Elections in India: behaviour and trends (2014)
(→2014:(Once again) votes obtained do not proportionately translate into seats) |
(→2014: the success rate of defectors) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
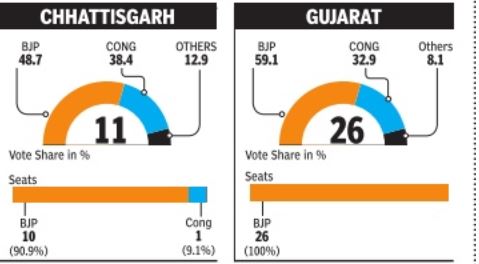
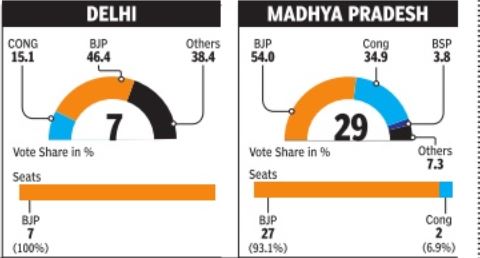
The simplest contests were in the states where two parties like BJP and Congres slugged it out straight, as in Gujarat, MP, Chhattisgarh, and Rajasthan. With its dominant support and vote shares, BJP swept them, decimating Congres. In Maharashtra, too, it was a similar situation except that on both sides were alliances. | The simplest contests were in the states where two parties like BJP and Congres slugged it out straight, as in Gujarat, MP, Chhattisgarh, and Rajasthan. With its dominant support and vote shares, BJP swept them, decimating Congres. In Maharashtra, too, it was a similar situation except that on both sides were alliances. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 20:30, 26 May 2014
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Proportionate representation?
2014:(Once again) votes obtained do not proportionately translate into seats
Why parties got votes aplenty but zero seats
They got the votes, not the seats
By Subodh Varma
The Times of India May 18 2014
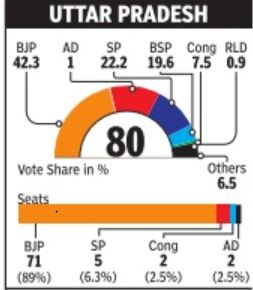
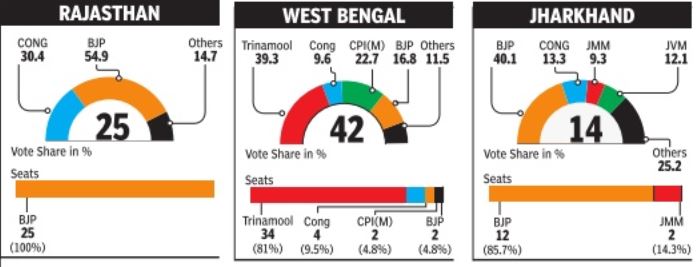
Mayawati's BSP got 20% votes in Uttar Pradesh and no seats. got 20% votes in Uttar DMK polled 26% votes in Tamil Nadu and still, Karunanidhi landed a zero in Lok Sabha. Congres secured just 10% votes in north central Bengal but it translated to four seats.
The bizarre figures are thanks partly due to our first-past-the-post electoral system and the specific na1 ture of vote distribution. 3 The candidate getting the 1 largest number of votes in any seat wins. So, in a multi-cornered contest, a candidate with say 20% votes may win a seat because each of the others have individually got less than that, never mind that his/her share on its own does not seem very impressive.
The other factor in play is “the wave“. In most of the states where parties with lots of votes have gone with less (or no) seats, there is one party that gets bulk of the votes. In Tamil Nadu, it was AIADMK, while in UP it was BJP . So, the unfortunate candidates who landed a was BJP . So, the unfortunate candidates who la quarter of the votes polled still scored no seats. Who sent most SC/STs, women, moneybags to LS? BJP has most SC&ST (11) and women MPs (30) while Trinamool has the highest percentage of SC& ST MPs. And if the 16th Lok Sabha is 3 times richer than the 15th, it's due in part to MPs of Telugu Desam Party, several of whom are building barons.
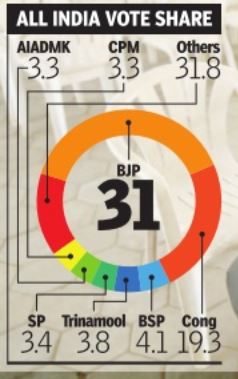
Parties Like DMK In TN, Left In Bengal, BSP In UP Did Not Benefit From A Significant Vote Share At the national level, the story of votes (not seats) obtained by various parties and alliances is fairly straightforward. BJP and its allies got about 38% votes, Congres and its allies got 23%, the four major regional outfits -SP, BSP, Trinamool and AIADMK -got about 14% votes together, and the Left got about 5%.
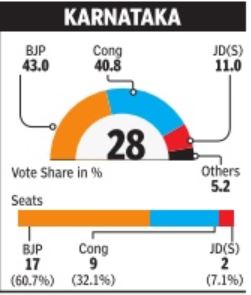
Move from this big picture to the state-level shares of votes, and an intricate mosaic emerges. It reveals the huge strength of nearly a dozen parties at the state level. Note that the two big parties, BJP and Congres, have got just about 50% votes nationally -the balance is distributed amongst parties with regional bases.
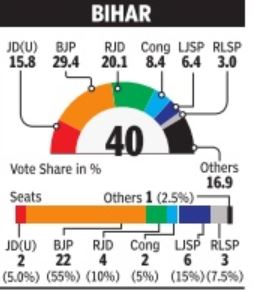
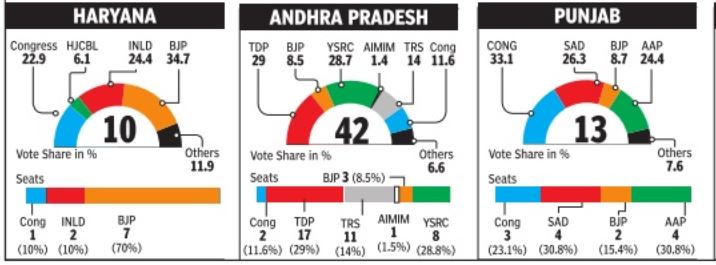
The vote shares show the great advantage of the right kind of alliances, and the burden of dead wood. For instance, BJP benefited from key alliances with Paswan's Lok Janshakti Party (LJP) in Bihar and the Telugu Desam (TDP) in Andhra Pradesh, while Congres managed to stay afloat in Bihar due to its tie-up with Lalu Prasad's Rashtriya Janata Dal (RJD).
One of the biggest surprises of this election was that no candidate of the Mayawati-led Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP) won in Uttar Pradesh, which is BSP's stronghold, though it managed a creditable 20% of votes. In the outgoing Lok Sabha, it had 21 members.
There are other states where a similar anomaly can be seen. In West Bengal, the Left got nearly 30% votes but had to be satisfied with just 2 seats. In Tamil Nadu, DMK and its small party allies garnered 27% votes and got no seats. In Odisha, Congres got 26% votes but no seat while the BJP got 22% and just one seat.
The reasons for these bizarre results lie partly in the electoral system and partly in the specific nature of vote distribution. In the `first past the post' system the candidate getting the largest number of votes in any seat wins.
So, in a multi-cornered contest, a candidate with say 20% votes may win a seat because each of the others have individually got less than that.
One well-known solution to this problem is adopting a proportional representation system in which seats are allocated according to share of votes, a system practiced in many countries. But there is another factor to be kept in mind: the wave. In most of these states where parties with lots of votes have gone with less (or no) seats, there is one party which is getting bulk of the votes. In Tamil Nadu and in Odisha, the winning party -AIADMK and Biju Janata Dal respectively -got an overwhelming 44% of votes. So, even if you get 25% votes you lose badly.
In West Bengal, Mamata's Trinamool Congres got near ly 40% votes, outstripping its main challenger the Left front. But what explains the four seats captured by Congres getting just 10% votes.
That's because these votes were gained in a concentrated belt of north central Bengal, and gave Congres an edge over others in that region.
Elsewhere it was wiped out.
Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) may not have performed well considering that it was much hyped in the media and had put up over 400 candidates across the country. But its performance in two states, Delhi and Punjab, is creditable. In Delhi it got 33% votes, improving upon its vote share from last December's state assembly elections when it had got about 28% votes. It lost out decisively to BJP this time round because BJP itself improved its vote share to over 46%, from 33% in December.
In Punjab, AAP got nearly 25% votes, and managed to get four members in the Lok Sabha. This, despite the fact, that the BJP-Akali alliance got about 35% votes and the resurgent Congres 33%. In this genuinely triangular contest, everybody walked away with a few seats.
Assam indicates a worrying polarization of votes on religious lines with BJP getting nearly 37% votes and the All India United Democratic Front (AIUDF), an outfit with support in the minority com munity , getting 15% votes.
This led to a sweep by AIUDF in lower Assam and a sweep by BJP elsewhere.
The simplest contests were in the states where two parties like BJP and Congres slugged it out straight, as in Gujarat, MP, Chhattisgarh, and Rajasthan. With its dominant support and vote shares, BJP swept them, decimating Congres. In Maharashtra, too, it was a similar situation except that on both sides were alliances.