National Capital Region (India): Rural Development
This article has been sourced from an authoritative, official readers who wish to update or add further details can do so on a ‘Part II’ of this article. |
The source of this article
Draft Revised Regional Plan 2021: National Capital Region
July, 2013
National Capital Region Planning Board, Ministry of Urban Development, Govt. of India, Core-4B, First Floor, India Habitat Centre, Lodhi Road, New Delhi-110003
National Capital Region Planning Board
National Capital Region (India): Rural Development
BACKGROUND
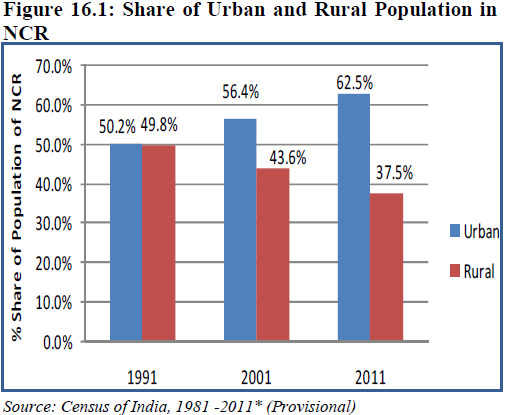
As per Census 2011, the total rural population of NCR is 172.6 Lakhs, which accounts for 37.5% of the total NCR population. The proportion of rural population has gone down by 6.1 % during the last decade 2001-2011. There were 7528 rural settlements in NCR in 2001 (Figure 16.1).
Rural settlements, located in the fast growing Central National Capital Region, are undergoing physical
and socio-economic changes, particularly in the settlements along the major transport corridors.
The Regional Plan-2021 proposed strategy for
rural development which envisages provision of
facilities and services in appropriate hierarchy to
stimulate production and increase the income of
rural masses, diversify the economy, make
villages attractive to live and work.
The Plan proposed six-tier hierarchy of settlements out of which three are for rural settlement system. They are Service Centres, Central Villages and Basic Villages. The Service Centres shall be the small town or a large village having linkages with immediate rural hinterlands. These centres would cater to the rural hinterland as agro-service centre in the collection and distribution of agricultural goods and services with processing, marketing, warehousing and storage facilities. Central Village is the higher order village having central location and potential for development within its service area, with relatively better services and facilities in terms of education, health, communication, accessibility and has the capacity to serve a group of Basic Villages.
This centre is proposed to provide basic social facilities for population engaged in agriculture and other primary activities. All other Census villages with a population of less than 5,000 have been classified as Basic Villages and would be provided with basic facilities like link roads, water supply and electricity, paved streets and low-cost common sanitary facilities as well as the minimum required social infrastructure as per planning norms.
It was proposed that these settlements would be identified in the Sub-regional Plans and District Development Plans as per provision of the Constitution (74th Amendment) Act, 1992 by the respective State Governments based on their growth potential, size, connectivity and ability of performing required functions. They will prepare detailed rural development programmes and incorporate the same in the District Development Plans keeping in view the policies and proposals of the Regional Plan-2021 and develop strategies for these settlements.