Income Distribution:India

This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Contents |
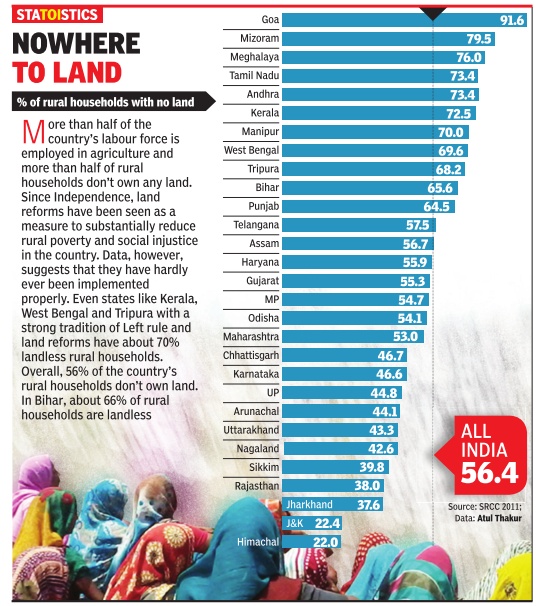
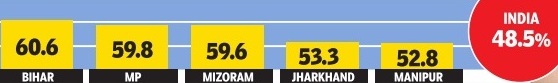
Rural households’ incomes
2011-13
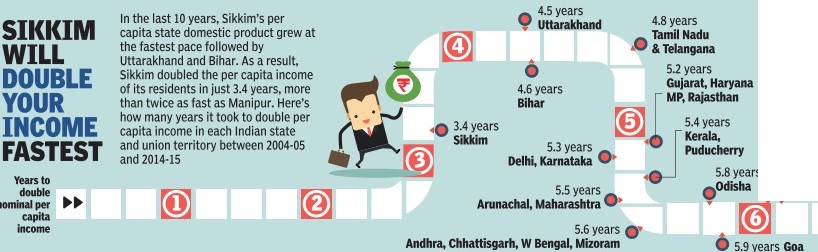
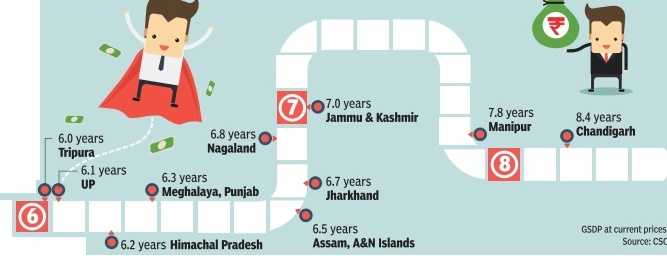
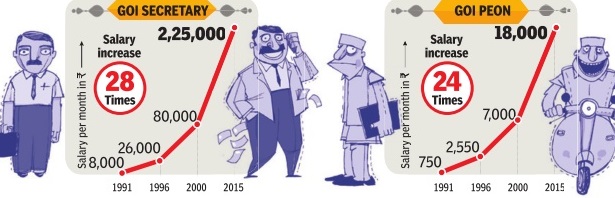
The Times of India, Jul 04 2015

Subodh Varma
92% village homes run on less than Rs 10,000 a month
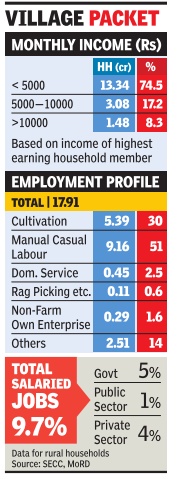
Giving a more storied picture of rural India, the Socio-Economic and Caste Census (SECC) released says that a staggering 92% of rural households reported their maximum income below Rs 10,000 per month. Nearly three quarters of all rural households said that the income of the highest earning member was Rs 5,000 or less. The SECC was conducted during 2011-12 with some states completing it in 2013, due to a lengthy process of seeking objections on collected data. It found that about 18 crore households lived in rural areas, including outgrowths of towns.
The SECC found that over 9 crore households were living by doing casual manual labour. That's more than half of all rural households. Cultivators were reported as numbering 5.39 crore households, making up about 30%. The muchheralded non-agricultural enterprises were providing livelihood to just 29 lakh households, a meagre 1.6% of the total.
There seems to be a significant difference with Census 2011 figures. The Census counts people, and according to it, in 2011 there were 9.2 crore cultivators and 8.1 crore agricultural labourers. This would translate to about 2 crore cultivator households and 1.7 crore agricultural labourer households.
However, Abhijit Sen, former member of the Planning Commission who was involved in designing the survey, told TOI that this comparison should not be done because the SECC asked about incomes while the Census asked about work.
“Also, everybody in a household doesn't work. So converting Census-based worker figures to households will not give a true picture,“ he added.
But on one issue, the SECC is perhaps better reflecting the lives of rural people. The Census gives figures for `agricultural labourers' whereas the SECC gives figures for those working as casual manual labourers, which is not confined to agricultural labour alone. Due to pressure on land,fragmentation, and low returns, a vast army of people, both men and women, are turning to any kind of casual labour to earn a living.
“Each rural household will have different kinds of casual workers. The SECC is reflecting this reality,“ Sen said.
SECC reports that only about 10% of rural households have salaried jobs. Of these, about two thirds are in public sector, and a third, 6.4 lakh in all, work regular private sector jobs. And, less than 5% of the rural households pay income tax or professional tax. This is mainly because agricultural income is not taxed and with over 92% households earning less than Rs.10,000, most don't qualify .
Urban India
No source of income for 35 lakh households
The Times of India, Jul 04 2015
35 lakh urban families have no income
At least 35 lakh families in cities and towns have no source of income while 90 lakh households are headed by women, according to raw and unreleased data from the Socio-Economic and Caste Census in urban areas, reports Dipak Dash. About 1 crore households own at least one of four items -fridges, landline phones, washing machines and twowheelers; 86 lakh households own all these.