banks.
According to Harshala Chandorkar, chief operating officer of TransUnion CIBIL the pattern of defaults raises the question whether the market is lagging in creating new job opportunities for those graduating from category II and III academic institutions.
"While delinquencies may be still better than the overall ratio of non-performing assets of many banks, the defaults are much higher than in other personal loan segments whether it is home loans, consumer durable loans, or even credit card outstanding," she said. Incidentally, the defaults that are now being experienced by banks are in respect of defaults witnessed on loans disbursed a few years earlier as education loans contain a moratorium, giving them time until they start earning to repay the loan.
TransUnion CIBIL research also indicate that since 2012, the number of new education loans disbursed annually has been showing flat to negative growth. The overall amount of loans disbursed has been showing a steady positive growth. This growth is driven by a marked shift towards loans of ticket size over Rs 15 lakh, which currently amount to over half the loan amount disbursed.
2015>’17: Defaults increase 47% on weak job market
Education loan defaults soar 47% on weak job mkt, December 23, 2017: The Times of India

From: Education loan defaults soar 47% on weak job mkt, December 23, 2017: The Times of India
A weak job market and wilful default by even those in well-paying jobs have hit the education loan portfolio of state-run banks with non-performing assets soaring by almost 47% between March 2015 and last March, data shared in Parliament showed.
The finance ministry told the Lok Sabha that NPAs, or bad debt, went up from Rs 3,536 crore at the end of March 2015 to Rs 5,192 crore on March 31, 2017. The surge took place in 2015-16, with the pace slowing down during the last financial year. The problem is so acute for at least five lenders that the stock of bad loans has more than doubled, with UCO Bank and Indian Bank leading the pack. At the same time, the increase in loan flow has also been less than 10% during this two-year period.
‘Absence of guarantees makes it easy to default’
But what is even worse is that there was only 3.4% riseduring 2016-17, on the back of a 5.6% growth in the previous year, indicating that either demand was tepid or banks were reluctant to lend. Bankers, however, said that they had not gone slow on education loans.
They said that defaults were rising as several students had not found good jobs, especially when it came to those who pursuedMBAsor engineering degrees.
However, there are cases where even students from good colleges who were employed by leading companies are refusing to pay.
For instance, an engineer with a global technology giant stop repaying theloan and was tracked down through social media. When confronted, he cleared the dues, said a bank executive. “The problem isthe absence of security and guarantees, which makes it easy todefault,” he added.
The government toldParliament that to reduce the incidence of NPA in education loans, the IBA Model Education Loan Scheme has been modified to factor in the the needs of students. The changesinclude a repayment holiday or a moratorium of course period plus one year, additional moratorium to account for spells of under-employment or unemployment, and extension of the repayment period to 15 years to reduce the equated monthly instalment.
The Centre has also launched a CreditGuaranteeFund Scheme for Education Loans (CGFEL) for loans upto Rs 7.5 lakh to provide guarantee up to75% of thedefault amount.
2018: 9% PSB loans turned bad
9% PSB edu loans turned bad in FY18, January 5, 2019: The Times of India
Nearly 9% of the education loans extended by public sector banks were categorised as NPAs in the last financial year, according to the government.
“According to information provided by the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA), NPAs of PSBs increased from 7.2% as on March 31, 2016 to 8.9% as on March 31, 2018,” minister of state for finance Shiv Pratap Shukla said in a written reply to the Lok Sabha. He was replying to a question whether NPAs in education sector rose to 9% during the two years period (2016-18). As of March 31, 2015, the bad loans in the education sector stood at 5.7%, the minister said.
Loans: Home Loans
Home loan closure checklist
The Times of India, Apr 18 2016
Home loan closure checklist
1 Refer to the `list of documents to submit' when making the application for a loan, and make sure that all the original documents are recovered.
2 Ensure that the documents are complete and received in good condition, in the pre sense of a bank official, before signing the acknowledgement.
3 Take an NOC from the lender, specifying the address of the property against which the loan was taken, name of the borrower and the loan account number.
4 Request the lender to inform CIBIL re garding the closure of the loan account.
The process should take about 30 days from the date of loan closure.
5 Ensure that any lien is removed after the clo sure of the loan. An existing lien will create problems during the sale of the property.
Home loan growth slows, affordable segment rises
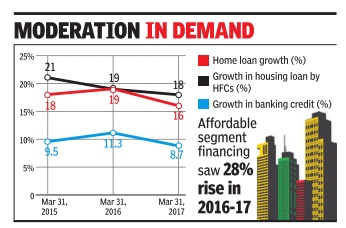
Even as housing credit growth moderated to 16% in 2016-17 as against 19% in 2015-16, the affordable housing segment holds promise, according to rating agency ICRA report.
The report said that lowering of interest rates and various government initiatives -Prime Minister Awas Yojana (PMAY), according infrastructure status, to boost affordable housing will increase the demand for the segment, which may see credit growth of up to 30%. As against an overall growth of 16% in the housing loan sector, total disbursal of credit in the affordable segment grew at 28% to Rs 1.2 lakh crore in 2016-17.
Despite moderation, the 16% credit growth in housing loan sector is still a bright spot in the economy if one sees it in the backdrop of growth in the non-food credit of entire banking sector which is languishing at 8.7% in 2016-17 as against 10.9% in 2015-16.
“While the slowdown was across both HFCs and banks, the decline in the pace of growth of banks was higher declining from 19% in 2015-16 to 16% in 2016-17 -largely because they were operationally tied up in second half of 2016-17 on account of demonetization,“ according to the report. Housing finance companies' (HFCs) loan portfolio also dipped to 18% in 2016-17 from 19% in the previous year.
2014>18: Self-employed segment grows; so do their defaults
April 9, 2018: The Times of India
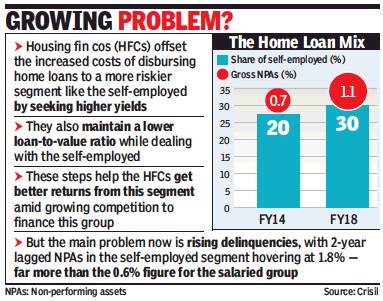
From: April 9, 2018: The Times of India
Segment Accounts For 30%, But NPAs Hit 1.1% Of Industry
A subdued loan demand from businesses is increasing competition in home loans, leading to a rise in the number of self-employed individuals getting mortgages. Home loans to self-employed accounted for 30% of mortgages in fiscal 2017-18 as against 20% earlier. But the flip side is that delinquencies are also rising.
Gross non-performing assets (NPAs) in the segment are estimated to have inched up by 40 basis points (100bps = 1 percentage point) to around 1.1% by the end of fiscal 2018, compared with about 0.7% a few years back. According to a report by ratings agency Crisil, home loans to the self-employed segment have been growing at a compounded annual growth rate of 33% in the past four years compared to overall 20% expansion in housing finance. Outstanding home loans in this segment are expected to have topped Rs 2 lakh crore by the end of fiscal 2018.
What has been driving growth is the entry of a host of new housing finance companies (HFCs), which have been growing aggressively in this segment. Also, larger HFCs are pushing into the self-employed segment as banks ratchet up presence in retail following weak credit demand from corporates and asset quality pressures, Crisil said in the report.
Crisil Ratings senior director Krishnan Sitaraman said, “Several initiatives of both the government and the regulator in the recent past have led to fast growth in home loans taken by the self-employed. We expect such mortgages to continue showing good growth because of the sharp focus of smaller HFCs and increasing interest of the larger ones.” Crisil Ratings director Rama Patel said, “The two-year lagged NPAs in the self-employed segment, at around 1.8%, is much higher compared with about 0.6% in the salaried segment, where the portfolio quality has remained largely stable over the years.”
Jan 2018/ Home loans up to ₹2L witness highest NPAs

From: Allirajan M , Affordable housing: Loans up to ₹2L see highest NPAs, January 12, 2018: The Times of India
With a sharp rise in loan disbursements and number of beneficiaries in the affordable housing segment, loans of up to ₹2 lakh has ended up with the highest level of non-performing assets (NPAs) in home loans. Public sector banks reported higher NPAs in the sub-Rs 2 lakh housing loans slab than housing finance companies in 2016-17 and 2015-16, according to an RBI report on ‘Affordable Housing’.
NPAs for housing loans of up to ₹2 lakh stood at a whopping 11.9% for PSBs during 2016-17. Housing finance companies also saw a sharp surge in housing loan NPAs in this slab. NPAs went up from 6.1% to 8.6% for the sub-₹2 lakh slab between 2015-16 and 2016-17. NPAs stood at 10.4% for this slab. The overall NPAs for housing loans stood at 1.5% and 0.6% respectively for PSBs and housing finance companies during 2016-17. The government’s recent thrust on affordable housing through policy measures that include incentive schemes, accordance of infrastructure tag, interest subsidy scheme under PMAY (Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana) have resulted in sharp rise in new housing projects in the affordable segment for low income groups. New unit launches in the affordable housing segment registered a 10.1% y-o-y growth in 2016-17. Affordable housing was the only segment in the residential real estate sector that saw a double digit growth. New launches in the mid-range and high-end segments fell by 11.7% y-o-y and 26.7% respectively in 2016-17.
There has been a more than three-fold increase in the number of houses completed under PMAY between April-December 2017. Investments to the tune of ₹1.72 lakh have been made under PMAY projects for constructing nearly 32 lakh houses.
Loans: Personal loans
2018: Loans against property up 33%, defaults cross 3%

From: Mayur Shetty, Loans against property up 33%, but defaults cross 3%, December 20, 2018: The Times of India
Loans against property (LAP), which is the fastest growing segment in personal loans in calendar year (CY) 2018 across banks and finance companies, has also recorded the biggest increase in delinquencies, according to an analysis of borrower data by TransUnion (TU) Cibil.
Delinquencies are defined as loans with overdues of more than 90 days.
LAP, which constitutes 1.6 million total accounts, saw a more pronounced delinquency rate as compared to other businesses (see graphic). Defaults rose 73 basis points (100bps = 1 percentage point) year-over-year to 3.03% in the quarter ended September 2018.
“Lenders must judiciously monitor their risk-management processes. LAP has risen at a rapid rate. At the same time, delinquency rates for these loans have now crossed 3% for the first time in several years. Lenders must now determine if the rapid demand for these loans, which are an excellent generator of revenue, outweighs the recent delinquency increases,” said TU Cibil vicepresident (research & consulting) Yogendra Singh.
The TU Cibil report includes loan data from all lenders including banks, non-banking finance companies and housing finance companies. Nonbank lenders have been driving growth in the LAP business. “The difficulties faced by non-banks were October onward and fresh origination of loans would have slowed down in the October-December 2018 quarter,” said Singh.
Credit card accounts increased by nearly 32% to 3.69 crore by Q3CY18, while personal loan accounts rose 26% to 1.5 crore in the same period. Indian LAP borrowers held average balances of Rs 34.93 lakh in Q3CY18. Comparatively, the average personal loans size per borrower was Rs 2.52 lakh. In credit cards, the average balance per holder was Rs 46,000.
Loans: Policy repo rate
2014-17
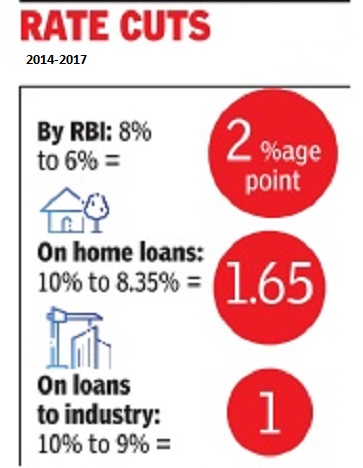
Following the [August 2017] announcement, the policy repo rate -the rate at which RBI lends to banks -stands reduced to 6.0% from 6.25%, the lowest since November 2010. Consequently , the reverse repo rate -the rate at which RBI borrows from banks -stands adjusted to 5.75%
From The Times of India
See graphic:
Rate cuts, 2014-17
2018: 25-basis-point increase to 6.25%
1st rate hike in Modi govt’s 4 yrs could make home loans dearer, June 7, 2018: The Times of India
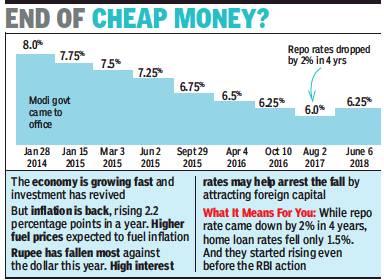
From: 1st rate hike in Modi govt’s 4 yrs could make home loans dearer, June 7, 2018: The Times of India
Fear Of Inflation Drives RBI Move
Prompted by inflation fears and emboldened by growth, Urjit Patel on Wednesday delivered his first rate hike since taking over as Reserve Bank of India governor in September 2016. It’s also a first during Narendra Modi’s four-year tenure as PM.
While economic growth makes every government happy, it dreads sharp price rises, especially ahead of elections. The Modi government will be praying for a good monsoon because it’ll help spur growth and check inflation.
All six members of the RBI’s monetary policy committee (MPC) voted in favour of a 25-basis-point (100bps=1 percentage point) hike in the policy rate, taking it to 6.25%. It could lead to another round of marginal increases in home loan rates in the coming months; all major banks have in the last one week raised lending rates by 10bps.
Wednesday’s hike follows five rate cuts during Raghuram Rajan’s time as governor – 4 of 25 bps each and one of 50 bps – and two, both of 25bps, by Patel, the last in August 2017.
Eco activity has shown sustained revival, says RBI
RBI governor Urjit Patel has maintained the RBI’s stance at neutral, which means that the central bank could go either way in the next policy in August.
Patel said RBI's decision was driven by its inflationtargeting mandate. The last rate hike – for 50 bps, to 8% – was by Rajan in January 2014.
In its statement, the RBI said that domestic economic activity has exhibited sustained revival in recent quarters and the output gap has almost closed. “Investment activity, in particular, is recovering well and could receive a further boost from swift resolution of distressed sectors of the economy under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code,” it added.
What has tempered the positive sentiment created by sharper growth – the Central Statistical Organisation last week announced a healthy 7.7% economic expansion for January-March – is the spectre of inflation. Data released since RBI’s April policy showed inflation jumped to 4.58% in that month from 4.28% in March. It is showing signs of firming up further with crude oil prices rising more than 10%. The rupee has also come under pressure with the US dollar gaining against most emerging market currencies.
According to Bank of India MD & CEO Dinabandhu Mohapatra, the fact that the RBI has revised its consumer price inflation forecast upward to 4.8-4.9% for the first half of FY19 shows that it will keep a hawk eye on retail prices in the months ahead. While a rate hike will lower the value of banks’ bond portfolios, the RBI has provided lenders some relief by allowing them to spread losses over four quarters. Also, medium and small enterprises have been given some relief in loan repayment. And the RBI’s decision recognizing banks' government bond holdings for meeting liquidity coverage norms will leave banks with more funds for lending, which is expected to keep rates under check.
The RBI’s rate hike may have surprised some analysts, but the growth forecast of 7.5% for FY19 boosted market sentiment with the sensex closing 276 points higher. Yes Bank MD & CEO Rana Kapoor said, “While the rate action is primarily in response to global uncertainty, especially from crude oil prices, it also signifies that the central bank is comfortable on the improving growth outlook.”
CARE’s chief economist Madan Sabnavis said, “The upside risk to the inflation emanates from the rising crude oil prices globally along with minimum support price impact.” He said the pace of inflation would depend on the progress and spread of monsoon.
“We expect one more interest rate hike by at least 25bps during the calendar year 2018, whereas we cannot rule out the possibility of two rate hikes by the end of the financial year 2018-19,” said Sabnavis.
“Investment activity, in particular, is recovering well and could receive a further boost from swift resolution of distressed sectors of the economy under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code,” RBI said in its statement
2018, Jan-Sept, vis-à-vis US Fed, BoE

From: October 6, 2018: The Times of India
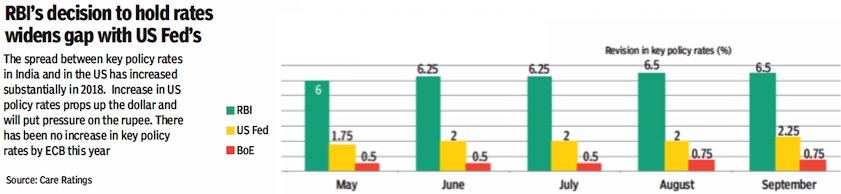
From: October 6, 2018: The Times of India
See graphics:
2018, January-April: RBI’s key policy rates, vis-à-vis those set by the US Fed and BoE
2018, May-September- RBI’s key policy rates, vis-à-vis those set by the US Fed and BoE
2017 Aug- 2019 Feb
Mayur Shetty, Das debuts as RBI guv with surprise rate cut, February 8, 2019: The Times of India

From: Mayur Shetty, Das debuts as RBI guv with surprise rate cut, February 8, 2019: The Times of India
6-Member Panel Voted 4-2 For 25bps Reduction
Unveiling his maiden monetary policy on Thursday, RBI governor Shaktikanta Das announced a quarter percentage point (25 basis points) rate cut, citing lowerthan-expected inflation. It was the first rate cut in 18 months and came after two rate increases in the interim period.
The decision to reduce rates was a split one. Of the sixmember Monetary Policy
Committee, four, including Das and RBI ED Michael Patra, voted in favour while deputy governor Viral Acharya and external member Chetan Ghate voted against cutting rates. However, a change in policy stance from “calibrated tightening” to “neutral” was approved unanimously.
Asked whether banks would cut rates in response, Das said he would be meeting bank chiefs within the next fortnight and raise the issue of monetary policy transmission.
It was vital to act decisively, says RBI guv
The RBI governor on Thursday triggered concerns of back-tracking on the central bank’s move to peg retail loans to an external benchmark from April 2019, by referring to RBI’s earlier circular as a discussion paper. A clarification from the central bank is awaited.
Das also made it easier for banks to lend to top-rated finance companies. He also indicated that an interim dividend to the government was forthcoming.
Explaining the rationale for the rate cut, Das said it was “vital to act decisively and in a timely manner to address the objective of growth once price stability as defined (in RBI's inflation-targeting mandate) is achieved.”
Following the policy, the repo rate stands reduced to 6.25% from 6.5%. According to Acharya, the outlook for prices had changed in December itself following a crash in oil prices, but the central bank did not change the stance, choosing to move in small steps.
The RBI has forecast GDP growth of 7.4% for FY20 with the first half growth expected to be in the range of 7.2-7.4% and 7.5% in the third quarter. RBI has also forecast a CPI inflation path of 2.8% for Q4 of FY19 followed by 3.2-3.4% in the first half of FY20 and 3.9% in the third quarter of the next fiscal.
Loan/ debt resolution
The NDTV case
Terming Any Loan Settlement As Criminal Raises Concerns
Private sector bankers say that if NDTV's loan settlement with ICICI Bank is termed criminal, it could hit resolution of bad debts. The concerns follow the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) alleging that ICICI Bank officials may have caused wrongful gains to NDTV promoters by agreeing to cut the interest rate to settle the loan.
“Settlement of any stressed loan involves some sacrifice by the banker. Often this is done to protect the loan amount since stand-off might result in loss of the principal well,“ said a banker who didn't want to be identified. If this sacrifice were to be construed as wrongful loss to the bank and a gain to the borrower, loan resolutions would not be possible, he added.
Multinational banks in India have been able to clean up their balance sheet the fastest as they have taken large haircuts in loans that were in default. The government is pushing for settlement of close to Rs 4 lakh crore of bad debt owed by top 50 borrowers which account for over 40% of the banking sector's bad loans.
Banks are likely to make a representation to the government and the RBI through the Indian Banks Association on commercial decisions being questioned. This is the second instance of CBI action against a commercial decision, the first being the arrest of senior officials of IDBI Bank on charges of improper loan sanctioning to Kingfisher Airlines.
The CBI, in a statement on Tuesday , said that the investigation did not pertain to loan default but to the interest relief. “ICICI Bank took the entire shareholding of the promoters in NDTV (nearly 61%) as collateral and then accepted prepayment of the loan by reducing the interest rate from 19% p.a. to nearly 9.5 % p.a. and as a consequence thereof, causing a wrongful loss of Rs 48 crore to ICICI Bank and a corresponding wrongful gain to the promoters of NDTV ,“ the agency said.
In May 2017, the government passed an ordinance authorising the RBI to issue directions to banks to initiate insolvency resolution process under the provisions of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016. This new legislation was aimed at breaking the logjam in the banking industry over banks' inability to resolve over Rs 7 lakh crore of bad loans.
A key feature of this legislation was creation of oversight committees to ratify decision taken by bankers. Having a panel in place is expected to shield bankers from action by investigating agencies who may later look into loan recasts.
However, the government has said that there will not be any blanket protection for bankers. Also proposals have to be referred to the oversight panels by banks.
Locker facility
Banks have no liability for loss of valuables in lockers: RBI
Banks have no liability for loss of valuables in lockers: RBI , Jun 25, 2017: The Times of India
HIGHLIGHTS
Banks say that "the relationship they have with customers with regard to lockers is that of lessee (landlord) and lessor (tenant)".
In such a relationship, the lessor is responsible for his or her valuables kept in the locker which is owned by the bank.
NEW DELHI: Do not expect any compensation for theft or burglary of valuables in safe deposit boxes of public sector banks as the locker hiring agreement absolves them of all liability.
This bitter truth was disclosed in an RTI response by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and 19 PSU banks.
Stung by the revelation, the lawyer who had sought information under the transparency law has now moved the Competition Commission of India (CCI) alleging "cartelisation" and "anti-competitive practices" by the banks in respect of the locker service.
He has informed the CCI that the RTI response from the RBI has said it has not issued any specific direction in this regard or prescribed any parameters to assess the loss suffered by a customer.
Even under the RTI response, all public sectors banks have washed their hands of any responsibility.
According to the information availed by the lawyer, the unanimous reason given by the 19 banks, including Bank of India, Oriental Bank of Commerce, Punjab National Bank, UCO and Canara, among others, is that "the relationship they have with customers with regard to lockers is that of lessee (landlord) and lessor (tenant)".
The banks have contended that in such a relationship, the lessor is responsible for his or her valuables kept in the locker which is owned by the bank.
Some banks, in their locker hiring agreements, have made it clear that any item stored in the locker is at the customer's own risk and he or she may, in their own interest, insure the valuables.
The common feature of all locker hiring agreements states, "As per safe deposit memorandum of hiring locker, the bank will not be responsible for any loss or damage of the contents kept in the safe deposit vault as a result of any act of war or civil disorder or theft or burglary and the contents will be kept by the hirer at his or her sole risk and responsibility.
"While the bank will exercise all such normal precautions, it does not accept any liability or responsibility for any loss or damage whatsoever sustained to items deposited with it. Accordingly, hirers are advised in their own interest to insure any item of value deposited in a safe deposit locker in the bank," they have said.
Aggrieved by the responses, the lawyer — Kush Kalra — raised questions before the CCI — why not just keep the valuables at home after insuring them, instead of paying rent to the bank for a locker when it is not going to take any responsibility for the contents.
He alleged that all these banks, also including State Bank of India, Indian Overseas Bank, Syndicate Bank, Allahabad Bank and others, have formed a "cartel" to indulge in such "anti-competitive" practices.
He further alleged that the bank by forming an association or cartel are "trying to limit the improvement of services which is directly affecting the competition in the market and interests of the consumer".
The lawyer has sought a probe under the Competition Act into the allegation of cartelisation by the banks in respect of the locker service.
Losses


2015: Crisis in the Banking sector
The Hindu, February 13, 2016
Banks, it is often said, are the fulcrum of a robust economy. Healthy banks are an essential prerequisite for placing the economy on a higher growth orbit. The banking scene in India, however, presents an absolutely scary picture. A combination of factors ranging from poor credit appraisal to political interference and mismanagement by borrowers have conspired to push the banking industry into a messy cobweb. Bank after bank, especially the government-owned, has come out with poor third-quarter results. The stressed assets (comprising gross non-performing assets plus written-off assets and restructured assets) account for 14.1 per cent of total bank loans as of September 2015, up from 13.6 per cent in March 2015. For public sector banks, the stressed assets were in the vicinity of 17 per cent at the end of September, while the figure for private sector banks stood at 6.7 per cent. The rising stress level, or increase in bad loans, has yielded a twin fallout — of declining profitability at banks and poor credit disbursal. The double effect is already telling on the economy in various ways. For long, banks have either managed to, or rather been allowed to, keep the stress invisible, giving the outside world very little clue as to the happenings inside the industry.
The Reserve Bank of India under Raghuram Rajan’s stewardship, however, has decided to clean up banks’ books rather than letting them camouflage the real picture. “There are two polar approaches to loan stress,” he said at the CII Banking Summit in Mumbai this week. “One is to apply band-aids to keep the loan current, and hope that time and growth will set the project back on track. Sometimes this works. But most of the time, the low growth that precipitated the stress persists. The fresh lending intended to keep the original loan current grows. Facing large and potentially un-payable debt, the promoter loses interest, does little to fix existing problems, and the project goes into further losses.” Indeed, legacy problems should be given a burial, and should not be allowed to persist. So hinting, Dr. Rajan articulated the need for surgical action to retrieve the health of the industry.
Forcing banks to recognise a problem is one thing, and finding a viable long-term solution to it is quite another. That requires not just holistic thinking but an out-of-the-box approach as well, especially in the evolving global context. A meaningful fix can happen only if banks are given functional autonomy at various levels. Restricted freedom inevitably leads to a blame game, making it even more difficult to fix responsibility. The concept of arm’s- length relationship especially needs to be clearly defined and implemented in letter and spirit in the banking industry. It is not just about how much money the Central government will freshly pump into stressed banks. The litmus test for the government lies in its ability, and capacity, to let go of control. The banking system indeed needs a change in the way it is managed.
Loss in scams: 2011-15
Mar 27 2015
In four years, Rs 25 banks lost Rs 12k cr to fraudsters
Chethan Kumar
Twenty-five nationalized banks have lost Rs 12,620 crore to frauds in the last four financial years, according to documents obtained from the finance ministry. Of these, Rs 2,060.75 crore were lost by five banks headquartered in Karnataka alone -Canara Bank, Vijaya Bank, Corporation Bank, Syndicate Bank and State Bank of Mysore. The documents revealed that there have been 4,845 cases of bank frauds over this period. Finance ministry sources said in most cases bank staff either connive with the fraudsters or are negligent.
The latest instance surfaced on Wednesday when the CBI registered a case against an Ahmedabad-based telecom company and its directors following a joint complaint from State Bank of India, Vijaya Bank and Canara Bank. “It is alleged that expressing urgency , the company promoter got Rs 40.4 crore released from the three banks even though some documentation was pending. He disappeared after seeking time until August 31, 2013, to repay the loan,“ the CBI said in a statement.
Among the documents the promoter submitted were letters of credit (LCs), which turned out to be fake. A term loan of Rs 86 crore was also released to this firm, which too was allegedly siphoned off. There is an estimated total loss of Rs 126.4 crore to the banks.
In another case, the CBI on Thursday arrested a former managing director of a Bhopal-based private firm, who was absconding in a case relating to alleged loss of Rs 3.63 crore to State Bank of Indore.He conspired with bank officials to obtain credit facilities on the basis of fake collateral during 2003-2004.
Q4/ 2016: High losses
The Times of India, May 19 2016
PNB Q4 loss highest by an Indian bank

Following a RBI-driven clean-up programme, PNB joins scores of other lenders which have reported losses, including Corporation Bank, which reported a loss of Rs 511 crore for the March quarter. The Delhi-headquartered lender had reported a steep fall in profit during the October-December quarter but had avoided loss that several other players, in cluding Bank of Baroda and Bank of India, registered.With annual loss a shade under Rs 4,000 crore, PNB lags Bank of Baroda, which has been in the red for two straight quarters.
So far in January-March quarter, public sector banks have together reported losses of around Rs 14,000 crore.
On the positive side, there are fewer restructured loans that are turning into NPAs, which are loans that remain unpaid for 90 days. But, banks have to deal with a huge pile of bad debt which doubled to Rs 55,818 crore at the end of March from the level a year ago.
Indian banks have seen their NPAs surge as companies in several sectors such as steel and textiles have witnessed pressure of imports, especially from China. In the infrastructure space, several corporate groups are facing stress as projects have not taken off due to regulatory factors. Although the government has been trying to resolve these cases, there has been limited success. In addition, several companies are still dealing with over-capacity as rural demand remains weak.
Money lost to theft and fraud
Between April 2013 and November 2016, the country's top 51 banks lost Rs 485 crore to theft.
More than 24 lakh people, or roughly 22% of Delhi's population, could have withdrawn Rs 2,000 using this much cash. Documents obtained from the Union finance ministry show that Rs 212 crore was lost to 2,492 cases of robbery , theft and burglary at ATMs. Another Rs 156 crore and Rs 74 crore were lost to credit card and debit card cloning, respectively , while Rs 42 crore was lost to netbanking fraud.
The number of thefts from ATM kiosks has been increasing every year. In 2015-16, 922 cases of theft totalling Rs 78.6 crore were reported, an increase from 698 cases (totalling Rs 51.7 crore) in the previous year.There were 596 cases (totalling Rs 34.34 crore) in 2013-14. The first quarter of 2016-17 has wit nessed 276 cases involving a theft of Rs 48.3 crore.
A major factor for the rising number is that the ecosystem lacks experts to deal with ATM thefts and other cases of technology-related fraud in the financial sector.
“Not all banks have forensic or technology experts.Plus, there is no coordination.Banks must make use of experts from Nasscom and the Centre, while police across the country need to get updated,“ said IPS officer P Harishekaran. Between 2013-14 and the second quarter of 2016-17, there have been 30,259 cases of credit card cloning costing Rs 156 crore. There were 12,033 cases of debit card cloning costing Rs 74 crore in the period.Another Rs 42 crore was lost in 559 cases of netbanking fraud in the same period.
“Police can only conduct post-theft investigation; the onus on prevention is completely on the banks, and there needs to be special risk-management teams and experts working round the clock to protect data,“ cyber expert Mirza Faizan Asad said. Experts also point out that dependence on foreign equipment should be reduced, and the banking sector should procure Indian products to be ensure data safety.
Banks lose Rs 1.6 crore/hour to cheating, forgery
March 14, 2018: The Times of India

From: March 14, 2018: The Times of India
HIGHLIGHTS
Indian banks lose Rs 1.6 crore to just “cheating and forgery”- one of the eight categories of fraud listed by RBI
Such fraud basically involves obtaining loans using forged documents, or cheating banks by making false claims
Of the Rs 42,226 crore lost to ‘cheating and forgery’, 89 per cent (Rs 37,583 crore) was lost by public sector banks
Every hour, Indian banks lose Rs 1.6 crore to just “cheating and forgery”, one of the oldest methods of frauds which accounts for a little more than 60 per cent of all money lost by banks.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has eight categories of frauds for the sake of uniform reporting by banks, and just one — cheating and forgery— saw Indian banks lose a whopping Rs 42,276 crore in three years of 2014-15, 2015-16 and 2016-17, with Public Sector Banks (PSBs) bearing the brunt. Data for 2017-18 is being compiled.
Experts say this points to a major vulnerability in the system resulting from lack of training, security frameworks and overall hygiene.
Such fraud basically involves obtaining loans using forged documents, or cheating banks by making false claims. Of the Rs 42,226 crore lost to ‘cheating and forgery’, 89 per cent (Rs 37,583 crore) was lost by public sector banks (PSBs), while private banks lost Rs 4,683 crore. The State Bank of India lost the most — Rs 5,743 crore — accounting for 15 per cent of money lost by PSBs.
The money was lost in 7,505 cases and 4,702 cases were reported by PSBs, while private banks saw 2,803 cases. “This kind of fraud, on this scale, cannot take place without insider involvement. Data show these are clearly not stray cases which means the system needs to be evaluated more carefully now,” Tobby Simon of Synergia Foundation, a multi-disciplinary think-tank based in Bengaluru, said. A retired bank official said RBI has clear policies regarding frauds. He, however, claimed it’s unclear how frauds of such magnitude continue to haunt the system.
The money lost to ‘cheating and forgery’ in the three years accounts for 60 per cent of all frauds, which is slightly higher than Rs 70,000 crore. All these are only cases where the fraud involved is more than Rs 1 lakh, and experts say frauds involving money less than Rs 1 lakh could have cost the banks at least another few hundred crores.
2018: The Modi- Choksi scam
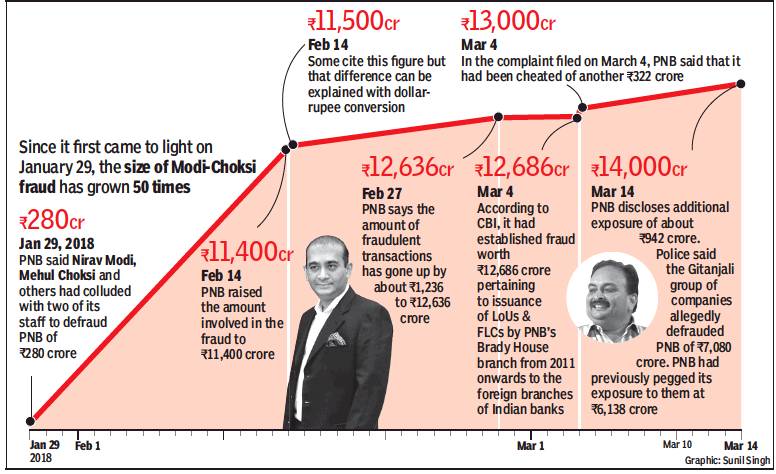
From: March 15, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Between 29 Jan 2018, when it first came to light, and mid- March 2018, the known size of the Modi- Choksi scam grew fifty times
Performance
2005-19: Vis-à-vis new private banks
PSU Banks Inefficient On Every Parameter, February 1, 2020: The Times of India
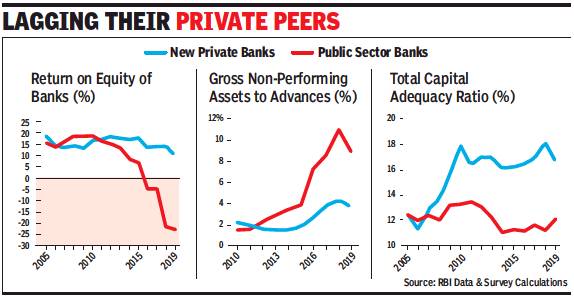
From: PSU Banks Inefficient On Every Parameter, February 1, 2020: The Times of India
Every Rupee Invested Lost 23 Paise Till 2019: Survey
In a strong critique of the performance of public sector banks (PSBs), the Economic Survey said while Rs 4.3 lakh crore of taxpayers’ money has gone into PSBs, every rupee invested has lost 23 paise as on 2019. The survey also described Indian banks as suffering ‘dwarfism’, with only one bank in the top 100, while six are needed for an economy like India’s size. PSBs should be asked to share corporate data among themselves through a GSTNlike entity (PSB network) and undertake analytics of the data using fintech. PSB employees should hold stake through Employee Stock Option Scheme across all levels. “Part-ownership of PSBs by employees will reduce agency problems. This is because employees who own shares are incentivised to increase market value of equity.” Assessing the performance of government banks after completion of 50 years of nationalisation in July 2019, the government’s report card on economy said on every performance parameter ‘PSBs are inefficient compared to their peer groups’.
As of January 2020, every rupee of a taxpayer’s money invested in PSB is fetching a market value of Rs 71 paise. As against that every rupee invested in a private bank fetches a market value of Rs 3.7, which is five times of the return in PSBs.
According to the report, if the market-to-book ratio of each PSB becomes equal to that of the second-worst new private bank, the improvement would gain the government Rs 9.1 lakh crore, which is about 8.5 times the disinvestment budget for 2019. Highlighting the importance of banks, the survey said historically the top-five economies have always been supported by their banks. “India becoming a $5-trillion economy will require at least eight Indian banks to be large enough to belong in the top 100 globally.” However, credit growth in PSBs has been sluggish, largely because of their large stock of bad loans. In 2019, PSBs reported gross non-performing assets (NPAs) of Rs 7.4 lakh crore, which is 11.9% of their loans. “NPAs of Indian banks, particularly PSBs, could have been prevented if data and analytics were employed in corporate lending.”
While there have been arguments of the social impact of bank nationalisation, the survey said there have been multiple factors at work. Noting that rural branches have increased 10-fold and credit to rural areas rose 20-fold in the first decade after nationalisation, it said some caution is necessary in interpreting the above trends as being entirely caused by nationalisation. “A key confounder in such an interpretation is the role played by other interventions around bank nationalisation. For instance, the government initiated a green revolution and anti-poverty programmes.” To further confound matters, the RBI had introduced directed lending programmes, which set priority sector targets for banks and the RBI used both formal means and moral suasion to persuade lenders to achieve its targets. Explaining reasons for disproportionate share of bad loans among PSBs, the report card said a plausible explanation could be that in Indian economy’s growth phase between 2004 and 2011, PSU banks grew their loan portfolio but this credit growth was of suspect quality.
On outlook for banks, the survey highlighted the country’s demographics and the Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile combine as the two big driving forces.
As against the earlier reports that made a push for dilution of government stake, the survey made a strong pitch for employee ownership of PSBs. Even as the Indian Banks Association is negotiating a wage settlement with unions, it said the current flat compensation contracts and pressures from ex-post monitoring by the vigilance agencies, it is hardly surprising that the staff prefer safety and conservatism over risk-taking.
2014
Nationalised and private banks, total bank deposits
19 nationalized lenders' combined m-cap less than HDFC Bank's Rs 2.64L cr
Mayur Shetty The Times of India Feb 03 2015
Investors Lose Interest In PSBs As Bad Loans Rise
The 19 nationalized banks in India account for almost half of the total bank deposits in the country as against private banks, which together have an 18.7% share. However, the surge in bad loans among public sector banks (PSBs) and the technology gap they have vis-à-vis their private peers has resulted in these lenders losing investor interest. As a result, the Rs 2.39 crore combined market capitalization of the nationalized banks is less than the Rs 2.64 lakh crore market capitalization of HDFC Bank the most valuable pri vate lender.
The nationalized banks exclude market leader, SBI which has a market cap of Rs 2.43 lakh crore. But even if the market capitalization of the 19 nationalized banks and the SBI were to be added together, it would still be less than the combined market capitalization of HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank as per Friday's closing prices. In cidentally, SBI is the only public sector lender with a market cap of over Rs 1 lakh crore. The next public sector bank is Bank of Baroda, which is a distant second in the public sector with a market capitalization of Rs 46,985 crore.
While the nationalized banks are being shunned by investors, the new generation private banks have been hit ting new highs on the back of new initiatives, which include digital technology . Besides HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank, two other private lenders have crossed the Rs 1 lakh crore mark. Kotak Mahindra Bank, which has been rallying after its recent inorganic initiatives -acquisition of ING Vysya and a deal to pick up stake in MCX -was worth Rs 1.02 lakh crore on Friday.
What the valuations mean is that the markets are discounting the market share of public sector banks in loans, their real estate assets worth thousands of crores and their customer base which accounts for almost the entire working class population of the country. Analysts say the main reason for despondency in PSU bank stocks is their disproportionate share in bad loans.
Here is what research firm Emkay Global Financial Services said about Bank of Baroda – a better performing public sector bank. “We expect the weak asset quality to persist.
While capitalization is better than peers, weak return ratios coupled with higher Basel III requirement will pose a challenge in the medium term unless there is sharp recovery. Also, capital infusion by the government, if below book value, would contain RoE improvement.”
Most NBFCs don't seek bank licence
Chennai: Several non-banking finance companies, including the Shriram Group, have stayed away from applying for a differentiated banking licence, as a January 1 clarification issued from the RBI forbids both NBFC and bank's co-existence.
The first set of guidelines dated November 27, 2014 for a differentiated bank licence, there was no explicit exclusion for NBFCs to co-exist along with these banks. The only inference was with respect to guidelines which dealt with financial and non-financial activity of the promoters, which was expected to be ring-fenced. These restrictions, according to sources in Shriram Group, vitiates the level-playing field between banks and NBFCs and also between existing banks and new ones, since the existing banks in several promoter groups like HSBC, HDFC, Federal Bank, Kotak are operating their NBFCs.
2014: Deutsche is no. 1
The Times of India Dec 22, 2014
Reeba Zachariah & Boby Kurian
Deutsche Bank has emerged as India's top dealmaker by fees earned during 2014. The European giant grossed $31 million in investment banking revenue, moving up from the fifth position it held in the previous calendar, according to Dealogic data.Wall Street biggie Citigroup retained the second position collecting $27 million in a year when i-banking fees declined nearly 13% from $398 million to $347 million.
Deutsche, which had a good run in equity and debt market deals, has an 8.9% share. Citigroup, ahead in M&A deals, staked claim to 7.7% share of the fee pool. The overall i-banking revenue slipped despite a pickup in the capital market activity as many private investments and certain M&A deals in emerging sectors like consumer internet were struck without advisers.
Standard Chartered Bank, with $25 million and 7.3% share, came third -up from sixth place last time -after advising M&A deals such as United Spirits' divestment of Whyte & Mackay , sale of Neotel by Tata Communications and Wilmar's stake purchase in Shree Renuka Sugars. Credit Suisse and JP Morgan were neck and neck, clocking $20 million in fees with 5.7% share each, while Axis Bank came in sixth with 4.5% share.
The big bankers said the street activity was set for a boost in the New Year. “As in vestment picks up, the requirement for new money and desire to access new capital pools will increase, which could trigger supply of issuances,“ said Amit Bordia, MD & head of corporate finance, Deutsche Bank.
I-banking fee charts are important, and closely monitored, as they usually set the tone for bonus payouts announced in January after the Christmas-New Year holidays. Within the total wallet, debt instruments brought in the highest revenue at $156 million followed by M&A with $112 million and equity capital issuances $78 million.
“2014 saw a pickup in capital market activity, especially qualified institutional placements and M&A transactions, in the latter half. This resulted in a concomitant increase in fee pool, moderated down by the fact that some deals have not had advisers,” said T V Raghunath, MD & CEO, Kotak Investment Banking. M&A and equity market deals increased to $47 billion and $11 billion respectively in the current calendar from $32 billion and nearly $10 billion in 2013.
Debt market deals, however, declined from almost $58 billion to $40 billion. The traditional i-banking fees do not count syndicated lending revenue, in which State Bank of India (SBI) has a lion's share with $83 million in earnings.
But, according to bankers, their bonus payouts were getting de-linked from fees earned in recent years. “Unlike the region, where marquee deals will dictate bonus numbers -no such luck in India. Neither league table rankings nor being one of the top fee generators will have any material effect on year-end numbers, which will be flat to down with the occasional outliers,” said Sourabh Chattopadhyay , partner, Wellesley Partners, a Hong Kong-based recruitment firm focused on financial services sector.
China, for instance, saw its i- banking revenue top $5 billion 2014.
2015: 3 Indian banks in top 5
The Times of India Jan 11 2016
Reeba Zachariah & Boby Kurian
TNN
The merger advisory units of Axis Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank and ICICI Bank have made it to the list of top five dealmakers by fees earned during 2015, a Dealogic report has revealed. This marks the return of Indian tigers, overtaken by American and European investment banks since mid-2000s.
Axis rose from No. 4 in 2014 to No. 2, grossing $25 million in investment banking revenue and garnering nearly 8% of the total fee pool last year. Kotak Mahindra, which didn't even figure in the top 10 list of 2014, came third with earnings of $17 million. ICICI, with $15 million in revenue, moved three ranks up from 2014 to bag the fifth spot last year.
JM Financial had topped Bloomberg's merger and acquisition (M&A) chart by the size of the deals advised during the previous calendar year.
The investment banking revenue compiled by Dealogic comprises fees earned from M&A advisory , debt deals and equity transactions. Despite the strong showing by domestic dealmakers, Citigroup earned most fees, which was pegged at $32 million last year. Citi, with 10% share of the fee pool, was active in technology and consumer internet deals as startups gathered heft and deals got bigger, attracting the attention of foreign investment banks.
The total wallet of India's investment banking industry shrunk to $329 million last calendar compared to $408 million in 2014. M&A brought the highest revenue of $137 million, followed by $100 million fetched by debt deals and $92 million by equity issuances.
“Domestic banks have far superior execution capabilities and ear to the ground, reflecting on the performance of every deal this year and have hence beaten foreign banks,“ said Dharmesh Mehta, MD & CEO, Axis Capital, the M&A advisory arm of Axis Bank.
Besides Citi, the only other foreign bank in the top five list was JP Morgan, which jumped from the sixth position in 2014 to the fourth, garnering $15 million in fees last year. 2014's topper Deutsche Bank tumbled to the eighth position.
Sourabh Chattopadhyay , country head, Wellesley Partners, a Hong Kong-based placement firm focused on the financial services industry , said, “The underlying stories from last year's performance by foreign banks include Citigroup's re-emergence to the top, the continuing capital market success of Morgan Stanley and Credit Suisse's performance despite losing key senior members. There is measured optimism for 2016 as selective upgrading has picked up“.
2018

From: March 9, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Market capitalization/ Valuation of India’s leading banks, 2018
2018: M-cap vis-à-vis income

From: April 19, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Market capitalization vs. the total income of India’s five leading banks, as in April 2018.
The ownership structure in private banks/ 2017
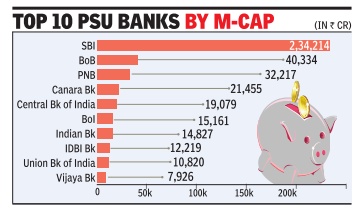

At a time when PSU banks in India need about Rs 2 lakh crore for recapitalisation to tackle rising nonperforming assets (NPAs), Kotak Bank alone may sell shares worth a similar amount. This is because the RBI has asked promoters Uday Kotak and family to cut their stake from the current level of 32% in the country's third largest private sector lender to 15% by March 2020.
The Rs 2-lakh-crore amount is more than the current market cap of ICICI Bank, which is the third largest bank in the country after HDFC Bank and SBI respectively . It is also more than the market cap of eight top PSU banks (except SBI) put together.
A report by proxy advisory firm SES pointed out that given the situation at Kotak Bank, it's high time the banking regula tor looks at ownership structure in private banks. Otherwise, like ICICI Bank and HDFC Bank, foreign funds will hold a majority in Kotak Bank also.
If the bank issues shares to dilute the promoters' stake to the level stipulated by the RBI, it would need to issue about 210 crore shares over the next three years, but the same should be done in tranches. The report said that if the bank increases the share price by 5% in each tranche it sells, the total funds required would be about Rs 2.20 lakh crore.
“After such an issue, the bank will have the highest net worth in the country's banking system and will lose its sheen unless it grows by leaps and bounds and overtakes leaders like SBI and HDFC Bank in terms of business, which does not appear to be a practical target,“ it noted. “Therefore, such a step will cause performance metrics to become weak and at the end not only both investors and promoters will lose, but all stakeholders will lose as the bank will not be the same as it is today ,“ it said.
The report also pointed out that it's only the foreign funds that can have the money power to buy such large chunks of shares and, hence, their share in Kotak Bank is sure to rise. Currently , foreign funds hold 42.1% in HDFC Bank, while they hold nearly 47% in ICICI Bank and almost 39% in Kotak Bank.
Mergers
1993-2019

From: March 6, 2020; The Times of India
See graphic:
Bank mergers in India, 1993-2019
Micro-Finance Institutions ( MFI )
1969-2016
Mohit Satyanand , Rich like us , “India Today” 14/11/2016
Indira Gandhi's nationalisation of 14 private banks in 1969 placed 85 per cent of the country's bank deposits under the government's control, and signalled its lurch to the left. Ostensibly, the move would take credit and banking facilities to the poor, especially in rural areas. No such revolution came about. Instead, we watched government banks accumulate a vast pile of 'non-performing assets', or bad loans, advanced to large industrialists, typified by Vijay Mallya. Meanwhile, entrepreneurs rooted in rural reality recognised that there was a need for credit in our villages and slums, which would require new paradigms of lending. Learning from experiences in Bangladesh, Thailand and the Americas, a star IIM-Ahmedabad alumnus, Vijay Mahajan, was the first to set up a micro-finance institution (MFI), in 1996. Popularly known as BASIX, the Hyderabad-based finance corporation received extensive support from Indian bankers, industrialists and foreign funders. By 2010, BASIX had a loan book of Rs 1,800 crore, and was seen as a model for credit to the poor. Following in its footsteps, and also based in Andhra Pradesh, SKS Microfinance was floated as a publicly listed company, and the consequent access to funds fuelled its meteoric growth.
By 2010, Indian MFIs had bank finance worth Rs 30,000 crore, and Andhra Pradesh was by far the most active locus of their operations. This high visibility made the industry a political football, and in 2010, the Congress chief minister, K. Rosaiah, promulgated laws that severely curtailed MFI operations, alleging malpractices in lending and collection. The ousted chief minister, Chandrababu Naidu, proclaimed that these measures were inadequate, and loans from MFIs should be waived. Borrowers figured they had political sanction to stop repaying loans, and the consequent cash squeeze pushed the industry to the wall. BASIX crumbled, and SKS went into a protracted crisis, leading to the ouster of its founder, Vikram Akula. Meanwhile, another MFI, Bandhan, had grown out of West Bengal, and had relatively little exposure to south Indian markets. Led by Chandra Shekhar Ghosh, a man of humble origins, Bandhan was established in 2002. Every year, it set itself rolling three-year targets, and every year, it exceeded them. By 2005, it was far-sighted, and confident, enough to bring in Deloitte to audit its systems. In 2007, Forbes rated Bandhan as the second most successful MFI in the world. Unroiled by the MFI debacle of 2010-11, Bandhan gathered momentum in this decade, and by August 2015, had 6.7 million borrowers, and a loan book of Rs 10,500 crore. In that month, it became the first of the Indian MFIs to receive a banking licence. Within a year of beginning operations, Bandhan Bank has issued 8.1 million debit card cards, significantly more than much older banks such as Kotak Mahindra and Yes Bank. Clearly, Bandhan has a dynamic DNA. In the book named for it, veteran journalist Tamal Bandyopadhyay traces Bandhan's growth under the restless Ghosh, and explores the unusual man who still runs it. It is a compelling story, of a man with an acute sensitivity to the poor, and the ability to drive high growth at a low cost. Though exceedingly well-researched, full of both context and detail, Bandhan often frustrates the reader, repeating facts and data points, flipping back and forth in time and theme. With skilled editing, it could have made a highly relevant story into a much more absorbing one.
Mobile banking
Unified Payment System/ UPI
The Times of India, August 26, 2016
Mayur Shetty
The RBI has cleared a Unified Payment System a platform which links bank account numbers to virtual payment addresses (aliases). The UPI-enabled app in effect turns your smartphone into a bank and has come as a boost to a cashless economy .
Just as an ATM of one bank can be used to access accounts in all banks in the network, any UPI-enabled app can be used to log into one's accounts in other banks. Second, the interface overcomes one of the biggest pain points in sending money online -that of knowing 15-digit account numbers and an 11digit IFSC code (used to identify bank branches). Instead of account details, the receiver has to merely share an alias like xyz@axisbank. The UPI makes use of the existing Immediate Payment System (IMPS) which allows funds transfer using bank account number, an IFSC code and other credentials.
“Real-time sending and receiving money through a mobile application at such a scale on interoperable basis has not been attempted anywhere else in the world. The UPI app will be made available on Google Play Store by banks,“ NPCI managing director and CEO A P Hota said here on Thursday .
Twenty-one banks will go live over the next couple of days. But the country's largest bank, SBI, has expressed concerns and has kept it on hold until it gets more clarity from the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), the umbrella organisation for retail payment systems in India. Of the 21 banks, eight banks have gone live.
“Our app is still under development. We have raised some security concerns on the registration process and transactions being timed out. The NPCI has not yet come back.We will be ready by Septemberend. But the decision to join will depend on NPCI coming back to us with clarifications,“ said Manju Agarwal, deputy MD, SBI. HDFC Bank too is working on its application and expects to be ready in three weeks. ICICI Bank has announced that it will integrate its iMobile and Pockets app with UPI in the next few days. iMobile is for the bank's customers, while Pockets is an app with a prepaid instrument available to anyone who downloads it.
Kotak Mahindra Bank has decided to play it safe and provide a separate application for UPI. “We are in process of development and certification of UPI-enabled app. We will launch a new app which will be UPI-enabled in 4-6 weeks. “ said Deepak Sharma, chief digital officer, Kotak Mahindra Bank.
2018: mobile banking increases
Mayur Shetty, When m-app matters more than branches, December 5, 2018: The Times of India
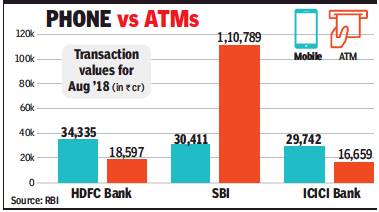
From: Mayur Shetty, When m-app matters more than branches, December 5, 2018: The Times of India
Mobile Is Primary Channel For Transactions At HDFC Bank
HDFC Bank’s mobile banking outage has caused a bigger stir than the usual closure of all bank branches on weekends.
A glitch had made HDFC Bank’s new mobile app nonfunctional for six days. Why was the HDFC Bank mobile app blackout such a major issue? The reason is the sheer volume of transactions that take place through this channel. HDFC Bank’s mobile app accounted for Rs 34,335 crore of transactions in August, which is almost twice the Rs 18,597 crore that its customers conducted through ATMs.
If non-financial aspects such as balance enquiry are included, more than twothirds of all transactions today take place through the mobile app for HDFC Bank. According to a source in the bank, the mobile app has become the primary channel for many customers with all the functionalities of internet banking available within it.
Meanwhile, HDFC Bank finally restored its mobile services on Tuesday evening by providing its older app on Android Play and Apple’s App Store, thereby restoring the m-banking channel.
In terms of value, HDFC Bank accounts for 15% of all mobile banking transactions in the country. Also, HDFC Bank and other private lenders have been most successful in digitising their customers compared to PSU peers. For instance, while State Bank of India records a higher volume of mobile banking transactions, the value of its m-banking transactions at Rs 30,411 crore is less than a third of the value of ATM transactions at Rs 1.10 lakh crore.
According to bankers, the security level in banking through mobile applications is also higher because there are several levels of authentication, including the device and mobile number. “In India, many customers have leapfrogged to mobile banking without using internet banking. Even in internet banking — where customers log into the bank’s website — it is the mobile device that is being used,” said an executive with a private bank. Given that many customers do not visit the bank branch even once a month, savings account holders are more affected by a mobile banking downtime than a bank strike, he added.
Mobile banking transactions
The Economic Times, Mar 22, 2016
Mayur Shetty
Top 5 banks generate 92% of mobile banking value
Mobile banking penetration in India is concentrated among customers of five banks. According to data released by the Reserve Bank of India, the top five banks account for more than 92% of the entire value of mobile banking transactions in the country.
State Bank of India leads the pack with 36% market share, followed by ICICI Bank (21.5%), HDFC Bank (17.8%), Axis Bank (12.8%) and Kotak Bank (4.7%). These banks have managed to increase the number of mobile transactions by being proactive in development of mobile apps and making mobile banking feature-rich.
According to Deepak Sharma, head of digital banking at Kotak Mahindra Bank, his customers are leapfrogging to mobile banking directly from branch banking without using the browser. "Around 35% of our online banking customers are coming in from their mobile phones without having used net banking," he said. As against its market share of 1.4% of deposits, the bank has over 4.5% share of mobile banking. He said that online has already become the primary channel for most of the customers in the bank.
"Overall, 60% of fixed deposits have moved online. But if you look at only retail, nearly 80% of FDs are opened online," said Sharma. He added that it was largely bu sinesses that were obtaining fixed deposits in the branch.
"In terms of number of logins, mobile banking had overtaken net banking more than six months ago. Now mobile banking is ahead of net banking in terms of transactions as well," said Sharma. He said that the fastest growing segment is online recharge, which is driving transactions.
"We are now getting more and more categories online, like bill pay and IPO subscription. We are also seeing systematic investment plans (SIPs) gaining traction. We feel that any simple product that is easy to start, liquidate and monitor will pick up online," said Sharma.
In terms of volumes, the top five banks account for more than 85% of all mobile banking transactions. While the banks are the same as the toppers in transaction value, the rankings and consequent market shares vary slightly for volumes.State Bank of India again led the pack with a 38.5% market share, followed by ICICI Bank at 17.7%, Axis (15.3%), HDFC Bank (9.9%) and Kotak Bank (4.3%).
2018: UPI

From: Dilip Asbe, UPI 2.0 can turn into a mega citizen-scale pay system, January 11, 2019: The Times of India
The writer is the MD & CEO of NPCI
India capable of replicating China’s digital economy — better & faster
India enters 2019 on the cusp of a digital revolution, mainly due to major influencers. First, we have a regulator defining the landscape by innovation-led policies, fuelling new-age business models and maintaining security and risk management standards to highest levels. Second, we have a government that is focused on moving towards a digital or less-cash economy. Third, we have banks embracing technology to accelerate digital payments, proliferation of financial inclusion and superior customer services. And last, we have fin-tech innovators who are re-imagining solutions for our day-to-day problems and providing superior consumer experience for digital payments.
The Unified Payments Interface (UPI), the most advanced payment system in the world, was launched in 2016, designed on the principles of interoperability, consumer choice and forging partnerships between banks and fintechs, leveraging each other’s strengths. The RBI’s payment system division DPSS, under the governorship of Raghuram Rajan, played a key role in bringing banks together to promote this initiative. Support of the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) and leading lenders has been a critical factor in its success. In the second half of 2018, the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) launched UPI 2.0 with the support of regulatory teams under former RBI governor Urjit Patel and deputy governor B P Kanungo to incorporate path-breaking features.
Several milestones were achieved in domestic payments last year. India’s RuPay Card crossed 500 million and Bharat BillPay on-boarded over 100 billers in its ecosystem. The Aadhaar payments services, too, surpassed 100 million unique customers every month. After demonetisation, the UPI-based ‘Bharat Interface for Money’ (BHIM) app, launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has acted as a catalyst to nudge many third-party providers to launch the UPI app. We are
now seeing the results. Sticking to the design principle of “consumer choice”, there are now over 90 BHIM UPI apps provided by banks or thirdparty providers to customers of 130 banks.
The Supreme Court’s decision to limit the use of Aadhaar database was a setback. The fintech community is relying on the government to identify a solution to use Aadhaar systems based on voluntary sharing by the customer. The NPCI had to stop the e-NACH (National Automated Clearing House) using e-sign due to the SC judgment. However, we are working to create alternatives, but it may take time.
While it was a practice to look towards the latest trends in Silicon Valley in the US, with UPI, the West has turned to partner with India for innovation. Many global giants (Google, WhatsApp, Amazon, Samsung, Truecaller, Xiaomi, etc) and Indian unicorns (Paytm, PhonePe, Hike, etc) have joined the UPI bandwagon in collaboration with banks.
Unlike China that operates mobile payments mostly under two players in a closedloop manner, the RBI has been
clear from the start to set UPI as an interoperable system. When it comes to mobile payments and financial inclusion using Aadhaar, India has an edge due to innovation.
While there are multiple ways for making payments, the market is broadly divided into three parts — a) financial inclusion that covers the JAM trinity, i.e. Jan-Dhan, Aadhaar and mobile (additionally, it covers Direct Benefit Transfers, e-KYC, etc), b) mobile and internet payments powered by UPI, IMPS (Immediate Payment Service), net/mobile banking and interoperable QR codes, and c) card-based payments.
In the coming years, we will see a significant shift to a mobile-first strategy with consumers using functionalityrich and user-friendly apps for P2P (peer-to-peer) or P2M (peer-to-merchant) payments. The electronification of all kinds of C2G (citizen-to-government) payments is a big opportunity. I’m glad to see the efforts from all government divisions pushed by the ministry of electronics and information technology (MeitY) and the department of financial services (DFS).
If the growth momentum continues, we hope that the use of UPI will take the shape of citizen-scale payments system. Volumes may come down in the short term once firms go slow on promotional offers. However, the outlook is very strong for medium to long term. We have started an awareness campaign to protect customers from social frauds. But, more needs to be done. Now that diverse payment platforms are available to customers, our goal would be to drive adoption among the masses. We have the potential and capability to do what China has done to build its digital economy, better and faster. Startups/fintechs, in collaboration with banks, should build specific-use cases to drive adoption that will be the main attraction of 2019.
Minimum balance
‘Unreasonable fee for breach of minimum balance’
December 29, 2017: The Times of India
Ashish Das is a professor of statistics with the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai.
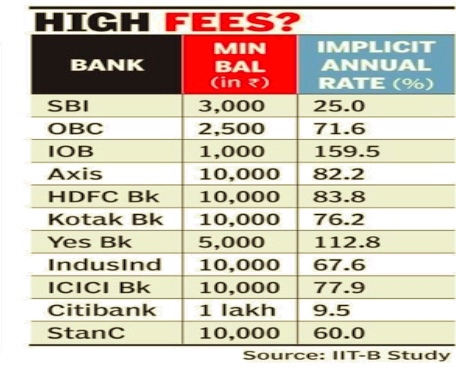
From: Mayur Shetty, December 30, 2017: The Times of India
HIGHLIGHTS
An IIT-Mumbai professor's study has revealed that banks impose unreasonable charges for failing to maintain minimum balances
The data suggests Indian Overseas Bank imposes annual charge of 159.48 per cent on shortfall in minimum balance, followed by Yes Bank, HDFC Bank and Axis Bank
Public sector as well as private banks have been imposing unreasonable charges on customers for failing to maintain minimum balances in their savings accounts, a study by an IIT-Mumbai professor has claimed.
The study, by Ashish Das, showed that some banks like Yes Bank and Indian Overseas Bank have been imposing penal charges of over 100 per cent per annum on shortfall in maintenance of minimum balance in customers accounts. The Reserve Bank guidelines mandate that charges for non maintenance of minimum balance in savings bank accounts be "reasonable and not out of line with the average cost of providing the services".
According to the study: "With many banks charging at an average high rate of 78 per cent per annum of the shortfall amount, it makes the whole regulation of reasonableness of charges as per cost quite shallow".
As per the data provided by Das, Indian Overseas Bank imposes annual charge of 159.48 per cent on shortfall in minimum balance. Yes Bank charges 112.8 per cent, followed by HDFC Bank (83.76 per cent) and Axis Bank (82.2 per cent).
The largest lender SBI charges 24.96 per cent penalty, says the study.
The minimum balance requirement in different banks range from Rs 2,500 to Rs 1 lakh. The RBI, the study said has formulated the penal charges rule with an objective of bringing in fairness from the customers' angle. "Thus, it is time to plug the regulatory and supervisory gaps in a holistic manner and formulate clear guidelines on the formation of slabs and how to measure reasonableness of charges based on costs of funds," it said.
SBI slashes fine for not keeping min balance
SBI slashes fine for not keeping min balance, March 14, 2018: The Times of India
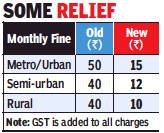
From: SBI slashes fine for not keeping min balance, March 14, 2018: The Times of India
Move Expected To Help 25 Crore Account Holders
In a move that will benefit 25 crore account holders, State Bank of India (SBI) has reduced charges for non-maintenance of average monthly balance (AMB) in savings accounts by more than 70%. The revised charges will be effective from April 1, 2018.
The charges for nonmaintenance of AMB for customers in metro and urban centres have been reduced from a maximum of Rs 50 per month plus goods and services tax (GST) to Rs 15 plus GST. For semi-urban and rural centres, the charges have been reduced from Rs 40 each month plus GST to Rs 12 and Rs 10 plus GST, respectively.
“We have reduced these charges taking into account the feedbacks and sentiments of our customers. SBI also offers its customers options to shift from regular savings bank account to basic savings account on which no charges are levied,” the bank said.
SBI had faced a lot of flak after it came to light that it earned more from minimum balance penalties than its profits (which were contained because of bad loan provisions). Also, many students and underprivileged customers lost their balances because of wrongful classification of their accounts as regular savings accounts.
SBI has 41 crore savings bank accounts, out of which 16 crore accounts are either under Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana or basic savings bank accounts. Both these do not have minimum balance requirements.
Additionally, pensioner/minor/social security benefit holder accounts were already exempted. Also, students up to the age of 21 years are exempted. So the latest revision in AMB will benefit 25 crore customers.
Meanwhile, a news agency report said that SBI had closed more than 41 lakh savings accounts between April and January in the current fiscal year for not maintaining AMB. Last April, the nation’s largest lender had re-introduced the penal charges on non-maintenance of AMB after a gap of five years. Later in October, it had revised down the charges to some extent, followed by the latest decision to reduce these further on Tuesday.
“Due to provisions of penalty on non-maintenance of minimum balance, the bank has closed 41 lakh savings bank accounts between April 1, 2017 and January 31, 2018,” the bank replied to an RTI query filed by Chandra Shekhar Gaud from Neemuch in Madhya Pradesh.
Nationalised banks
2007-18, infusion of govt. funds; 2010-18: losses
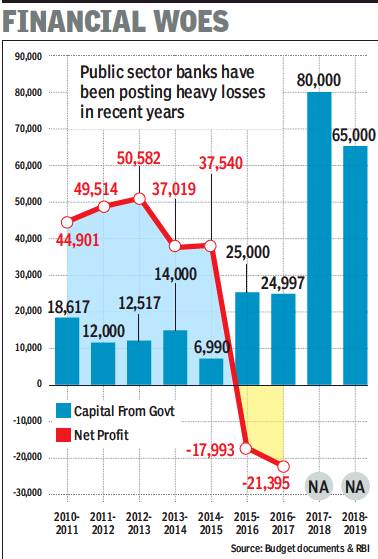
infusion of govt. funds;
Losses poted by public sector banks.
From: Sidhartha, Sidhartha, Centre has pumped ₹2.6 lakh cr into govt-run banks over 11 yrs, February 19, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Nationalised banks, 2010-18:
infusion of govt. funds;
Losses poted by public sector banks.
Taxpayer Foots Bill As Bad Debt, Frauds Hit PSBs
Every year, finance ministers face twin challenges — meeting spending requirements, especially to improve social sector schemes, while keeping an eye on the deficit given that tax collections are insufficient. In recent years, they have had to tackle another pressure — the need to keep pumping money into public sector banks, which have been grappling with a record pile of bad debt and corporate fraud.
Over 11years, three finance ministers — Pranab Mukhjeree, P Chidambaram and Arun Jaitley — pumped close to Rs 2.6 lakh crore into government-run entities with their requirement for funds rising steadily as more skeletons keep tumbling out. The amount is more than the highest estimate of notional loss from the 2G scam that the CAG had put out. It is more than twice the Centre’s allocation for rural development for the current year and three-anda half-times the outlay for the roads ministry.
Keeping aside the Rs 1.45 lakh crore earmarked for recapitalisation by the Centre during the current and the next financial year, the banks received close to Rs 1.15 lakh crore equity from 2010-11 to 2016-17. During this period, their profits added up to Rs 1.8 lakh crore, with SBI and other nationalised banks reporting combined losses during the last two financial years as they set aside more funds to deal with potential losses from bad debt, or non-performing assets.
This year is expected to be no different with SBI, the country’s largest lender, reporting its first quarterly loss in 18 years, and others, such as Bank of Baroda, too, faring poorly. “It does appear that the worst may not yet be over for PSBs with regard to NPAs and March 2018 will be the next touch point that will provide further guidance,” ratings agency Care concluded recently.
Losses hit return on equity of public sector banks
Not surprisingly, losses have impacted the return on equity or the capital of public sector players. Against an ROE of a shade under 12% for private lenders, SBI group offered -0.7%, and the score for other nationalised banks was even worse at -2.8% in 2016-17, RBI data showed.
While the state run-lenders accounted for around 70% of the banking business, their share of funds set aside for NPAs was estimated at over 80% in 2016-17 — an improvement from 87% in the previous year.
The public sector players fare poorly on other counts too. For instance, in 2016-17, RBI estimated wage bill added up to 8.7% of the income of private banks, much lower than the 12.7% for the SBI group and 10.7% for nationalised banks.
As a result, chief economic adviser Arvind Subramanian’s call for private participation in these banks will appeal to many taxpayers as well as policymakers, who believe that bankers have been careless in lending. But a part of the problem is self-afflicted as, first the Congress-led UPA and now the BJP regime have opted to maintain majority state control in these banks, trashing the Vajpayee government’s attempt to lower Centre’s holding to 33%.
On their part, public sector bankers believe that they are hobbled by unnecessary bureaucratic restrictions, ranging from limited flexibility due to oversight by agencies such as the CAG and the Central Vigilance Commission that private players don’t have to deal with. Similarly, state-run players have to disburse credit under various government schemes such as Mudra or restructure loans for SMEs or even large corporates, as was the case after the 2008 financial crisis.
2017: 6 stressed banks get ₹ 7,500 cr capital
Sidhartha, 6 stressed banks get ₹7.5k cr capital, December 30, 2017: The Times of India
The government has provided over Rs 7,500-crore fresh equity to six stressed state-run banks to help them meet the prescribed regulatory capital requirement and state its commitment to keep banks well-funded.
Bank of India, IDBI Bank, Uco Bank, Bank of Maharashtra, Dena Bank and Central Bank of India have received equity through preferential issue of shares with two of them informing stock exchanges about the decision.
When contacted, financial services secretary Rajiv Kumar confirmed the development. “Banks will not suffer due to shortage of regulatory capital. But we will monitor their functioning to ensure that they undertake clean, responsible and prudent business to enhance stakeholder value,” he told TOI.
The details of the monitoring plan are expected to be announced shortly. While announcing a mega Rs 2.11-lakh-crore recapitalisation plan, finance minister Arun Jaitley had said strict conditions will be put in place to avoid a repeat of unbridled lending that has resulted in record non-performing assets (NPAs) for Indian banks, especially those in the public sector. At the same time, it is working on an incentivising the better performers.
The six banks are on the list of players that are part of prompt corrective action initiated against state-run lenders whose performance has slipped due to a pile-up of bad debt.
While the government decides the mode for recapitalisation of all state-run banks, it advanced the release of funds to these six to help them meet their equity requirements and enable them to resume normal business.
Uco Bank informed the stock exchanges that on Thursday, the finance ministry communicated its sanction for release of Rs 1,375 crore towards preferential allotment of equity shares. Similarly, IDBI Bank has received Rs 2,729 crore. In the Union Budget, the government had budgeted for Rs 10,000 crore for recapitalisation of public sector banks but, given the increase in NPAs, the allocation is set to be enhanced in the next Budget.
2017-18: Losses and NPAs
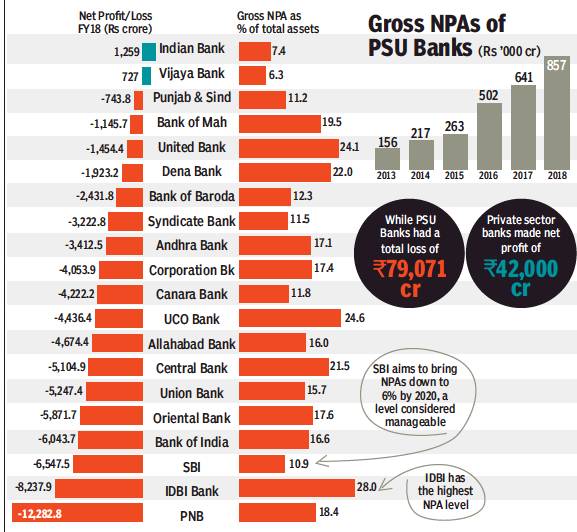
i) Losses in 2017-18; ii) NPAs in 2017-18;
Gross NPAs, 2013-18
From: May 30, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Public-sector banks
i) Losses in 2017-18; ii) NPAs in 2017-18;
Gross NPAs, 2013-18
Non-performing assets (NPAs)
Sub-sectors with the most, least stressed advances: 2016-18

From: January 2, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Sub-sectors with the most, least stressed advances: 2016-18
2013- 2018: Gross NPAs of Indian banks

From: Sidhartha, June 5, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
NPAs doubled after RBI made classification of NPA norms stricter- The graph shows Gross NPA- 2013-18
2014-18: Advances, NPAs; 2018: recoveries
PSBs’ recovery against NPAs doubled in 2018, December 27, 2018: The Times of India

From: PSBs’ recovery against NPAs doubled in 2018, December 27, 2018: The Times of India
Banks Recover ₹60,713Cr In First Half Of 2018-19
Public sector banks reported recovery of Rs 60,713 crore against non-performing assets (NPAs) in the first half of the current year, which is double of the amount recovered in the corresponding period last year and more significant returns on highvalue accounts are expected, the government has said.
In response to a parliamentary question, the finance ministry said following amendments to the Banking Regulation Act, the Reserve Bank of India directed banks to initiate insolvency proceedings before the National Company Law Tribunal in 41 cases, 12 of which had cumulative outstanding of Rs 1,97,769 crore as on March 31, 2017. The remaining 29 had an outstanding of Rs 1,35,846 crore as on June 30, 2017.
“As per RBI data on global operations (with provisional data for September 2018), during the last three and a half financial years, NPAs of scheduled commercial banks reduced by Rs 2,83,770 crore due to recoveries,” the government told BJP MPs Kirti Azad and Bharatiben Shiyal.
The government said measures such an asset quality review (AQR) initiated in 2015 for clean and fully provisioned balance sheets revealed a high incidence of NPAs that were piling up since 2008 — a period when UPA was in office. “As per RBI inputs, primary reasons for spurt in stressed assets is aggressive lending practices, wilful default, loan frauds, corruption in some cases and an economic slowdown,” it added.
The AQR enforced by the Modi government led to stressed accounts being reclassified as NPAs and expected losses were provided for. The transparent recognition of stressed assets led to gross NPAs of scheduled commercial banks increasing from Rs 2,51,054 crore as on March 31, 2014 to Rs 3,09,399 crore on March 31, 2015; Rs 5,66,247 crore on March 31, 2016; Rs 7,28,740 crore on March 31, 2017 and Rs 9,62,621 crore on March 31, 2018. This provisionally declined to Rs 9,46,062 on September 30, 2018.
The government said rise in NPAs was in good part due to banks being made to recognise stressed assets as NPAs and the withdrawal of restructuring schemes in 2017-18. This led to an honest appraisal of the state of bank finances and the role played by indiscreet and risky lending in the past.
With the adoption of a ‘creditor-in-saddle’ approach under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, and interim resolution professionals taking over management of a corporate debtor at the outset, the incentive to abuse the legal system has been taken away, the finance ministry said.
The Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002, has been amended to make it more effective with a threemonth jail term for a borrower who does not provide asset details and for the lender to get possession of mortgaged property in 30 days.
Public sector banks have created stressed asset verticals for stringent recovery, set our protocols for pre and post sanction and close monitoring of large value accounts.
2015: NPAs in India, major economies
Only 4 major nations have higher bad loans than India, December 28, 2017: The Times of India

From: Only 4 major nations have higher bad loans than India, December 28, 2017: The Times of India
Desi Banks Join League Of PIIGS Where Spain Has Lower Ratio
The 9.85% ratio of bad loans in banks has put India in the group of those nations that have very high nonperforming assets (NPAs). The only major countries with similar ratios are the troubled EU nations: Portugal, Italy, Ireland, Greece and Spain — commonly referred to as PIIGS.
According to a research report by ratings agency CARE, India’s NPA ratio — which excludes restructured assets that are around 2% higher than NPA — is one of the highest in the group of ‘high-NPA’ nations. The only countries with a higher NPA than India are Portugal, Italy, Ireland and Greece. Even among the troubled PIIGS, Spain has a lesser ratio of bad loans compared to India.
CARE chief economist Madan Sabnavis said in the report, “The seriousness of the NPA problem can be gauged by the absolute level of impaired assets in the system. Ever since the RBI had spoken of asset quality recognition (AQR) in 2015, there was an increase in the pace of recognising these assets. For the European nations, the bad loans are more of a legacy problem whereas for us it is something that got recognised only two years back.”
Indian banks started recognising stressed loans as NPAs only after former RBI governor Raghuram Rajan introduced asset quality recognition norms forcing banks to classify stressed borrowers as defaulters. According to Sabnavis, the NPAs have created a twin problem. First, they have rendered banks short of capital and, second, they have reduced banks’ capacity to lend for large long-term projects, which is why most public sector banks are now focusing on retail.
The report classifies major economies into four blocks — very low NPA, low NPAs, medium level NPA and high NPAs. The countries with very low level of bad loans are Australia, UK, Hong Kong, Canada and South Korea. Within the emerging market economies, China, Argentina and Chile had low ratios of 1-2%. According to economists, while the bad loan problem in India is serious, the economy has the advantage of being a higher growth economy, which puts it in a better position related to the other high-NPA countries in Europe.
2016: NPAs in India, major economies

From April 26, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
In 2016, in just one year, India made rapid progress in the ranks of major nations with bad loans, rising rapidly from no.5 to no.3.
2016: 16 banks breach the threshold
NET NPAs: HOW THEY STACK UP, April 15, 2017: The Times of India

Sixteen banks have net non-performing asset (NPA) ratios that breach the thresholds which place them on RBI's watch list under the prompt corrective action (PCA) plan. If they do not improve their net NPA ratios in the March 2017 results, the central bank will place restrictions on activities. One bank has breached the thresholds set for return on assets. However, on tier-1 capital, most banks are within the regulatory requirement.
NPAs in 2016, 2017
PNB failed on all fronts to check NiMo fraud, says RBI, June 13, 2018: The Times of India
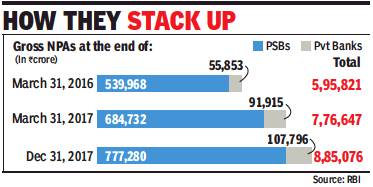
From: PNB failed on all fronts to check NiMo fraud, says RBI, June 13, 2018: The Times of India
Guv Seeks Amendments For More Teeth To Monitor PSBs
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) put the blame of the $2-billion Nirav Modi-Mehul Choksi fraud on Punjab National Bank (PNB), including its board, and accused the state-run lender of furnishing “factually incorrect” compliance reports. The RBI also defended its supervision on the grounds that the onus was on lenders and it was not possible for the central bank to audit over one lakh bank branches in the country.
“As regards the LoUs (letters of undertaking) issued for years without collateral by the PNB branch (in Mumbai) which went unnoticed, it is pertinent to recognise that primary responsibility of understanding the risks undertaken by a bank and ensuring that the risks are appropriately managed through necessary risk mitigants, controls, etc, clearly rests with the board directors of the bank concerned,” the regulator told a Parliamentary Standing Committee when RBI governor Urjit Patel appeared.
At the same time, it demanded fresh powers, arguing that the laws needed to be amended to give the regulator more teeth in supervising state-run banks.
The RBI contended that SBI and other nationalised banks were not “banking companies” defined by the Banking Regulation Act and they were governed by other laws. It then listed nine powers that it lacked, including the mandate to appoint and remove public sector bank chiefs, license them, convene a meeting of their boards or supersede the board. Further, the RBI said it did not have powers to order voluntary amalgamation or winding up or seek the Centre’s help for suspension of a state-run bank’s business and preparation of a restructuring plan.
The statement is expected to set the stage for a fresh battle with the finance ministry, which had questioned similar claims made by Patel earlier. Finance ministry officials have maintained that it only had powers to appoint and remove bank chiefs, which was also done in consultation with the Banks Board Bureau and the RBI.
In its submission to the Parliamentary panel, the RBI said it has suggested amendments to the law to empower the central bank to exercise “effective control” over public sector banks, as it did with the private players, on “an ownership-neutral basis”.
At the same time, the regulator sought to protect its turf and suggested that the proposal for an audit by CAG was “debatable” as there were three layers of audit — concurrent, internal and statutory. “It is debatable whether adding a fourth layer, of audit by CAG, will have much incremental impact.”
On the issue of fraud at PNB, the RBI’s detailed response said a bank’s risks were expected to be managed under three lines of defence. The first, it said, were the officials performing the line functions to assume, own and manage risks.
In the second line are risk monitors, specialising in overseeing decisions of the first line of defence. The final line are the audit functions. “In case of PNB, there seems to have been a failure of all three lines of defence, resulting in perpetration of such as large-value fraud,” it said.
2016, 2017: banks understate their NPAs
Bad loans divergence: Yes bank tops among peers, November 16, 2018: The Times of India

Other major banks and their divergence (%)
From: Bad loans divergence: Yes bank tops among peers, November 16, 2018: The Times of India
In 2017, the RBI for the first time asked banks to disclose in their balance sheet any divergence between bad loans identified by the central bank during its inspections and the non-performing assets (NPAs) recognised by the bank earlier. Sharp divergences indicate that banks have been hiding some bad loans.
Time-bound NPA resolution tough under bankruptcy code

The RBI's big bang announcement directing banks to proceed against 12 borrowers under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) has raised expectations of an early resolution. But experts say the new law is unlikely to be a magic wand to immediately cleanse balance sheets of banks, adding that legal tangles and lack of infrastructure for executing bankruptcies may emerge as impediments to early resolution of bad debts.
Borrowers have already been able to stymie lenders in the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT). Also, in one of the early cases filed by ICICI Bank, the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) fined the lender Rs 50,000 for inflating the claim against the defaulter. In another case, the appellate body overturned a ruling by the NCLT and declared the appointment of an interim resolution professional as illegal. In light of this experience, industry watchers say that prospects for either a resolution in 180 days (extendable by 90 days) or recovery through liquidation looks challenging.
“One needs to evaluate if the necessary infrastructure for executing such a mandate is available and prepared to manage these 12 cases. The entire ecosystem, including insolvency professionals, tribunals, banking and investors, is still building capacity and capabilities,“ said Ashish Chhawchharia, partner at Grant Thornton Advisory . Given the strict timelines under the code, it will take considerable efforts from all stakeholders to reach desirable solutions, he added.
Insolvency professionals step in after bankruptcy is initiated and manage the process until resolution. According to bankers, there are not enough insolvency professionals in the country to keep up with defaults. The RBI has not made the list of 12 borrowers public, but the names are already doing the rounds in banking circles and news reports (see graphic).
According to Karthik Sri nivasan, group head (financial sector ratings), ICRA, a key imponderable is the extent to which these decisions could be challenged in the courts, thus delaying the process. ICICI Bank had registered the maiden case with the IBC in midJanuary against Innoventive Industries, which has approached both the Bombay high court and NCALT on grounds that the principles of natural justice were violated since the company was not given adequate notice. “The outcome of the first case filed under IBC can be expected later this month or early next month, which will also provide clarity on kind of resolution agreements reached between different counter-parties,“ said Srinivasan.
The other concern is the relief that needs to be provided to businesses to make them viable enough to be sold. “Even the large stressed companies need a 30-80% reduction in interest burden to fully cover interest at current profitability . There fore, stress resolution will need additional provisioning and capital. ICICI Bank is the only corporate lender that appears comfortable on capital,“ said Ashish Gupta and Kush Shah of Credit Suisse in a research report.
While banks now have the power to sell off assets, offloading several steel plants at the same time might lead to a crash in valuations. “If there is alarge number of assets put up immediately for liquidation, mostly in the next one year, only a few may get closer to a realisable value while the rest may have to be liquidated at very high discounts,“ said M B Mahesh of Kotak Institutional Equities Research in a report. The option available to banks would be to temporarily take over the company by converting debt to equity .
May 2017: “Written-off” assets by banks
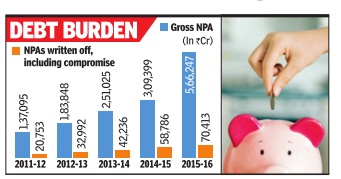
Just A Technical Exercise To Clean Up Accounts, Says RBI
All scheduled commercial banks (SCBs) wrote off Rs 2,25,180 crore cumulatively in the five-year period ended March 2016, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) said in an RTI reply filed by TOI. SCBs represent all public sector banks, private sector banks, foreign banks, regional rural banks and some co-operative banks.These represent over 95% of the formal credit given out by all financial institutions in the country. “This could be the highest ever write-off in a fiveyear period in absolute terms as are the total stressed assets in the banking system,“ said Abhishek Bhattacharya, director and co-head for financial institution India Ratings.
Banks and the RBI have often stated that these write-offs are just technical in nature and an exercise to clean up the balance sheets. They have further argued that banks continue to retain the right to recovery from these written-off accounts. “Writing off of non-performing assets (NPAs) is a regular exercise conducted by banks to clean up their balance sheets. A substantial portion of this write off is, however, technical in nature. It is primarily aimed at cleansing the balance sheet and achieving taxation efficiency . In `technically written off' accounts, loans are written off from the books at the head office, without foregoing the right to recovery . Further, write-offs are `generally' carried out against accumulated provisions made for such loans. Once recovered, the provisions made for those loans flow back into the profit and loss account of banks,“ the RBI said in a clarification to a media report, based on an RTI reply in February 2016.
Be that as it may , the recovery from written-off accounts constitute only a tiny fraction of the overall written-off accounts, available data shows. In the financial year 2014-15, banks could recover only 11.85% (Rs 6,968 crore) of the written-off accounts in that year and 13.8% (Rs 9,717 crore) of the written-off accounts in FY 2015-16. The data for previous three years is not available with the RBI, it said.“The information on recovery from written-off accounts from FY 2011-12 to 2013-14 is not available with us,“ the RBI said in its RTI reply.
Though the amount from recovered loans in FY15 and FY16 might not pertain to that financial year alone, the numbers show the actual recovery to be only a tiny fraction of the total amount written-off and also to be a long protracted process.
In each of these five years, loans written off showed an increasing trend -at an average addition of over Rs 12,000 crore each ye ar. The worst year was FY15, when banks cumulatively wrote off Rs 16,550 crore more than the previous year. Banks reduce written-off loan accounts from their overall nonperforming assets. Adding the same back, the actual gross NPAs at banks could look a lot worse every subsequent year than it already does.
Written-off loans accounted for 11-16% of overall bad loans of the bank in each of those years (see table). Since 2011, banks started lending heavily to large corporates and, according to analysts, the problem suddenly became a lot bigger as “corporate leveraged built up“. The traditional tools of recovery like debt recovery tribunals, and Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (Sarfaesi) Act, 2002, have become blunt in the face of such huge bad loans from large corporate accounts.
“Newer mechanisms are needed to deal with these big loans and they have to be dealt with on a going-concern basis. The usual recovery mechanism will not work,“ said Bhattacharya. He added, “Recovery will take time and won't happen in hurry .“
RBI to expand oversight committee
RBI steamrolls resolution of bad debt, expands oversight panel, May 23, 2017: The Times of India
Asks Bank Boards To Empower Execs To Tackle Bad Loans
The RBI has said that minority lenders who stymie a decision by majority lenders on bad debt resolution will face enforcement action. The central bank has also directed boards of banks to empower executives to take decisions to address bad loans.
The RBI has said that it will expand its current two-member oversight committee with a large number of members to endorse proposals for resolution of bad debt from banks. The large number of members brought into the oversight committee will man various benches to clear proposals from banks. The expansion of the oversight committee is aimed at providing protection to executive decisions by banks to take haircuts on loans to bring them back on track.
Currently , the two-member oversight committee has a very limited role. “While the current members will continue in the reconstituted oversight committee, names of a few more will be announced soon,“ the RBI said.The RBI clarified that a corrective action plan could include flexible restructuring as well as a strategic debt recast -a scheme where banks acquire stake and find new owners for defaulting business. It would also include the more recent Scheme for Sustainable Structuring of Stressed Assets (S4A). Under the S4A scheme, banks identify how much of a stressed debt is sustainable and provide relief by converting debt to equity.
The RBI has said that rating agencies would have a major role to play in the new scheme of things. However, to prevent rating-shopping or any conflict of interest, the RBI has said that it is exploring the feasibility of rating assignments being determined by the RBI itself and pay for from a fund to be created out of contribution from the banks and the central bank.
In an attempt to ensure that multiple lenders in a consortium are able to move ahead on resolving bad debt, the RBI said that consent required for approval of a proposal was changed to 60% of lenders by value instead of 75% earlier. In terms of numbers of lenders, at least 50% will have to continue to agree. Minority lenders who do not agree must either exit by bringing in a new lender or adhere to the decision of the Joint Lenders Forum (JLF). All lenders have to implement the decision of JLF without any additional conditionality .
2018: Recapitalisation plan
₹88,000cr bank recap, reforms plan unveiled, January 25, 2018: The Times of India

From: ₹88,000cr bank recap, reforms plan unveiled, January 25, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Capital allocation for state-run banks, 2017-18
The government unveiled details of its bank recapitalisation plan with a capital infusion of over Rs 88,000 crore in the current financial year for 20 state-run banks and linked it to a sixpoint reform agenda to restore their health and step up lending to aid growth.
Last year, the government had announced a package to breathe life into ailing PSBs through a Rs 2.11 lakh crore infusion to provide them capital for lending and reviving investment, crucial for job creation in Asia’s third-largest economy.
We inherited major problem: FM on NPAs
According to government’s plan, over the next two years it will use recapitalisation bonds worth Rs 1.35 lakh crore. It will also provide support of Rs 18,000 crore and the remaining Rs 58,000 crore will be raised by banks. “We inherited a very major problem and therefore, we have been involvedin finding a solution to that problem”, finance minister Arun Jaitley told a news conference.
“Our role really is not only to find a solution but also to create an institutional mechanism to make sure that what happened in the past is not repeated. Now the entire objective of this exercise is that the government has the prime responsibility of keeping the public sector banks in good health,” he said.
The capital infusion plans for 2017-18 include Rs 80,000 crore through recapitalisation bonds and Rs 8,139 crore as budgetary support. In addition, the banks will raise Rs 10,312 crore through share sales. The government expects that the measures undertaken will help additional credit offtake capacity of state-run banks by more than Rs 5 lakh crore.
“Each public sector bank (PSB) is an article of faith. All PSBs will be adequately capitalised and enabled to serve people and support inclusive growth,” said Rajiv Kumar, secretary, department of financial services, asserting that no state-run bank willfail.
The reform agenda is aimed at EASE (enhanced access and service excellence) and focusses on six themes of customer responsiveness, responsible banking, credit offtake, UdyamiMitra for small and medium enterprises, deepening financial inclusion and digitalisation and developing personnel. The government will also launch a survey by an independent agency to monitor the rollout of reform measures and measure public perception about improvements in access and service quality. Results of the survey wouldbe publishedevery year.
“Capital infusion by the government is contingent on performance of PSBs on the reform. Whole time directors of PSBs would be assigned theme wise reforms for implementation. Their performance in this regard would be evaluated by the bank board,” a finance ministry statement said.
As part of the reform agenda, banks will need to tie up with agencies for specialised monitoring for clean and effective post sanction follow up in loans above Rs 250 crore. For large consortium loans the minimum exposure should be 10%. Banks will also needtoset up a stressed asset management vertical and all corporate lending will have to follow rigorous due diligence. They will also needto appoint a chief risk officer to check “aggressive and imprudent” lending.
2018, Sept
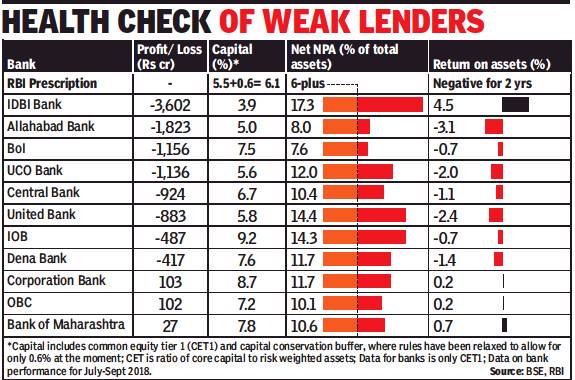
From: November 26, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
The NPAs of the weaker Indian banks, as in 2018 September
Ombudsman
2017: ‘misselling’ made punishable
For 1st time, RBI makes banks accountable for misselling, June 24, 2017: The Times of India
Ombudsman's Ambit To Cover Mobile Banking Complaints
Banks for the first time have been made accountable for misselling third-party products like insurance policies or mutual fund schemes. Customers can also file complaints against banks for problems with mobile and digital banking services.
The RBI said that it has widened the scope of its Banking Ombudsman Scheme 2006 to include deficiencies arising out of sale of third-party investment products by lenders. Under the amended scheme, a customer would also be able to lodge a complaint against banks for non-adherence to the RBI instructions with regard to mobile or electronic banking services.
Following the amendment, the pecuniary jurisdiction of the ombudsman to pass an award has been doub led from Rs 10 lakh to Rs 20 lakh. The ombudsman has been empowered to award compensation not exceeding Rs 1 lakh for loss of time, expenses incurred and also harassment and mental anguish suffered by the complainant. There is also an option for customers to go in for appeal in respects to closed complaints which was not available earlier.
Until now, if the buyer of an insurance policy or mutual fund was missold she had to seek redressal from the insu rance company or the mutual fund. This was a departure from global practices. For instance, last year in UK four of the biggest banks, Barclays, HSBC, Lloyds and RBS, faced large fines for misspelling payment protection insurance.
There are 20 ombudsmen in India, each with a territorial jurisdiction. Aggrieved customers can lodge their complaints with the ombudsman either through an email or a post. However, before filing a complaint with the ombudsman the customer has to approach the grievance redressal department of the bank and wait 30 days for a response. Unlike the courts, no fees are required to be paid.However, the ombudsman can refuse to hear a complaint if it is time-barred or already heard in some other court. In FY16, the office of banking ombudsman received 1.03 lakh complaints.
Performance
Best and worst performing banks
2020 Feb
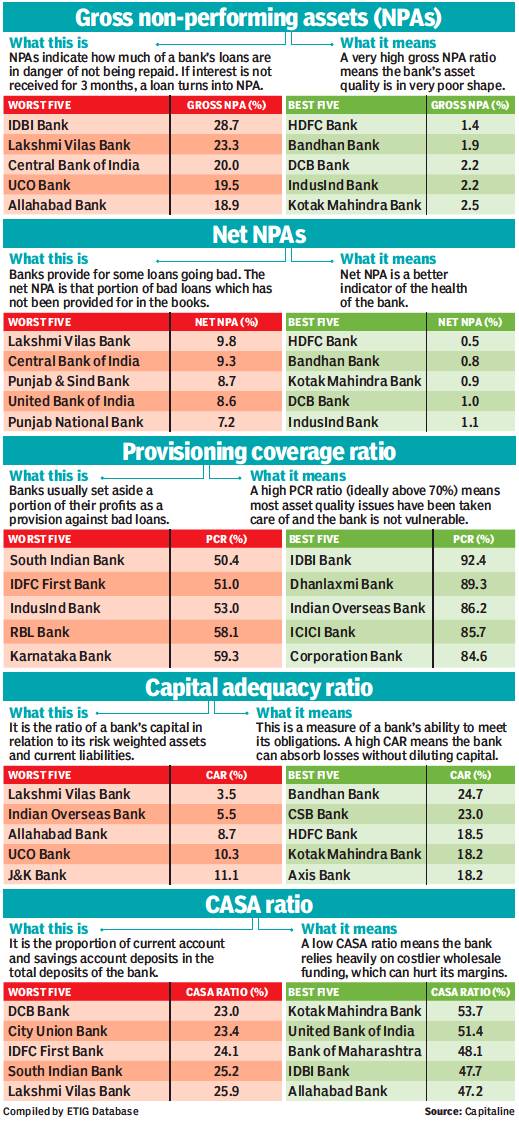
From: Sanket Dhanorkar, March 30, 2020: The Times of India
See graphic:
India’s best 5 and worst 5 performing banks as judged by NPAs, net interest margin’, capital adequacy ratio, Current Account Savings Account (CASA) ratio, credit-deposit ration etc., presumably as in 2020 Feb
Savings bank deposit accounts, basic (BSBDAs)
Banks sometimes convert them into regular a/c’s

Percentage of basic savings bank deposit accounts (BSBDAs)
From: Mayur Shetty, Just 4 debits can freeze Jan Dhan a/cs, banks turning them into regular a/cs, May 28, 2018: The Times of India
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has gone on a promotion overdrive for the ‘zero balance, zero charges’ account that banks provide.
The RBI has been sending bulk SMSs about this account during IPL matches. However, crores of basic savings bank deposit account holders — including those having Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana accounts — risk having these accounts abruptly frozen by banks.
The accounts allow only four free debits a month and, since banks are not allowed to impose any kind of charge on customers, many are freezing the accounts once four transactions are complete. A few like HDFC and Citi are converting these accounts into regular ones if the number of transactions exceed four, which means the account holder pays a regular penalty if minimum balance is not maintained.
Unlimited e-transactions should be allowed under basic a/cs: Report
The basic savings bank deposit account (BSBDA) was aimed at financial inclusion and, therefore, kept free of all charges. To make it viable for banks, the RBI kept the maximum withdrawals from the account at four a month, going by average withdrawals.
However, banks have extended the term free debit transactions to include not just ATM withdrawals but also debit by way of real-time gross settlement (RTGS), NEFT, clearing, branch withdrawal, transfer, internet debit, and EMIs.
For the purpose of withdrawal, the account stands frozen once four transactions are completed in a month. This means that if a customer withdraws money twice and uses the debit card twice in 20 days, he will have to wait until the next month to access his money again.
The issues with the BSBDA have been highlighted in an IITBombay technical report — ‘Can BSBDA depositors have long innings? Be aware and remain vigilant’ — authored by Ashish Das, who has for years been researching and surveying impact of steps taken towards financial inclusion.
Of the banks covered in the report, State Bank of India (SBI) and Axis Bank prevent customers from undertaking any debit transaction beyond four in a month, virtually freezing accounts thereafter for the customer. HDFC Bank and Citi say that they will convert the basic account into a regular account if a customer withdraws for a fifth time. ICICI Bank in the past used to charge for the fifth transaction, but has refunded the amount after being told that they cannot apply charges. It currently allows free transactions beyond four. Other banks do not divulge what measures they will be taking after the four free transactions are exhausted.
In the report, Das pointed out that after four debits in a month from a BSBDA, the customer would no longer be able to make online purchases, transfer money through BHIM or use RuPay debit card at merchant locations for his day-to-day purchases. “Inhibiting the financially included folks to transact digitally through their bank accounts is a blow to our country’s digital payments drive. The very nature of the RBI regulation has forced banks to limit the BSBDA usage,” said Das.
The report has suggested that banks should give unlimited electronic transactions under BSBDA and the restriction should apply only to cash withdrawals. Incidentally, banks earn a fee when their debit cards are used for shopping.
Small finance banks
2018

From: March 11, 2019: The Times of India
See graphic:
Small finance banks in India, 2018.
Technology
Banking robot
Rachel Chitra | TNN | Nov 11, 2016,Lakshmi, country’s first banking robot, makes debut in Chennai
CHENNAI: Endearing, interactive and superfast with data, India's first banking robot Lakshmi made her debut on Thursday in the city. Launched by the Kumbakonam-based City Union Bank, the artificial intelligence powered robot will be the first on-site bank helper.
Top private lender HDFC Bank, which is also experimenting with robots to answer customer queries, is testing its humanoid at its innovation lab. Lakshmi, which took more than six months to develop, can answer intelligently on more than 125 subjects.
Want to know your account balance? Interest rates on home loans? Deferred payments or possible charges to be incurred on fixed deposit closure? Lakshmi can answer it all. "Apart from answering generic questions, we have also programmed it to connect to the core banking solution. If a customer wants to know his bank account details or transaction history, the robot can flash the answer on its display," said N Kamakodi, MD and CEO, City Union Bank.
Sensitive financial information like account details are displayed discreetly on the robot's screen and not voiced. "Lakshmi only talks out loud on generic subjects. If you visited our branch with your girlfriend, she won't embarrass you by showing your low account balance," joked its CEO.
Lakshmi, who currently speaks in English, gestures, turns around and engages in a very life-like manner in conversations. Unlike most robots her speech is not formal, but more relaxed and casual. "Since its artificial intelligence, the robot is constantly learning from customers - the more interactions it has with customers the better it gets," said a bank executive.
And what if a question stumps Lakshmi? "She then asks you to get in touch with the branch manager. But at the back-end, we will be collecting all the questions she was unable to answer and equip her with better data sets, so she can service customers. Today she can give real time updates of foreign exchange movement, current interest rates at banks for different asset classes like personal, educational, two-wheeler and home loans, possible charges on withdrawals or deposits. But going forward, she might be able to more than that," said its assembler Vijay V Shah of Coimbatore-based Vishnu Engineering.
Cash deposit machines (CDMs)
Mayur Shetty, Cash deposit machines not to work for 6 weeks, Nov 21 2016 : The Times of India
Unlike ATMs, which can be recalibrated, CDMs, which identify and separate currency , are “taught“ to detect counterfeit notes by presenting different kinds of fakes. This may take several weeks, or even months.
To promote self-service and make available all banking services around the clock, banks have been installing CDMs and pass book printers in e-banking kiosks, in addition to ATMs. CDMs are distinct from ATMs that also accept cash deposits in envelopes, although they are operated in the same manner using a debit card. The advantage of a CDM is that all successful transactions are immediately credited to the customer's account.
According to Navroze Dastur, India MD & CEO of ATM maker NCR, ATM manufacturers require six weeks to tune the CDMs to accept new high-denomination notes and to identify fakes.
CDMs can count the notes, verify denomination, quality and authenticity and do everything that a bank teller can. “Before the CDMs starts accepting new currency , the developers need to come to India and programme the machines to identify the new notes. The bigger challenge is getting the machine to learn wat is a fake note,“ said Sunil Udupa, MD, Securens Systems, which offers ATM services to banks. Helping the machine identify fake currency notes requires samples of fake notes which are currently not there for the new notes, said Udupa.
There are close to 30,000 cash deposit machines in the country and they have made life easier for banks in accepting bulk deposits. These machines have been imported from international manufacturers -Wincor Nixdorf, NCR, Diebold and OKI. Their engineers will need to come and reset the machines. Until they are reconfigured, the machines can be used only for the Rs 50 and Rs 100 notes, which continue to be legal tender.
In the one week after the demonestisation of Re500 and Re1000 notes (on Nov 9 2016), SBI saw 45 lakh transactions at its 6,000 CDMs between November 10 and November 16, helping Rs 7,384 crore to be deposited. The total value of transactions in CDMs has been more than the Rs 3,565 crore the bank has seen in its ATM network.
Unified Payments Interface
2019, Mar: Kotak first to charge for UPI use
Digbijay Mishra, April 1, 2019: The Times of India

From: Digbijay Mishra, April 1, 2019: The Times of India
Unified Payments Interface (UPI), which has been leading the digital payments push since demonetisation, will no longer be free to use for peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions as Kotak Mahindra Bank has become the first lender to charge beyond a monthly limit of 30 transactions from May.
Several other banks have held discussions with National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), the umbrella payments body that manages UPI, to bring fees and cap the number of free monthly P2P transactions from one bank account, said sources.
Kotak Mahindra, in an email notification to some of its account holders, said it will charge Rs 2.50 for every transaction worth Rs 1,000 or less while the same would be Rs 5 for transactions of more than Rs 1,000. This will be applicable across all platforms, including Paytm, PhonePe and Google Pay, three players who now control 90% of the transactions.
A Kotak Mahindra Bank spokesperson defended the move, saying that 95% of its customers do an average of 5-10 UPI transactions per month. A PhonePe spokesperson said the company will not charge users for P2P transactions while Paytm and Google Pay did not immediately offer a comment.
While bigger consumerfocused banks like SBI or HDFC Bank are yet to levy such fees, executives of new-age payments firms said charging P2P transactions goes against the idea of UPI and would have a negative impact on the digital payments ecosystem, driving consumers to opt for cash payments.
Withdrawals
Diwali withdrawals, 2008-18
Mayur Shetty, Diwali drained ₹50k cr cash from banks, November 16, 2018: The Times of India
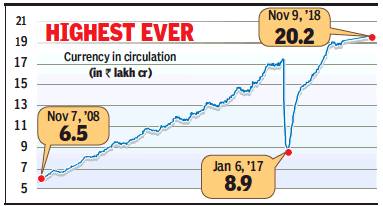
From: Mayur Shetty, Diwali drained ₹50k cr cash from banks, November 16, 2018: The Times of India
Close to Rs 50,000 crore moved out of banks as Indian accountholders withdrew wads of cash ahead of Diwali. According to data released by the RBI, currency in circulation shot up to Rs 20.2 lakh crore as on November 9 — an increase of Rs 49,418 crore in the Diwali week, the highest growth ever outside the demonetisation period.
The biggest weekly increase in currency in circulation was in the week ending January 13, 2017, which saw an additional Rs 52,786 crore flow out of banks as currency presses worked overtime to replace demonetised notes.
After demonetisation, the year-on-year growth in currency in circulation had been negative for 53 weeks. The currency in circulation recovered to pre-demonetisation level of nearly Rs 18 lakh crore in March this year. While there were indications that increase might plateau off, demand for banknotes has been strong this year with year-on-year growth being in excess of 20% for most of the year. However, withdrawals have been strong with accountholders pulling out over Rs 2.6 lakh crore from ATMs every month.
An increase in currency in circulation reduces the lendable resources of banks and pushes up interest rates. However, bankers say that historically currency returns to the banking system after festivals as individuals spend money and businesses deposit the cash back in banks.
The currency in circulation witnesses a sharp increase ahead of elections. In 2013, former governor Raghuram Rajan had said that “Around election time, cash with the public does normally increase... You can guess as to reasons why, we can also guess,” . He added: “You see some (spike) not just in the state going to elections, but also in the neighbouring states. There is something... We need to understand it better.”
See also
And the list is growing…
Banking, India: II (government data)
Banking, India: I
Industries: India (ministry data)







