National Capital Region (NCR) India: articles about
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers can send additional information, corrections, photographs and even Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Contents |
Territory
The NCR includes 19 districts
Uttar Pradesh
Ghaziabad, Gautam Budh Nagar, Meerut, Baghpat, Hapur and Bulandshahr are the six UP districts included in NCR.
Infrastructure
It’s still a next-to-capital region
Dipak Kumar Dash TNN 2013/07/03
New Delhi: The pathetic state of infrastructure and poor quality of life in a dozen districts such as Hapur, Bulandshahr and Mewat falling under National Capital Region (NCR) even after 25 years of their inclusion show how the concept of “integrated & holistic” development of the region has failed. While politicians and bureaucrats maintain greater growth of the NCR would help reduce burden on Delhi, planners tell how states are just setting up towns on the capital’s periphery —termed as ribbon development.
“This is just squatting on Delhi’s borders. Why are the states allowing more real estate development on the borders of Delhi if they are not driving the realty growth? They must develop the entire state if they are so interested in reducing stress on Delhi’s infrastructure,” said H R Suri, former president of Institute of Town Planners India.
Sewage
Infrastructure available in the existing NCR (excluding Mahendragarh, Bhiwani and Bharatpur) also proves how the NCR tag has done little good for several towns. According to Draft Revised Regional Plan-2021, out of 108 towns, only 33 have “partial” sewage system. In UP sub-region only six out of 63 towns are partially covered while in Haryana sub-region 24 out of 35 towns are partially covered. In Rajasthan sub-region two towns are partially covered out of the total nine. “NCR is way behind the MoUD bench mark of 100% coverage, though it’s better than national average of 12.2%,” it says.
Solid wastes
It’s no better in solid waste generation and management either. NCR generated about 13,199 million tones solid waste per day in 2011. By 2021, it would increase to 19,238 million tones while there is increasing scarcity of landfill sites. As far as water supply in rural areas is concerned, states need to work a little more. The document says while 63% rural areas in Rajasthan sub-region are fully covered, it’s little better at 64% in Haryana.
All these indicators also raise questions on the success of NCR Planning Board (NCRPB) in achieving its goal to “evolve harmonized policies” for land use control and infrastructure development to avoid “any haphazard development”. The individual development plans need to conform to the regional plan and the board has the mandate to ensure states follow this.
However, as land is a state subject, NCRPB has little control on how the local authorities push development in their areas. Even the board officials admit how it’s almost impossible to go through each of the 180 Master Plans that they receive. “We have no punitive power. But as and when we come to know of any violation, we stop providing soft loan to that state or town,” one of them said.
The official said the real issue is not “getting teeth”, but getting every state on board by coordination and collaboration. NCRPB sources said they have been doing the “best possible” within the framework. “We have a regional plan and all sub-regional plans prepared by states need our approval. We ensure these plans by states follow norms for harmonious growth,” the source said.
NCR Planning Board (NCRPB)
NCRPB soft loans
UP shows no interest in soft loans for its districts
Dipak Kumar Dash & Purusharth Aradhak TNN 2013/07/03
New Delhi/ Noida: It has a third of all NCR districts yet, surprisingly, Uttar Pradesh has been a reluctant borrower of concessional funds meant for their development. And depending on whom you ask the question, both the state government and the regional planning board get the blame for this state of affairs.
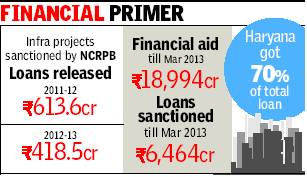
UP has six of the 19 districts comprising the National Capital Region (NCR) but accounts for only 11% of the soft loan provided by the NCR planning board. Haryana, in contrast, has taken 70% of the funds disbursed so far.
Sources in the Union urban development ministry say UP has shown little interest in pitching its projects to NCRPB for availing low-interest loans to augment and create infrastructure. In 2011-12, the board funded 35 projects—30 from Haryana but none from UP. Last year, NCRPB released funds for 23 projects, of which 22 were from Haryana and one from Rajasthan.
The board now offers loans for infrastructure at 7.25% interest with a 0.25 percentage point rebate for prompt repayment. “
An official said UP may not be interested in the NCRPB loans as the amount is small relative to its annual plan. “Moreover, the state can directly tap long-term soft loans from multilateral bodies such as Asian Development Bank (ADB) and World Bank.”