Suicides: India
This is a collection of newspaper articles selected for the excellence of their content. |
A
The legal position
2017/ Mental Healthcare Bill decriminalises suicide
Parliament passes bill to decriminalise suicide bid, March 28, 2017: The Times of India
Survivors of attempted suicide will no longer have to undergo prosecution, with the Lok Sabha passing the Mental Healthcare Bill 2016, which decriminalises suicide and provisions for right to better healthcare for people suffering from mental illness.
The bill, passed by the Rajya Sabha with 134 official amendments in August last year, was passed in the lower House by voice vote as all parties supported the legislation. PM Narendra Modi had spoken about mental depression in his radio broadcast, `Mann Ki Baat', on Sunday , maintaining that the illness can be overcome. Union health minister J P Nadda thanked lawmakers across party lines for supporting the mental healthcare bill. While proposing the bill for passage, Nadda said in a lighter vein, “I am hopeful that all of us sitting in the House are in good mental health. If anyone has any problems, one should come forward.“
“The bill gives legal righ ts to individuals to seek treatment for mental illness. Moreover, it decriminalises suicide attempts and identifies the caretakers. It also curtails and punishes inhuman treatment or imprisonment to a person with persistent mental illness,“ said Nadda.
The minister said, “As per this law, we cannot separate a child for three years...Also, one cannot chain a mentally-ill person.“ He clarified that the aim of the legislation is to see that the patient is protected and no coercive method is adopted.
BJP MP Ashwani Kumar Choubey suggested inclusion of music therapy as one of the remedies for mental treatment.
One of the features of the bill is that it allows adults to make an advance directive on how they wish to be treated in case they suffer from mental illness in future. A person can also nominate a caregiver in such a case.
The bill clearly defines mental illness and mental healthcare, Nadda said, adding the earlier definition was vague. There are also provisions preventing a person from being sterilised just because he or she is a mental patient.
The bill focuses on community-based treatment.Special provisions for women and health have been provided for. Among the various objectives, it provides for ensuring healthcare, treatment and rehabilitation of people with mental illness “in a manner that doesn't intrude on their rights and dignity .“
Sorabjee: In favour of decriminalisation
The Times of India, Aug 12 2016
Soli J Sorabjee
It is irrational to punish one who has tried to kill self
If a person succeeds in his attempt to commit suicide and dies that's the end of the matter. But if the person doesn't, the suicide attempt may see him behind bars and is punishable under Section 309 of our penal code by simple imprisonment for a term which may extend to one year or fine or with both. To Rajya Sabha's credit, it re cently passed the Mental Health Care Bill 2015 which provides that anyone attempting to commit suicide wouldn't be punished under Section 309. The proposed law doesn't in terms repeal or amend Section 309 but in substance nullifies its penal consequences.
The issue of sui The issue of suicide has been debated in our country and elsewhere. The Law Commission in its 42nd Report in June 1971 recommended repeal of Section 309 based on cogent reasons. A Bill, the Criminal Law Amendment Act, 1978, was introduced in the Rajya Sabha for repeal of Section 309. But before the Lok Sabha could pass it, the government fell. The Bill lapsed.
The issue arose before the Supreme Court in the P Rathinam vs Union of India case. A Supreme Court bench comprising Justices R M Sahi and B L Hansaria after elaborate discussion in its judgment dated April 26, 1994 held Section 309 a cruel and irrational provision, and it may result in punishing a person again (doubly) who has suffered agony and would also be suffering ignominy because of his failure to commit suicide. Consequently , according to the bench, the section was violative of Article 21, hence unconstitutional.
The issue also arose before different high courts. The majority of them held Section 309 unconstitutional. Thereafter, the issue came up for consideration before a Supreme Court constitution bench comprising Justices J S Verma, G N Ray , N P Singh, Faiz Uddin and G T Nanavati. The bench after a detailed discussion, after referring to high court judgments and writings of foreign scholars concluded that Section 309 isn't violative of Article 14 or Article 21. It's not unconstitutional. The constitution bench disapproved of the Supreme Court judgment in P Rathinam's case. The court ruled that it wasn't possible to “construe Article 21 to include the right to die as part of the fundamental right guaranteed therein. Right to life is a natural right embodied in Article 21 but suicide is an unnatural termination of life, therefore, incompatible and inconsistent with the concept of right to life“.
The Law Commission, understandably in its 156th report, followed the constitution bench judgment and favoured retention of Section 309. I had occasion to appear before the constitution bench. Unfortunately , I failed to persuade the bench that it has been universally acknowledged that a provision to punish attempted to commit suicide is irrational and Section 309 is unconstitutional.
Wisdom dawns though belatedly. The Law Commission in its 210th report recommended decriminalisation of Section 309.That's good news. It's fervently hoped that the Law Commission's recommendation is accepted.
When I was arguing the case I got the impression that the silent premise of the mindset and predilection of the constitution bench was that suicide is morally wrong and unethical. It failed to appreci ate that if Section 309 is invoked, persons of integrity who fast unto death for laudable ob jectives would be crimi nals punishable under Section 309. Should we tolerate such a bizarre situation? Su-rely a ra tional person in good physical and mental N state has the right to choose whether he should continue his journey on this planet or escape the treadmill to which the person is chained and fulfil his desire to meet his Maker.The crux of the matter is that the choice is his or her personal decision which has no baneful consequences in society and the state has no legitimate right to interfere, much less treat the person as a criminal and impose punishment.
Retention of Section 309 is an anachronism unworthy of any decent and civilised human society like ours. It's monstrous to inflict further suffering on an individual who for no fault of his has already found life so unbearable, his chances of happiness so slender, that he's willing to face pain and death to cease living. Those for whom life is bitter shouldn't be subjected to further misery . To do so would be inhuman and smack of sadism.It's noteworthy that in 1961, the UK removed the provision under which a person surviving suicide attempt was punished. Replying to the debate on the Bill, health minister JP Nadda termed it humane and progressive and said its focus was to provide better support to people suffering from mental illnesses.
There should be no dilly-dallying in removing this cruel provision which has caused acute suffering to several unfortunates and has besmirched the image of our nation. was conducted as part of the on-going research in the new field of epigenetics that examines how gene expression changes.
The Mental Health Bill 2016
The Times of India, Aug 12 2016
Defanging suicide-attempt law brings new hope to life
At long last, India has joined liberal democracies by moving to decriminalise suicide.The Mental Health Bill passed by the RS gets around Section 309 of the IPC that makes attempting suicide a criminal offence.
This law, which essentially says that a person in extreme distress either kills herself efficiently or face legal punishment, is a colonial hand-me-down. While most western nations struck it down after the French Revolution, and even England and Wales followed suit in 1961, former colonial territories such as Pakistan, Bangladesh, Malaysia and Singapore persist with it. “Only 25 nations criminalise suicide now; most have realised that investment in mental health is more useful than prosecuting someone already tortured,“ says Dr Lakshmi Vijayakumar, founder of Chennai-based NGO Sneha and a consultant to WHO on suicide prevention.
The law is no deterrent to suicide, say psychiatrists. Sri Lanka decriminalised suicide in 1998 and suicide levels dropped, possibly because of concerted suicide-prevention programmes.
There are cultural underpinnings for our attitudes towards self-destruction.
Unlike Abrahamic religions such as Christianity and Islam, dharmic traditions such as Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism don't have a sense that god has a claim on life. In Japan and India, suicides driven by honour and duty -seppuku and sati, for instance -were culturally endorsed. Suicide, some sug gest, can be driven by egoistic reasons, to make a point, for a social cause, because of loneliness, material deprivation, physical illness and other factors.
“There's no one reason for suicide, it has always been a part of humanity ,“ says Johnson Thomas of Mumbai's Aasra suicide helpline.
We need a suicide prevention programme, say experts. Suicide rates have soared globally and India has specific vulnerabilities -for instance, given the large number of suicides among housewives, marital status isn't a protection against suicide as it tends to be in the West. The WHO, seeing suicide as a preventable public health problem, has tried to analyse national risk factors.
In India, criminalisation of suicide has meant substantial under-reporting, says Vijayakumar, making it difficult to identify at-risk groups or provide support. A 2002 Sneha study found that suicide was prevalent among students who failed in one subject. The Tamil Nadu government softened its policy allowing them to retake the exam without losing a year. “Suicides halved in the next decade,“ says Vijayakumar.
Early identification of vulnerable individuals, and adequate mental health workers are crucial to avert suicide. This is where India has a problem.“There's a stigma around seeking professional help for mental illness,“ says Thomas. There's a deficit of mental health professionals and infrastructure, with only 0.3 psychiatrists per 100,000 people. The Mental Health Bill acknowledges the lack of resources, but “the government must put its money where its mouth is,“ says Thomas.
Suicide bids decriminalised: 2016
The Times of India, Aug 10 2016
Dhananjay Mahapatra
Britain took a similar step in 1961
It took the government 45 years and a failed bid to finally move towards decriminalising attempt to suicide, which under Section 309 of Indian Penal Code is punishable with a maximum sentence of one year imprisonment. The move came through passage of the Mental Health Care Bill, 2013 in Rajya Sabha which provides that anyone attempting to commit suicide would not be punished under Section 309.The proposed law does not attempt to amend the IPC, but takes an indirect legislative route to nullify the penal effect of Section 309. Attempt to suicide is decriminalised in most countries except a handful like India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Malaysia and Singapore. In 1961, the UK removed the provision under which a person surviving an attempt to suicide was punished, from its penal law. Ten years later, Law Commission of India in its 42nd report in June 1971 scrutinised the IPC provisions and recommended repeal of Section 309. “We are definitely of the view that the penal provision is harsh and unjustifiable and it should be repealed,“ it had said. It took the central government seven years to act on this recommendation. The Janata Party government moved the Indian Penal Code (Amendment) Bill, 1978 for repeal of Section 309 and Rajya Sabha passed it.However, before it could be passed by Lok Sabha, the Janata Party government fell and Lok Sabha was dissolved.
In 1985, the Delhi high court in State vs Sanjay Kumar Bhatia was moved by the facts of the case in which police sought to prosecute a young man who attempted su icide. The HC had used strong words against Section 309. It had said, “Instead of society hanging its head in shame that there should be such social strains that a young man (the hope of tomorrow) should be driven to suicide compounds its inadequacy by treating the boy as a criminal. No wonder so long as society refuses to face this reality, its coercive machinery will invoke provisions like Section 309 IPC which has no justification to continue to remain on the statute book.“
In Maruti Shripati Dubal case, the Bombay high court in 1987 had termed as unconstitutional the IPC provision treating attempt to suicide as a crime. The high court had said right to die or to end one's life was not something new or unknown to civilization.Some religions like Hinduism and Jainism had approved the practice of ending one's own life through certain means but had condemned it in other circumstances, it said.
The issue was taken up by the SC in P Rathinam case [1994 (3) SCC 394]. It ruled that right to life under Article 21 could have a logical corollary that a person could not be forced to live a distressed life and hence, Section 309 violated Article 21 and was unconstitutional. It said, “Suicide is a psychiatric problem and not a manifestation of criminal instinct. What is needed to take care of suicide-prone persons are soft words and wise counselling and not stony dealing by a jailor.“ But a five-judge constitution bench revisited the contentious issue in Gian Kaur case [1996 (2) SCC 648]. It overruled the Rathinam case ruling and said right to life could not be construed ever as right to die. It upheld the constitutional validity of Section 309 IPC and said, “Right to life is a natural right embodied in Article 21 but suicide is an unnatural termination or extinction of life and, therefore, incompatible and inconsistent with the concept of right to life.“
Abetment of suicide
Abuse for loan repayment is abetment
The Bombay high court refused to drop charges of abetment of suicide against two moneylenders, saying that beating up a debtor in his family's presence at his home and at his workplace, and demanding the documents of his house, certainly amounts to instigation and provocation to commit suicide.
The accused moneylenders, Gurunath Gawli and Sangita Gawli, had moved the court with a revision plea against an order passed last year under the Bombay Moneylenders' Act, which refused to discharge them from a case of abetting suicide in 2014.
In an FIR, the widow of Umesh Bombley had accused the duo of harassing him to return a loan of Rs 19 lakh. She alleged that her husband, a cutlery seller by profession, was regularly beaten up and intimidated, police said.
Rejecting the plea, the court observed, “ A prudent family man when meted with such treatment daily would certainly think of committing suicide. The accused persons' conduct in assaulting the deceased for getting back the loan amount appears to be wilful and its gravity seems to propel or compel a person of ordinary prudence to commit suicide.“
The court based its decision on a Supreme Court ruling which held that at the pre-trial stage, suspicion was enough to frame the charge, and marshalling of evidence was not required. It also relied on the conduct of the accused prior to the suicide to show that the suspicion pointed towards them provoking and facilitating him to commit suicide.
“Cornered by such behaviour of the accused, the victim was bound to think it is better to die than suffer humiliation in front of his children and family ,“ the court said, adding that the observation was prima facie and would not affect defence arguments during trial.
Actual convictions are rare
The Times of India, Aug 12 2016
Dhananjay Mahapatra
Though Section 309 has been in operation for more than a century and punishes suicide attempts, courts have hardly convicted and punished anyone for the “offence”.
A five-judge SC constitution bench on March 21, 1996 -in the Gian Kaur case -upheld the constitutional validity of Section 309 overruling a twojudge SC bench decision in the P Rathinam case in 1994 terming criminalising suicide attempts unconstitutional.
When Dubal's case came up before a two-judge bench on August 29, 1996, it was bound by the constitution bench decision and had no option but to strike down the Bombay HC judgment.But, on facts, it had a softer approach -Section 309 may be valid as per law but the court had the discretion not to jail a distressed person. It quashed the case against Dubal.
Dubal had served as a Bombay Police constable for 19 years, had in a 1981 accident suffered head injuries. Though he recovered physically, he became mentally ill and depressed. He attempted to commit suicide in 1985.
The court noted Dubal's reason for taking the extreme step.“He has become mentally disbal anced and undergoing psychiatric treatment. He was suffering from schizophrenia and put on heavy tranquillisers.“
The judges referred to the constitution bench judgment, which had said: “In appropriate cases, even fine can be imposed for offence under Section 309“.
The two-judge bench said incidents have been cited where courts have awarded nominal punishment and given benefits of the Probation of Offenders' Act to the accused convicted for attempting suicide.
But, the bench quashed the case against Dubal.
It said: “Considering the serious ailments Dubal was suffering, it appears...that it'll not be desirable to proceed further with the trial of the criminal case against the accused for allegedly attempting suicide after such (a) long lapse of time.“
“In the facts of the case, even if he's found guilty after completion of trial, Dubal deserves to be treated sympathetically in the matter of awarding punishment... We do not think Dubal deserves to be subjected to trial for attempting suicide. To do complete justice we direct for quashing of the criminal case against Dubal,“ the court said.
Disclosure of (phone sex) could be planned harassment
A woman cannot be booked for abetting his suicide because she indulged in phone sex with her banker husband’s friends, Bombay high court ruled.
Justice Mridula Bhatkar said there was no material to charge the woman for abetting her husband’s suicide. The Thane-based banker had set himself on fire in his house in July 2015. The police charged the woman contending he was traumatised after he learnt his wife engaged in phone sex sending “vulgar messages” to one of his friends in the city and another friend in Dubai.
Though the woman did not dispute the claim, her lawyers made the case that her acts were secret and, hence, she could not be blamed for driving him to suicide.
Justice Bhatkar said while the woman may have engaged in infidelity, there was no material to prove she had actively instigated or abetted the suicide.
“If at all the accused would have indulged in phone sex deliberately, disclosing this repeatedly (to her husband) despite his warning to desist, it would have been considered planned harassment. The guilty mind is to be necessarily linked with infidelity, but not abetment to commit suicide,” said the court.
The Jiah Khan suicide (2013)
Experts pick holes in Jiah Khan suicide abetment case
Vijay V Singh, Rebecca Samervel & Bharati Dubey, TNN | Jun 13, 2013
Lawyers’ views
Lawyer Ameet Naik handled the Navin Nischol case in which the actor was acquitted despite his wife leaving behind a suicide note blaming him (in this case, legal experts are not even sure whether Jiah Khan's letter can be treated as a suicide note). "A mere letter is not reason enough to arrest him. In the Navin Nischol case, there was a suicide note but the prosecution was unable to establish real mens rea (intention) in abetment. There could be several other reasons for the suicide. Police needs to find if there is circumstantial evidence before making such arrests," Naik said.
Lovers’ tiff can’t be abetment of suicide: SC
Prosecution Must Prove Intent, Knowledge
Dhananjay Mahapatra TNN
A boy proposes to a girl. She rejects it. Feeling humiliated, the boy commits suicide. Should she be prosecuted for abetment of suicide?
Actress Jiah Khan’s suicide has again brought to fore a question — what constitutes abetment of suicide? — which has been discussed extensively by the Supreme Court through the decades.
The Supreme Court has consistently held that a word uttered in a fit of anger or emotion without intending to trigger a step as extreme as suicide can’t be said to be abetment of suicide.
The Supreme Court has also consistently clarified that to prosecute a person for abetment of suicide, prosecution has to prove that the accused had the intention and knowledge that a specific act on his part could trigger suicidal tendency in the victim.
Normal marital skirmishes or what the court put it as “normal wear and tear of marriage” could not be counted as a reason for abetment of suicide by a partner.
In that case — State of West Bengal vs Orilal Jaiswal [(1994) 1 SCC 73] — the SC had cautioned that the court should be very careful in assessing the facts and circumstances of each case and the evidence for purpose of finding whether cruelty meted out to the victim had in fact induced her to commit suicide.
“If it appears to the court that a victim committing suicide was hypersensitive to ordinary petulance, discord and differences in domestic life quite common to the society to which the victim belonged and such petulance, discord and differences were not expected to induce a similarly circumstanced individual in a given society to commit suicide, the conscience of the court should not be satisfied for basing a finding that the accused charged of abetting the offence of suicide should be found guilty,” it had said.
Three years ago, the SC in S S Chheena vs Vijay Kumar Mahajan had said there had to be a positive act on the part of the accused to instigate the victim to take the step of taking her own life.
“Abetment involves a mental process of instigating a person or intentionally aiding a person in doing of a thing. Without a positive act on the part of the accused to instigate or aid in committing suicide, conviction cannot be sustained.”
In its 2001 judgment (Ramesh Kumar vs Chhattisgarh), the court dealt with a classic case. After a quarrel, the husband told the wife — “you are free to do whatever you wish and go wherever you like”.
The wife committed suicide and the husband faced abetment charges. The court quashed the charges and said: “The present one is not a case where the accused had by his acts or omission or by a continued course of conduct created such circumstances that the deceased was left with no other option except to commit suicide, in which case instigation may have been inferred. A word uttered in the fit of anger or emotion without intending the consequences to actually follow cannot be said to be instigation.”
Spouse's infidelity
Spouse's infidelity, by itself, not an abetment to suicide
A person cannot be convicted for subjecting his wife to cruelty only on the basis of his extramarital affairs, the Supreme Court ruled on Thursday and acquitted a man whose spouse had committed suicide because of his alleged extramarital relationship.
An extramarital affair may be illegal or immoral, but it does not necessitate conviction of a husband for cruelty to his wife as “other ingredients are to be brought home so that it would constitute a criminal offence“, the court said.
A bench of Justices Dipak Misra and Amitava Roy also said a spouse's infidelity wasn't enough ground for conviction under abetment to suicide charge. In this case, the woman (Deepa) killed herself after seven years of marriage, unable to bear her spouse's alleged extramarital affair. Her mother and brother also ended their lives. The court said the concept of mental cruelty de pends upon the milieu and strata which the persons come. “Extra-marital relationship per se would not come within the ambit of Section 498-A IPC (subjecting wife to cruelty),“ the bench said.
“There is no denying that cruelty need not be physical but a mental torture or abnormal behaviour that amounts to cruelty or harassment... It will depend upon the facts of the said case,“ the court said.
“Solely because the husband is involved in an extramarital relationship and there is some suspicion in the mind of his wife, that cannot be regarded as mental cruelty... for satisfying the ingredients of Section 306 IPC (abetment of suicide),“ it said.
The court said a woman could seek divorce and other remedy. “Having said that we intend to make it clear that if the husband gets involved in an extra-marital affair that may not in all circumstances invite conviction under IPC Section 306 (abetment to suicide) but definitely that can be a ground for divorce,“ it said.
The trial court had convicted the man under IPC Section 498 A and the Dowry Act and sentenced him to two years. Karnataka HC also convicted him for abetment of suicide and awarded four years' rigorous imprisonment besides a fine of Rs 50,000 to be paid to the woman's father. SC has set aside the verdict.
“It needs to be noted that Deepa, being not able to digest the humiliation, committed suicide. The mother and the brother of Deepa also followed the same path. In such a situation, it is extremely difficult to hold that the prosecution has established the charge under Section 498A and the fact that the said cruelty induced the wife to commit suicide,“ the bench said.
Suicide note
Suicide note not enough proof of abetment: Bombay HC
Swati Deshpande, TNN | Aug 28, 2013
The Bombay high court on Tuesday observed that a suicide note alone was not enough proof in a case of abetment of suicide and dismissed an appeal against acquittal in one case. MUMBAI: The Bombay high court on Tuesday observed that a suicide note alone was not enough proof in a case of abetment of suicide and dismissed an appeal against acquittal in one case. In the absence of independent evidence to prove a case of abetment, Justice A H Joshi dismissed the appeal filed by the victim's family.
The judge was hearing an appeal filed by the family of a suicide victim against the acquittal. The appeal, filed last year by one Sunil Bhavsar, challenged a sessions court verdict of acquittal. His lawyer argued that it was a case in which a woman was pushed into committing suicide and that a suicide note she left behind "proved the abetment charge". She was harassed and threatened, the lawyer argued.
The case was from Nashik and the lawyer said a complaint was filed in 2010 with the Nashik police about the harassment and threats she faced that led to her eventual suicide. Hence, the abetment to suicide charge is proved, he argued and the acquittal ought to be overturned.
The state did not file an appeal. The appeal itself was dismissed, by default, by the HC earlier in March 2013 as the lawyer for the appellant had not turned up on a date when it was scheduled for a hearing.
When the lawyer for the victim's family stressed on the suicide note and threats she allegedly received before the suicide, Justice Joshi said, "This is no mathematical equation, that a suicide note plus threat equals abetment...If harassment is proved, show the proof," the HC said. The judge said, "A threat to kill is not abetment. (Giving) An advice to kill is also not abetment."
In case of a suicide, higher courts have held that in each case the circumstances and evidence is crucial to decide whether there was abetment, which would involve acts by another person to actually instigate the person into committing suicide, the SC has held.
WHAT THE SC HAS HELD
"If it appears to the Court that a victim committing suicide was hypersensitive to ordinary petulance, discord and difference in domestic life quite common to the society to which the victim belonged and such petulance, discord and difference were not expected to induce a similarly circumstanced individual in a given society to commit suicide, the conscience of the Court should not be satisfied for basing a finding that the accused charged of abetting the offence of suicide should be found guilty."
Teacher’s slap no abetment to suicide
June 23, 2018: The Times of India
If a teacher chastises a child for indiscipline, it doesn’t make a case for abetment to suicide, the Madhya Pradesh high court said, dismissing a petition filed by the uncle of a Class X student who hanged herself in November last year after being scolded by her principal.
“The principal and teachers don the mantle of a parent during the time the child is in school. Like a parent, who would — and is expected to — admonish a child who errs with the intention of correcting the child, so are the principal and teachers expected to admonish and chastise students when they transgress discipline of the school,” Justice Atul Shridharan said in his order.
The girl, a resident of Kotma town of Anuppur district, had committed suicide on November 14, 2017 after being scolded and allegedly slapped by principal R K Mishra, who had seen her with two friends outside the school before classes got over. She hanged herself after recounting the punishment to her uncles.
Her family tried to file an FIR against the principal under section 306 of Indian Penal Code (abetment to suicide), but they refused. An uncle then moved court, saying his niece committed suicide out of humiliation as the principal had “slapped and scolded her in the presence of two friends”.
Justice Shridharan said: “It goes without saying that the days of ‘spare the rod and spoil the child’ are long gone, but it does not mean that the principal and teachers of a school languidly watch and ignore acts of indiscipline and indiscretions of a child. Correction by way of admonishment and chastisement, as and when required, remains a sacred duty of those imparting education... Behind every person languishing in prison as a convict are a man and woman who failed as parents and a system of education that could not transcend the three ‘Rs’.”
Stressing the importance of drilling good values in students, the judge observed: “Brilliance without integrity and character is a social and national liability rather than an asset. Schools must emphasise this. Admonishment and chastisement may form an integral part of that exercise. Yes, in the process, it may be natural for the child to feel embarrassed or humiliated, but it is these very emotions that would prevent the child from repeating the mistake.”
It goes without saying that the days of ‘spare the rod and spoil the child’ are long gone, but it does not mean that the principal and teachers of a school languidly watch and ignore acts of indiscipline and indiscretions of a child
Workload is not abetment: SC
HIGHLIGHTS
SC has ruled that superiors cannot be held responsible for abetment if an employee, depressed because of a heavy workload at office, commits suicide
The SC said a superior officer assigning a load of work to an employee could not be assumed to be of a criminal bent of mind
In a decision with important workplace implications, the Supreme Court has ruled that superiors cannot be held responsible for abetment if an employee, depressed because of a heavy workload at office, commits suicide. The SC said a superior officer assigning a load of work to an employee could not be assumed to be of a criminal bent of mind who intended to harass an employee or force him to end his life. It rejected the argument of the Aurangabad bench of the Bombay HC that the officer was culpable even if there was no direct abetment on the grounds that the conditions created could lead to unbearable mental tension.
Kishor Parashar, working in the Aurangabad office of the deputy director of education in Maharashtra government, committed suicide in August 2017. His wife filed a complaint with the police accusing her husband’s superior officer of abetting the suicide. She alleged the superior used to assign a heavy workload to Parashar, requiring him to work till late evening.
She said the senior called him for work at odd hours and also on holidays, stopped salary for a month and threatened to stop increment. She claimed her husband remained silent at home and the superior was responsible for his suicide. After the Aurangabad police registered an FIR, the senior officer moved the Aurangabad bench of the Bombay HC for quashing the FIR.
On January 23, the HC rejected the plea to quash the FIR. The HC had said, “The facts indicate that there was no direct abetment and the applicants cannot have any intention that the deceased should commit suicide. Even when the accused persons have no such intention, if they create a situation causing mental tension so as to drive the person to commit suicide, they can be said to be instigating the accused to commit suicide.”
When the superior officer appealed before the SC, the plea was opposed by the Maharashtra government’s standing counsel Nishant Katneswarkar. A bench of Arun Mishra and U U Lalit found the HC’s logic in roping in the superior officer on the charge of abetting suicide untenable. Justice Lalit, who authored the judgment, said, “It is true that if a situation is created deliberately so as to drive a person to commit suicide, there would be room for attracting Section 306 of the IPC (abetment to suicide). However, the facts on record in the present case are inadequate and insufficient (to reach that conclusion).” The bench quashed the FIR against the superior officer.
B: TRENDS
Age-, state- and gender- wise statistics
2000-15: age and gender
Sushmi Dey, Young adults account for 33% of suicides, June 21, 2018: The Times of India
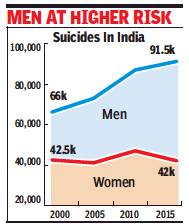
From: Sushmi Dey, Young adults account for 33% of suicides, June 21, 2018: The Times of India
Suicides in the country increased by 23% from 2000 to 2015 with the maximum number of such deaths being reported in the 30-45 age group, followed closely by young adults between 18 and 30 years, according to data released by the National Health Profile, 2018.
Of the 1,33,623 suicide deaths in India in 2015, as compared to 1,08,593 in 2000, over 33% (44,593 deaths) were in the age group of 30-45, while the 18-30 age group accounted for 32.8% (43,852) of deaths. The two age groups together accounted for more than 66% of suicides in 2015.
Children below 14 and those between 14 and 18 accounted for nearly 1% and 6%, respectively, of the total suicides in 2015. Around 19%in the age group of 45-60 and those above 60 accounted for 7.8% deaths.
Suicide deaths higher among men in India, shows govt data
In 2005 and 2010, suicides increased to 1,13,914 and 1,34,599, respectively. Data shows suicide deaths were higher among men. As many as 91,528 committed suicide in 2015, as against 66,032 in 2005 and 87,180 in 2010. Among women, the number of suicides increased marginally during 2000-2015. The average life expectancy in India is 68.35 years.
Experts say socio-cultural issues, discrimination, and competition for highly paid jobs are the most common reasons for suicide among youth. India has recently put in place a mental health policy to focus on creating awareness to address such problems.
According to the WHO’s Mental Health Atlas 2017, very few countries have suicide prevention strategies .
The report highlighted a global shortage of personnel trained in mental health issues and lack of investment in communitybased mental health facilities.
2005-14: state and gender

See graphic:
Number of suicides, state, gender and year-wise, 2005-14
Gender: Men outnumber women
Men outnumber women when it comes to suicides
The Times of India Sunitha Rao R,TNN | Jul 23, 2014
Of the 1.34 lakh people who committed suicide in the country in 2013, 64,098 were men and 29,491 were women as per the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) Report 2013. The overall male:female ratio of suicide victims for the year was 67.2:32.8, showing a marginal increase of male and marginal decrease of female ratio as compared to 2012 (66.2:33.8).
The proportion of boys to girls (up to 14 years of age) was 53.5:46.5 in 2013 as compared to 48.4:51.6 in 2012. Over 80,000 were in the 15-44 age group, the most productive years of human life. Youths (15-29 years) and lower middle-aged people (3044 years) were the prime groups resorting to the extreme step. Around 34.4% of suicide victims were youths in the 15-29 age group and 33.8% were middle-aged people in the 30-44 age group.
In India, as many as 15 suicides took place every hour last year. In 48.6 per cent of suicide cases, the causes are unknown. According to Dr G Gururaj, head of department, epidemiology, Nimhans, prevention of suicide becomes difficult if the reasons remain unknown.
"The reasons attributed by NCRB for reported suicides are vague. A blanket head like family problems does not convey much. Besides, it has only captured the cases reported, whereas many suicides go unreported. There would be a minimum 10 attempts before actual suicide. Not every suicide is an impulsive act. The person who does it might even have thought about it for at least two years but the warning signs may have been ignored by family members," says Dr Gururaj.
Any rapid transformation in society is accompanied by stress and it's never smooth, says Dr A Jagadish, psychiatrist from Abhaya hospital. "Economic downturn and relationships are major issues among those who come with depression. If an adult man thinks of self-harm, he does inflict it most often," he adds.
A 42-year-old patient of his attempted suicide thrice as he found it difficult to cope with his brother's unemployment and related problems, he recalls.
Dr S G Murali Raj, head of the department of psychiatry, Manipal Hospitals, says women can manage a relationship breaking up better than men. "Suicides among men can also be attributed to alcohol-induced depression. Men are more prone to alcohol addiction leading to poor impulse control," he adds.
Younger people, married women
Neeraj Kaushal, India’s Youth Suicide Binge, February 7, 2019: The Times of India
The writer is Professor of Social Policy at Columbia University
Younger people, and married women, are more prone to suicide in India
In most countries suicide mortality increases with age. In India, the opposite happens. The suicide rate among young adults aged 15-29 is more than three times the national average. This makes us a country with one of the highest suicide rates among youth in the world.
What explains this oddity? The answer lies in yet another oddity: India has a relatively high suicide rate among young adult women.
Globally, suicide is much commoner among men than women. The battle to reduce suicide has also been more successful for women than men. Across nations, suicide rates for men are three to seven times as high as for women. The same pattern prevails in India across most age groups, though here the gender gap is less sharp.
The oddity is among young adults for whom the gender gap virtually vanishes, and in certain locations, suicide is higher among women. One study published in the Lancet a few years ago found that suicide rate of girls aged 15-19 around Vellore, Tamil Nadu, was 148 per lakh, almost thrice the rate for similarly aged boys.
The gender gap in suicide gets worse after marriage. Here is another oddity. In most Western countries, married women are less likely to commit suicide than formerly married women. India is an outlier: married women are more likely to commit suicide than divorced, widowed and separated women, according to the Million Death study, a research project based on a nationally representative mortality survey on the causes of death occurring in 1.1million homes in 6,671areas chosen randomly across the country.
Science does not tell us much about the exact cause of suicide. Broadly, we know that biological, environmental and cultural factors make certain populations more vulnerable than others. High suicide rates for young married women in India could flow from a combination of these factors.
It is tempting to interpret this high rate as the result of psychological and physical torture from husbands and in-laws, that is common in India. Curiously, a geographic element weakens the gender explanation of high suicide rates among young married women. South Indian states, well-known for better gender relations and female empowerment than north Indian states, have much higher youth mortality. Neighbouring Sri Lanka, with excellent social indicators and higher women’s empowerment, also has a high youth female suicide rate. This could simply reflect greater sociocultural tolerance of suicide as a way out of mental stress.
In India, we have a tendency to link suicides with income or economic distress. Farmers have captured all the recent attention on suicides. Suicide among farmers is considered evidence of exceptionally high economic distress among them. Public discourse is politically motivated, highly charged, generally irreverent of facts, and substantially non-serious. In fact the suicide rate is lower for farmers than non-farmers.
Most extant research does not associate poverty with suicide mortality. Indeed, suicide mortality in India is higher among the more educated, who are typically better off than the less educated. Cross-country comparisons also reject a link between poverty and suicide. Among well-off OECD countries, Japan has the highest suicide rate at 20 per lakh population, followed by Switzerland at 14 per lakh. Much-poorer India’s suicide rate is 11 per lakh population.
Data across Indian states lead to the same conclusion. Suicide rates are up to 10 times higher in richer southern states than in poorer northern states. Now, economic or other shocks can push the vulnerable over the edge. The collapse of the Soviet Union, for instance, sharply increased the suicide rate there. What matters is a relative worsening of economic conditions, not the absolute level of incomes.
While the exact causes of suicide remain obscure, the good news is that, globally, the battle against suicides has been a successful one. Since 1994, suicide rates have fallen by more than a third globally. The sharpest decline has been in Russia, South Korea and Japan – the three countries that also have among the highest rates in the world.
As in many dimensions of well-being, China has been a leader in the battle against suicide. Its rate has fallen to 7 per lakh in recent years. Like India, China used to have high suicide rates for young women, but that rate has fallen by 90% since the mid-1990s. A contributing factor is urbanisation that granted women greater freedom of work; opportunities to leave violent husbands and in-laws; and live relatively stress-free lives in cities.
Means restriction is one of the most effective strategies. In Britain, simply repackaging of painkillers from bottles to blister packs reduced suicide death from overdose of paracetamol by 44%. Limiting access to guns in Australia and restricting alcohol distribution in Russia lowered suicides. In India, toxic pesticides are often used to end life. Better packaging and restricted access of pesticides could reduce the risk of suicide in rural areas.
Globally, a major factor contributing towards reduced suicide is better diagnosis and treatment of mental illnesses. Anti-depressants, psychiatric help, access to suicide lifelines, and just the availability of somebody to talk to sympathetically can curb suicides. It would have to be a societal effort and not just something left to the government. This requires compassion and caring towards a targeted vulnerable population, and cannot be simply addressed with buckets of money. Farm loan waiver, every politician’s favourite policy choice to tackle suicide, is extremely blunt, leaky and wasteful. Imagine the chance that a state or nation-wide loan waiver will reach the 0.008% of farmers who are at risk of committing suicide?
Causes
Biological reasons
FROM THE ARCHIVES OF ‘‘THE TIMES OF INDIA’’: 2008
Dark secrets of suicides decoded
Study identifies changes to a gene during major depression
Toronto: Canadian researchers claim to have found a clue as to why people commit suicide or go into deep depression. In a ground-breaking study, they found elevated levels of a particular protein in the brains of those who committed suicide. An international research group, led by Michael Poulter at the University of Western Ontario and Hymie Anisman of Carleton University, found that the elevated levels of protein affected a particular gene that controls stress and anxiety. During autopsies, they found higher levels of that particular protein — affecting genes that control stress and anxiety — in the brains of those who committed suicide, compared to those who died of other causes. They said these proteins caused chemical modification of the particular gene in a process called epigenomic regulation. This modification resulted in the shutting down or malfunctioning of that anxietycontrolling gene, impairing the individual’s ability to handle stress and commit suicide. Researchers said this particular gene plays a major role in regulating brain activity. “The nature of this chemical modification is long term and hard to reverse, and this fits with depression,” said Poulter.
“These observations open an entirely new avenue of research and potential therapeutic interventions,” he added. “The whole idea that the genome is so malleable in the brain is surprising. Finding that epigenetic mechanisms continue to influence gene expression is pretty unusual,” said Poulter. The study

Getting more failproof?
It might seem like many kids are committing suicide today because the rat race is steadily getting worse.
The truth, however, is that the `good old days' of forty-odd years ago saw a much higher rate of suicides due to `failure in examination', according to NCRB data. The situation then improved dramatically, before apparently worsening again. Could the introduction of the 10+2+3 system in 1977 have helped ease the pressure on students by putting in place a uniform system which replaced different schooling systems and also adding one additional year of schooling? Perhaps. Today's suicide rates due to exam failure may actually be closer to this period if one considers the student population rather than the overall population, since a much larger section of the population are students now.
Student suicides, 1995-2019
Chethan Kumar, September 7, 2020: The Times of India
In 2019, at least one student died by suicide every hour in India. The year recorded the highest number of student suicides, 10,335, in the past 25 years for which data is available.
Between January 1, 1995, and December 31, 2019, India lost more than 1.7 lakh students to suicide. Of these, nearly 52% were reported in the past decade, while the remaining 85,824 were reported between 1995 and 2008, according to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB).
Both sociologists and psychologists TOI spoke with said depression, mental health issues and addiction to drugs were the most common reasons. Dr MS Dharmendra, consultant psychiatrist, Manasa Neuropsychiatric Hospital, told TOI: “Coping mechanisms and support systems are important. Biological factors like genetic predisposition to mental illnesses also play a role. A person with a higher level of predisposition may go on to develop a clinical illness which can become a risk factor for self-harm or suicide. It depends on how they are able to handle stress.”
While 2019 saw the highest number of student suicides in absolute terms, this category accounted for 7.5% of overall suicides (1.39 lakh), which is marginally less compared to 7.6% in 2017, which saw 9,905 cases. However, the overall number of suicides in 2017 was more than 7% lower than in 2019.
A state-wise analysis in 2019 shows that just five — Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh — account for more than 44% of 10,335 student suicides that year.
Child rights activists also point out that many students, especially those above the age of 10 or 12 years, struggle to find avenues to vent their anxiety, which makes stress management difficult.
Between 1995 and 1999, student suicides accounted for more than 5.2% on average, with 1995 (6.6%) being the worst year. In five years between 2000 and 2004, only one year saw student suicides making up 5.5% of the total suicides, while it was under 5% in four years and 5% in 2001. From here, the next five years also saw such cases being under 5.5%. Between 2010 and 2014, the last two years saw such cases make up more than 6% of the total. From there, every year has seen such cases account for more than 6%. In the past four years, such cases have accounted for more than 7% of the total suicides.
Between January 1, 1995, and December 31, 2019, India lost more than 1.7 lakh students to suicide. Of these, nearly 52% were reported in the past decade, while the remaining 85,824 were reported between 1995 and 2008, according to the National Crime Records Bureau.
Economic reasons
Unemployment, poverty and bankruptcy/ 2019
More than 1.3 lakh people committed suicide across the country in 2019, and 8% of the deaths were linked to unemployment, poverty and bankruptcy, according to the latest report of the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB). There were more deaths because of financial distress compared to 2018, reports Chethan Kumar.
Among the states, Karnataka reported the highest number of suicides — 2,474 — mainly because of the three factors — with only Maharashtra (2,410) coming close. The growth in Karnataka’s statistics in these categories was higher than the national average.
Psychiatrists say financial uncertainty is deeply upsetting people with and without means and stress levels are higher for those with families. Many people whose financial status and standard of living dropped after a period of stability or affluence struggle to cope more than others. “Social stigma and ignorance often prevent people from seeking treatment. But in most cases, a severely depressed individual cannot afford treatment, which can add to stress,” said a psychiatrist.
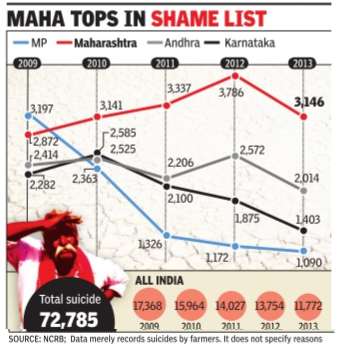
Farmers' suicides
See also Farmer suicides: India
No let-up in suicides by farmers
Deeptiman.Tiwary @timesgroup.com New Delhi:
[The Times of India] Aug 03 2014
A look at government data since 1995 to 2012 shows that no party has succeeded in putting a stop to this scourge.
In fact, in its previous stint in power the NDA fared worse than the Congres. It saw a 31% increase in farmer suicides compared to the previous regime. Under UPA's next five years the figure marginally increased by 2%.
Among states, Maharashtra has the worst record for farmer suicides. During 1995-1999, BJP-Shiv Sena regime saw 10,000 farmers end their lives. From 1,083 farm er suicides in 1995, the re gime witnessed 2,409 farmer taking their lives in 1998.
The following Congres regime was worse. Between 1999 and 2003, over 16,000 farmers committed suicide in the state. In the next nine years of Congrss-NCP rule in Maharashtra, 33,702 farmers ended their life.
In Madhya Pradesh, BJP's second showcase state after Gujarat, the situation has been no better. During the Congres regime of 19982003 under Digvijaya Singh, over 13,000 farmers committed suicide. Since then over 22,000 farmers have ended their lives in MP under the BJP regime.
In Andhra Pradesh, both TDP and Congres, which have ruled the state during the period, sail in the same boat. During TDP's regime of 1995-2003, over 16,000 farmers committed suicide. In the following 10-year regime of the Congres's YS Rajasekhara Reddy and others this figure increased to over 21,000.
In Karnataka, between 1995 and 1999 under Janata Dal government, over 10,000 farmers committed suicide. This increased to 12,000 in the next regime under Congres. Between 2004 and 2012, under two years of Congres and rest of BJP rule, over 18,000 farmers ended their lives.
In undivided AP
Health-related suicides alarmingly high in AP
TNN | Jul 1, 2013
HYDERABAD: Disease pushed more people in Hyderabad and rest of the state to end their lives than in any other state in 2012, according to data recently released by National Crime Records Bureau.
The data also shows that illness has become the single largest cause for suicide in the state.
Andhra Pradesh recorded 4,232 suicides last year that was attributed to illness, the highest for any state in the country. Of the total 14,238 suicides reported in the state during 2012, illness was found to be largest causative factor accounting for 30% of the deaths and far outnumbering poverty or unemployment, which were said to be cause for 1,308 suicides.
The state also topped the national chart in 2011 and registered a slight increase this year.
Also, of total suicides in the state, 5,094 were in the high productivity age group of 30-44 years, second only to Maharashtra which reported 5,311 suicides — the highest in the country — which experts say is not a good sign for any economy.
Major diseases driving people to commit suicide include AIDS, cancer, paralysis and mental illness. While 145 suicides were attributed to AIDS, 134 cancer victims killed themselves. The figures for these two diseases are also highest in the country. Mental illness resulted in 1,162 suicides.
"Despite widespread education there still is stigma associated with diseases like AIDS. Learning about the diagnosis itself could drive people to take the extreme step, particularly women. But in the case of cancer-related suicides, it is high treatment costs," said Dr Sukanya Rao, a private practicing gyneacologist in the city.
"Despite existence of schemes like Arogyasri in the state, we get to hear from relatives of deceased that they were unaware of their options. Creating awareness about such schemes is an important aspect of intervention," she added.
A senior police officer on anonymity explained that intervention may not be possible for government due to the nature of investigations being carried out by the police.
Suicides due to illness
One in 5 suicides in India due to illness
Ekatha Ann The Times of India Nov 05 2014
Chennai:
2013: 26,426 People Suffering From Various Ailments Chose To End Their Life
Shame and pain caused by an ailment was the reason for one in every five suicides in India last year.
Data compiled by the National Crime Records Bureau show 26,426 people in the country suffering from various ailments, including cancer, AIDS and paralysis, chose to end their lives last year. Tamil Nadu had the highest number of suicides linked to illness in 2013, with 4,362 people taking the extreme step. o “After family problems, termi nal illness is one of the biggest reaa sons for people to take the extreme l step,“ said P V Sankaranaraya e nan, a counsellor at suicide pret, vention organization SNEHA, l which also operates a helpline. He w said most of the calls they receive f are from those who are bedridden s, or in pain. “They feel guilty for bea ing a burden on their families.
Some are lonely and frustrated.
They think no one understands k their pain,“ he said, adding that 2 the number of such suicides could be higher as families tend to cover it up as natural death.
After prolonged illness, “insanity“ was the second reason that pushed people to the edge, constituting 30% of suicides linked to ailments. “There are studies showing the link between mental health and suicide. A physical ailment only pushes the person further to the brink. Unfortunately , secondary depression because of an illness is often ignored,“ said Dr R Padmavati of Schizophrenia Research Foundation.
The number of people with cancer committing suicide has seen a significant jump, with Kerala taking the lead with 155 such cases. Dr C S Mani of Cancer Research and Relief Trust said patients who come to him feel “setbacks“ at multiple levels: during diagnosis, when they have a relapse and when they are recommended palliative care. “There comes a point when there's no treatment available to cure the patient as the chemotherapy and the medication have proved ineffective. That's when we treat just the symptoms and wait for the disease to take over. Sometimes death is quick, at times it is long and painful,“ said Dr Mani. “For many , it is the fear of pain that takes over,“ he said, adding that suicidal tendencies usually creep in at this stage.
Dr N Kathiresan, an oncologist at the Cancer Institute, Adyar, said many patients preferred death over amputation. “We show them examples of people who have reached heights despite not having a limb. Often it works, sometimes it doesn't,“ he said. He recalled a recent case of a boy from Bihar who had to get his leg amputated. “He didn't respond to the chemotherapy . When we told the family we would have to amputate his leg, the family refused to comply . We tried advising them. The disease soon took over,“ he said.
Experts say besides giving importance to palliative care, hospitals could have more counsellors. “Doctors must also be trained to handle patients sensitively and pick up signs of depression. The mental and emotional health of a patient is often ignored. This has to change,“ said Dr Padmavati.
Spouse
Wife’s Suicide: Cruel man not always guilty
From the archives of The Times of India 2010
New Delhi: A husband found to have tortured his wife cannot be automatically held guilty of abetment of her suicide, the Delhi high court has said. HC made the observation on an appeal filed by a man challenging the judgment of a lower court which had convicted him of torturing his wife and abetting her suicide.
‘‘Merely because the court has held that Shailender (husband) is guilty of subjecting wife to cruelty and has convicted him under Section 498-A IPC (cruelty), by itself, would not be sufficient to convict him under Section 306 (abetment of suicide) as well,’’ Justice A K Pathak held. ‘‘Conviction of Shailender under Section 498-A is maintained. But his conviction under Section 304-B IPC and sentence awarded therein are set aside,’’ the court said.
Sonia, a student of Delhi College of Engineering, committed suicide in 2005. Cops found that she didn’t share a good relation with her husband who used to harass her. The trial court had convicted him for subjecting her to cruelty and said this forced her to commit suicide. But HC noted, ‘‘The utterances to the disliking of the deceased and the other acts of Shailender may be sufficient to attract ingredients of offence under Section 498-A, but it would not be sufficient to presume that he had abetted her suicide.’’
Husband’s affair not cruelity: SC
Feb 19 2015
Husband's affair not cruelty, says SC in woman's suicide case
The Supreme Court has ruled that a husband's illicit relationship with another woman may not amount to `cruelty' towards his wife or count as a ground for abetment to her suicide. In a case from Gujarat, a married couple had a strained relationship and were contemplating divorce. The wife had confided in her sister about the breakdown of the marriage, saying she would leave her marital home soon. But later, she committed suicide by consuming poison.
The prosecution accused the husband and his parents of cruelty and alleged that the woman was driven to suicide as her husband had an illicit relationship. The trial court and the high court convicted the accused.
But an SC bench of Justices S J Mukhopadhaya and Dipak Misra noted that the husband and wife had started living separately in the same house. “True, there is some evidence about the illicit relationship and even if the same is proven, we are of the considered opinion that cruelty , as envisaged under the first limb of Section 498A IPC, would not get attracted. It would be difficult to hold that the mental cruelty was of such a degree that it would drive the wife to commit suicide,“ it said.
Writing the judgment for the bench, Justice Misra said, “Mere extra-marital relationship, even if proved, would be illegal and immoral, as has been held by the Supreme Court earlier but it would take a different character if the prosecution brings some evidence on record to show that the accused had conducted in such a manner to drive the wife to commit suicide.“
The SC bench acquitted the accused in the absence of any other evidence to establish mental cruelty of the degree alleged.
Mass- (simultaneous multiple-) suicides
Delhi/ NCR: 2013-18
Somreet Bhattacharya, Why this ‘mass suicide’ was different, July 2, 2018: The Times of India

From: Somreet Bhattacharya, Why this ‘mass suicide’ was different, July 2, 2018: The Times of India
In Most Cases, Depression Or Money Crisis Led To Step
Suicide pacts are nothing new in the national capital, but deaths on such a large scale as what was witnessed in Sant Nagar, Burari have never been seen in the past. Moreover, such extreme steps being taken over extreme religious beliefs have also never been witnessed. In most cases where a person killed self and other family members, the reason was either financial duress, depression, illness or death of a family member.
In February this year, a couple hanged themselves at their home in Govindpuri. They were depressed due to financial losses. The man, Mohit Bagga, and his wife Arpita had sent a WhatsApp message to their relatives in Ranchi telling them about their last wishes.
In March, three members of a family, including a 10-year-old girl, were found dead at their house in Okhla. The man, Vikas, had poisoned his wife Lalita and daughter before consuming rat kill. Their six-year-old son, who had gone to a neighbour’s house to get “prasad”, was saved.
On December 31, 2017, three members of a family, including an eight-year-old boy, were found dead at their house in southwest Delhi’s Chhawla. The man, Ajay Kumar, also tried to kill his daughter, but she survived. Relatives had told TOI that Ajay was suffering from depression after his elder brother committed suicide a few days before this incident.
On September 9, 2016, a businessman, Bhagwan Das, his wife Sharda and their daughter Sunita allegedly entered into a suicide pact and killed themselves at their house in Jaffarpur Kalan. The man wanted his only son to become a doctor and settle abroad. After the youth, who was pursuing MBBS from Russia, died suddenly, the family went into depression.
An officer with an intelligence agency had killed himself along with his wife and two children at their home in Defence Colony in 2014.
In 2013, two incidents of alleged suicide pacts came to the fore. On April 8, 55-year-old Rajinder Saxena poured kerosene on his wife Amrita and sons Tipu and Soyam and set them on fire before jumping in with them at their house in Uttam Nagar. On May 31, the wife, son and daughter of a Delhi Police ASI committed suicide in east Delhi after he scolded them over their exam results.
The same year, a family of three committed suicide at their house in Begumpur due to financial losses. The man, Rajesh Gupta, strangled his wife Uma and eight-year-old daughter Shweta and then consumed poison.
Student suicides
2014-16
Chethan Kumar, One student kills self every hour in India, January 8, 2018: The Times of India

From: Chethan Kumar, One student kills self every hour in India, January 8, 2018: The Times of India
Data Sent To MHA By UTs, States Paints Grim Picture
On May 14, 2017, Bhopal police said that at least 12 students, 6 of them girls, had committed suicide in parts of Madhya Pradesh as they were depressed over their Class X and XII results. In August, a 15-year-old west Bengaluru student’s death was linked to the dangerous online game, Blue Whale Challenge, but it was later found to be otherwise.
From issues at college and school to drugs and depression over broken families, to fights with friends and breakups, students in India are killing themselves at afast rate, with 26 suicides reported every 24 hours. Going by the latest data sent to the home ministry by all states and UTs, 9,474 students committed suicide in 2016 — at the rate of more than one every hour — with Maharashtra and Bengal recording the most, while there was none reported in Lakshadweep.
While psychologists say clinical depression, followed by conditions like schizophrenia and other mental health issues and addiction to drugs and alcohol are the three top reasons, sociologists and rights activists point to what they say is psychosocial problems.
Sociologist Samata Deshmane says, “Society is transforming, and people are finding it difficult to cope with it, whether it is apparent or otherwise. One of the oldest definitions of our species says that we are social animals, but today we are less social and more individualistic. Apart from things like caste and religion, which also unite people at a superficial level, people are forced to be competitive and worry only about oneself, often depriving several others of a cushion.”
Bengaluru-based Child Rights Trust director Nagasimha G Rao argues that students, especially those aged over 10, don’t have avenues to vent their feelings, and other experts agree with him.
“Students are unable to manage their stress. They don’t have a place to vent their thoughts either at home or at school or college. Many battle an identity crisis. Uncertain about their future, they begin to isolate themselves and eventually slip into depression,” Rao says.
Overall, an average of three years — 2014 to 2016 — shows that the trend was similar with at least one student committing suicide every hour. The three years together saw 26,476 students take their own lives in the country.
Dr MS Dharmendra, a consultant psychiatrist, says, “There can be multiple factors. There could be sociological and psychological factors too, and it all depends on how they are able to handle stress. And then there are biological factors: All of us are born with a certain predisposition to depression. Some have low vulnerability, in a few others it may be high. The same situation may cause depression in some, and not in others.”
C
Year-wise statistics
1990-2016
Rate in India much higher than international average
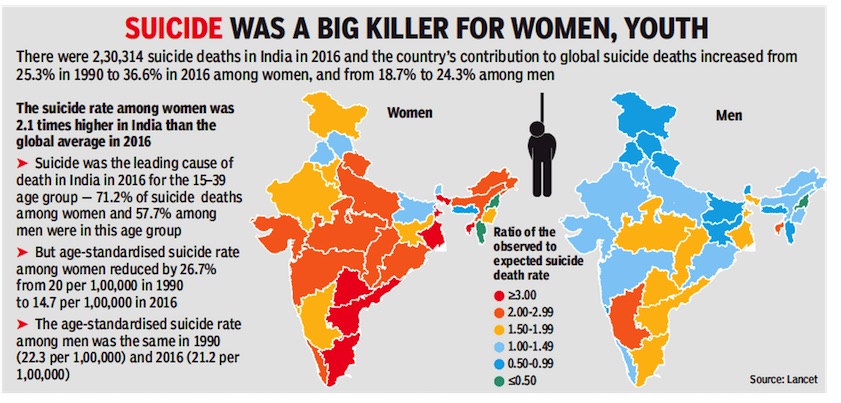
From: September 13, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Suicidal rate in India- 1990-2016
Details of the study
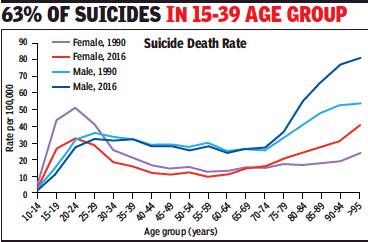
From: DurgeshNandan Jha, ‘37% of women committing suicide in world are Indians’, September 13, 2018: The Times of India
Men Account For 24% Of Cases: Lancet
Every third woman who committed suicide in 2016 was an Indian. Although Indians accounted for 18% of the global population in 2016, a study published in the Lancet Public Health journal on Wednesday showed that India accounted for 37% of the global suicide deaths among women and 24.3% among men.
Rakhi Dandona, one of the lead authors of the study, told TOI that married women account for the highest proportion of suicide deaths among women in India.
Marriage, she said, is known to be less protective against suicide for women because of arranged and early marriages, young motherhood, low social status, domestic violence, and
economic dependence. “Lack of access to mental health facilities for women could also be a factor behind the high incidence of suicide related death among them,” Dandona, a professor at Public Health Foundation of India, added. She said trends in Suicide Death Rate in women suggest the need to further assess the complex relationships between gender and suicidal behaviour in order to facilitate women-specific suicide prevention strategies.
The study, titled ‘Gender differential and state variations in suicide deaths in India: the Global Burden of Diseases Study 1990-2016’, is based on an analysis of suicide death trends across the country. It shows that 63% of all suicide deaths are in the 15-39 age group. “Suicide is the top cause of death in this age group in India. Globally, it is ranked third,” it said.
The study said there was an increase of 40% in the number of suicide deaths between 1990 and 2016, with an estimated 2,30,314 deaths in 2016. It found wide variations in the suicide rates across states. Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, West Bengal and Tripura had high rates for both men and women while Kerala and Chhattisgarh had high suicide death rates for men.
The suicide death rate for women in India is 15 per one lakh women, which is double than the global suicide rate for women in 2016, which is 7 per one lakh women.
Suicides in 2012
Half of Mumbai's suicide victims below age 30
Sumitra Deb Roy & V Narayan, TNN | Jun 25, 2013
The metros
Suicides in Mumbai rose by an alarming 12% in 2012 after witnessing a dip the previous year. A staggering 50% of those who took their lives in the city were younger than 30 and among these more than half were women, reveals the latest data of the National Crime Records Bureau.
A total of 1,296 people killed themselves in the financial capital last year, placing it fourth in the list of Indian cities with the highest suicide incidence. Chennai led the death chart with 2,183 suicides, followed by Bangalore (1,989) and Delhi (1,397).
National suicide rate
The national suicide rate (total suicides per lakh population) stood at 11.4 in 2012, a few points higher than Mumbai's 7 and a few points lower than Maharashtra's 14.
Gender
Generally, men accounted for more suicide deaths than women. The trend was true in Mumbai, where 59% of the suicide victims were men, and in Maharashtra, where 70% of the victims were males. Nationally too, the ratio of male to female suicide victims was 66.2 to 33.8. An exception to the trend was the age group of up to 14 years; in Mumbai, thrice the number of girls in this age bracket killed themselves than boys.
Dr Lakshmi Vijaykumar, who was responsible for the inclusion of suicide prevention in the National Mental Health Policy of India, said there is wide variation in suicide rates within the country. "The southern states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu have a suicide rate of more than 15, while in the northern states of Punjab, UP, Bihar and Kashmir, the suicide rate is less than 3. This pattern has been stable for the last twenty years."
Vijaykumar added that smaller cities are worryingly catching up with metros in recording high suicide rates. "Also, the fact that 71% of suicides in India are by persons below the age of 44 imposes a huge social, emotional and economic burden on our society."
Causes
Family problems were revealed in the NCRB data to be the single largest factor driving people to end their lives. The factor was given as the cause of 40% suicides-264 men and 262 women-in Mumbai and 26% suicides across the country. Major illnesses, such as cancer and AIDS, taken together constituted the second biggest suicide cause-causing 28% of the deaths-in Mumbai. They were followed by drug addiction (6.9%), failure in exam (4.5%) and love affairs (4.5%). Boys and girls alike took their lives over love affairs.
Emotional reasons like failed marriage, relationship and love affairs drove most of the 534 female suicides in Mumbai. By contrast, the causes of the 762 male suicides were economic, relating to poverty and employment.
Method of suicide
Hanging emerged to be the most employed method to end one's life, with 917 of the 1,296 victims in the city using it. In Maharashtra, 7,055 people killed themselves this way. Self-immolation was the second most common suicide method in Mumbai and consuming poison the third. Surprisingly, only one person committed suicide in the city by coming under the train, though the figure for the category was 128 in the state.
Referring to the allegations of abuse, criminal lawyer Adhik Shirodkar questioned how they could be proved with the victim dead. "A suicide note helps police give direction to the probe and establish the cause of death. But it can't be the sole basis for arresting someone."
Many lawyers, who have worked on similar cases, called for guidelines to control police action in such cases. "This type of action may also lead to questions about the police's intentions in going after people without any real evidence," a criminal lawyer said.
India, 2012-16: The world's suicide capital?

The Times of India Sep 05 2014
India is world's suicide capital with 2.6L cases/ yr
India records by far the largest number of suicides in the world, accounting for nearly a third of the global total and more than twice as many as China, which is second on the list.
India also has the highest rate of suicides among young people — those aged 15 to 29 years.
These were among the sobering facts revealed in a report released by the WHO, “Preventing Suicide, A Global Imperative”. The report noted that an estimated 8 lakh suicide deaths occurred worldwide in 2012. It is the second leading cause of death in 15-29-year-olds.
In 2012, India recorded nearly 2.6 lakh suicides, dwarfing China’s 1.2 lakh.
India’s overall rate of suicides (incidents per lakh population) was 12th at 20.9. The worst countries on this parameter were North and South Korea, Guyana, Lithuania and Sri Lanka. Hungary, Japan, the Russian Federation and Belarus also had higher suicide rates than India. The Scandina vian countries, Sweden, Norway and Denmark — often perceived as societies with high suicide rates — had much lower rates.
In richer countries, three times as many men die of suicide as women, but in low and middle-income countries, the male-to-female ratio is much lower at 1.5 men to each woman. Globally, suicides account for 50% of all violent deaths in men and 71% in women. n India, the ratio was about I 1.6 with close to 1.6 lakh men committing suicide in 2012 compared to just under 1 lakh women. In four countries in India's immediate neighbourhood -China, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Afghanistan -women outnumbered men among suicides. Only in Iraq and Indonesia was the proportion of women to men among those committing suicide higher than these countries.
India, despite its horrific statistics, has actually seen a decline in the tendency to commit suicide since 2012, with the rate declining by 9.2% over this 12-year period.China, in the same period, saw its suicide rate drop by 59%.
India is a clear exception to the global pattern of the 70+ age group having the highest suicide rates. At 21.1 per lakh population, suicides among this age group are only about as common as among the entire population. Risk factors associated with the health system and society at large include difficulties in accessing health care and in receiving the care needed, easy availability of the means for suicide, inappropriate media reporting that sensationalizes suicide and increases the risk of “copycat“ suicides, and stigma against people who seek help for suicidal behaviours, or for mental health and substance abuse problems.
Suicides in 2013
Numbers
2013 records 15 suicides every hour
Deeptiman Tiwary New Delhi:
TNN
The Times of India Jul 01 2014
As many as 15 suicides took place every hour in 2013 in India with suicides due to illegitimate pregnancies showing a sharp rise of 64.5%. The latest data from National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) for 2013 shows that more than one lakh people (1,34,799) took their lives for various reasons ranging from family problems to illness during the year.
According to the data, Tamil Nadu (12.3%), Maharashtra (12.3%), AP (10.8%), West Bengal (9.7%) and Karnataka (8.4%) together contributed 53.5% of suicide victims.
`Family problems' (24.0%) and `Illness' (19.6%) continue to be the greatest killers accounting for 43.6% of suicides.
It also seems to suggest senior citizens are most depressed in Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh, where 54.9% of suicide victims were in the age group 60 years and above.
Nearly 70.8% of the suicide victims were married men while 66.6% were married women. Students constituted 6.2% of the total suicide victims while one in every six victims was a housewife.
Causes
More people ended lives over love than poverty
Deeptiman Tiwary TNN
The Times of India Jul 02 2014
More people commit suicide daily due to unrequited love or a failed affair than due to poverty , bankruptcy or unemployment in the country .
According to the 2013 NCRB data, there were 12 suicides every day due to love affairs comparedto five for poverty, seven for bankruptcy and six for unemployment. In fact, love affairs have turned out to be third biggest kill ers after family problems and illness. This is well reflected in the fact that 135 suicide victims fall in the age group of 0-29.
The data shows that 89 people commit suicide every day due to family problems while 72 do it because of illness. Cancer has turned out to be the biggest reason for which most suffering from illness commit suicide, followed by paralysis and AIDS.
2014

2014, NCRB: Suicides and poverty
The Times of India, Jul 27 2015
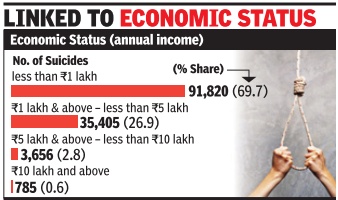
Deeptiman Tiwary
70% of all suicide victims had annual income of Rs 1L
14 data showed poverty linked to deaths
While people commit suicide for various reasons, a poor person is more likely to kill himself for the same reason than one who is rich.
The data from NCRB for 2014 shows a direct relationship between poverty and suicide. While the exhaustive data segregates suicides according to various causes, the common thread running through a majority of suicides is poverty . According to the data, 70% of all suicide victims had an annual income of less than Rs 1 lakh. Conversely, those who earned over Rs 10 lakh a year made up for just 0.6% of victims. This simply means that even if the reason for suicide is absolutely personal, such as failure in love or a family dispute, a poor person is more likely to end his life than a rich person. The data shows that as the economic prosperity of people improves, their rate of suicide decreases. It also shows that those who earned between Rs 1-5 lakh made up for 27% of victims, while those who made between Rs 5-10 lakh accounted for 2.8% of suicides.
Curiously , Bihar being one of the poorest states had one of the lowest suicide incidents among the poor (with income of less than Rs 1 lakh). It recorded just 408 suicides as against a prosperous Maharashtra which had the highest share of poor (12,590) people ending their lives. Another prosperous state, Tamil Nadu, was a close second with 11,738 suicides by the poor. Given that in India, one's educational qualification is often related to one's economic status, it is also reflected in suicide trends.
According to NCRB data, 75% of those who committed suicide had not studied beyond Class 10. It can be presumed that this must have affected their employability in better jobs and thus adversely impacted their economic wellbeing. That the government is rightly stressing on skill development is reflected in the fact that those with professional qualifications are least likely to commit suicide.
2014: Self employed more prone to suicides than service men
The Times of India, Jul 20 2015

Deeptiman Tiwary
`Self-employed more prone to suicide than those in service'
Of all those who ended life in 2014, 7.5% were bizmen: NCRB
Self-employed people are more prone to committing suicide as compared to those engaged in service. In service too, private sector employees are more likely to commit suicide than those working in the government's employ . National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data for 2014 shows that self-employed people (including agriculture and business) accounted for 19.7% of all suicides, making them the biggest single group among those who committed suicide. Among the self-employed though, businessmen were safer than those engaged in agriculture. Of all the suicide victims in 2014, 9.4% were engaged in agriculture while only 7.5% were engaged in business. The salaried class, with financial security , is just as vulnerable as businessmen, accounting for 7.5% of all suicides. Government service, however, is a much safer bet for a long life. People employed in government service comprised only 1.7% of the to tal number of suicides. With no job security , private sector employees are more vulnerable. They accounted for 4.7% of all suicides. Employees of public sector undertakings (PSU) accounted for only 1.1% of the victims. Students and the unem ployed accounted for 6.1% and 7.5% of the total number of suicides, respectively . However, the group most vulnerable to suicide is housewives. They accounted for 15.3% of all suicides committed in 2014. Making a case for economic independence of women, they also made up for 47.4% of all female victims.
Most housewives committed suicide in Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh. The two states accounted for 24.5% and 24.1% of the nationwide suicide toll among housewives, respectively .
Government servants accounted for 22.2%, 16%, 15.4%, 12.2% & 6.9% of the total suicides in Daman & Diu, Manipur, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram, respectively . In Andaman and Nicobar, 52.9% were employed in the private sector. In Chandigarh, the figure stood at 27.6%.
2014: Married men twice likely to commit suicide than married women

The Times of India, Jul 26 2015
Deeptiman Tiwary
Govt data reveals trend, rate drops after divorce
NCRB DATA - Hubbies twice as likely to end lives than wives
Married men are twice as likely to commit suicide than married women. However, after divorce or in the case of the spouse's death, men's propensity to commit suicide falls sharply . According to latest data by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), close to 60,000 married men committed suicide in 2014 as compared to 27,000 married women. However, 1,400 widowers ended their lives compared to 1,300 widows. Similarly , around 550 divorced men committed suicide as compared to 410 divorced women.
The data shows that, overall, 66% of all suicides were committed by married people. Only 21% of those who ended their lives were unmarried, while widows widowers and divorced people made up for less than 3% of all suicides. The data throws no light on why such a trend exists. How ever, analysis of other data on suicides gives some explanation.
First, in overall suicides too men score twice as much as women. Close to 90,000 men committed suicide for various reasons in 2014 as against about 42,000 women.According to the 2011 census, widowed and divorced women far outnumber men with similar status.There are 3.5 times more widowed women than men and more than double divorced women than men.
Among reasons, family problems score the highest. They claim lives of over 21% of all suicide victims. It is also the biggest killer of men, claiming over 18,000 lives in 2014. Family issues cost over 9,900 women their lives. Illness as a reason follows closely , leading to 18% of all suicides.Here, too, number of men (16,078) is twice that of women (7,663).
Age-wise analysis of suicides also compares with data on suicides of married men and women. Till the age of 18, data shows that men and women are equally prone to suicide. For about 5,500 men who committed suicide in 2014 in this age group, there were 5,300 female victims. The gap begins to increase af ter 18 years -the age after which people choose to marry . In the 18 30 age group, 60% of victims wer men. In the 30-45 bracket, abou 72% victims were men, while in the 45-60 group, men accounted for almost 80% of victims.
See also
Suicides: India