Insurance (life): India
This article has been sourced from an authoritative, official readers who wish to update or add further details can do so on a ‘Part II’ of this article. |
Contents |
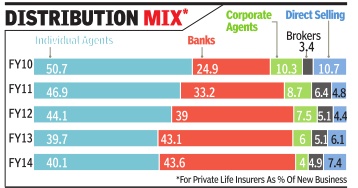
Private life insurers, 2010-14
`Indian control' norms affect insurers' valuations
The Times of India, Nov 27 2015
Mayur Shetty
`Indian control' norms hurt insurers' valuation
The valuation of a inancial services firm is usually a straightforward business as there are ample benchmarks available. But in the case of insurance, a host of issues are queering the pitch for arriving at a value appropriate for a stake sale. Primary among his is the issue of Indian-owned and controlled', which is among the softer aspects of negotiations outside he hard numbers. By January , each of the 24 life insurance companies will have to rework their joint venture agreements to ensure that they are in compliance with the norms pertaining to Indian management. According to Sanket Kawatkar, head of life insurance consulting for Milliman India, which has conducted valua ions for 17 of the 24 companies, “A large component of the va uation would include softer aspects -the keenness of the oreign partner to do business n India and the desire to conti nue with the Indian partner.“
This is weighed with the fact that, under the new norms, multinationals can no longer enter into agreements which give them a veto power.
Companies' promoters are now scrambling to find out the worth of the business they have invested in. The traditional method of computing an insurance firm's valuation would be to arrive at an embedded value -a number which factors in not just present earnings but also takes into account future profits. But this global measure is not the basis on which deals are being worked out.
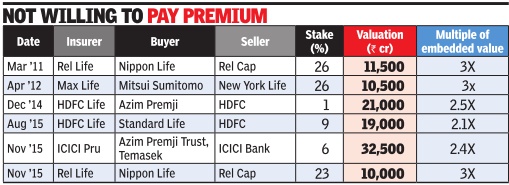
Foreign promoters running joint ventures will suddenly find themselves in a weaker position than they were in before the legislation allowing 49% was passed. This has changed the dynamics and many are unwilling to pay the premium they might have done earlier. In the case of Reliance Life, the deal for sale of an additional 23% stake to Nippon Life valued the company at Rs 10,000 crore -marginally lo wer than the Rs 11,500 crore at which the earlier investment was done. In HDFC Life, the foreign partner has bought stake at a lower valuation when compared to what strategic investor Azim Premji paid in 2014.
The other disruptions in the valuation process has been the regulator's push for an open architecture in banks.
“People also tend to forget that interest rate on 10-year government bonds had fallen close to 5.5% some years back. If this happens, the margins in some policies will turn negative because of the assured maturity benefits,“ said Kawatkar. He added that the assured maturity benefit portfolio of private insurance companies ranged between 10-20%.
The other disruption is likely to come from online. “India is arguably leading the way in the online experience. It is quite likely that future entrants will not follow what others are doing and will take the direct route for selling,“ said Richard Holloway , MD, South East Asia & India, Milliman.
Death after refusing treatment
The Times of India, May 24 2016
Ajay Sura The family of a terminally ill person who decides to stop treatment against medical advice and dies cannot be denied insurance claim, the Punjab and Haryana high court has ruled.
The high court has also clarified that a patient's desire not to be treated is an issue of `patient autonomy' and `embracing dignity in death'.
It is an important development since many insurance companies tend to use Leave Against Medical Advice (LAMA) as an excuse to deny the family of the deceased their claims, say medical experts.
The judgment comes in a case where the insurance company challenged the order of a claims tribunal to pay Rs 35.46 lakh to the family of a deceased who was admitted to hospital after suffering severe head injury in a road accident but decided to leave against doctors' advice when they did not see much chance of recovery . The insurance company claimed it was not liable for the damages because the deceased had left the hospital against medical advice. The high court rejected their plea and ruled in favour of the family of the deceased.
“Whether the patient shall be allowed to die by withdrawal of life support is quite different from a patient expressing desire not to be treated. In the former, we are broaching issue of passive euthanasia and in the latter, it is an issue of patient autonomy ,“ the bench of Justice K Kannan said in its order that could come as major relief to many such families who are burdened with huge medical costs. Justice Kannan, in his or der delivered last week, took the subject to a higher level stating that patient autonomy in the manner of treatment is a facet of human right and it cannot be ever contended in court that the patient ought to have taken treatment that had a good prognosis for recovery.“There have been instances where due to religious beliefs (for instance, Jehovah's witnesses' denial of blood transfusion), patients have declined to take treatment and courts have confronted these problems as well and come to decisions of hands-off approach,“ he said.
The court passed these orders while dismissing an appeal by Oriental Insurance Company , which had stated that a family of an insured person leaving treatment against medical advice was not entitled for a claim after death.
See also
Insurance, life and general: India
Insurance (life): India