Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore
(→Research projects) |
(→2017/ Malaria new tool for diagnosis created) |
||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
==2017/ Malaria new tool for diagnosis created== | ==2017/ Malaria new tool for diagnosis created== | ||
| − | [http://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/iisc-new-tool-to-diagnose-malaria/article19896288.ece Aswathi Pacha, October 21, 2017: The Hindu] | + | [http://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/iisc-new-tool-to-diagnose-malaria/article19896288.ece Aswathi Pacha, October 21, 2017: ''The Hindu''] |
| Line 143: | Line 143: | ||
According to the researchers, the tweezers technique can be used as a general screening tool for all stages of malarial infection. “The technique is very easy and does not require trained personnel as it is fully automated. Very little blood is needed, and it can be drawn at any time of the day. The changes can be seen in the blood even when the parasite count is very low due to the bystander effect,” Paul adds. | According to the researchers, the tweezers technique can be used as a general screening tool for all stages of malarial infection. “The technique is very easy and does not require trained personnel as it is fully automated. Very little blood is needed, and it can be drawn at any time of the day. The changes can be seen in the blood even when the parasite count is very low due to the bystander effect,” Paul adds. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Superbugs’ antibiotic resistance/ 2021 == | ||
| + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL/2021/08/12&entity=Ar00904&sk=82F5C445&mode=text Chethan Kumar, August 12, 2021: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Researchers of the Molecular Biophysics Unit, Indian Institute of Science (IISc), have found a way to block bacteria from flushing out antibiotics. This holds the potential of making existing drugs more effective against drug-resistant bacteria or superbugs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | They used a specific antibody found in Indian camels (at the National Research Centre on Camel, Bikaner) to block the transporter. The team, led by Aravind Penmatsa, assistant professor, MBU, has demonstrated it in laboratory conditions. Bacteria are generally killed by antibiotics. One of the mechanisms they use to gain resistance is called efflux, the process in which bacteria transport compounds such as drugs outside the cell, and transporters play a crucial role in enabling the pathogen to perform this. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Transporters are among major components in multidrug resistance armoury of bacteria. IISc said its researchers “have solved the atomicresolution structure of one such transporter, NorC, in complex with an Indian camelid antibody (ICab).” | ||
| + | |||
| + | “The process of efflux is very important for bacteria and a major strategy that hasn’t yet been explored as a therapeutic mechanism is to develop molecules to block it. If we can block these transporters, the drugs will gain efficacy. We can enhance efficacy of available antibiotics if we have blockers of efflux,” Penmatsa told TOI. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An IISc spokesperson said: “These insights will significantly help formulate strategies to counter transportermediated antibiotic resistance in pathogenic bacteria, using tools like camelid antibodies.” The study was primarily funded by the DBT-Wellcome Trust India Alliance and the department of biotechnology. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|IINDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE (IISC), BANGALORE | ||
| + | INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE (IISC), BANGALORE]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Institutions|IINDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE (IISC), BANGALORE | ||
| + | INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE (IISC), BANGALORE]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Name|ALPHABETINDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE (IISC), BANGALORE | ||
| + | INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE (IISC), BANGALORE]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE (IISC), BANGALORE]] | ||
| + | [[Category:S&T|IINDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE (IISC), BANGALORE | ||
| + | INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE (IISC), BANGALORE]] | ||
==2021: low-cost ventilator== | ==2021: low-cost ventilator== | ||
Revision as of 05:22, 14 August 2021
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Contents |
Ranking in the world, year-wise
2013: IISc among world’s Top 400
IISc only Indian institute in top 500 global ranking
Seethalakshmi S | TNN
Bangalore: Bangalore-headquartered Indian Institute of Science (IISc) has once again made the country proud. It is the only Indian institute that has made it to the top 500 in the 2013 Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU) which was released by the Center for World-Class Universities at Shanghai Jiao Tong University. The 104-year-old entity is ranked in the 301-400 category.
IISc, which was ranked 45 in the world ranking for Chemistry last year, is on 43rd spot this time. The premier institute has shown a dramatic improvement in Computer Science as well. From 101-150 in 2012, it is now listed in the 51-75 bracket. In Math, however, it retained last year’s ranking in the 151-200 slot. Harvard tops the global ranking, followed by Stanford and University of California, Berkeley. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Cambridge University are in fourth and fifth position respectively, in the ARWU rankings.
2017: 8th in small universities' ranking
IISc listed among world’s best small universities, Mar 07, 2017: The Hindustan Times
The Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, is in the eighth place in the list of top ten small universities in the world, according to an assessment that has three institutions each from France and Italy in the list.
CalTech is placed at the top of the Times Higher Education’s Best Small Universities in the World 2017, a release said.
The three French universities in the top 10 are École Normale Supérieure (second), followed by École Polytechnique (fourth) and École Normale Supérieure de Lyon (seventh).
Italy’s three in the top 10 are Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa in fifth place, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna in sixth and Free University of Bozen-Bolzano, tenth.
Small universities are defined by the publication as having fewer than 5,000 students and teach and research across more than four disciplines.
Seeta Bhardwa of Times Higher Education said: “The Best Small Universities in the World for 2017 highlights that small universities provide high student satisfaction and good working relationships between students and their professors”.
“Many students are drawn to smaller class sizes, higher teacher to student ratios and the community-like feel that a small university can provide”.
Collaboration with Rolls-Royce: low-noise technology for aircraft engines
IISc makes jet engines quieter
Rajiv Kalkod, TNN | Jul 14, 2013
Bangalore:Scientists at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore and IITBombay have helped Rolls-Royce develop low-noise technology for aircraft engines that are fitted in longhaul planes such as Boeing 747s and Dreamliners.
An 11-member team led by U Ramamurthy of IISc’s department of materials engineering began research in 2006 in collaboration with the UK-based company and recently delivered the technology.
Developed using ‘shape memory’ alloys, the technology brings down engine noise during landing and take-off. Defeaning noise levels of aircraft have triggered global protests from many residents staying near airports and forced adoption of rules such as a blanket ban on nighttime landings.
Partners: Rolls-Royce, IIT-Bombay, Imperial College, London
Rolls-Royce was involved in a tripartite research agreement with research groups in IISc and IIT-Bombay as well as Imperial College, London.
CUTTING EDGE
IISc & IIT-B develop low-noise technology to minimize engine sound while planes take off & land Tech involves silencer vanes that can operate at temperatures of 200 degrees Celsius and more IISc and IIT-Bombay collaborate with Imperial College, London, to make Rolls-Royce engines
Discovery goes beyond jet engines
The objective was to discover high-temperature shape memory alloy compositions with a new technique which could be adapted for engines,” IISc’s U Ramamurthy said.
The professor and his student Vyasa Shastri explained that a chamber in the engine is fitted with silencer vanes. “When the plane takes off or lands, the silencers become operational. This reduces engine noise,” Ramamurthy said. The vanes were capable of operating at temperatures of 200 degrees Celsius and higher.
“It’s been a great collaboration, developing a method to screen a large number of alloys. This has applications beyond the current material that could develop into actuators for more aircraft, into a general tool for developing alloys. It’s been very high-profile within Rolls-Royce, and very exciting for the group,” said David Dye of the department of materials, Imperial College, London.
Shape memory alloys
T hey are materials capable of remembering their original shape (hence called “smart materials”). The trigger for memory is usually temperature. For nickel-titanium (the leading shape memory alloy), the temperature range is minus100 degrees celsius to 80 degrees celcius
IISc slides 130 rungs in global varsity rankings
Chethan Kumar,TNN | Aug 26, 2014 The Times of India
BANGALORE: On an average, at least 10 institutions have overtaken Indian Institute of Science (IISc) every year in the global ratings since 2003, even though it continues to be the only one from India in the top 500. It has dropped 130 ranks in 11 years.
IISc, just like in 2013, continues to be ranked among the top 500 institutes in the Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU) 2014 done by the Center for World-Class Universities at Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
However, in 2013, it was close to 300, while its ranking is near 400 now, with over 50 institutes having overtaken it.
ARWU ranks universities on the basis of academic and research performance, including highly cited researchers, papers published, indexed in major citation indices, and per capita academic performance.
When IISc first made it to ARWU's list of top 500 institutes in 2003, it was in the 270-275 range. A decade later, it's near the 400 mark, dropping 130 ranks.
ARWU attributes this to the consistent drop in performance in subject-wise ranking. In 2013, IISc ranked 43 in Chemistry, while the ranking dropped to the 51-75 group this year. In 2009 (Chemistry), it ranked in the group of 76-101, retained the same position in 2010, jumped to 49th rank in 2011, 45th in 2012 and 43rd in 2013. But dropped to the 51-75 range this year.
In Computer Science, from the 51-75 group in 2013, IISc dropped to 101-150 this year. In English, where it had been in the 76-100 group since 2009, it dropped to the 101-150 group in 2014.
In natural sciences, the institute has stayed in the 151-200 group, the same as last year.
Sources in IISc credit other institutions of having performed well and feel the quality at the institute hasn't really dropped. IISc director Prof Anurag Kumar argues that the results of the efforts put in the past decade will yield results in a couple of years.
Research projects
2016: Ashwagandha offers hope for Alzheimer's
The Times of India, Jan 28 2016

Seethalakshmi S & Sunita Rao
IISc research offers hope to those with Alzheimer's
Ashwagandha May Reverse Memory Loss
The Indian Institute of Science (IISc) is in the midst of a path-breaking research using ashwagandha that offers a hope for people suffering from Alzheimer's disease. Dr Vijayalakshmi Ravindranath, chairperson at Centre for Neuro Sciences at IISc, is using an extract of the ashwagandha root (an ayurvedic plant) on mice with Alzheimer's disease. Her preliminary finding is that it can reverse memory loss.
The Tatas have pledged Rs 75 crore grant for the research being done on the IISc campus.
“Research worldwide both in pharmaceutical companies and academia have failed to find a cure for Alzheimer's disease. There is far less optimism as most drugs have failed in clinical trials We need to leverage the knowledge base of the tradi tional system of medicine such as ayurveda, which has been practised for more than 2,000 years. Understanding the knowledge base of these systems of medicine and using it effectively in the mo dern context is essential as we are set to see a large increase in cases of disorders of the ageing brain,“ Ravindranath told TOI.
“We are now purifying the mixture and reducing the effective dose. What is interesting is the way the ashwagandha worked in the mice. The extract did not work directly on the brain. Instead it enhanced a protein in the liver that is broken down and released into the blood to act as a sink for the amyloid and helps pull out the amyloid from the brain,“ she added.
The 2015 Nobel Prize for medicine was won by Chinese scientist Tu Youyou's for her discovery of artemisinin, a drug based on traditional Chinese herbal medicine. The drug is now part of standard anti-malarial regimens.
2017/ Malaria new tool for diagnosis created
Aswathi Pacha, October 21, 2017: The Hindu
The tool tests the rigidity of the cell
By studying the properties of normal red blood cells (RBCs) and parasite-infected RBCs, scientists at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, (IISc) have developed a new diagnostic tool for early detection of malaria.
Currently, visual microscopic identification of the malarial parasite Plasmodium inside red blood cells (RBCs) is used, but the new tool can detect the disease even in RBCs that do not themselves host the parasite but lie near the infected ones. RBCs that lie close to the infected ones appear rigid much like the affected ones and this helps in easy diagnosis. The results were recently published in Biomedical Journal.
Optical-tweezers
Blood samples with malaria infections caused by P. falciparum and P. vivax were collected from the Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute and studied. RBCs were separated out from the blood, and a single RBC was trapped in an optical tweezer trap. In this technique, laser beams are focused at the micron-sized RBC (like tweezers holding the RBC) under a microscope and imaged with a video camera.
The Brownian motion (random movement of particles) of the normal RBC was found to be different from the infected ones.
A photodetector was used to measure this motion of the trapped particle. The researchers quantified the fluctuations using the ‘corner frequency’ measurement. The corner frequency of normal cells was 25 hertz whereas it was 29 hertz for infected cells. The change in frequency was due to the difference in the rigidity of the cells; the infected cells were more rigid compared to the normal ones.
When trapped, the RBC gets folded as it is biconcave in shape and the time taken for folding inside the trap was measured. As the infected cells were more rigid they took about 1.33 seconds to fold whereas normal cells took only 0.8 seconds. A measure of folding time can also be used to determine whether a cell is infected.
Bystander effect
“Only 2-5% of the RBCs host the parasite. But we can see the rigidity in other RBCs in the infected pool also. This is called the bystander effect and it is very helpful in our tweezers study. P.vivax infects mainly the immature RBCs (reticulocytes) but due to this effect we could see changes in the mature RBCs not hosting the parasite too. We are yet to understand what exactly is released into the blood stream that causes rigidity even in the non-hosting cells,” says Apurba Paul from the Department of Physics at IISc and first author of the paper.
According to the researchers, the tweezers technique can be used as a general screening tool for all stages of malarial infection. “The technique is very easy and does not require trained personnel as it is fully automated. Very little blood is needed, and it can be drawn at any time of the day. The changes can be seen in the blood even when the parasite count is very low due to the bystander effect,” Paul adds.
Superbugs’ antibiotic resistance/ 2021
Chethan Kumar, August 12, 2021: The Times of India
Researchers of the Molecular Biophysics Unit, Indian Institute of Science (IISc), have found a way to block bacteria from flushing out antibiotics. This holds the potential of making existing drugs more effective against drug-resistant bacteria or superbugs.
They used a specific antibody found in Indian camels (at the National Research Centre on Camel, Bikaner) to block the transporter. The team, led by Aravind Penmatsa, assistant professor, MBU, has demonstrated it in laboratory conditions. Bacteria are generally killed by antibiotics. One of the mechanisms they use to gain resistance is called efflux, the process in which bacteria transport compounds such as drugs outside the cell, and transporters play a crucial role in enabling the pathogen to perform this.
Transporters are among major components in multidrug resistance armoury of bacteria. IISc said its researchers “have solved the atomicresolution structure of one such transporter, NorC, in complex with an Indian camelid antibody (ICab).”
“The process of efflux is very important for bacteria and a major strategy that hasn’t yet been explored as a therapeutic mechanism is to develop molecules to block it. If we can block these transporters, the drugs will gain efficacy. We can enhance efficacy of available antibiotics if we have blockers of efflux,” Penmatsa told TOI.
An IISc spokesperson said: “These insights will significantly help formulate strategies to counter transportermediated antibiotic resistance in pathogenic bacteria, using tools like camelid antibodies.” The study was primarily funded by the DBT-Wellcome Trust India Alliance and the department of biotechnology.
2021: low-cost ventilator
Shilpa Phadnis & Sujit John, May 19, 2021: The Times of India
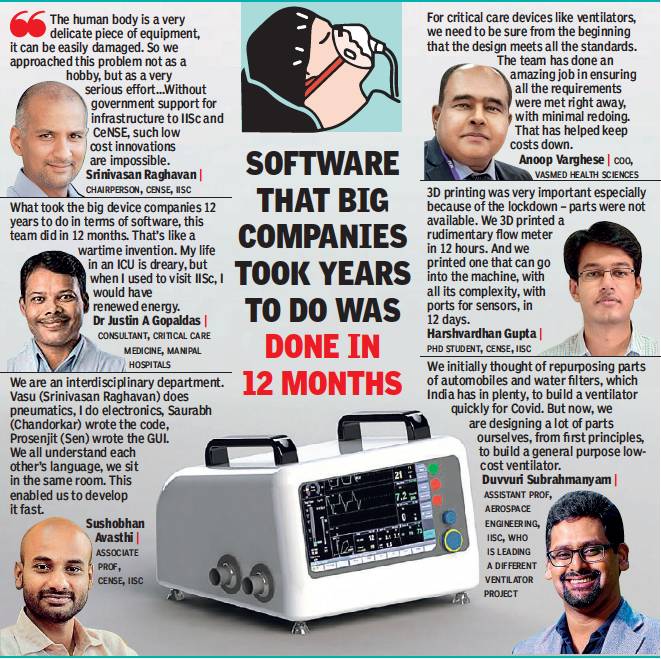
From: Shilpa Phadnis & Sujit John, May 19, 2021: The Times of India
In March last year, as the Covid-19 pandemic hit India, Srinivasan Raghavan, chairperson of the Centre for Nano Science and Engineering (CeNSE) at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) in Bengaluru, asked Dr Justin Gopaldas, consultant at the Critical Care Medicine department at Manipal Hospitals, what kind of healthcare requirements might emerge. Dr Gopaldas felt ventilators may soon be in short supply. Raghavan assembled a team from CeNSE, understood the intricacies of a ventilator from Dr Gopaldas, and decided to build as sophisticated a ventilator as they possibly could in the short time they had.
A ventilator is a complex equipment, designed mostly by the world’s big medical device companies. It is needed when our lungs fail, which is what happens in serious cases of Covid-19. The ventilator gets the air from outside the body into the blood, so that the various parts of the body function well until the lungs heal. And as the lungs heal, the ventilator should allow the body to take control.
Badly designed ventilators can cause harm. “When we breathe, we suck air and generate drag. But a ventilator pushes air, it stresses the lungs, making them vulnerable,” Dr Gopaldas says. There are different kinds of patients – those who can breathe a little, those who can’t. Some Covid infected lungs are very tight, so difficult to blow air into. A ventilator has to handle all these different requirements, and deliver the precise pressure, volume, and volumetric flow rate a patient needs.
So, the device is a mix of the pneumatics through which the air flows, and lots of sensors and control codes that control the pneumatics. “We quickly realised that 80-90% of the ventilator is not the pneumatics, but the support electronics and the controls. So we moved towards a microcontroller based system,” says Sushobhan Avasthi, associate professor at IISc. The lockdown made the team’s task tough. Many components were not easily available. They weren’t getting flow meters, so Harshvardhan Gupta, a PhD student at IISc, went into the CeNSE lab and 3D printed the parts.
Saurabh Chandorkar, assistant professor at IISc, wrote 80% of the code. “He’s an ex-Intel person, and he’s very good at writing those kinds of things,” Avasthi says. Prosenjit Sen, associate professor, wrote the graphical user interface (GUI) – the touchscreen that doctors use – in a week.
In 10 days, the first prototype was ready. And by day 17, a second version. But soon after, the first wave of the pandemic had waned, and the team slowed down. And it was only last month, when Dr Gopaldas saw his ICU overflowing that he once again called Raghavan about the state of the project. The team had started working with a medical device maker, Vasmed Health Sciences, to make the ventilator. The project was fasttracked. A final certification is expected any day now. The plan is to make 25 units by the end of the month.
The ventilator will be sold initially at Rs 1.5 lakh, a fraction of the Rs 7 lakh to Rs 20 lakh and more that imported versions cost. “We are able to do it because of all of IISc’s infrastructure funded by the government, and all of our salaries paid by the institution. The control codes are the heart of the ventilator and they are developed by us. But we will make it available free,” says Raghavan.
A lot still depends on funding to take the product to market. Or the government committing to procure a certain number of ventilators. Nonetheless, it’s a great story of what an industry-academia partnership is capable of.