Crimes against women: India
(→See also) |
(→Reporting of crime: Delhi, Mumbai) |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
Also see graphic. | Also see graphic. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Domestic violence= | = Domestic violence= | ||
Revision as of 19:01, 2 November 2017
This is a collection of newspaper articles selected for the excellence of their content. |
Conviction rate
Maharashtra among worst 10 in conviction rates
Atul Thakur, TNN | Aug 24, 2013
MUMBAI: The conviction rate for crimes against women in India is depressingly low, but Maharashtra's record is even more abysmal than the national average. In cases of rape, for instance, Maharashtra's conviction rate of 16.1% is about two-thirds of the 24.2% that the country averages.
For rape
The conviction rate for rape among the bigger states ranges between 10% and 16% for Gujarat, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and West Bengal while it is lower than 10% in Jammu & Kashmir. All other major states fare better than Maharashtra.
Several studies, in India and abroad have revealed that a majority of sex criminals are repeat offenders . A 2010 news report mentions a study by Swarnchetan, an NGO dealing with rape cases, which showed that nearly 70% of rape accused inmates in jails were repeat offenders. That is a telling statistic on just what the cost of a low conviction rate can be.
By type of crime
A look at data from the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) shows that Maharashtra ranks among the 10 worst states in terms of conviction rates for most offences against women. These include insulting the modesty of woman, dowry deaths and cruelty by husbands or their relatives.
Barely one in every 11 person, chargesheeted for assault on a woman with intent to outrage her modesty gets convicted in Maharashtra . The national average is almost one in four. Among the bigger states, only Gujarat , Karnataka and Jammu & Kashmir have a poorer record on this count.
In cases of insult to the modesty of a woman, nearly 95% of those accused walk free after trial in Maharashtra . Again, only Assam, Bihar and Karnataka among the major states fare worse. The all-India average conviction rate under this offence is 36.9%.
When it comes to offences under IPC section 498A, which deals with cruelty by a husband or his relatives, not even one in every 50 accused gets convicted in Maharashtra . This is just a little over one-tenth the national average of 15%. Maharashtra's 16.9% conviction rate for dowry deaths is also close to half the national average of 32.3%.
Of course, this is not to suggest that the rest of the country is doing a wonderful job of punishing those accused of crimes against women. The national average of conviction rates for IPC crimes against women is just 21.3%, which means almost four out of five accused walk free. It is also much lower than the 38.5% overall conviction rate for all IPC crimes.
The Justice Verma Committee, constituted to recommend amendments in criminal law to speed up trails in cases dealing with sexual offences against woman, also noted the abysmally low conviction rates for crimes committed against woman. The report observed that even today the victimized woman, rather than the rapist, is put to trial.
Conviction rate vis-a-vis the party ruling the state
No party has made it safer for women
Subodh Varma | TIG
See also the chart titled For the year 2012 , which is on this page.
over the past years there’s been growing protest at spiralling violence against women. All registered crimes against women went up by 70% between 2001 and 2012, rape increasing by 55%, assault with intent ‘to outrage modesty’ rising 32%, dowry deaths by 20% and cruelty by husbands and relatives by 117%. This is the tip of the iceberg because a very large number of crimes against women go unreported.
But what’s the record of political parties in curbing crime against women?
At the states’ level, the picture is revealing and puts paid to the tall claims made in manifestoes. In BJP- ruled Gujarat, MP and Chhattisgarh conviction rates for rape are lower than the national average which is already very low. In Gujarat, conviction rate dips to just 15%. In assault with intent to rape cases MP and Chhattisgarh do better than the national average but in Gujarat conviction rate is 2%. In cruelty by husband cases too, Gujarat has a 4% conviction rate compared to 15% at the national level and 56% in MP. Clearly, the BJP-ruled states are not doing much to punish the guilty. BJP has been ruling these states for over a decade.
In Congres-ruled states things are slightly better. Taking three of them as examples, conviction rates are worse than the national averages in Assam and Maharashtra. In Haryana they’re about the same for rape and assault, although much lower for cruelty. In these states Congres has been ruling for a decade or more.
Surprisingly UP has better conviction rates than most big states. They are two to three times the national rate. Apart from UP, other states ruled by non-Congres, non-BJP parties show trends similar to BJP or Congres-ruled states. TN has low conviction rates for rape but in the other two crimes it performs better.
Conviction rate vis-a-vis the party ruling the state
No party has made it safer for women
Subodh Varma | TIG
over the past years there’s been growing protest at spiralling violence against women. All registered crimes against women went up by 70% between 2001 and 2012, rape increasing by 55%, assault with intent ‘to outrage modesty’ rising 32%, dowry deaths by 20% and cruelty by husbands and relatives by 117%. This is the tip of the iceberg because a very large number of crimes against women go unreported.
But what’s the record of political parties in curbing crime against women?
At the states’ level, the picture is revealing and puts paid to the tall claims made in manifestoes. In BJP- ruled Gujarat, MP and Chhattisgarh conviction rates for rape are lower than the national average which is already very low. In Gujarat, conviction rate dips to just 15%. In assault with intent to rape cases MP and Chhattisgarh do better than the national average but in Gujarat conviction rate is 2%. In cruelty by husband cases too, Gujarat has a 4% conviction rate compared to 15% at the national level and 56% in MP. Clearly, the BJP-ruled states are not doing much to punish the guilty. BJP has been ruling these states for over a decade.
In Congres-ruled states things are slightly better. Taking three of them as examples, conviction rates are worse than the national averages in Assam and Maharashtra. In Haryana they’re about the same for rape and assault, although much lower for cruelty. In these states Congres has been ruling for a decade or more.
Surprisingly UP has better conviction rates than most big states. They are two to three times the national rate. Apart from UP, other states ruled by non-Congres, non-BJP parties show trends similar to BJP or Congres-ruled states. TN has low conviction rates for rape but in the other two crimes it performs better.
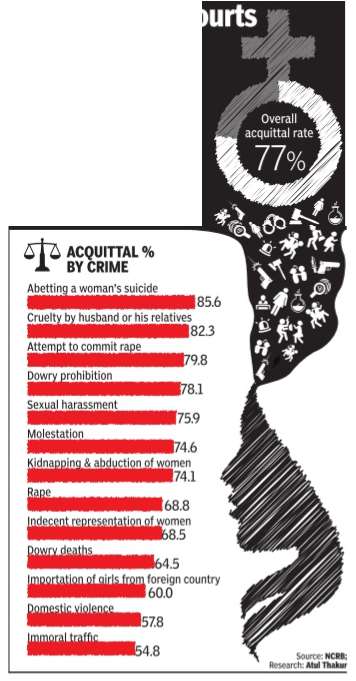
For all crimes: 2015
While violence against women is becoming a major concern, the conviction rate for gender crimes is extremely low. In 2015, around three-fourths of the people accused of committing crimes against women were acquitted by courts.
Also see graphic.
Domestic violence
Domestic violence makes up 1/3 of crimes against women
Arun Dev, TNN | May 29, 2013
BANGALORE: Women in Karnataka are as unsafe inside their homes as outside, in the big bad world. In case of Bangalore, though, the situation is marginally better.
Statistics with the Karnataka police show that one-third of the cases of violence against women take place within the confines of their home. The corresponding figure for the state capital is slightly above 25%.
In 2012, of the 10,789 cases of crime against women in Karnataka, 3,688 cases (34%) were reported from within their homes. In Bangalore city, of the 1,993 cases of crime against women, 524 were incidents of domestic abuse, filed specifically under Section 498A of the Indian Penal Code - violence by spouse or relatives. Domestic violence is the single largest category in crime against women.
Over the past few years, there has been an increase in the number of cases booked against women. But domestic violence cases, as a percentage of overall crime against women, has not changed much. Of the 7,698 cases of violence against women reported in 2008, 2,638 cases (34%) were of violence by family members.
According to a senior police officer, the official statistics do not give a complete picture of domestic violence in the state, as most such cases go unreported. "In such a situation, we are helpless. We can't force someone to file a police complaint," says the officer.
SOCIETY STILL TRADITIONAL
Society's outlook is still unchanged and doesn't support a woman who goes against her husband and files a case of domestic violence, points out Dr Shaibya Saldanha of the NGO Enfold Trust. "There are many women who are doing well in the corporate sector, but wouldn't report domestic violence fearing social norms," she added.
In the past decade, the criminality of domestic violence has been acknowledged. However, there is no visible reduction in the number of instances of domestic violence. "What we've seen is that many women prefer going to a third party than the police. Considering this number, the magnitude of domestic violence must be big," says Dona Fernandez, founder of Vimochana, The Forum for Women's Rights.
The admission of activists and police that many instances of domestic violence go unreported, flies in the face of those raising a hue and cry about the misuse of the anti-domestic violence law by women seeking vengeance.
Dona agrees there have been incidents of abuse, but they are very few. "There should be a change in perspective. Recently, a judge announced that rape laws were being misused. Almost every law in the country is misused, but remarks are made in the open only about sensitive laws. Even if there is a small number of cases of misuse of the law, we shouldn't forget there are many cases where this law has saved the lives of many women," she adds.
Dowry deaths
Dowry deaths: One woman dies every hour
PTI | Sep 1, 2013
NEW DELHI: One woman dies every hour due to dowry related reasons on an average in the country, which has seen a steady rise in such cases between 2007 and 2011, according to official data.
National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) figures state that 8,233 dowry deaths were reported in 2012 from various states. The statistics work out to one death per hour.
The number of deaths under this category of crime against women were 8,618 in 2011 but the overall conviction rate was 35.8 per cent, slightly above the 32 per cent conviction rate recorded in the latest data for 2012.
The number of dowry deaths in the country has seen a steady growth during the period between 2007 and 2011. While in 2007, 8,093 such deaths were reported, the numbers rose to 8,172 and 8,383 in 2008 and 2009 respectively.
In 2010, 8,391 such deaths were reported, according to the NCRB.
The agency is the central nodal department to collect and process crime statistics at the national level.
Suman Nalwa, additional deputy commissioner of Delhi Police (Special Unit for Women and Children), said the problem is not only limited to the lower or middle class.
"Higher socio-economic strata is equally involved in such practices. Even the highly educated class of our society do not say no to dowry. It runs deep into our social system," she said.
The Dowry Prohibition Act of 1961, prohibits the request, payment or acceptance of a dowry, "as consideration for the marriage" and dowry here is defined as a gift demanded or given as a pre-condition for a marriage.
"The existing law has certain loopholes and needs to be made stricter. Despite the amendments made to the Dowry Act in 1983, good results are still desired to be achieved," Nalwa said.
However, Kamini Jaiswal, a senior Supreme Court lawyer, says improper investigations by the police at the initial stage of a case slow down the process of judicial proceedings.
"We need quick conviction in such cases. Our judicial procedure has become very slow, police does not record a case at initial stage," she said.
Evidence
Accused can be convicted if victim testimony trustworthy: SC
SC: Corroboration Not Mandatory Unless Serious Infirmities Exist’
Holding that a “socially sensitised judge“ offers a better and more effective statutory armour than penal provisions to deal with cases of crime against women, the Supreme Court has said that the corroboration of a victim's statement is not mandatory .
An accused can be convicted if the victim's testimony is “natural and trustworthy“ and does not suffer from serious infirmities, Justice R Banumathi, who was part of the bench that upheld the death sentence for the Nirbhaya rape-murder convicts, said in her verdict in the brutal case that shook the nation.
The court has asked judges to be sensitive during trials for rape cases, and keep in mind the testimony of a survivor, as “no self-respecting woman will put her honour at stake by making false allegations of sexual offences against herself “. “(The) Persisting notion that the testimony of the victim has to be corroborated by other evidence must be removed. To equate a rape victim to an accomplice is to add insult to womanhood. Ours is a conservative society and not a permissive society . Ordinarily , a woman, more so, a young woman, will not stake (sic) her reputation by levelling a false charge concerning her chasti ty,“ Justice Banumathi said.
She said the corroboration of a rape survivor's testimony was not a requirement of law and only a rule of prudence, and courts should not insist on it.
“There is no rule of law that the testimony of the prosecutrix cannot be acted upon without corroboration in material particulars. She stands at a higher pedestal than an injured witness,“ she said, adding, “However, if the court of facts finds it difficult to accept the version of the prosecutrix on its face value, it may search for evidence, direct or circumstantial, which would lend assurance to her testimony.“
“A socially sensitised judge, in our opinion, is a better statutory armour in cases of crime against women than long clauses of penal provisions, containing complex exceptions and provisos,“ she said while referring to an earlier verdict of the apex court. The judge said courts should deal with rape cases sensitively, examining “the broader probabilities of a case and it should not be swayed by minor contradictions and discrepancies“ of witnesses.
It is now well settled that conviction for rape can be based on the testimony of the prosecutrix corroborated by medical evidence and other circumstantial evidence.
Annual statistics
2012: 2,160 kidnap cases of girls registered
According to the NCRB figures for 2012, Delhi’s share of all crimes committed in the country was 2.83%. Among states and UTs, Bengal leads the pack with a share of 12.67%.
As many as 2,160 kidnapping cases in which women or minor girls were the victims, were registered last year in Delhi. There were 134 dowry deaths and 1,985 cases of cruelty to women by husbands or relatives.
Seeking to downplay the numbers, Delhi Police said statistics did not reveal the actual picture. Senior cops said gave a number of reasons for the rise in crime in Delhi over the past decade. They said rapid growth in the city’s population, socio-economic imbalances and urban anonymity were encouraging deviant behaviour. They said the city’s adverse sex ratio (866/1000) and loosening of social structures were also playing a part in rise of crime.
Among the new initiatives for controlling crimes, the cops said 255 city routes had been identified as being the most frequented by women late in the evening. More than 400 women sub-inspectors and 2,088 women constables were being deployed on these stretches.
Earlier, a document submitted by a Delhi ministry in the assembly had criticized a few rape victims themselves for inadvertently contributing to the low conviction rate in such cases. “Victims sometimes do not support prosecution during trial. At other times, there are compromises made between both parties,” the ministry stated.
Murder of women in Mumbai: 2012
Shocker: Over 200% rise in women murders in Mumbai in a year
V Narayan, TNN | Jul 14, 2013
MUMBAI: The latest Mumbai police crime report has thrown up a shocking fact— the number of city women murdered more than tripled from 9 in 2011 to 30 in 2012. It translates into a 233% rise.
The numbers till May 2013 are still more shocking with 17 cases already registered throwing up the scary prospect of a further rise this year. Between 2008 and May 2013, the city recorded murders of 81 women, 66 children and 992 men.
The statewide figures are worse. The latest National Crime Record Bureau (NCRB) report says on an average 83 women or girls are killed every month in Maharashtra. The state has the dubious distinction of topping the list of states with most number of women murdered for five consecutive years between 2008 and 2012 with as many as 5,158 cases of female murders.
Crime experts, psychiatrists and investigators said most adult women's murders are over suspected infidelity, extra-marital relationships and failed relationships.
Crime of passion is the commonly observed reason for such violent crime against women. Study of past cases highlighted that the maximum number of women killed fall in the 18-30 age group. The reason is jealousy. While killing of women above 50 years is mainly for property, said Himanshu Roy, joint commissioner of police (crime).
The report said from 2008 to 2012, the major female murders in the state were in the age group of 18-30 with 2,614 cases, followed by 1,541 cases in the 30-50 group, and 450 and 374 cases of those aged above 50 years and up to 10, respectively.
Younger women protest, fight back against injustice and therefore are attacked. Crimes of passion always involve the young as they are involved in such relationship till it gets sour, said psychiatrist Dr Harish Shetty. Women of all ages are vulnerable to violence.
With women venturing out more in a number for jobs and for other professional reasons, chances of their falling prey to strained personal relations and emotional setbacks have risen," said S P S Yadav, former Thane police commissioner. Former IPS officer turned lawyer Y P Singh added that an overwhelming number of women killed either by way of murders or abetment to suicides is because of dowry demands of husbands or his relatives. While failed love affair or dispute over extramarital affair is another major reason.
Most murders of women fall in the age group of 18-30 because they may not know how to handle relations, Mamta Sharma, chairperson of the National Commission for Women ( NCW) in New Delhi, told TOI.
Murder of women in other states: 2012
Maharashtra leads with 5,158 cases, though Andhra Pradesh is ahead in killings of women aged above 50 and Uttar Pradesh tops in the 10-15 and 15-18 age category, the report said.
Crimes against women in 2012
(See chart/ box)
After 2012, a marked increase in registration of cases

Since the December 2012 Nirbhaya gang rape-murder, a case that shook the nation's conscience and triggered countrywide protests over the wide prevalence of crime against women. But not much seems to have changed on the ground as crime statistics from the years since show.
According to data from the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), while close to 35,000 rape cases have been reported, on average, every year since 2013, close to 1.4 lakh rape cases were on trial at the end of 2015.
Since 2012, there has been a marked increase in the registration of cases relating to crimes against women across the country , on account of increased awareness and prompt registration of FIRs.While 24,923 rapes were reported in 2012, the figure was 33,707 in 2013.
The number rose to 36,735 in 2014, out of which 2,346 per tained to gang rapes. However, in 2015, the number of cases fell to 34,561, including 2,113 gang rapes.
According to the NCRB's data, of the 34,651 cases, the survivors knew the offenders in 33,098 (95.5%) cases. Crimes against women, on the whole, including cruelty by husbands or their family members, followed a similar pattern. While 2,44,270 cases were reported in 2012, the number went up to 3,09,546 in 2013 and 3,37,922 in 2014. The number fell to 3,27,394 in 2015.
The conviction rate for crimes against women remains abysmal. According to the NCRB, around 10.80 lakh cases of crimes against women were pending in trial courts at the end of 2015. In 2015, only 27,844 cases ended in conviction, just 21.7% of the number in which trial was completed.
In rape cases, out of the 24,486 people whose trial was completed that year, 7,185 were convicted and 16,849 acquitted. In 2014, 26,660 cases relating to crimes against women ended in conviction -21.3%. At the end of 2014, a total of 9,82,516 cases were on trial. Courts across India convicted 6,637 people and acquitted 16,575 in rape cases in 2014.
Crimes against women in 2013
Dubious distinction: Delhi tops increase in crime against women
Deeptiman Tiwary New Delhi:
TNN
The Times of India Jul 01 2014
Delhi Sees Up To 340% Hike, Mum Next With 90% Rise
The Nirbhaya case may prove a watershed moment in how police respond to crime against women, with registration of offences of rape jumping by a significant 35% in 2013 as compared to the previous year.
The latest National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data for 2013 shows a spike in registration of crimes against women even as murders have dropped by 3.6%. Besides rapes, there is a 56% increase in crimes described as outraging the modesty of women, involving assault, and a 37% rise in the offense of insult to women.
Delhi leads the pack with a 340% rise in crimes against women.
Next is Mumbai, which recorded a jump of around 80%-90%. Chennai, proving to be the exception, recorded a negative growth in the category .
The data, released on Monday , shows incidences of rape increased by 35.2% over 2012 and 112.7% over 2003 across the country . The same figure for assault with intention to outrage the modesty of a woman recorded an increase of 56% over 2012 and 114.8% over 2003.
In cases of abduction of women there was a rise of 35.6% over 2012 and 290.2% over 2013. A senior NCRB officer said, “The sharp spurt in crime against women seems more as a result of increase in registration of cases than increase in crime per se.“
2013-2014: Delhi
3 of 4 accused of crimes against women go free
Richi Verma The Times of India Mar 09 2015

For every four Delhiites charged with sexual offences, nearly three go scot free. Figures from Delhi Commission of Women's latest annual report (2013-14) shows the acquittal rate in the capital for crimes against women continues to be as high as 70% even as the number of cases steadily rises.
According to the report, released on International Women's Day , not only are women in the capital still vulnerable and unsafe, even justice for assault survivors is delayed. DCW's rape crisis cell has 3,877 active rape cases pending, which means thousands still await justice.
Rape was the most preva lent crime against women referred to the DCW, accounting for 50% cases. DCW's rape crisis cell saw 1,703 new cases registered in 2013-14, of which almost 50% cases (804) were of rape. These cases increased from the first quarter of 2013-14 to the second quarter, but then saw a decline from 218 rape cases in JulySeptember 2013 to 143 in October-December 2013. However, by the final quarter of 2013-14, rape cases had shot up almost 200% to 337.
In all, while 243 cases of crimes against women were reported in April-June 2013, these almost tripled to 725 in the January-March quarter.In 2013-14, DCW's rape crisis cell disposed of 645 cases of crimes against women, of which 192 were convicted and the rest, 453, acquitted.
DCW chairperson Barkha Singh called the high acquittal rate “alarming“ and said more fast-track courts were needed. “It's unfortunate that conviction rates are so low. If one goes into appeal, the trial has to end. The current lot of fast-track courts which deal with crimes against women still function like other courts,“ she said.
DCW's rape crisis cell was established almost 11 years ago and works in coordination with Delhi Police in tackling crimes against women.The number of rape cases in DCW's annual report include minor rapes and rapes in livein relationships, in line with HC's observation last week. “After the Nirbhaya incident on December 16, 2012, there has been an increase in reporting crimes against women. Many times, women who have suffered through crime, remain silent and do not come forward. Their families tell them to stay quiet due to pressure from society . But now, more and more women are coming forward...they want justice and are willing to fight for it,“ said Singh.
2015, crime against women, city-wise
See graphic

See also
Rapes in India<> Rapes in India: court verdicts <> Rape definitions unique to India<> Rapes in India: the legal position after 2013<> <>Rapes in India: Compensation and help for survivors <> Rapes in India: annual statistics
Crimes against women: India