Age at marriage: India
(→Impact of 2017 Consent judgement on Rajasthan) |
(→2015-16: 25% of wives aged 14-20 married as minors) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
[http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=25-of-wives-aged-14-20-tied-knot-12102017012020 Sushmi Dey, 25% of wives aged 14-20 tied knot when minors, October 12, 2017: The Times of India] | [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=25-of-wives-aged-14-20-tied-knot-12102017012020 Sushmi Dey, 25% of wives aged 14-20 tied knot when minors, October 12, 2017: The Times of India] | ||
| − | [[File: Child brides, some statistics, urban, rural and total, 2015-16, and a comparison with 2005-16.jpg|Child brides, some statistics, urban, rural and total, 2015-16, and a comparison with 2005-16; [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=25-of-wives-aged-14-20-tied-knot-12102017012020 Sushmi Dey, 25% of wives aged 14-20 tied knot when minors, October 12, 2017: The Times of India]|frame|500px]] | + | [[File: Child brides, some statistics, urban, rural and total, 2015-16, and a comparison with 2005-16.jpg|Child brides, some statistics, urban, rural and total, 2015-16, and a comparison with 2005-16; <br/> From: [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=25-of-wives-aged-14-20-tied-knot-12102017012020 Sushmi Dey, 25% of wives aged 14-20 tied knot when minors, October 12, 2017: The Times of India]|frame|500px]] |
Though the number of women marrying before 18 years of age in India has declined drastically over the last decade, it continues to be significantly high with more than a fourth of married women in the age group 14-20 having wedded as minors. | Though the number of women marrying before 18 years of age in India has declined drastically over the last decade, it continues to be significantly high with more than a fourth of married women in the age group 14-20 having wedded as minors. | ||
Revision as of 06:36, 13 October 2017
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Contents |
Age of marriage
The practice in other countries

From The Times of India

From The Times of India
The international practice
How widespread is the prevalence of underage marriages?
2005-15: Literacy rate, and percentage of women married before 18

See Graphic, 'Indian women: Literacy rate, and percentage of women married before 18, 2005- 2015...'
CENSUS 2011 - In 33% of marriages, women weren't 18
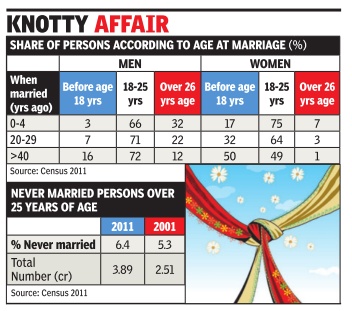
The Times of India Apr 03 2015
CENSUS 2011 - In 33% of marriages, women weren't 18
Subodh Varma
Far-reaching changes seem to be occurring in the way marriages are fixed in India, and one of these is the age at which marriages take place. About one-third of all married women in the country tied the knot before turning 18. Among men, this proportion was much smaller at just 6%. But, the overwhelming majority of women got married by the time they were 25, revealing social pressures -and perhaps lack of employment -still at work.
These and related findings, including a rising trend of men and women not marrying at all, emerge from the recently released Census 2011 data on marriage.
Among those married up to four years prior to 2011, around 17% of women and just 3% men were below 18 years of age at the time of marriage. To compare this with the past, we can look at the age at marriage of people married 20 or 30 or even 40 years ago. Among such mid dle aged and elderly persons, 50% of women and 16% of men reported getting married before they were 18.
So, are people marrying later? Yes and no. Clearly , much less people are marrying before the legally permitted ages of 18 years for women and 21 years for men, compared to earlier. But here's another fact: 92% of women were married by the time they reached 25 years of age. This was the case among those married up to four years before the Census in 2011. Among women married for 20 to 29 years, a huge 96% had got married by the time they reached the age of 25.
For men, the situation was different earlier, and it has changed even more in recent years. Among men mar ried in the past four years, nearly one-third tied the knot after they had reached 26. Between 20 and 30 years ago, the proportion of such men was 22%. Forty years ago, 12% men married after age 26.
“Age at marriage is delayed, possibly due to increasing levels of education and campaigns to delay marriage,“ said Rajni Palriwala, professor of sociology at Delhi University . Another factor is finding the right match because nowadays, criteria beyond caste and present parental economic status are brought in and men's economic status is more uncertain, she told TOI.
What is the reason for the continuing trend of women getting married in their early 20s? Prevalent ideas in society about a woman's economic, social, and sexual security can is the main reason behind this, says Palriwala.
“For women and their families, values of marriage, ideas of reproductive period, stigma and perceptions of so cial and sexual dangers of single women, persisting ideas of marriage as women's primary life trajectory , and adverse sex ratio means that marriage is not delayed beyond the age seen as ideal for reproduction,“ she said.
The Census data also shows more men and women remain unmarried than earlier. In 2011, about 6.4% of all persons older than 25 years were unmarried. That works out to about 3.89 cr people -2.89 crore men and 1 crore women. In 2001, the proportion of never married persons in the above 25 years age group was slightly lower at 5.3%.That's 2.5 crore persons -1.95 crore men and 56 lakh women.
Palriwala explains that adverse sex ratios mean that in any age group there are more men than women and at first marriage for women, the more eligible men will be matched while others remain unmarried.“Long distance marriage for men in more prosperous areas has emerged as a path but not a solution. So there's persisting non-marriage for men,“ Palriwala explained.
2014: Number of married and separated teenagers, 10-14 years
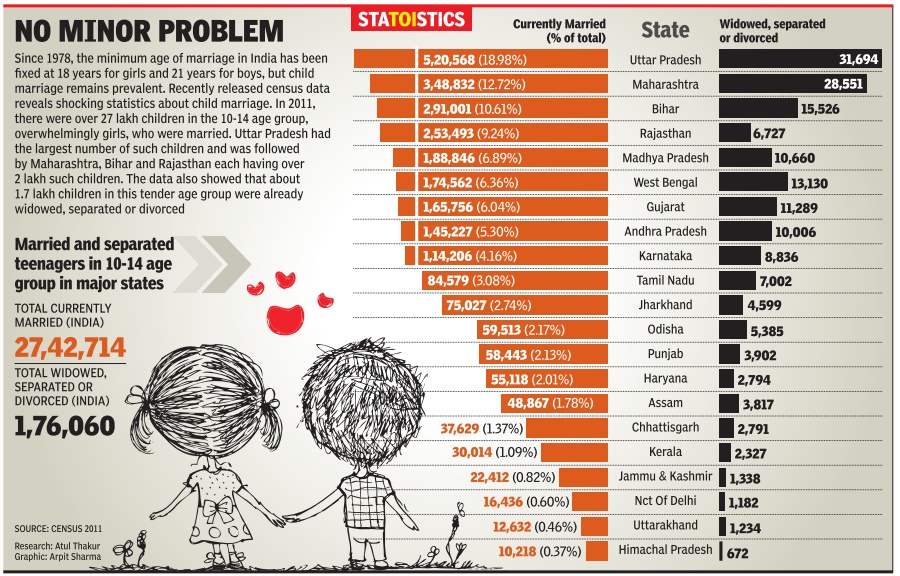
See graphic. 'Number of married and separated teenagers in major states, 10-14 years of age...'
2015-16: Decline in under-age marriages of girls
The Times of India, January 21, 2016
Sushmi Dey
Dramatic decline in under-age marriages of girls, says survey
Signaling a strong wave of women empowerment, indicators for female health, literacy , financial means and age of marriage over the past decade show positive upswings, the findings of the fourth national family health survey (NFHS-4) 2015-16 reveal.Findings of the survey depict a dramatic decline in under age marriages with women found to be marrying late even though the trend for men seems to be the reverse. For instance, in Bihar, less than 40% of women in the age group of 20-24 years were married before 18 years of age. This is compared to 60.3% of women in the same age group marrying before 18 years according to the third round of survey conducted in 2005-06. Similarly, Haryana has witnessed a sharp improvement with less than 19% of women marrying before reaching 18 years now, as compared to almost 40% during the previous survey.
But results of the survey co vering 13 states and two union territories show men are getting married at an early age now. In Goa, for instance, 10.6% of the men in the age group of 25-29 years married before 21 years of age, an increase from 7.2% 10 years ago. Similar trends were spotted in Tamil Nadu and Tripura.While in Tamil Nadu, percentage of the men marrying before the age of 21increased to around 17% during NFHS-4 from 14% 10 years ago, 22% of the men in Tripura married before 21 years, as against 19% earlier.
The latest survey shows a marked improvement in literacy rate of women. In around 11 out of 13 states, literacy rate of women have gone up over the past decade. While Goa tops the list with 89% literate women in the age group of 15-49 years, Sikkim is a close competitor with 86.6%. In Bihar, the female literacy rate jumped from 37% in the 2005-06 survey to 49.6%. The literacy percentage increased in Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal.
2015-16: 25% of wives aged 14-20 married as minors
Sushmi Dey, 25% of wives aged 14-20 tied knot when minors, October 12, 2017: The Times of India

From: Sushmi Dey, 25% of wives aged 14-20 tied knot when minors, October 12, 2017: The Times of India
Though the number of women marrying before 18 years of age in India has declined drastically over the last decade, it continues to be significantly high with more than a fourth of married women in the age group 14-20 having wedded as minors.
The figure is for 2015-16 and shows that the percentage of women getting married before 18 dropped from 47.4% in the Na tional Family Health Survey-3 of 2005-06 to 26.8% in NFHS-4. In fact, only 7.9% of women aged 15-19 years were already mothers or pregnant at the time of the survey of 2015-16 as compared to 16% in 2005-06.
The data assumes significance in the light of the Supreme Court ruling on Wednesday that sex with a wife who is under 18 years of age is rape and, therefore, a crime while rejecting the Centre's plea justifying the provision on the grounds that child marriage is a reality in India and has to be protected. The NFHS-4 data also shows violence against married women across the country has also come down in the last decade with percentage of ever-married women who faced violence from spouse dropping from 37.2% to 28.8% in around 10 years.
Experts said the verdict will reduce the incidence of early marriage and child trafficking, apart from addressing the challenges in population control.
Prohibition of Child Marriage Act
Tough to fix age of marriage for girls: Apex court
Says SC, Upholds High Courts’ Judgments Validating Marriage Of Minors Dhananjay Mahapatra TNN The Times of India 2013/07/25
New Delhi: The Supreme Court on Wednesday said it was difficult to arrive at a straightjacket formula on the marriageable age of girls to fit every case.
Commenting on identical verdicts by Delhi and Andhra Pradesh high courts which had allowed underage girls to marry their lovers, a bench of Justices J S Khehar and Dipak Misra said, “We do not find anything wrong in the two cases decided by the high courts... The parties have remained together. The families have remained united.”
Eight years ago, two high courts allowed minor girls to marry after they acknowledged that they had eloped voluntarily with their beaux, leading the National Commission for Women to rush to the Supreme Court expressing fear that this would legitimize marriage of minors — an offence under the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act.
Wide disparity in laws about marriageable age of girls
The NCW had said that given the wide disparity in various laws on the issue of marriageable age of girls, there was an urgent need to bring uniformity by addressing the question: “what is the correct statutory age for a girl to wed”.
The Supreme Court on Wednesday said it was difficult to arrive at a straightjacket formula on marriageable age of girls to fit every case. “We do not find anything wrong in the two cases decided by the high courts,” a bench of Justices J S Khehar and Dipak Misra said.
Delhi high court/ 2005; Andhra Pradesh high court/ 2006
The Delhi high court on October 5, 2005 and the Andhra Pradesh high court on February 1, 2006 had allowed underage girls to marry their lovers after dropping kidnapping charges registered against the men by police.
While assuring those whose marriages were held valid by the HCs not to worry and carry on with their lives, the SC in 2006 asked all courts not to draw inspiration from these two HC orders.
All cases need not fit the same formula
The bench of Justices Khehar and Misra said on Wednesday, “How can we say all cases must fit to the same formula? As long as there is no extraneous consideration, coercion, malice, misuse or assault, the HCs were perfectly placed to pass these orders. The parties have remained together. The families have remained united.”
In conflict with Prohibition of Child Marriage Act?
NCW counsel Aparna Bhat said there were laws in conflict with “secular laws like Prohibition of Child Marriage Act and permitted underage girls to marry” and requested the court to find an answer.
The bench said, “The two cases dealt by the high courts were not those where the girls were lured away or enticed. Can we pass an order annulling the marriage now? Have the girls who have now become adults given a statement contrary to what they had told the HCs then? As far as uniformity of marriageable age is concerned, the NCW must approach the appropriate authority. Who are we to bring in uniformity.”
The bench added NCW should register its protest when taking up cases where it finds the women were harassed, coerced or misused.
Issue of uniformity kept open
The court disposed of NCW’s appeals filed against the two HC judgments but kept open NCW’s plea for bringing in uniformity in legislations on marriageable age of girls.
It gave eight weeks to NCW and additional solicitor general Indira Jaising to hold consultations with stakeholders and report back to the court.
Court judgements
Make child marriages void: SC, 2017
Amit Anand Choudhary, Make child marriages void: Court, Oct 12, 2017: The Times of India
Terming child marriage a social evil that endangers the life and health of the girl child, the Supreme Court on Friday said such marriages should be declared void and stringent punishment prescribed for those who promote and such practices.
Although the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA) bars child marriages, these are held to be valid unless challenged by the minor, virtually giving legal approval to the institution of child marriage till its validity is challenged.
Only Karnataka has amended the Act and declared any marriage of a child, a female aged below 18 years and a male below 21 years, as void. Favouring amendment in the law to declare child marriage illegal, a bench of Justices Madan B Lokur and Deepak Gupta said that other states must follow Karnataka's example.
SC also suggested that penal provisions should be made stringent to punish members of a family who force a child into a matrimonial alliance. It said the punishment under PCMA was not sufficiently punitive and observed that PCMA was being misused as women promoting child marriages were kept out of the penal provision.
Impact of 2017 Consent judgement on Rajasthan
Himanshi Dhawan, Rajasthan's girls stare at a hopeless future, October 12, 2017: The Times of India

From: Himanshi Dhawan, Rajasthan's girls stare at a hopeless future, October 12, 2017: The Times of India
Reema Bairwal's (name changed) face is covered in a heavy green veil.Married last year, when she finished school, the 17-year-old lives in Sohela village in Rajasthan's Tonk district. “I wanted to study . Now my day is spent doing housework. I can't go out or meet anyone without permission,“ she says.
The Supreme Court criminalised sex with a minor wife. For young brides like Reema, the law provides for annulment of marriage and now even the right to file charges of rape against a husband for forced intercourse, but activists say young girls, often poor and illiterate, have no means or awareness to do this.
Neha (name changed), who was married last year as soon as she turned 16, seems resigned. “My parents did not have the money for a separate wedding so they married off my sister and me at the same time,“ she says.
When is she expected to go to her husband's house? “Soon,“ she says, hinting the consummation of marriage could happen anytime. She wasn't forced into the marriage but her vacant eyes reveal the hopelessness with which she views her future.
The 2011 Census by National Commission for Protection of Child Rights and Young Lives, an NGO, shows that 69.5 lakh boys and 51.6 lakh girls have been married before the legal age of 18 and 21 years, respectively. Rajasthan has the highest percentage of child marriages among girls (2.5) and boys (4.69).