International students in India
(→Number of international students in India) |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| + | |||
| + | =International students in Indian universities= | ||
| + | August 7, 2008 | ||
| + | |||
| + | '' From the archives of ''The Times of India'': 2008 '' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hemali Chhapia | ||
| + | |||
| + | At a time when American, European and Australian universities are vying with each other to woo international students, Indian varsities have decided to shape up for fear of being shut out when competition comes calling in the form of foreign campuses. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Enrolment of international students in domestic varsities went up from 13,267 in 2004-05 to 14,456 in 2005-06, according to a recent report published by a wing of the Union HRD ministry. Behind these numbers are amends that institutions have made — establishing exclusive departments for international students, setting up fully air-conditioned accommodation equipped with hot-plates, dryers and other things straight out of an American hostel. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In a year, the Indira Gandhi National Open University (Ignou) has seen enrolment figures rise by 300%. Currently, it has the maximum number of international students in India, up from 963 in 2004-05. Ignou went up the ladder after designing special information booklets for foreign students with handy data, instead of the earlier patchwork approach that required students to approach several windows to get information. “We have established an international students’ division too,’’ said vice chancellor V N Rajasekharan Pillai. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Manipal, Pune universities among favourites of foreign students== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mumbai: A study conducted by the Association of Indian Universities (AIU) shows that Ignou, with 3,000 enrolments in 2005-06, was followed closely by the University of Pune for the number of international students enrolled. Though the western university managed to get 300 more students than in 2004-05 after its international students’ cell strengthened its marketing pitch, it slid down from the numero uno position to have 2,455 international students on its rolls. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pune University also participated in several international education fairs throughout the year, selling the ‘Oxford of the East’ concept to many a West Asian. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Down south, the education boomtown of Manipal also attracted a larger pool of foreign students. For its MBBS programme, which attracts several Indian Americans, MAHE joined hands with international universities to allow medical aspirants to pursue a part of their programme at the Manipal campus and then transfer credits to an American medical college, thus bringing down the cost of higher education. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In most cases, Usha Rai Negi and Dayanand Dongaonkar, who collected data from across the country’s universities for 2005-06, pointed out that about 80% of international students were enrolled in undergraduate programmes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | “They all want to be in campus colleges or in institutions that are in the heart of the city and most of these foreign students are pursuing a course in commerce,’’ said Pental. Data collected by the AIU from 1992-93 to 2003-04 suggests that the number of international students coming to India has steadily increased during the first half of the 1990s, with a peak of over 13,000 achieved in 1993-94. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==2011: preference of international students, state-wise== | ||
| + | [http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chennai/Tamil-Nadu-among-top-5-choices-for-student-migrants/articleshow/55785593.cms Sivakumar B, Dec 5, 2016: The Times of India] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''HIGHLIGHTS''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh account for 57.33% of these migrants. | ||
| + | |||
| + | More than 50% of the migration triggered by the search for quality education, from one state to another and within aparticular state, has happened in just five states in 2001-11. The Census 2011 data on migration shows that Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh account for 57.33% of the total migrants who moved out for educational purposes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | More number of men than women migrated to these states to join professional or arts and science colleges in the last decade. In terms of medical and engineering colleges, the five states account for 50% of the total government as well as private medical colleges in the county. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In all, 80.09 lakh people migrated to various states for the sake of education. Of this, 47.76 lakh are women and 32.32 lakh women. Some of them might have migrated within the state or would have come from other states. The exact figures of intrastate and interstate migration are yet to be released by the Census department. | ||
| + | |||
| + | "The data shows that of the total number of people who migrated for education, 45.92 lakh went to just five states. States like Kerala, which has the best literacy rate in the country , or Bihar, which has the lowest literacy rate, records sparse interstate and intrastate migration for education ," Indira Gandhi Institute of Development research economics professor S Chandrasekar told TOI. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In Kerala, of the total interstate migrants, only 1.2% have migrated for the sake of education and in Bihar it stands at 2.8%, he said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Between 2001and 2011, many politicians and businessmen have opened professional colleges in the top five states. "Most of the private professional colleges in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh woo students from other states as well as from abroad. The best example can be a technology university located in north Tamil Nadu, which woos students from Africa and Arab countries," former vice-chancellor Vasanthi Devi said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An analysis of the duration of the stay of migrants shows that nearly 20% of those who have migrated to the top five states have been staying there for the past 10 years. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Educational hubs in India== | ||
| + | ===2011: Maharashtra, AP, TN, Karnataka, UP top=== | ||
| + | [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Maharashtra-top-choice-for-student-migrants-in-India-05122016017030 Sivakumar B, Dec 5, 2016: The Times of India] | ||
| + | [[File: Top 5 states in migration for education, 2011.jpg|Top 5 states in migration for education, 2011; [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Maharashtra-top-choice-for-student-migrants-in-India-05122016017030 Sivakumar B, Dec 5, 2016: The Times of India]|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Maharashtra top choice for student migrants in India''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | More than 50% of the migration triggered by the search for quality education, from one state to another and within a particular state, has happened in just five states in 2001-11 | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Census 2011 data on migration shows that Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh account for 57.33% of the total number of people who migrated for educational reasons. | ||
| + | |||
| + | More number of men than women migrated to these states to join professional or arts and science colleges in the last decade. In terms of medical and engineering colleges, the five states account for 50% of the government as well as private medical colleges in the county . In all, 80.09 lakh people migrated to various states for the sake of education. Out of this, 47.76 lakh are men and 32.32 lakh women. Some of them might have migrated within the state or would have come from other states. The details on intra-state and inter state is yet to be released by Census department. “The migration data shows that out of the total number of people who migrated for education, 45.92 lakh went to just 5 states.States like Kerala, which has the best literacy rate in the country, or Bihar, which has the low est literacy rate, account for very few migra tion into them for education, both from within as well as from other states,“ Indira Gandhi In stitute of Development research economics professor S Chandrasekar told TOI. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In Kerala, out of the total people who have migrated into it, only 1.2% have migrat ed for the sake of education and in Bihar it is 2.8%, he said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Between 2001 and 2011, many politicians and businessmen have opened professional colleges in the above mentioned five states. | ||
| + | |||
| + | “Most of the private professional colleges in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh woo students from other states as well as from abroad. The best example can be a technology university situated in north Tamil Nadu, which woos students from Africa and Arab countries,“ former vice-chancellor Vasanthi Devi said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Irrespective of the quality of education in these states, each year more and more students seek admissions there. “Fees in these colleges are pretty high and students, mostly from well-to-do families in Bihar, Jharkhand, Kerala and West Bengal, seek admissions. Apart from professional col leges, there are also other institutes like ca tering, fashion, film, in which mostly stu dents from other states join as they are able to afford the high fees,“ said Devi. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An analysis of the duration of the stay of migrants shows that nearly 20% of those who have migrated to the five states have been stay ing in those states for the past 10 years.Some of them must have gone to those states as stu dents and must have got jobs and settled there. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==2015: Drop in numbers== | ||
| + | [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Indias-appeal-fades-for-foreign-pupils-24112015008055 ''The Times of India''], Nov 24 2015 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: The number of international students studying in Indian universities, 2012-14.jpg| The number of international students studying in Indian universities, 2012-14; Graphic courtesy: [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Indias-appeal-fades-for-foreign-pupils-24112015008055 ''The Times of India''], Nov 24 2015|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chethan Kumar | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' India's appeal fades for foreign pupils ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '' No. of students from 7 nations that send most dropped 73% from '13 to '14 '' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Indian Institute of Management Bangalore (IIM-B) was jubilant in August when it hosted students from 19 global schools for a course. But barring such isolated cases, the number of foreign students coming to India has seen a drastic decline. | ||
| + | According to data from the home ministry , the number of students from the seven countries that account for the bulk of overseas pupils -the US, Germany , France, South Korea, Australia, China and Singapore -has fallen 73% from 13,961 in 2013 to 3,737 in 2014.There was a marginal increase (12.4%) in 2013 from 2012, when these countries sent 12,424 students. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Experts say no one reason can be given for the sudden dip, but the way forward -as pointed out by Bharat Ratna Professor CNR Rao, Infosys cofounder N R Narayana Murthy and others -is to improve the quality of institutions to attract more foreigners. Students from over 160 countries came to India in these three years. The decline is not seen just among students from countries ranked higher than India vis-a-vis education but even from those lower. The number of Afghan students fell 11%, from 6,508 (2013) to 5,738 (2014), Bangladeshis from 1,954 to 1,247 (36%), and Sri Lankans from 2,502 to 1,492 (40.36%). The Indian Institute of Science (IISc), the only Indian institute among the world's top 100, had just 25 fulltime foreign students in 2014. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The decline, some experts say , is a reflection of where Indian institutions stand globally. “The government has not understood the soft power of higher education. But we will have ambassadors for life. (Former PM) Manmohan Singh passed out of Cambridge 55 years ago, but still has a soft corner for it,“ said IIIT-B founder-director S Sadagopan. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pointing out that there needs to be an institutional change in the way foreign students are treated, he added: “One reason for the decline could be all the bad publicity India is getting.“ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some students here, however, are not bothered by the negative image. Jose Antonio Borrero, a student at IIM-B, said, “I just love India. I interned at Mumbai, and have asked my parents to join me after my course.“ | ||
=Number of international students in India= | =Number of international students in India= | ||
| Line 46: | Line 139: | ||
[[Category:India|S INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIA | [[Category:India|S INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIA | ||
INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIA]] | INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIA]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Education|S INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIAINTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIA | ||
| + | INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Foreign Relations|S INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIAINTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIA | ||
| + | INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|S INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIAINTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIA | ||
| + | INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS IN INDIA]] | ||
Revision as of 19:02, 16 August 2021
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
International students in Indian universities
August 7, 2008
From the archives of The Times of India: 2008
Hemali Chhapia
At a time when American, European and Australian universities are vying with each other to woo international students, Indian varsities have decided to shape up for fear of being shut out when competition comes calling in the form of foreign campuses.
Enrolment of international students in domestic varsities went up from 13,267 in 2004-05 to 14,456 in 2005-06, according to a recent report published by a wing of the Union HRD ministry. Behind these numbers are amends that institutions have made — establishing exclusive departments for international students, setting up fully air-conditioned accommodation equipped with hot-plates, dryers and other things straight out of an American hostel.
In a year, the Indira Gandhi National Open University (Ignou) has seen enrolment figures rise by 300%. Currently, it has the maximum number of international students in India, up from 963 in 2004-05. Ignou went up the ladder after designing special information booklets for foreign students with handy data, instead of the earlier patchwork approach that required students to approach several windows to get information. “We have established an international students’ division too,’’ said vice chancellor V N Rajasekharan Pillai.
Manipal, Pune universities among favourites of foreign students
Mumbai: A study conducted by the Association of Indian Universities (AIU) shows that Ignou, with 3,000 enrolments in 2005-06, was followed closely by the University of Pune for the number of international students enrolled. Though the western university managed to get 300 more students than in 2004-05 after its international students’ cell strengthened its marketing pitch, it slid down from the numero uno position to have 2,455 international students on its rolls.
Pune University also participated in several international education fairs throughout the year, selling the ‘Oxford of the East’ concept to many a West Asian.
Down south, the education boomtown of Manipal also attracted a larger pool of foreign students. For its MBBS programme, which attracts several Indian Americans, MAHE joined hands with international universities to allow medical aspirants to pursue a part of their programme at the Manipal campus and then transfer credits to an American medical college, thus bringing down the cost of higher education.
In most cases, Usha Rai Negi and Dayanand Dongaonkar, who collected data from across the country’s universities for 2005-06, pointed out that about 80% of international students were enrolled in undergraduate programmes.
“They all want to be in campus colleges or in institutions that are in the heart of the city and most of these foreign students are pursuing a course in commerce,’’ said Pental. Data collected by the AIU from 1992-93 to 2003-04 suggests that the number of international students coming to India has steadily increased during the first half of the 1990s, with a peak of over 13,000 achieved in 1993-94.
2011: preference of international students, state-wise
Sivakumar B, Dec 5, 2016: The Times of India
HIGHLIGHTS
Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh account for 57.33% of these migrants.
More than 50% of the migration triggered by the search for quality education, from one state to another and within aparticular state, has happened in just five states in 2001-11. The Census 2011 data on migration shows that Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh account for 57.33% of the total migrants who moved out for educational purposes.
More number of men than women migrated to these states to join professional or arts and science colleges in the last decade. In terms of medical and engineering colleges, the five states account for 50% of the total government as well as private medical colleges in the county.
In all, 80.09 lakh people migrated to various states for the sake of education. Of this, 47.76 lakh are women and 32.32 lakh women. Some of them might have migrated within the state or would have come from other states. The exact figures of intrastate and interstate migration are yet to be released by the Census department.
"The data shows that of the total number of people who migrated for education, 45.92 lakh went to just five states. States like Kerala, which has the best literacy rate in the country , or Bihar, which has the lowest literacy rate, records sparse interstate and intrastate migration for education ," Indira Gandhi Institute of Development research economics professor S Chandrasekar told TOI.
In Kerala, of the total interstate migrants, only 1.2% have migrated for the sake of education and in Bihar it stands at 2.8%, he said.
Between 2001and 2011, many politicians and businessmen have opened professional colleges in the top five states. "Most of the private professional colleges in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh woo students from other states as well as from abroad. The best example can be a technology university located in north Tamil Nadu, which woos students from Africa and Arab countries," former vice-chancellor Vasanthi Devi said.
An analysis of the duration of the stay of migrants shows that nearly 20% of those who have migrated to the top five states have been staying there for the past 10 years.
Educational hubs in India
2011: Maharashtra, AP, TN, Karnataka, UP top
Sivakumar B, Dec 5, 2016: The Times of India
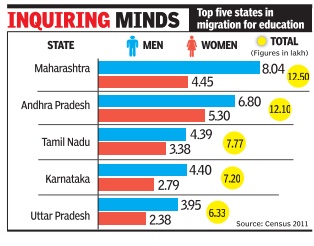
Maharashtra top choice for student migrants in India
More than 50% of the migration triggered by the search for quality education, from one state to another and within a particular state, has happened in just five states in 2001-11
The Census 2011 data on migration shows that Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh account for 57.33% of the total number of people who migrated for educational reasons.
More number of men than women migrated to these states to join professional or arts and science colleges in the last decade. In terms of medical and engineering colleges, the five states account for 50% of the government as well as private medical colleges in the county . In all, 80.09 lakh people migrated to various states for the sake of education. Out of this, 47.76 lakh are men and 32.32 lakh women. Some of them might have migrated within the state or would have come from other states. The details on intra-state and inter state is yet to be released by Census department. “The migration data shows that out of the total number of people who migrated for education, 45.92 lakh went to just 5 states.States like Kerala, which has the best literacy rate in the country, or Bihar, which has the low est literacy rate, account for very few migra tion into them for education, both from within as well as from other states,“ Indira Gandhi In stitute of Development research economics professor S Chandrasekar told TOI.
In Kerala, out of the total people who have migrated into it, only 1.2% have migrat ed for the sake of education and in Bihar it is 2.8%, he said.
Between 2001 and 2011, many politicians and businessmen have opened professional colleges in the above mentioned five states.
“Most of the private professional colleges in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh woo students from other states as well as from abroad. The best example can be a technology university situated in north Tamil Nadu, which woos students from Africa and Arab countries,“ former vice-chancellor Vasanthi Devi said.
Irrespective of the quality of education in these states, each year more and more students seek admissions there. “Fees in these colleges are pretty high and students, mostly from well-to-do families in Bihar, Jharkhand, Kerala and West Bengal, seek admissions. Apart from professional col leges, there are also other institutes like ca tering, fashion, film, in which mostly stu dents from other states join as they are able to afford the high fees,“ said Devi.
An analysis of the duration of the stay of migrants shows that nearly 20% of those who have migrated to the five states have been stay ing in those states for the past 10 years.Some of them must have gone to those states as stu dents and must have got jobs and settled there.
2015: Drop in numbers
The Times of India, Nov 24 2015
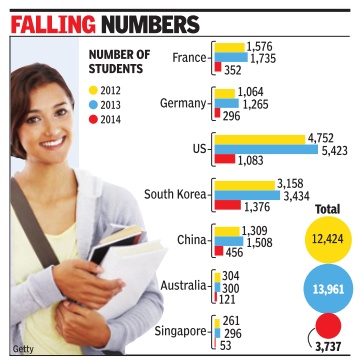
Chethan Kumar
India's appeal fades for foreign pupils
No. of students from 7 nations that send most dropped 73% from '13 to '14
Indian Institute of Management Bangalore (IIM-B) was jubilant in August when it hosted students from 19 global schools for a course. But barring such isolated cases, the number of foreign students coming to India has seen a drastic decline. According to data from the home ministry , the number of students from the seven countries that account for the bulk of overseas pupils -the US, Germany , France, South Korea, Australia, China and Singapore -has fallen 73% from 13,961 in 2013 to 3,737 in 2014.There was a marginal increase (12.4%) in 2013 from 2012, when these countries sent 12,424 students.
Experts say no one reason can be given for the sudden dip, but the way forward -as pointed out by Bharat Ratna Professor CNR Rao, Infosys cofounder N R Narayana Murthy and others -is to improve the quality of institutions to attract more foreigners. Students from over 160 countries came to India in these three years. The decline is not seen just among students from countries ranked higher than India vis-a-vis education but even from those lower. The number of Afghan students fell 11%, from 6,508 (2013) to 5,738 (2014), Bangladeshis from 1,954 to 1,247 (36%), and Sri Lankans from 2,502 to 1,492 (40.36%). The Indian Institute of Science (IISc), the only Indian institute among the world's top 100, had just 25 fulltime foreign students in 2014.
The decline, some experts say , is a reflection of where Indian institutions stand globally. “The government has not understood the soft power of higher education. But we will have ambassadors for life. (Former PM) Manmohan Singh passed out of Cambridge 55 years ago, but still has a soft corner for it,“ said IIIT-B founder-director S Sadagopan.
Pointing out that there needs to be an institutional change in the way foreign students are treated, he added: “One reason for the decline could be all the bad publicity India is getting.“
Some students here, however, are not bothered by the negative image. Jose Antonio Borrero, a student at IIM-B, said, “I just love India. I interned at Mumbai, and have asked my parents to join me after my course.“
Number of international students in India
2008-14
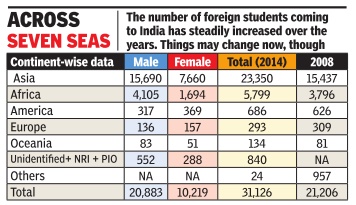
Graphic courtesy: The Times of India, March 30, 2017
See graphic:
International students in India, 2008- 2014
2018-19: Top 7 source countries
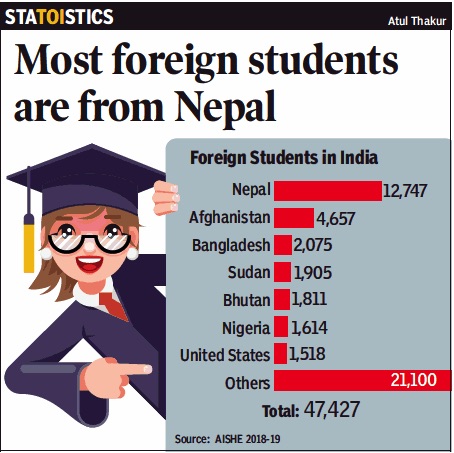
From: March 19, 2020: The Times of India
See graphic:
2018-19: The Top 7 source countries for international students in India
2020
Participation in protest rallies
Jayanta Gupta, March 4, 2020: The Times of India

From: Jayanta Gupta, March 4, 2020: The Times of India
Kamil Siedcynski, the Polish student at Jadavpur University who has been asked to leave the country by the Foreigner Regional Registration Office, has challenged the order in the Calcutta HC, invoking the principles highlighted in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (1966) that are applicable to all persons.
While the FRRO has found Siedcynski guilty of violating visa norms by participating in an anti-CAA rally, he has claimed in his petition that he was inadvertently caught in the protest. He has maintained that as a student with interest in Indian culture, he was merely watching the proceedings and had clicked photographs of the “carnival-like” proceedings from a sidewalk. Siedcynski has claimed in his petition that the FRRO order of February 14 is contrary to the principles of natural justice. His petition is likely to be heard.
He stated in his petition that he had been persuaded by other students to accompany them to the protest place on December 19. He apparently didn’t know what the protest meet was all about and soon got separated from his fellow students. He stood on the sidewalk watching the event and clicking photographs. He claimed there were other foreigners watching the protest as well and a person approached him wanting to know his name and views on the protest. The man also clicked his photograph after which he left for home. The next day, Siedcynski realised the man he had spoken to was a photojournalist and an article on him had appeared in a newspaper. He has claimed that much of what was written in the article was made up.
He received a notice from the FRRO thereafter and was asked to leave the country on February 14.