Research & Development(R&D): India
(→2018: Global in-house centres) |
(→Global tech R&D and India) |
||
| Line 224: | Line 224: | ||
''How GICs are remaking Bengaluru, as in 2018 '' | ''How GICs are remaking Bengaluru, as in 2018 '' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | =Women in Research and development= | ||
| + | ==2017-20== | ||
| + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2020%2F08%2F31&entity=Ar00103&sk=817D8FD1&mode=text Chethan Kumar, Women in R&D: Pvt sector outshines PSUs, August 31, 2020: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Research and development (R&D) activity in India’s private sector has a larger proportion of women compared to governmentsupported agencies, even as men continue to overwhelmingly dominate the sector. | ||
| + | |||
| + | At least seven out of every 10 women employed by private R&D facilities are involved in research, whereas not even half of the female staff in government-aided scientific agencies have the same role, according to the latest edition of the Science and Technology Indicators (STI-2019-20) compiled by the Government of India’s Department of Science and Technology that was released this month. The employment number is for the year 2017-18. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Only public units in the industrial sector compare well with private R&D facilities. The overall number of women on the rolls at such units is 10 times lesser compared to private R&D facilities. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' In govt-funded agencies, 10k of the 23k women engaged in R&D ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Percentage of women in other central and state government departments and scientific and industrial research organisations pales in comparison with the private sector. Of the 20,000-plus women employed in private R&D firms, over 15,000 were involved in research activities and 2,800 and 2,500 were in auxiliary or administrative activities. In major scientific agencies funded by the government, there are over 23,000 women employed but only 10,000 worked directly in R&D. | ||
| + | |||
| + | “Although there is a slight increase in women in academia, the divide between academic and research institutions means that not enough women are in R&D,” said Rohini Godbole, a senior physicist who has chaired a panel on women in S&T. Another scientist working with the government on the new S&T policy said, “You will see something good on this in coming policy.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | The private sector has outpaced public R&D investment over the years although the latter has put in more money in absolute terms. The investment data is up to 2018-19. While R&D investment by the government was about 120% more than the private sector in 2004-05, the gap has reduced to 40% by 2018-19. Compared to the 300% jump in public investment on R&D from 2004-05 to 2018-19, private sector investment spiked 600%. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|R | ||
| + | RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT(R&D): INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:S&T|R | ||
| + | RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT(R&D): INDIA]] | ||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
[[China vis-à-vis India: Levels of development]] | [[China vis-à-vis India: Levels of development]] | ||
Revision as of 23:09, 13 September 2020
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. the Facebook community, Indpaedia.com. All information used will be acknowledged in your name. |
Contents |
The state of S&T in India

ii) India’s expenditure on R&D, as a %age of the GDP; and
iii) India’s expenditure on R&D vis-à-vis comparable countries
From: Vishwa Mohan, At first look, India’s R&D spend seems up. But it’s actually down, January 17, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
i) India’s expenditure on R&D, 2004-15;
ii) India’s expenditure on R&D, as a %age of the GDP; and
iii) India’s expenditure on R&D vis-à-vis comparable countries
India’s gross research spending has consistently been increasing over the years but the country’s expenditure on R&D continues to be less than 1% of its GDP when other emerging economies, including China and Brazil, invest more under this head.
The study of the National Science and Technology Management Information System (NSTMIS) under department of science and technology (DST) shows that the country’s gross expenditure on R&D has, in fact, tripled in a decade — from Rs 24,117.24 crore in 2004-05 to Rs 85,326.10 crores in 2014-15 — with the government chipping in with more money as compared to private sector industries.
But, the country’s R&D expenditure as percentage of its GDP declined during the period. It has, in fact, been showing a consistent decline since 2008-09. The study shows that the Centre’s share in the gross expenditure was 45.1% followed by private sector industries (38.1%), state governments (7.4%), higher education sector (3.9%) and public sector industries (5.5%).
NSTMIS compared the pattern of expenditure in 14 countries, including South Korea, Japan, USA, Russia, Canada, Australia, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, UK, Mexico and China, and found that India topped the list in terms of share of government sector spending. In other countries, private sector industries and institutions of higher education spent more than the government.
“India tops in government spending in R&D with 81.3% (of government sector expenditure) coming from eight major scientific agencies — defence, space, atomic energy, ICAR, CSIR, DST, (department of) biotechnology and ICMR — during 2014-15,” tweeted Union science and technology minister Harsh Vardhan while referring to the findings.
The study noted that the public sector R&D was led by defence industries and fuels while private sector one was dominated by drugs, pharmaceutical and transportation during 2014-15.
Though the study restricted itself to India’s R&D expenditure till 2014-15, it estimated the expenditure under this head for 2015-16 at Rs 94,516.45 crore and for 2016-17 at Rs 1,04,864.03 crore, which would still account for less than 1% of the GDP.
As compared to India, other BRICS nations had spent more of their GDP on research. Most of the developed countries, in fact, spent more than 2% of their GDP on R&D.
On scientific publication, India has shown a rising trend during the last decade. The report noted that the country’s share in global research publications increased from 2.2% in 2000 to 3.7% in 2013.
2009-12: Research output improves
49% rise in PhDs in 3 years
Jump In India’s Contribution To World’s Research Publications: Tharoor
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
The Times of India 2013/08/16
New Delhi: Poor research output of students is considered one of the biggest drawbacks of Indian higher education. But government claims there has been a 49.27% growth in the number of research degrees (Ph.Ds) awarded by the Indian universities between 2008-09 and 2011-12.
Ministry of human resource development said: in 2008-09, 10,781 Ph.Ds were awarded that increased to 16,093 in 2011-12.
There has also been a massive jump in India’s contribution to world’s research publications. Citing a report by the UNESCO Institute of Statistics, the ministry said it increased from 26,000 in 2002 to 44,000 in 2007.
Despite the rapid strides in research, India is still way behind other nations. In the same period, the number of Ph.Ds in China increased from 14,706 to 48,112. Increase in Ph.Ds in the US was, however, marginal —from 40,024 to 41,464.
As for the contribution to the world publications UNESCO data shows that between 2002 and 2007, Brazil’s contribution increased from 16,000 to 29,000, Russia (31,000 to 32,000), China (62,000 to 1.94 lakh), the UK (93,000 to 1.25 lakh), the US (3.15 lakh to 3.58 lakh) and Japan (92,000 to 98,000).
Tharoor said government has taken various steps for promotion and growth of postgraduate level studies and research. New institutions for science education and research have been set up. Universities are getting centres of excellence, new and attractive fellowships are on offer as well as there is emphasis on strengthening the infrastructure of Research & Development in universities. Tharoor said the HRD ministry had also set up a task force for rejuvenation of basic scientific research under M M Sharma. The task force has been converted into an empowered committee to implement its own recommendations.
In social sciences various research councils — Indian Council of Historical Research, Indian Council of Social Science Research and Indian Council of Philosophical Research — have been asked to fund more research initiatives.
2009-13: 13.9% growth
The Times of India, May 02 2016
India's research work growing
Sushmi Dey
India's research performance in science and technology has improved significantly over the past few years. Scholarly output in the country grew by 13.9% during 2009-13, against a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% for the world. Moreover, India has also demonstrated a growing impact through its research worldwide. For instance, India's share of world patent citations and top cited papers increased between 0.8 and 1.2 percentage points from 2009 to 2013.
In 2013, India held over 3% of the world's top 10% cited papers. This indicates India is not just growing scientifically, but growing aggressively at the very top end of scientific excellence. India's share of world patent citation, or patent cited for later papers or patents, also improved from 2.2% in 2009 to almost 3% in 2013. Experts said, in absolute terms, the growth was significant with India registering 109 patent citations in 2013.
The findings are part of a new bibliometric study published in international scientific journal `Elsevier'.
The international comparative study , conducted by Department of Science and Technology , analysed India's research performance during 2009-13 using Scopus database, the largest of peer-reviewed literature.
According to the study , India's scholarly output increased from 62,955 papers in 2009 to 106,065 papers in 2013.
2016: The status of S&T in India
The Times of India Jan 10 2016

Subodh Varma
59% of secondary schools in India don't have an integrated science laboratory although science is compulsory till class 10. So, a vast majority of students `study' science without ever seeing any experiment, let alone doing it. At the +2 level where students opt for science, just 32% schools have separate rooms for laboratories and a quarter of them are `partially equipped'. Perhaps they are being taught via the web? No chance, because just 37% of schools have a computer with net connection.
Not an easy prospect since the problem begins in schools and colleges. Students who do go through the grind and finally get into science and technology related jobs see their dreams die in India's vast but faltering science establishment.
One of India's top genetic scientists and former director general of CSIR, Samir Brahmachari told TOI that the crisis in science is because it is not attracting the best minds. “Science education has moved from being a curiosity-driven exploration to a mark-scoring exercise to get admission in elite institutions and bag a fat corporate salary . In the process, academia has also lost high quality teachers who shape young minds,“ he said.
“Building a knowledge-based society demands significant increase in investment for S&T at several levels including education as well as research leading to outcomes in pure and applied areas,“ eminent space scientist K Kasturirangan, former head of ISRO and ex-member Planning Commission, told TOI. India has just 4 scientific researchers for every 10,000 people in the workforce, much lower than not just advanced countries like the US or UK but even China and Brazil (see box).
“The goal of spending at least 2% of GDP on scientific research -outlined in the govt's science policy of 2003 -has not been achieved. Even industry funding, which was declared as the magic wand for finances, hasn't delivered,“ rues Dinesh Abrol, visiting professor at JNU.
As per latest available figures, India is spending less than 1% on research and development com pared to 1.9% in China and 2.75% in US.The combined result of defective grounding at the schoolcollege level and limited resources for re search is evident in the met rics that provide a partial measure of India's scienDtific output and its significance. Scientific papers published by Indians numbered about 90,000 in 2013 compared to 4,50,000 by Americans and 3,25,000 by Chinese. Citations too were below the world average. Indians filed just 17 patents per million population compared to 541 in China and 4,451 in South Korea.
“I am not worried about the quantity as much as the quality of science coming from India. It is also not showing any improvement. India still contributes less than 1% of the world's top 1% of research,“ Rao said.
Brahmachari sees the glass half full. Given the low input, and that the best minds have left India for greener pastures, he feels Indian science has done “outstandingly well“.
Ramamurthy highlights another key problem in the way science is being practised in the country -the project mode. “In today's environment of research in project mode with well-defined objectives, milestones and deliverables, curiosity-driven research is a casualty,“ he said.
Research objectives too are increasingly disconnected from society, asserts Abrol. Giving the example of agriculture, he says that an obsession with increasing yield while ignoring the consequences of intensive agriculture in the five major grain producing states has led to a sustainability crisis -ground water depletion, waterlogging, chemical over-kill. “Yet our research goals continue to be better yielding varieties rather than sustainable productivity ,“ he said.
Comparisons with other countries
1996-2015, China vis-à-vis India

From: October 29, 2017: The Times of India
See graphic:
Research & Development, in India and China, 1996-2015
2013: vis-à-vis BRICS and OECD countries

See graphic, ' Patents, Researchers, Publications in India and other major countries: 2013 '
Global tech R&D and India
2013-16: Number of MNCs and R & D centres
Sujit John & Shilpa Phadnis, For MNCs, India remains R&D hub, March 2, 2017: The Times of India
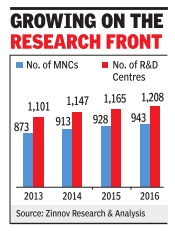
The number of R&D centres being established by MNCs in India continues to rise -the vast majority are from the US -and their headcount growth is particularly strong.
In 2016, as many as 943 MNCs were in India with 1,208 R&D centres -some MNCs have multiple units in the country.This is up from 928 MNCs with 1,165 R&D centres in the year before, according to consulting firm Zinnov's latest annual report on global in-house centres (GICs). A GIC is an R&D, business process management (BPM) or IT centre that a company establishes for its internal needs outside the home country .
India, along side China, has the highest number of GICs in the world, mainly on account of the large numbers of engineering talent it produces, and their lower costs in comparison to mature markets. Uber, LeEco and Diageo were among the MNCs that established GICs in India for the first time last year.
The number of people in the R&D centres rose12% to 3,63,000 in 2016, from 3,23,000 in the year before. Total GIC revenue is estimated at over $23 billion in 2016.Between 2010 and 2016, revenue grew at an estimated compounded annual growth rate of 12%.Bengaluru accounted for 35% of the GICs, with NCR a distant second with 15%. The R&D centres are seen to be maturing rapidly . While they started off in the 1990s and early 2000s providing low-end activities, today , many of them are driving global initiatives and designing and developing products for different markets. Preeti Anand, director and head of engineering excellence practice at Zinnov , said GICs in India now deliver more value with the objective of contributing directly to the headquarter's business. “From being an operations and delivery centre, GICs are becoming innovation hubs,“ she said.
Some 100 centres of excellence -entities that provide leadership, best practices, and research -have emerged in the GICs. Anand said much of the work in these centres of excellence, as also in many of the other GICs, is focused on digital initiatives, including advanced analytics, cognitive computing & machine learning, automation & robotics, and virtual reality. These technologies are used to create mobile and web apps, digital marketing and social engagement platforms, commerce platforms, and to get operational insights in real time. “Indian GICs have been increasingly managing complex projects and have developed end-to-end delivery capabilities,“ Anand said.
On the BPM (what previously used to be called BPO) side, while the number of new centres continues to rise, people additions have sharply slowed because of increasing adoption of what Zinnov calls robotic process automation. Automation is going well beyond the rule-based automation of the past to cognitive platforms, systems that can understand unstructured data, recognise voice, tone, gestures. Anand pointed out instances where banks could use these systems to increase the number of account closures from 12-13 per hour to 200 an hour, and where company audits that took 6-10 hours were brought down to a minute.
2015: No. 1 choice for global tech R&D
The Times of India, Dec 09 2015
Sujit John
India No. 1 choice for global tech R&D
69% Of All New Offshore Tech Centres Established In 2015 Came Up In Country
India remains he No. 1 location for MNCs o establish product engineering and R&D centres outside their home countries, and he growth of these centres n India is outpacing the average global growth. India accounted for $12.3 billion, or 40%, of the total of $31billion of globalized engineering and R&D in 2015, according to a study by consul ing firm Zinnov. Compared o 2014, the revenues of the captives in India grew by 8.3%, as against the growth of 7.6% for all captives. China follows India with revenues of $9.7 billion.
Zinnov, which has been ocused on this space since it was founded over a decade ago, finds that 69% of all new offshore technology centres his year were set up in India.The past two years have seen a spate of new centres being set up and the older ones expanding, including those of Exxon Mobil, Lowe's, Visa, Victoria's Secret, JC Penny , CME Group, Wells Fargo, and British Telecom.
Software & internet accounts for 35% of the work be ng done in the captives, telecom & networking follows with 14% and semiconduc ors 12%. Consumer electronics, automotive, computer peripherals, medical devices, industrial, and aerospace & defence are other areas of work.
Zinnov finds another in eresting trend: engineering and R&D outsourcing to third parties is beginning to outpace growth of captives in India.
ndia is the second biggest outsourcing destination, after Western Europe, where companies like Altran, Alten, Ak ka Technologies, Assystem and Harman Connected Services are strong.
India accounted for $7.8 billion, or 21.6%, of the total outsourced engineering and R&D services of $36 billion in 2015. Compared to 2014, it grew at 12.7%, as against the global growth of 8.7%.
“Five years ago, the growth was coming primarily from captives. Now, the captives have matured, and it is the third-party service providers who are growing faster,“ Sidhant Rastogi, partner in Zinnov , said. While captives do more of the work they consider proprietary and those that involve new technologies, they outsource a lot of the rest of the work.
Independent software vendors and telecom outsourcers dominated the outsourced pie. But the fastest growth came in the automotive, software and medical segments, the first thanks to the trend towards connected cars and change in labour laws in Germany.
TCS, Wipro and HCL Technologies have traditionally been the leading players in this space. “However, Infosys, Tech Mahindra, L&T and Aricent are giving good competition to the top 3. Even European players like Altran and Alten are setting up centres in India,“ Rastogi said.
Total R&D spending by the top 500 R&D spenders in the world grew by 2% to reach $614 billion this year.That means, globalized and outsourced R&D together ($67 billion) accounts for 11% of total R&D.
Rastogi said the outsourced R&D space was seeing a huge acquisition trend. Aricent acquired SmartPlay to get embedded and semiconductor competency, Altran acquired Nspyr and Sicontech to grow in the US market, Quest Global acquired Nest to diversify in embedded software services, Capgemini and Harman entered the product engineering services market through acquisition of mid-sized engineering firms.
“No one has grown more than 13% without acquisitions. So Indian players will have to acquire to grow faster,“ Rastogi said.
2018: Global in-house centres
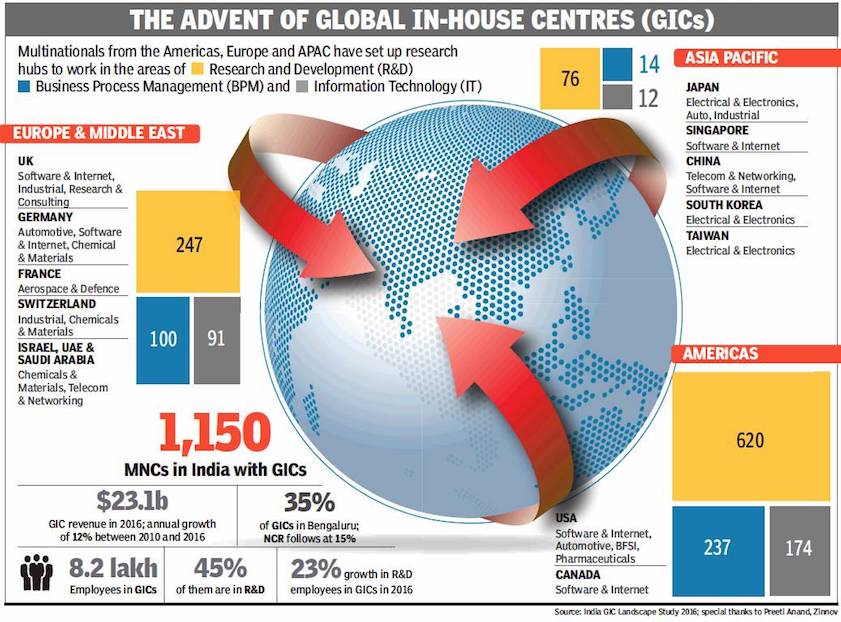
From: Sujit John & Shilpa Phadnis, Why MNCs are moving core ops to India, April 10, 2018: The Times of India

From: Sujit John & Shilpa Phadnis, Why MNCs are moving core ops to India, April 10, 2018: The Times of India
‘The centre of gravity of Fortune 500 companies is shifting to India. The future strategies of these companies are being invented here,” says Lalit Ahuja, a retired Navy man who runs Ansr, a venture in Bengaluru that helps multinational companies establish engineering and research and development centres — known as global inhouse centres or GICs — in India. Among the companies it’s worked with are Target, JCPenney, AB (Anheuser-Busch) Inbev, Saks Fifth Avenue and Grant Thornton.
“Conversations are no longer about cost. It is digital technology that is bringing companies here,” says K S Viswanathan, IT industry body Nasscom’s head of industry initiatives whose responsibility includes dealing with GICs. A total of 1,150 multinationals have global in-house centres that employ more than 8 lakh people in the country.
For years, India was linked with cheap processing and outsourcing work. Today, an increasing amount of the work is in big data and analytics, mobility, artificial intelligence, machine learning, internet-of-things (IoT), blockchain and robotics. These new digital technologies are becoming drivers of business, creating new sources of revenue for the MNCs, not just reducing costs or improving productivity.
For instance, some of Adobe’s biggest products — Acrobat, Illustrator, InDesign — are entirely developed and managed out of India. Car technology systems for Fiat Chrysler, GM, Volkswagen, Hyundai and Tata Motors were built at Harman’s India research centre, where local engineers designed a costeffective hardware and a simpler software architecture that embraced open source technology.
Multinationals set their sights on Bengaluru in the 1980s, after US chip design firm Texas Instruments set up an R&D centre in 1985, but the pace has accelerated since 2000. Corporations need engineers to re-do their technology infrastructure and build innovative solutions, and India is the only place where they can get them in the numbers and quality required. Earlier, companies would outsource technology work to IBM, Accenture, TCS or Infosys. But these technologies are new even for these specialists. Global companies figure they can do a better, quicker and more customised job if they took on the onus themselves.
Bengaluru’s long history with public sector defence undertakings and their research arms, and academic and research institutions such as IISc laid the foundation. This environment bred the IT services industry, and encouraged Texas Instruments to set up here. Since then, the city has attracted tech talent from across the country. The growing maturity of talent in IT services companies, as also those in new-age companies like Flipkart, gives GICs a ready base of talent. The city’s weather and cosmopolitan culture too have played major roles in consolidating its attractiveness.
Today, there’s a strong ecosystem that keeps reinforcing the city’s strength. Pari Natarajan, CEO of Zinnov, provides an example from financial services. Wells Fargo, JP Morgan and Goldman Sachs have major tech arms in Bengaluru. So do those who provide banking software — Broadridge, Fiserv and Misys — as also those who provide enterprise software, SAP and Oracle, and infrastructure platforms such as Microsoft and Dell. Natarajan says the network effects are tremendous when companies that depend on one another are in close proximity.
“Cost arbitrage is not a factor,” said Sonali De Sarkar, director-HR at storage and data management company NetApp India, which has had operations in India for a while, but recently opened a new campus in Bengaluru. “Our India site is the biggest in the world. We drive global charters from India. There are people in the US reporting to people here,” she says. NetApp’s techniques of using new-age flash media in a way that its cost equals that of traditional diskbased solutions were created in India.
Sarv Saravanan, who heads storage and data management company EMC’s centres of excellence in Asia Pacific and Japan out of Bengaluru, said tech products could earlier be built once in three years, now it needs to be done every six months. This requires critical skill sets at scale. And MNCs’ home countries don’t have that, India does.
Manu Saale, managing director of Mercedes-Benz R&D India, says not even China has this kind of talent. “The Chinese tend to be focused on the local market. India is focussed on global initiatives. I haven’t seen the kind of international mindset, outspoken thought and engineering capabilities that the world is looking for in China,” he says.
Banks are trying to digitise every process to make transactions simple and fast. Deutsche Bank COO Kim Hammonds has increased the number of engineers in the bank since she joined in 2013. “I believe engineers solve problems,” she told TOI recently. She is looking at processes run out of in India to see how automation, machine learning and AI can be applied to drive efficiency. “We had a 24-hour hackathon with 450 technologists in 12 locations, and the India team won,” she said, adding that the solution the team developed is going into the bank’s operations.
In retail, just about every big brand in the US is rushing to India to find digital solutions to take on Amazon’s might. In the past few years, Walmart, Lowe’s, L Brands (Victoria’s Secret), JCPenney, Saks Fifth Avenue and Ann Taylor have come in to create digital platforms that can provide an omnichannel experience to customers, make supply chains more efficient, and analyse humongous amounts of data.
“The India centres are now the front office,” says Ansr’s Ahuja. “We are providing insights, and increasingly, the foresight — who is going to come to my website, what is she going to buy, how much is she going to spend? We are writing the future.”
GE, Honeywell, Airbus, Boeing use engineers in India to design more efficient, bigger and faster aircraft. GE’s technology centre in Bengaluru has become its largest R&D centre, housing engineering teams across healthcare, aviation, transportation, power and energy. Oil and gas major Shell opened a tech centre in Bengaluru in 2006, and expanded to a new 52-acre campus last year. The campus has over 1,000 people with expertise in liquefied natural gas, subsurface modelling, data analysis and engineering design.
Soon after Dinesh Paliwal, who had led the establishment of ABB’s R&D centre in India, took over as Harman CEO in 2008, he decided to change Harman’s “crazy cost structure” using Indian expertise. The team here designed a more cost-effective hardware and a simpler software architecture that embraced more open source technology, and put the two together. Today, the India-built platforms run on numerous brands globally, including Fiat Chrysler, General Motors, Volkswagen, Hyundai, Subaru, Kia, and Tata Motors, Paliwal told TOI in 2016, a few months before the company was bought out by Samsung for $8 billion.
“If you challenge Indians and say, here’s the product, take this, reverse engineer it, bring down the cost to a third of what it is…they will do it. Indians are creative geniuses,” Paliwal had then said. The transformation has become the subject of a study by the Harvard Business School.
For all Mercedes car lines, the rear seat safety mandate is in India. The engineers in India compute all the parameters for seat safety, compute every load case, and provide the result. The India team then participates in the testing in a crash hall somewhere in the world. The centre here also works on certain doors and chassis, and has built numerous cutting-edge algorithms — involving over 250 patents — that help parent company Daimler simulate and test a variety of systems.
India has Daimler’s biggest R&D presence outside of home country Germany. Thomas Weber, adviser to Daimler AG, and a former member of the board of management of Daimler, told TOI on a visit to the centre a little over a year ago: “In every Mercedes car, there’s a huge part of India.”
On the same occasion, there were also journalists from Europe, and one asked Weber: “Can we say the artists are in Silicon Valley while Bangalore has the craftsmen who implement it?” Weber’s reply was striking: “That’s the process we started with, but it’s totally changed now. These guys are competitors of those in Silicon Valley. The game has changed.”
How GICs are remaking Bengaluru
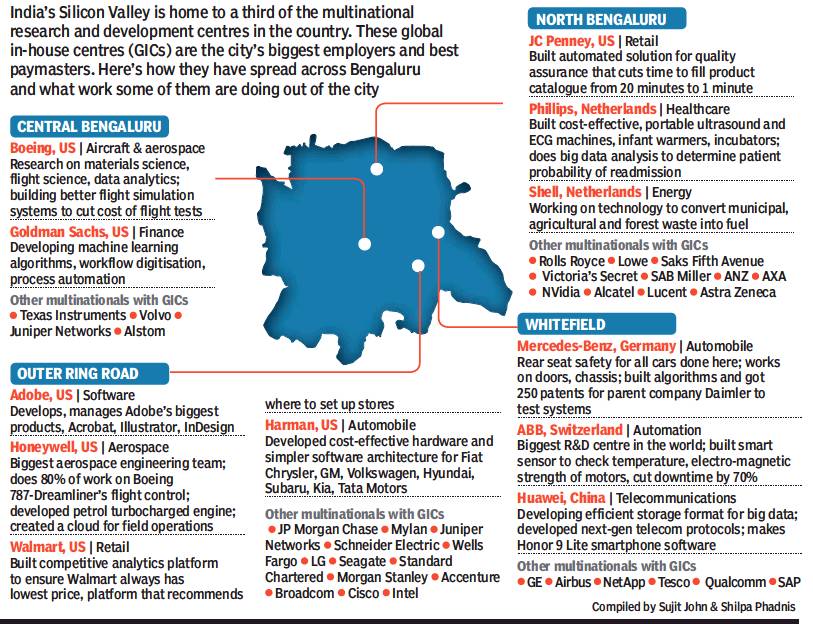
From: April 10, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
How GICs are remaking Bengaluru, as in 2018
Women in Research and development
2017-20
Chethan Kumar, Women in R&D: Pvt sector outshines PSUs, August 31, 2020: The Times of India
Research and development (R&D) activity in India’s private sector has a larger proportion of women compared to governmentsupported agencies, even as men continue to overwhelmingly dominate the sector.
At least seven out of every 10 women employed by private R&D facilities are involved in research, whereas not even half of the female staff in government-aided scientific agencies have the same role, according to the latest edition of the Science and Technology Indicators (STI-2019-20) compiled by the Government of India’s Department of Science and Technology that was released this month. The employment number is for the year 2017-18.
Only public units in the industrial sector compare well with private R&D facilities. The overall number of women on the rolls at such units is 10 times lesser compared to private R&D facilities.
In govt-funded agencies, 10k of the 23k women engaged in R&D
Percentage of women in other central and state government departments and scientific and industrial research organisations pales in comparison with the private sector. Of the 20,000-plus women employed in private R&D firms, over 15,000 were involved in research activities and 2,800 and 2,500 were in auxiliary or administrative activities. In major scientific agencies funded by the government, there are over 23,000 women employed but only 10,000 worked directly in R&D.
“Although there is a slight increase in women in academia, the divide between academic and research institutions means that not enough women are in R&D,” said Rohini Godbole, a senior physicist who has chaired a panel on women in S&T. Another scientist working with the government on the new S&T policy said, “You will see something good on this in coming policy.”
The private sector has outpaced public R&D investment over the years although the latter has put in more money in absolute terms. The investment data is up to 2018-19. While R&D investment by the government was about 120% more than the private sector in 2004-05, the gap has reduced to 40% by 2018-19. Compared to the 300% jump in public investment on R&D from 2004-05 to 2018-19, private sector investment spiked 600%.