Crop stubble burning: India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
Origin of burning crop stubble
Background
Amit Bhattacharya The Times of India, Nov 03 2015
Widespread crop burning began over dozen yrs ago
Satellite images reveal age-old norm
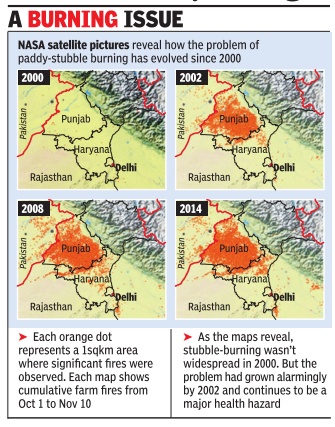
The practice of burning paddy stubbles in Punjab and Haryana has of late been recognised as a major contributor to air pollution in the national capital region during October-November. Satellite images, however, reveal that the problem had already reached alarming proportions as early as 13 years ago.
Farm fires in the region began to register in satellite images in year 2000. Not that stubble burning did not take place before that, but the practice probably became widespread enough in 2000 for it to show up in the 1-square-km resolution satellite images. By 2002, the `fires spots' in the satellite pictures had filled up almost the entire state of Punjab and parts of northern Haryana.
TOI obtained the data from Nasa's FIRMS Fire Mapper website, which enables users to access satellite imagery from the past.
To get a season-wide picture perspective, cumulative fire data was considered from October 1 to November 10 -a 40-day period when farmers in the region burn their paddy stubble to prepare the fields for the next crop.
What the information reveals is that successive governments in the states have failed to check the practice despite a law that bans stubbleburning. The problem assumes more serious proportions with each passing year due to the fact that pollution from other sources are on the rise in NCR. So, the added pollutants that come from biomass burning make the situation graver.
The concentration of farm fires in Punjab and northern Haryana shows the extremely high proportion of farmers opting to grow paddy during the kharif season. As Ruby Singh Sandhu, a big farmer from Mallekan village in northern Haryana puts it, “Farmers in the cotton growing areas of Punjab and Haryana have been slowly shifting to paddy for more than a decade now.“
Disadvantages of burning crop stubble

From: Jayashree Nandi, Happy seeders beyond farmers’ reach, f ield f ires still a sad reality, May 5, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
The multiple disadvantages of burning crop stubble
Did mechanical harvesting start the epidemic?
The advent of combine harvesters in Punjab, Haryana and UP, in the late 1980s and early 1990s, is being blamed for the practice of burning crop stubble. To save time and money, as well as to tackle labour shortage, more and more farmers are opting for mechanical harvesting of crops using combine harvesters.
Farmers say the blades of combine harvesters don't cut the crops close to the ground, and leaves the plant stalk, usually up to two feet high, standing.
Sarabjit Singh, a farmer from Virpur village of Bijnor district in UP , said the people who operate combine harvesters don't cut the crop close to the ground since they are more concerned about getting the grain. “The operators try to clear the maximum possible area in a day since they charge per acre. Hence, they leave the task of clearing the crop to the farmers. The crop stalk is very high at times,“ he added.
Farmers find it difficult to plough the crop residue back into the soil using harrows and, instead, resort to burning the stubble to clear the fields for the next crop. The problem is more pronounced in the winter, with little time available for farmers to prepare the fields for sowing wheat after harvesting paddy.
The prevailing rates for harvesting paddy using combine harvesters in north India are in the range of Rs 1,300-1,500 per acre. On the other hand, labour charges of harvesting paddy manually are around Rs 1,600 per acre, a practice more prevalent in UP, MP and parts of Haryana.
Another farmer, Baljinder Singh Sidhu from Kotbhara vil lage in Punjab's Bathinda district, said the days of manual harvesting were better: “Earlier, when paddy was manually harvested, the crop was cut close to the ground. While the grain was obtained after threshing, the leftover plant stalk or straw was stored as fodder for cattle.“
Sadhu Singh, director of Akhtiar Agro King, an agriculture machinery manufacturing unit in Moga, said the problem was acute in Punjab since the farmers don't consider paddy straw to be of any use.
“In case of wheat, the combine harvesters usually cut the crop close to the surface. However, farmers in Punjab don't keep paddy straw, so they don't insist on a close cut for the crop,“ he added.
Alternatives, solutions
Biogas from stubble/ IIT/ D
Manash Gohain, IIT-D shows how Punjab can re-use farm waste, Nov 13 2016 : The Times of India
Instead Of Burning, Paddy Straw Can Be Used To Make Biogas
Are you a farmer? How about earning a handsome amount from the stubble left behind in your field instead of burning it and adding to the pollution level?
How about also getting biofertiliser and sustainable energy in the same deal?
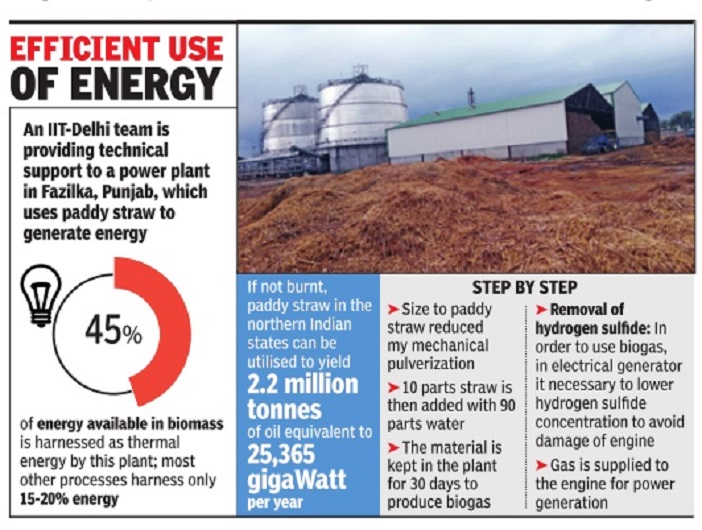
An IIT-Delhi team has provided technical support to Asia's first biogas-based power plant which is now operating on paddy straw for largescale biogas production in Fazilka, Punjab. The system is based on 100% use of paddy straw and has been generating nearly 4,000 cubic metres per day of biogas from 10 tonnes of straw. This is in turn generating 1MW power.
This sounds like welcome way out of the pollution mess that the capital has found itself in. Going by reports, 70% of Delhi's air pollution is due to stubble burning in Punjab, Haryana and other parts of north India.
Professor V K Vijay of Centre for Rural Development and Technology (CRDT) of IIT-D said paddy straw, if not burnt, could yield 2.181 million tonnes of oil equivalent or 25,365 gigaWatt hours per year.“Straw burning can be avoided through installation of commercial biogas industries by using these agro biomass for both power generation and biofertiliser production to enrich soil health. The present level of utilisation at Fazilka has shown a saving of 120 gigaJou les per day energy which otherwise would have been released to the atmosphere by direct combustion along with the release of enormous pollutants,“ said Vijay.
He added, “Burning straw biomass amounts to 30kg of particulate matter, 600kg of carbon monoxide, 14.6 tonnes of carbon dioxide and 20kg of sulphur dioxide emissions, which have significant toxicological properties and are potential carcinogens.“
Abhinav Trivedi, a doctoral fellow working under the guidance of Vijay , developed this process that has better efficiency than conventional processes for biogas generation.
Dr Ramchandra of CRDT said the project was started in December 2011 by the Punjab government in association with Sampurn Agri Ventures Pvt Ltd. “After our intervention for around six months, the plant is running for nearly eight hours per day for the same amount of straw against two hours earlier. It is generating 7,500 kiloWatt hour per day and nearly five tonnes of bio-fertilisers per day ,“ he said. Ramchandra also said that the system was able to harness over 45% of energy available in the material.
Cattle fodder from stubble
Jasjeev Gandhiok, November 8, 2020: The Times of India
A simple solution to curb farm fires, ask this duo
New Delhi:
While bio-decomposers are being used by Delhi government to tackle stubble burning menace this season, two farmers hailing from southwest Delhi’s Jhuljhuli village have been providing a simple and easy solution to local farmers for close to a decade now. They have been collecting their stubble and then processing it before providing it to gaushalas in the region. Farmers get paid close to Rs10,000 per hectare.
The two brothers say this has notonly ensuredthestubble is notseton fire,butit also providesemploymentto 33 labourers.
Hailing from Bihar’s Sitamarhi district, the two brothers — Lalu Yadav (40) and Chote Lal (34) moved to Delhi close to two decades back. While initially working to supply animal feed, the two brothers say they were given the idea by local farmers, who requested for some assistance to clear their farm of stubble so that the next crop could be planted. The brothers have been collecting stubble with the help of labourers since 2010.
“This has been an old practice that people in villages still follow. They manually clear the fields of stubble. It started at a small scale, but now, it has spread to five villages and we currently cover stubble from 200-300 hectares each year,” said Yadav, the elder of the two brothers.
He says gathering the paddy and processing it take close to two months, after which they sell it as fodder in the wholesale market, or approach gaushalas. The two brothers have been assisted by local NGOs Sambhav and CYCLE India, which provide them technical assistance in managing the stubble.
Among the villages being covered by them at present are Rawta, Malikpur, Galibpur, Sarangpur and Jhuljhuli and the brothers say they are gradually planning to assist farmers across Delhi. “Farmers understand the pain of other farmers and if they are provided a solution, they will adopt it. While technological solutions are also welcome, this will help generate employment and ensure farmers do not burn their fields,” said Lalu Yadav.
Sambhav had also written recently to the chief minister, asking for this initiative to be scaled up to provide more employment across Delhi’s villages. “Close to 1,000 hectares can be managed this way and 150 people will get employment. At present, 200-300 hectares are being covered by the two brothers and his 33 labourers,” said Deepak Yadav from the NGO.
“We’ve approached 11 more villages, asking them to manage stubble locally,” Yadav added.
Fuel-grade ethanol
Dec 25 2016, The Times of India’'
There might be some solution in sight as the biofuels in tion in sight as the biofuels industry now says fuel-grade ethanol could be a more valuable product from crop residue that, when burnt, not only causes air pollution but literally sends crores of rupees up in smoke. According to Pramod Chaudhari, executive chairman of Praj Industries, a leading biofuels technology provider, 250 litres of fuel grade bio-ethanol can be produced from a tonne of farm residue using second-generation processing technology .
A step towards increasing biofuel availability will be taken when Pradhan and food processing minister Harsim rat Kaur Badal lay the foundation stone on Sunday of the first bio-ethanol refinery at Bathinda in poll-bound Punjab. Alive to the issue, the government has asked state-run fuel retailers to set up bio-ethanol refineries. “Second-generation ethanol production technology using rice-paddy straw in Punjab and Haryana will be a permanent solution to crop burning,“ oil minister Dharmendra Pradhan said in a November 7 tweet.
Estimates, including those by Nasa, pegged the quantity of farm residue burnt at 32 million tonnes in Punjab alone. This could mean some six billion litres of bio-ethanol. This can also translate into a big saving for the country, which meets 80% of its crude requirement through imports, since adequate availability of bio-ethanol will boost the government's plan to achieve 20% blending of petrol and diesel by 202122. That level of blending, a recent report by the Dehradun-based University of Petroleum and Energy Studies said, could save $6.12 billion in oil import bill.
Besides producing bioethanol for the fuel blending ethanol for the fuel blending programme, the new refineries will provide additional income for farmers, create jobs in rural areas and help air quality management.
Happy Seeder, straw spreader

From: Amit Bhattacharya, 4-fold rise in green solution to burning of paddy stubble, December 18, 2017: The Times of India
Tech Is Proven, Needs Sop For Big Push: Experts
For the past two years, Manoj Kumar Munjial hasn’t set fire to a single straw of paddy residue in his fields sprawled over 45 acres at Taraori in Haryana’s Karnal district. Instead, the young farmer uses the straw as an input for future crops. Even as the new wheat crop grows, the old residue sits in the field enriching the soil, conserving water, nourishing the new plants and creating conditions for decreased use of fertilisers.
Welcome to the post-stubble-burning future. Munjial is among a growing tribe of farmers in Haryana and Punjab who are using paddy residue for greener agriculture. The technology has existed for years. But recent improvements, say experts, have made it a more viable and scalable solution to the vexed problem of stubble-burning. It registered an estimated four-fold increase this season, which is still less than 2% of the area under rice cultivation in northwest India.
The technology is a combination of Happy Seeder and straw spreader (straw management system or SMS) for rice-wheat farming. Developed by Ludhiana’s Punjab Agricultural University, the Happy Seeder is a machine that sows seeds without the need to till the field or remove paddy straw. It works best when the straw is spread evenly on the field through the SMS device attached to a combine harvester.
How this tech is a win-win for farmers, environment
Stubble Burning: Combination Of SMS & Happy Seeder Way Forward
In two years, I have recovered my Rs 1.05 lakh investment on Happy Seeder. Apart from my own farm, I hired it out on 120 acres of other farmers’ fields this year. Last year, that figure was 80 acres. Each acre gives me a return of Rs 800-900, after deducting diesel costs for running the tractor,” Munjial said.
According to estimates by the international non-profit research body, Borlaug Institute for South Asia (BISA), the use of Happy Seeders increased almost four times this sowing season over the previous year, with an estimated 75,000 hectares coming under it in Punjab and Haryana.
“The combination of straw management system (SMS) and Happy Seeder is a win-win for farmers and the environment. It does away with stubble-burning while increasing farmers’ profitability and promoting climate-smart agriculture. The spinoffs are significant — lower chemical load on soil, more crop per drop, reduction in CO2 emissions, better soil health, less weeds and sturdier plants with deeper roots. These benefits are scientifically documented,” said M L Jat, a senior scientist at BISA.
Despite the strides, the technology is not catching on fast enough to make a significant dent in stubble-burning. Even after rising concerns and a crackdown on cropburning, the area under Happy Seeders this season was just around 1.7% of the 4.3 million hectares under rice cultivation in Punjab, Haryana and west Uttar Pradesh.
Though there’s a subsidy of Rs 50,000 for SMS and Happy Seeder machines, these implements still cost over Rs 1lakh each. Experts say these technologies, including the reversible plough (for potato and vegetable farming after rice crop), need to be further incentivised and a major push needs to come from the Centre and state governments well ahead of next year’s burning season.
Sources say the matter was discussed at the PMO committee under PM’s principal secretary Nripendra Misra earlier this month. A policy brief prepared by the National Academy of Agricultural Sciences had proposed various multiple business models for popularising Happy Seeder and SMS. These include custom hiring of the implements through agricultural cooperatives, medium farmers such as Munjial and specialised startups. Farmer unions have demanded higher subsidies and proposed that government make the implements available through local bodies and cooperatives.
“We are prepared to scale up production of Happy Seeders for the next season but we need an early and clear signal from the government,” said Joginder Singh of Kamboj Mechanical Works, one of the major producers of the machine.
Kamboj sold around 200 Happy Seeders this season, up from 100 last year. Landforce, another big producer, reported sales of 400 this year, significantly higher than the 10-15 Happy Seeders the company sold in 2016.
Better returns for farmers
Amit Bhattacharya & Ritam Halder, August 9, 2019: The Times of India

ii) Happy Seeder, its advantages and lack of greater acceptance.
From: Amit Bhattacharya & Ritam Halder, August 9, 2019: The Times of India
Farmers make headlines in north India every year in October-November, when millions of acres of burning fields contribute to an ‘airpocalypse’ that chokes the region. Yet, the hazardous practice of stubble-burning continues mainly because a majority of farmers believe it’s the cheapest option they have to clear their fields for the winter crop. But, is it?
A study published in the journal Science shows that alternatives such as the use of Happy Seeder along with straw management systems can actually give farmers up to 20% higher returns than the most common method that involves burning stubble. Happy Seeder is a tractor-mounted implement, developed at Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, that can sow seeds in fields where stubble from the previous crop hasn’t been removed. The straw acts as mulch, retaining moisture in soil and providing nutrients to future crops.
Most farmers growing rice and wheat in north India prepare their fields for the wheat crop in October-November by burning the stubble left after the rice crop has been harvested, ploughing the field and sowing wheat using conventional seeders. The study — Fields On Fire: Alternatives To Crop Residue Burning In India — compared 10 common alternatives used by farmers, three of which involve residue burning.
The authors evaluated the public and private costs as well as the benefits and potential scalability of each method. They found that methods based on use of Happy Seeders gave on average 10% higher returns than the burning option (with zerotill seeders) and were around 20% more profitable than the most common method that involves burning the crop residue and using conventional seeders (see graphic).
The study said the higher profits from methods using Happy Seeder came from both slightly better yields and lower input costs. Baling, another alternative to burning in which the crop residue is packed into bales by machines for sale as fuel, was not found to be as profitable. Another method, incorporation of residues into the soil, offered the lowest average returns.
The authors — who include scientists from The Nature Conservancy, the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), the Borlaug Institute for South Asia (BISA) and the University of Minnesota — relied on data from peer-reviewed experimental field trials, farmer field trials, farm household surveys, government data and primary datasets, all from Punjab and Haryana, the two states where most burning takes place.
The findings tie in well with the Centre’s Rs 1,151-crore package, announced last year, to promote in-situ management of crop residue (through use of Happy Seeders and other methods that leave the stubble in the field) in Punjab, Haryana, UP and Delhi. As a result of the Centre’s subsidy, Happy Seeder sales shot up to an estimated 10,000 last year, a 10-fold increase from 1,000 seeders sold in 2017. Trilochan Mohapatra, DG of ICAR, said use of Happy Seeder/zero tillage technology spread to 8 lakh hectares in north India last year following the Centre’s package.
“Considering the findings of the Science article as well as reports from thousands of trials, our efforts have resulted in an additional direct farmer benefit of $131 million, compared to a burning option,” Mohapatra said in a statement.
Yet, the study points out that much more needs to be done to end crop burning. Its survey of farmers, done in 2017, showed that while most knew about the Happy Seeder, relatively few (around 11%) had used it. The in situ techniques, in which straw is left on the soil as mulch, have other advantages, said ML Jat, principal scientist at CIMMYT and a co-author of the study. “These methods help capture and retain moisture, reducing the need for watering, and also improve soil quality. Crops grown under these techniques are more resilient to climate stresses,” he said.
Ploughing stubble back into the soil
Manish Sirhindi, October 19, 2018: The Times of India
Farmers in ‘model’ Punjab village don’t burn crop stubble, plough it back into soil
When smoke from burning paddy stubble was choking Delhi last year, a village near Nabha in Punjab was doing its bit to keep the air clean. Not a straw was burnt in Kalar Majra, where 60 families farm about 700 acres.
“The government chose our village as a model, and gave all the machinery needed to manage the crop residue,” says Bir Dalvinder Singh, a Kalar Majra farmer who persuaded his neighbours to heed the government’s call against burning stubble. The eco-friendly step earned praise from the National Green Tribunal.
Although there is no assistance from the government this year, about 70% of Kalar Majra has decided not to burn paddy stubble, with good reason. Ploughing it back into the soil is good not only for Delhi’s air but also the farmers’ bottom line.
Few know this better than Surjeet Singh of Sandhugarh village in Punjab’s Fatehgarh Sahib district. He hasn’t burnt crop residue on his 45 acres for the past 15 years. “I use a ‘happy seeder’ to manage the stubble, and for the last two harvests I used the straw management system of a combine harvester,” he said.
Surjeet had his moments of doubt when costs shot up in the first two years. “It appeared to be a bad decision,” he said, but he started saving on fertiliser and fuel from the third crop onwards. He claims his use of fertiliser has halved. “Despite that my crop yield has increased by at least 20%.” Parvinder Singh, of Mavi Kalan village near Patran, is another advocate of the happy seeder. It not only saves diesel at the time of tilling, but also water, as the fields don’t need irrigation before sowing.
Cost of giving up stubble burning too much for some
Yet the yield goes up by 2-2.5 quintals of wheat per acre, as the paddy straw acts as a crop nutrient,” Parvinder Singh said.
So, why do most farmers in Punjab still burn their crop residue? Bir Dalvinder, who used to be a techie in Gurugram and has braved Delhi’s yearly smoke episodes, says cost is the main hurdle. Jeet Mohinder of Kularan village in Patiala district agrees, saying residue management costs Rs 2,000 to Rs 3,500 per acre in the first two years. “Most farmers consider it a risk, and take the easy way out by burning the stubble.”
Pressure from farmers’ unions is another deterrent, says Bir Dalvinder. “Some marginal farmers have been misled by the kisan unions. They say they will burn the residue if the government does not provide help. But we are trying to persuade them not to fall for the misinformation campaign.”
The government has tried to encourage stubble management with subsidies on equipment, but Jeet Mohinder says it should give farmers financial benefits for the first three years instead. Once the decomposed stubble boosts soil fertility, “farmers will realise the benefits of not burning it. They will be eager to find ways to dispose of it in an environment-friendly way.”
Some farmers bury stubble to increase soil fertility

From: IP Singh, Not all farmers burn stubble, some use it to improve harvest, November 13, 2018: The Times of India

From: IP Singh, Not all farmers burn stubble, some use it to improve harvest, November 13, 2018: The Times of India
Several Cultivators In Punjab Are Employing Paddy Residue To Create Fertilisers That Are Ploughed Back Into Their Fields
Come autumn and the vexatious issue of stubble burning in northern India sets off alarm bells and leads to much hand-wringing in policy circles and civil society with little, however, to show by way of a solution. But some farmers in Punjab have applied innovative strategies to dispose of their paddy stubble that doesn’t involve the setting of their fields on fire.
Farmers in Punjab have started sowing wheat as paddy harvesting enters the last stage with just one-fifth of the crop left to be cut in fields. But it is the lack of a gap between harvesting paddy and sowing wheat and the increased time and high cost of operating subsidised straw management machines that leaves farmers who are keen to stop burning stubble with no choice.
However, amid all the hue and cry over crop burning, there are instances of farmers in Punjab who have employed novel methods to manage paddy stubble at low or negligible costs.
Take for example Mukesh Chander of Rani Bhatti village near Bhogpur in Jalandhar district. He revealed that he had collected stubble on a small portion of his field and sprayed urea on it. “This helps to convert stubble into fertiliser in around two months, which we plough back into the field at an appropriate time between the harvesting and sowing of a crop,” he said.
The use of this innovative method is a win-win scenario for farmers. “It saves a lot of expenditure on diesel, which is consumed for managing the stubble with machines, and has also reduced my consumption of fertilisers. I have calculated that although a small portion of the field is used to pile up the crop stubble, the final compensation in terms of savings is more,” said Mukesh, who cultivates over 100 acres of land that he takes on contract.
Gurdev Singh of Navan Qila village, near Shahkot, also in Jalandhar district, said he had experimented by throwing cattle dung over stubble piled up at a side of his field with a view to converting it into fertiliser. “If one can mix cattle dung and stubble after a few weeks using an earth-moving machine, then it can be ploughed back as fertiliser in the fields in six months. I have been using this method for most of the last decade and this has been much cheaper,” he said.
Shaminder Singh Sandhu of Aahli Kalan village in Kapurthala district, whose family cultivates over 300 acres, said they did not burn stubble and had ploughed it back into the fields. “This has reduced our consumption of fertilisers. Most people in our village did not burn stubble,” he said.
Lakhwinder Singh, from the same village, whose family has been cultivating 100 acres, said he only used mulcher to break down stubble into fine parts and did not spend on ploughing it back. “We have already sown wheat and it has started growing well,” he said. “The shredded stubble would ultimately get mixed in the soil during irrigation and would decompose further on its own. I have been using this method for the last three years and this has reduced my consumption of fertilisers as well as the spending on stubble management,” he added.
Although media reports suggest that there is a visible reduction in the volume of post-harvest stubble-burning in Punjab and Haryana this year, a good chunk of farmers is still reluctant to use the ‘Happy Seeder’ — a machine which allows sowing without removing the stubble, thus obviating the need for stubble burning — fearing lower yields.
Seasonal burning of crop stubble and smoke from fireworks lit to celebrate Diwali on November 7 have aggravated already high smog levels in the past few days in national capital Delhi from vehicle emissions, industrial gases and construction work.
But turning stubble into fertiliser, as some farmers have done, should serve to address the issues of both crop burning and farm yields for farmers in northern India.
Commercial utilisation of stubble/ 2019
Punjab has 75 lakh acres of land under paddy cultivation. Every October after the harvest, these vast fields are left with crop residue, also known as stubble or straw, which farmers usually burn to prepare their fields for the wheat crop. The smoke ends up choking Delhi and other parts of north India. But now some firms are not only turning crop waste into money but also saving lungs in the process.
Farm2Energy Pvt Ltd, a three-year-old business based in Ludhiana’s Bija village, is run by two farmer brothers, Sukhbir and Kamljeet Singh. Its balers and tractors scoop up the stubble, roll it into bales and sell it to neighbouring sugar, cement and oil factories as well as power plants who burn these in a controlled environment to fire boilers.
At the Bio-lutions factory in Ramnagara, Bengaluru, eight machines convert three tonnes of paddy straw from Punjab into pulp every day. The pulp is then used to manufacture sustainable tableware and packaging material.
‘Straw biz yielding operating profit’
Nitin Jain, chief financial officer of Farm2Energy, says, “Since we started in 2016, we have cleared straw from 20,000 acres of farmland in Punjab. “We also make biocoal from crop stubble and plan to monetise it from the next financial year.”
The stubble business is already showing an operating profit, says the CFO.
Three tonnes of straw processed in the Bengaluru factory is just a fraction of the rice straw generated in Punjab but it’s a beginning, says Kurian Mathew, CEO, Bio-lutions India. The company produces plates, bowls, trays to pack vegetables in supermarkets and kidney trays used in hospitals.
In Delhi, a bunch of engineers and scientists have floated a company to tackle the issue. Operating from the IIT campus, Kriya Labs is running a pilot unit which breaks down agricultural residue to pulp, which can be used to make tableware. Ankur Kumar, CEO, Kriya Labs says, “We purchased 500kg of paddy straw at Rs 5/kg, and our current facility can produce 50kg of pulp a day”. If these firms succeed commercially, it will mean relief for residents of North India who have to deal with respiratory disorders. A study by the USbased International Food Policy Research Institute and partner institutes has estimated that the health and economic costs of crop burning in northern India amount to over $30 billion annually.
Economic cost
1.7% of India’s GDP/ 2010s
Economic cost of crop fires: ₹2Lcr a year, March 5, 2019: The Times of India
Study Pegs Damage To Health In Delhi, Haryana, Punjab In 5 Years At 1.7% Of India’s GDP
The economic cost of exposure to air pollution from stubble burning in north India has been pegged at $30 billion, or nearly Rs 2 lakh crore, annually for Punjab, Haryana and Delhi.
Data related to this was published in a study unveiled on Monday by researchers from the US-based International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) and partner institutes, which found that living in districts with air pollution caused from intense stubble burning has been a leading risk factor for acute respiratory infection, particularly in children less than five years.
The study , Risk of acute respiratory infection from crop burning in India: estimating disease burden and economic welfare from satellite and national health survey data for 250,000 persons, has been co-authored by IFPRI’s Samuel Scott and Avinash Kishore; CGIAR Research Program on Agriculture for Nutrition and Health’s Devesh Roy and University of Washington’s Suman Chakrabarti.
It estimates for the first time the health and economic cost of stubble burning in northern India and found that this led to an estimated economic loss of over $30 billion annually.
“The levels of airborne particulate matter in Delhi on certain days spiked to 20 times the World Health Organization’s safety threshold. Among other factors, smoke from the burning of agricultural crop residue in Haryana and Punjab, especially contributed to Delhi’s poor air, increasing the risk of acute respiratory infection by threefold for those living in the districts with intense crop burning,” Scott said.
The study, which will be published in the upcoming edition of the International Journal of Epidemiology, analyses the health data from over 250,000 individuals of all ages residing in rural and urban areas in India. It uses NASA satellite data on fire activity to estimate the health impact of living in areas with intense stubble burning by comparing them with areas not affected by it.
The researchers observed that as stubble burning increased in Haryana, respiratory health worsened. Health was measured by the frequency of reported hospital visits for acute respiratory infection symptoms. In five years, the economic loss due to burning of crop residue and firecrackers was estimated to be $190 billion, or nearly 1.7% of India’s GDP, they said.
“Severe air pollution during winter months has led to a public health emergency. Stubble burning will add to the pollution and increase healthcare costs over time if immediate steps are not taken,” said Chakrabarti, adding that the negative health effects will also lower the productivity of residents and may lead to a long-term adverse impact on the economy and health.
Kishore from IFPRI explained that, “It is not only the residents of Delhi, but those in rural Haryana are also the first victims of stubble burning. Much of the public discussion on its ill-effects ignores this immediately affected vulnerable population.” The study suggests that targeted government initiatives to improve crop disposal practices are worthy investments, researchers claimed.
The researchers noted that stubble burning has been a widespread global practice, and in India, is concentrated in northwest and has spread to other regions in the past decade.
Health issues
Study links straw burning to cancer, kidney damage
Crop residue fires in Pun jab and Haryana are en hancing concentrations of toxic gases like benzene and toluene, according to research from Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Mohali.
In the months right after the harvest of paddy , the levels of these gases were found to be 1.5 times higher than the annual average concentrations, according to a recent study that monitored air at a site in Mohali a few kilometres downwind of paddy fields, between 2012 and 14. Farmers set fire to crop residue after harvest, which sends massive plumes of smoke into the air.
The study also detected, for the first time, a compound known as isocyanic acid at annual average levels close to the toxic threshold of 1ppb (parts per billion). Exposures above this level can lead to cataracts and rheumatoid arthritis.
Annual concentrations of benzene, a known carcinogen, exceeded the National Ambient Air Quality Standard of India limits of 1.6ppb. Such benzene exposure could raise cancer risk by 25 per million children and 10 per million adults, the study estimated, at sites 10-15 km downwind of the fields.
The cancer risk would be even higher for farmers and villagers closest to the fields, the study said, adding that mitigating crop fires could reduce these risks.
The findings come from the first long-term field measurement in India of the impact of post-harvest agricultural fires on ambient levels of gases known as volatile organic compounds. The gases measured in the study include acetonitrile, benzene, toluene, and aromatic hydrocarbons. These substances have direct effects on human health -high levels of toluene can cause dizziness, eye irritation, kidney damage, for instance -but can also react with other substances to form secondary pollutants.
Unlike particulate matter, which gets filtered to some extent by the nose and throat, gases like benzene go straight into the lungs, said Vinayak Sinha, an associate professor at IISER's Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences who led the research team. The emission of isocyanic acid was of particular concern, he said. “This substance is related to methyisocyanate, which was emitted in the Bhopal accident, and is very dangerous,“ Sinha said.
Isocyanic acid is known to be produced by biomass burning, diesel exhaust and other sources. But its measurement as an environmental pollutant has only recently begun.
Sinha and others first identified the emission of benzene and related gases from harvest fires in 2013 by studying the effects of a single plume on a single night in 2012. The latest study , published recently in the journal `Environment International', quantifies the contribution of crop residue burning to the levels of these gases over multiple years.
Norms to administer the practice
Norms to curb crop residue going up in smoke
Vishwa Mohan, Norms on crop residue go up in smoke, Nov 09 2016 : The Times of India
2 States Violate Two-Year-Old Guidelines With Impunity
If Delhi's neighbouring states had adhered to the guidelines of the two-yearold national policy for management of crop residue (NPMCR), the national capital and other cities in the NCR would have been perhaps spared of current alarming situation of air pollution, attributed mainly to stubble burning.
After formulating the comprehensive national policy to deal with the issue of crop residue in November 2014, the Union agriculture ministry had even held a workshop on stubble burning in Chandigarh in January 2015. But such ef forts did not appear to move Punjab and Haryana -the two states where farmers contin ued to indulge in stubble burning in the post-harvest season.
Agriculture minister Rad ha Mohan Singh reviewed the issue on Tuesday and urged the states to promote use of equip ment for crop residue management in a big way . He also emphasised on creating awareness among farmers and exploring various incentives for them to switch over to ecofriendly measures to dispose of stubble. “The states have also been asked to encourage farmers to use all those machines for crop residue management which were distributed to them under various schemes in the past,“ said an official.
The review meeting was held in the backdrop of alarming air pollution in Delhi and neighbouring cities. Though pollutants from other sources contributed immensely to air pollution in the capital, stubble burning on a massive scale in Punjab and Haryana too turned out to be a key reason.
The 2014 national policy envisages adoption of technical measures, including diversified uses of crop residue, capacity building and training along with formulation of suitable legislation, to deal with the issue of disposing of stubble.
Reasons for continued practice
Ploughing Back Of Stubble Is Tedious, Costly
Jayashree Nandi, Why crop burning may continue this year too, April 22, 2017: The Times of India

Ploughing Back Of Stubble Is Tedious, Costly
A few patches of black disturb the golden spread of ripe wheat ready for harvesting in Haryana's Karnal district. These are tracts that were set on fire recently after the standing crop was reaped to ready the field for paddy planting in the monsoon. Many more fields will be set afire in a week or so when harvesting work ends in Punjab and Haryana. This year, however, such fires will be covert actions. Already farmers are claiming the field fires of recent weeks were accidental. Satellite surveillance by the Punjab government and stringent monitoring by Haryana government to prevent stubble burning have left farmers apprehensive.
Stubble burning is being discouraged for its massive pollution impact. For the moment though, despite wheat and paddy stubble burning destroying the soil and causing severe heat stress on farmland, the cultivators cannot change this farming tradition, they say. Subsidies for agri equipment, such as happy seeder or rotavor that can sow seeds without the need to remove the remains of the paddy stubble, haven't reached most farmers.Wheat farmers who can afford it use a reaper that costs around Rs 2 lakh. It only leaves a short stubble close to the ground that is burnt by most or ploughed back into the soil by some. Those who plough the stubble into the soil are not happy because, they claim, this method can damage the paddy seedlings. Plus, ploughing back is often labour and time intensive.
Satellite images show fires have just started in Punjab and Haryana, though Karan Avtar Singh, chief secretary of the state, insisted, “Only 5 to 10 incidents have been reported this season. Many panchayats have assured us of zero stubble burning.“
But Rattan Singh Mann, Haryana chief of Bharatiya Kisan Union, admitted, “We recently courted arrest when we set our fields on fire.“ He explained that wheat can be cut low to leave less stubble, but all alternatives to burning the rice stalks was too expensive.
Among the options, the stubble doesn't have many takers as fodder either. “Cattle don't eat stubble because of the frequent fuel spill during cropping,“ explained Ramanjaneyulu GV , executive director, Centre for Sustainable Agriculture.
At the root of the pollutioncausing problem is Punjab and Haryana's wheat-paddy combination. After harvesting paddy in October, burning the residue is the quickest way to prepare the field for wheat sowing in late October or November. “Rice cultivation should be banned in these regions, but not many agree with me,“ said Mann. Rice plant stubble is not the only problem, paddy requires a lot of water too. “Farmers here have to dig down 400 feet to get water,“ revealed Mahtab Kadyan, another farmer leader.
At Jundla village, Sulakhan Singh Kamboj argued, “We cannot plant replacement crops such as oilseeds or pulses unless the government procures our produce at good prices. Last year I planted peas that I finally sold at Rs 5 per kilo. That did not even cover the labour cost.“
Farmers with the Kheti Virasat Mission in Punjab are, however, gradually moving away from paddy . They claim not to burn the wheat stubble also, but “either make manure of it or mulch it“, according to Umendra Dutt, KVM member.
Recent NASA images show large fires in Madhya Pradesh and parts of east India. According to Ramanjaneyulu, these could be signs of forest fires, stubble burning or slash-and-burn cultivation. “Wheat stubble burning across the country is on the rise because getting labour to deal with it is tedious and expensive,“ he added.
Why Punjab can't end stubble burning
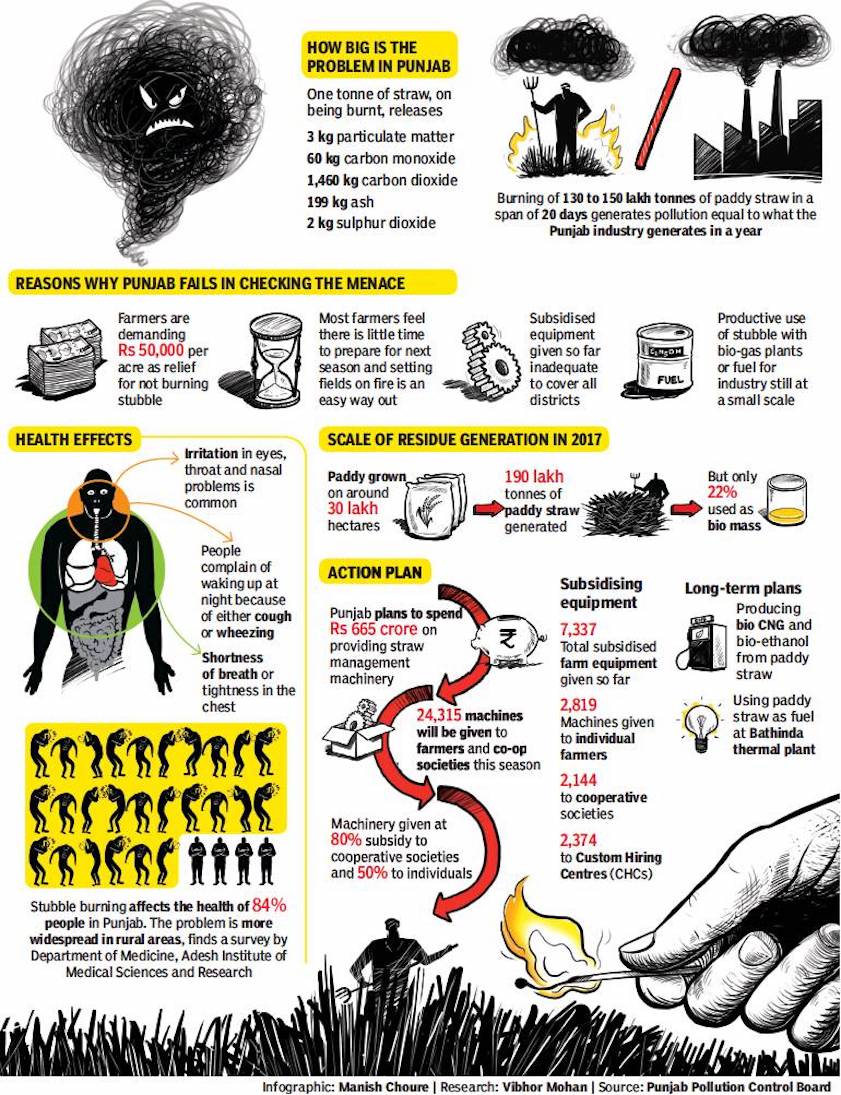
From: October 20, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Why Punjab cannot end stubble burning
Punjab, Haryana’s laws to save groundwater
Delaying Paddy Sowing For Rains Left Little Window To Prepare For Next Crop
Punjab and Haryana are facing a peculiar situation where an attempt to save water turned out, by default, to be disastrous for air quality across northern states, including Delhi.
Facing a situation where groundwater was depleting fast, both states had in 2009 enacted separate legislations, prohibiting paddy sowing before notified dates. The idea was to fix the sowing date in a manner that this water guzzling paddy could be irrigated with minimum wastage, while relying more on monsoon rains for cultivation.
Enforcement of the Punjab\Haryana Preservation of Sub-Soil Water Act, 2009 was relatively easy as the government could easily cut off free power supply to ensure compliance. It, however, resulted in a very short window (two to three weeks) available for farmers to prepare their farms for the next sowing (wheat) operation. Earlier, they used to get nearly 40-45 days after starting their paddy sowing in late May or early June.
“We could not start sowing before June 22. I, therefore, opted for early variety of paddy. Since I have now only few days left for wheat cultivation, I opted for stubble burning to clear the field quickly,” said Jitender Pal Singh, farmer of village Jaspal Bangar in Ludhiana district.
Asked why he opted to break the law by burning paddy straw, Singh who has six acres of land said, “If I use machines (straw management system for combine harvester and happy seeder), it will cost me an additional Rs 3,500 (rent of machines and diesel) per acre. I cannot afford this.”
Once both the states started implementing the ground water legislation strictly in the last 4-5 years, the farmers ended up resorting to stubble burning in bigger numbers to get their farms ready for wheat cultivation. Farmers narrated this strange situation during ground visits to villages of Patiala and Ludhiana districts in Punjab.
This year the dates notified for commencing paddy sowing was June 22 in Punjab and June 15 in Haryana.
“This is indeed a peculiar situation in Punjab. But, we are trying to create awareness among farmers about benefits of in-situ management of paddy straw and illeffects of stubble burning on soil and human health. Mixing of straw in the soil will ensure vital nutrients after decomposition,” said Gaurav Dheer, agriculture development officer of Sanewal in Ludhiana.
Though there are signs of change in both Punjab and Haryana where farmers opted for machines for managing paddy straw, the majority of farmers still find the alternative quite expensive making a complete enforcement of the ban difficult. Even then, it is almost certain the two states are going to report lesser number of farm fires this year as compared to 2017.
“The penalty provision is there to stop burning. But, it is considered quite an unpopular move, politically,” said an official. Punjab had imposed over Rs 8.92 lakh penalty on farmers for stubble burning till October 14, but it could collect only Rs 3 lakh - an indication of how the enforcement agencies have deliberately kept the collection process slow.
“We have been enforcing the ban sincerely after getting satellite data and corroborative evidence of farm fires on the ground. The total number of stubble burning will certainly be less this year as compared to last year (43,660 incidents),” said Krunesh Garg, member secretary of the Punjab Pollution Control Board (PPCB).
Officials in both Punjab and Haryana, however, said the real picture will be known only after October 25 when more and more farmers would go for paddy harvest. “We are confident of facing lesser number of incidents of stubble burning this year as the state has taken multiple measures to help farmers for switching over to in-situ management of paddy straw,” said Suresh Gahlawat, additional director of Haryana agriculture department.
“The state during September 25-October 19 period reported 2,138 incidents as compared to 3,070 during the corresponding period last year. We would, however, be able to know the final count only by early November,” said Gahlawat.
Under the central scheme to help states to promote insitu management of paddy straw, the government had approved over Rs 1,151 crore for Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Delhi for two years from 2018-20. The states have already been allocated over Rs 591 crore this year with Rs 269 crore being received by Punjab and Rs 137 crore by Haryana.
The states have been providing subsidy to the tune of 50% of the cost of machinery to individual farmers and 80% subsidy to cooperatives or self help groups.
Records show that Punjab had distributed 7,062 farm implements to individual farmers while Haryana had done it for 2,814 farmers till October 15.
“Farmers need help to switch over to alternatives. I think it is better to implement the scheme through creating awareness among them about benefits of using straw in the soil,” said Raj Singh Deswal, farmer leader and national secretary of the Bhartiya Kisan Union.
Trends, impact on air quality
2016-18: a decline in stubble burning

Punjab district highs, 2016-18, year-wise
From: Punjab stubble burning: Decline since 2016, but still a concern for Delhi air, November 5, 2018: The Indian Express
The number of incidents, in fact, has come down drastically from 27,000 during the corresponding period in 2016.
Until October 30, 2018, Punjab has seen 15,000 incidents of stubble burning in the current paddy season, according to state Pollution Control Board data. The number of incidents, in fact, has come down drastically from 27,000 during the corresponding period in 2016.
In all three paddy seasons between 2016 and 2018, Patiala and Tarn Taran have had among the highest counts of stubble burning incidents. These are down to 1,700 each during the 2018 season so far, from 2,400 (Patiala) and 2,100 (Tarn Taran) in the 2016 season at the same stage. Firozpur, on the other hand, has witnessed a smaller decline. Its 1,866 incidents is the highest among all districts this year, and is only slightly lower than the 1,939 recorded up to this stage in 2016. Bathinda, which is among the districts cited as a concern, is also among the six districts with 1,000 or more incidents each year.
The area under paddy in Haryana is 13 lakh hectares, as compared to the 29 lakh hectares under paddy in Punjab. This state, too, has witnessed the number of stubble burning incidents come down since 2016. From nearly 5,900 until October 30 in the 2016 paddy season, the number was down to under 4,400 at the same stage in the current season.
2017, Delhi, Haryana, Punjab

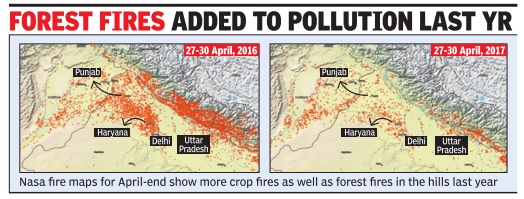
Crackdown By Punjab, Haryana Working So Far
There has been an increase in burning of wheat crop stubble in Punjab and Haryana compared with the previous one, Nasa's satellite pictures reveal. But the images also reveal a larger and more significant trend -the practice of crop-burning is down sharply in comparison with the same period in 2016
Ground reports suggest the two state governments' firm approach seems to be working but major challenges lie in the days ahead as angry farmers demand a viable alternative to the practice. Nasa's FIRM web fire mapper, which uses satellite imagery to map instances of fires on the ground, shows a marked reduction in `fire spots' in 2017 over the previous year. The same eight-day period (April 27-May 4) was used to make the comparison.Burning of stubble after the kharif (October-November) and rabi (April-May) seasons is seen as a major contributor to pollution in the region. Air quality in Delhi is another indicator of re duced crop burning this year. A comparison of an eight-day AQI average (April 27-May 4, both days included) of 2016 and 2017 shows air in the capital this year has been far healthier than the last.AQI during the period this year has been in the moderate zone (176) while it was `very poor' last year at 307. Of course, weather conditions as well as raging forest fires in Uttarakhand also contributed to air pollution in Delhi last year.
Last year's pattern, as seen in the satellite images, reveals that crop-burning peaked in the first week of May and started abating around May 12. This would suggest that there could yet be a spike in crop fires.
There are mixed reports from the ground on cropburning. “Farmers are afraid to burn their wheat stubbles this year because of the ad ministration's threat of action and fines,“ Ruby Singh Sandhu, a farmer from Ellenabad in northwest Haryana, said on phone.
In Punjab, many farmers have been protesting against the tough orders on cropburning. At many places, farmers have been openly defying the directions and burning the straw, despite the theat of cases and fines.
Farmers are demanding a compensation of Rs 2,000 per acre and eight-hour power supply to help prepare the fields through farm machin ery without burning straw.They have threatened to start burning wheat stubble collectively from May 10 if the demands aren't met.
Wheat was sown in nearly 35 lakh hectares in Punjab and state expects a bumper harvest this year. The state pollution control board, agriculture department and the districts are keeping a watch over burning of straw through remote sensing.Nearly 200 farmers have been fined in various districts till May 3. On Thursday , seven farmers were fined Rs 17,500 for burning straw in Muktsar district. The state has fixed a fine of Rs 2,500 for burning straw in fields up to 2 acres, Rs 5,000 for farms up to 5 acres and Rs 15,000 for those over 5 acres. Most of the fines slapped so far have been on fields below 5 acres, said a state government official.
“The Adesh institute of medical sciences and research (AIMSR) had in January 2016 carried out an extensive study to document the health impacts of stubble burning and found that smoke caused by burning of agriculture waste was adversely affecting the quality of life of farmers. It showed that nearly 85% people from all age groups suffered from one or the other health problems because of the smoke,“ said Vittul K Gupta, associate professor at AIMSR.
An agriculture department official said the state government has offered up to 50% subsidy on various implements as an alternative to straw burning. “We have even demanded suggestions from farmers for measures to be adopted to contain menace of straw burning,“ he said.
2017, May: stubble burning in Punjab rise sharply
The use of geo-spatial data and satellite imagery to crack down on farmers resorting to stubble burning has not changed things much on the ground in ending this practice.In fact, the number of crop burning cases has shot up from 1,553 to 13,054 in the last eight days -an over eight-time jump -with the end of the harvesting period.
The official figures accessed show that as on May 11, the cumulative number of crop firing cases reported by Punjab Remote Sensing Centre, was 12,370, while 684 cases were detected by other means. Sources in the Punjab Pollution Control board told TOI that they were finding it difficult to initiate action against violators.
2018: Stubble burning declines in Punjab, Haryana
Vishwa Mohan, Stubble burning drops in Punjab, Haryana, December 23, 2018: The Times of India

From: Vishwa Mohan, Stubble burning drops in Punjab, Haryana, December 23, 2018: The Times of India
Though they fell short of targets, Haryana and Punjab may have made a beginning in combating stubble burning by recording a 29% and 11% fall in incidence over 2017 of farm fires that are seen as a major source of winter pollution in Delhi and surrounding areas.
Together, the states recorded a 14% dip in number of such cases this year as compared to 2017. The results, following central funding and state measures for machines to encourage farmers to cut stubble instead of simply setting it ablaze to clear the land, fall short of the target 40-50% reduction but could mark a start in changing an ingrained habit.
In keeping with reports, Haryana performed better than Punjab in the first year that marked the government’s direct and active intervention to help farmers opt for alternatives, backed by subsidies.
Stubble burning is considered an important contributors to air pollution in Delhi and national capital region (NCR), specifically during the two-month harvest season (September 30 - November 30) when farmers cut summer crops, mainly paddy, and rush to prepare farms for sowing of winter crops that include wheat and mustard.
Underlining the problem, the Centre earmarked an outlay of over Rs1,151crore for two years to help states during 2018-19 and 2019-20 period. States are expected to help farmers buy subsidised machines for in-situ management of crop residues.
Final figures of the stubble burning cases for September 30 - November 30 period, shared by states with the Union environment ministry, show Haryana reported 9,232 cases of farm fires this year as compared to 13,085 in 2017 - a decline of 29%. On the other hand, Punjab reported as many as 59,695 cases this year as compared to 67,079 last year, a 11% reduction. The large number of farm fires in Punjab clearly remain the major problem area that needs to be tackled.
“Though we have not reached the expected target (40-50% reduction), it’s a good beginning. Even a decline of nearly one-third is an achievement. We have performed much better than Punjab. The Centre should, therefore, reward Haryana by extending more allocation for additional interventions in the second year,” said Suresh Gahlawat, additional director of Haryana agriculture department.
2018: the 11 worst offending districts of Punjab, Haryana
Ritam Halder , Sep 21, 2019: The Times of India

From: Ritam Halder , Sep 21, 2019: The Times of India
A study by IIT-Delhi researchers has stated that eight districts in Punjab and three in Haryana should be given priority for intervention by the government to reign in the stubble burning menace.
While the districts in Punjab — Amritsar, Firozpur, Ludhiana, Faridkot, Bathinda, Mansa, Patiala and Sangrur — contribute to nearly 45% of the total stubble burning emission, Kaithal, Hisar and Sirsa in Haryana add another 17%.
The study conducted by Sagnik Dey, associate professor, Centre for Atmospheric Sciences, IIT-Delhi, and coordinator, Centre of Excellence for Research on Clean Air (CERCA), classified stubble burning in north Indian states as intense, rampant, limited and large smoldering. Using satellite data, Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) fire count (from a height of 1km) and Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite fire count (from a height of 375m), the researchers observed a few intense fires in Hoshiarpur (Punjab), Panipat and Sirsa (Haryana).
Rampant burning was observed in Ludhiana, Firozpur, Moga, Patiala, Faridkot, Bathinda, Muktsar, Mansa and Fatehgarh Sahib in Punjab and Fatehabad and Hisar in Haryana. Limited burning took place in Gurdaspur, Rupnagar, Panchkula and Nawanshahr in Punjab and Faridabad, Gurgaon, Jhajjar, Bhiwani, Rohtak, Sonipat, Jind, Kaithal, Karnal and Kurukshetra in Haryana. Large smoldering fires were seen in Amritsar and Jalandhar in Punjab.
“Rather than uniformly distributing the resources, these districts or villages need to be prioritised and given more attention. We need to understand the local factors that are forcing the farmers to burn the stubble, especially in the villages or districts where it hasn’t shown any decline in recent years,” Dey told TOI. The main objective of the study, done in collaboration with Shruti Kumar and her team at McKinsey & Co, was to prioritise districts where things were not going as per expectations and which were contributing more to Delhi’s pollution load. “A 2018 report by The Energy and Resources Institute showed that open biomass burning contributes 20-25% to PM2.5 in Delhi. However, we must also keep in mind that stubble burning is only a seasonal issue occurring during October and November,” Dey said, adding that the last three years have shown a declining trend, which is a positive sign.
Most farmers in north India prepare their fields for the wheat crop in October-November by burning the stubble left after rice has been harvested. They plough the fields and sow wheat using conventional seeders. Due to stubble burning, 30kg of nitrogen per hectare, 13.8kg of phosphorus, 30kg of potassium, 6.5kg sulphur, 2,400kg carbon and several useful microbial organisms get perished in the fire, besides resulting in pollution.
The year-wise position
Punjab: 2008-2016; 4 states: 2016-2017
Jayashree Nandi, Delhi pins hopes on neighbours for clean air, April 8, 2018: The Times of India
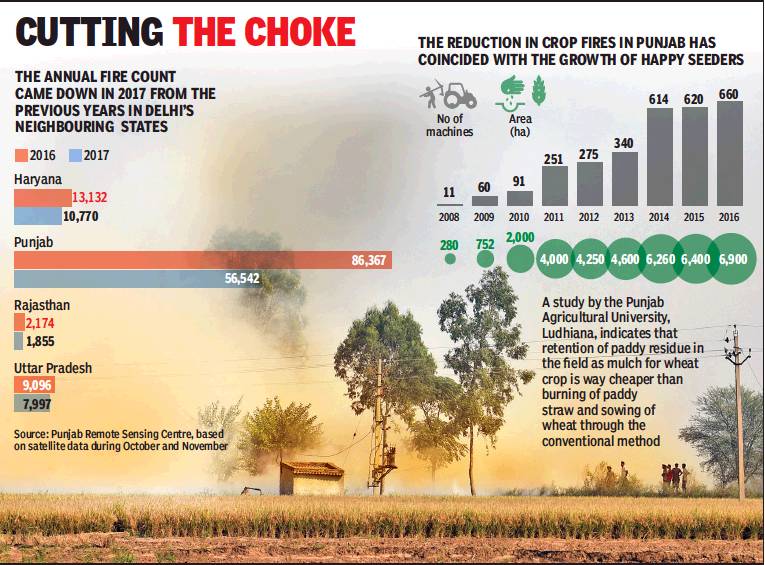
the Punjab, 2008-2016;
Haryana, Punjab, Rajasthan, UP: 2016-2017
From: Jayashree Nandi, Delhi pins hopes on neighbours for clean air, April 8, 2018: The Times of India
As Central Farm Subsidy Kicks In, All Eyes On Other States To Reduce Stubble Burning
This year will be a test case for curbing cropstubble burning in states neighbouring Delhi and whether this will improve air quality in the capital.
The Centre — having decided on an “in-situ management” of crop residue as opposed to collecting paddy straw to use as fuel in power generation or convert it products like bio-char used as fertiliser — has allocated funds to the affected states to subsidise farm machinery that can prevent stubble burning.
The Centre allocated Rs 1,140.3 crore for a sub-mission on agriculture mechanisation in this year’s Union budget, substantially hiking the funds from Rs 525 crore in 2017-18. NCR states are now rolling out the scheme. D K Behera, director, agriculture department, Haryana, told TOI, “Under the new scheme, we will promote custom hiring centres set up by farmer groups but will also cater to individual far mers.”
Haryana has been allocated Rs 216 crore and Punjab, Rs 365 crore for the scheme. “We will encourage farmers groups and cooperative societies rather than individual farmers to buy or rent this machinery. This approach will avoid financial liability and loans,” said Viswajit Khanna, additional chief secretary, agriculture, Punjab.
A sub-committee of the task force on prevention of stubble burning in Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh constituted by the cabinet secretariat submitted its final report to the Supreme Court in January. It advised that in-situ mechanisation allowing use of crop stubble as mulch was more cost effective than removing the plant remains. It also recommended large scale production of such machinery and their positioning in villages before September 2018.
A Niti Aayog-CII report had suggested alternatives to crop-residue burning, including ex-situ management processes. The cabinet secretariat panel, however, observed, “Bio-char production requires collection of paddy straw and its treatment in the field in temporary kilns. This option would require financial support of 9-10% of the minimum support price. Ex-situ options identified by Niti Aayog-CII require significant capital and operating subsidy to become sustainable.”
The central sub-committee instead recommended zero tilling machines for wheat, with paddy straw as mulch. To achieve this, every combine harvester would need to have a separate straw management system a cutter, spreader and a happy seeder. Use of these components as a package would solve the wheat sowing problem, the report assured. For planting of potato, peas and other vegetable crops, incorporation of paddy straw and its fast decomposition could be achieved using the Rotavator and mould board (MB) plough developed by the Punjab Agricultural University.
The sub-committee suggested the government could provide a flat subsidy of 50% of machinery cost to individual farmers or a subsidy of 75% of machinery cost to cooperative societies, custom hiring centres, farmer’s interest groups and gram panchayats.
The Supreme Courtmandated Environment Pollution Control Authority, which is overseeing the enforcement of the court’s directions on curbing air pollution in NCR, has endorsed the sub-committee’s report, but agriculture experts worry that this may not do much to resolve the ecological woes of farmers. While the main reason for the crop stubble burning is the very small window of 20 days between harvesting of paddy and sowing of wheat, experts said there are other problems related to wheatpaddy combination, including extreme water stress and reliance on pesticides.
“We have to understand that the rice-wheat system has problems,” said G V Ramajaneyulu, executive director, Centre for Sustainable Agriculture. “Instead we should opt for wheat-pulses or rice-legumes or vegetablelegumes combinations. Crop stubble burning is just a symptom of this problem and even this is being addressed only because of pollution in Delhi. But the intensive ground water depletion and water contamination due to high chemical usage in the rice-wheat system is not being addressed.”
2002-17, an increase
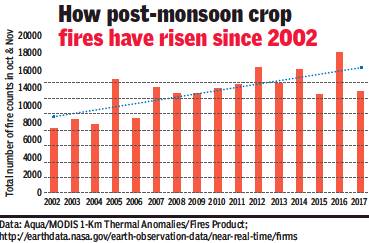
From: Jayashree Nandi, Nasa data shows no reduction in crop fires, 2016 worst yr, December 16, 2017: The Times of India
Crop fires have steadily increased in Punjab and Haryana since 2002, an analysis of Nasa satellite data suggests, contradicting official claims that a number of policies have been implemented to curb the practice of paddy stubble burning.
A study by Nasa research scientist Hiren Jethva found that crop fires are on the rise, with the highest number of hotspots detected in 2016. Jethva’s research also suggests that the increase in crop fires (about 500 per year between 2002 and 2016) could be linked to rising crop production in the region.
He analysed data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) sensor on Aqua satellite to track annual crop fire numbers. In his blog on the Nasa Earth Observatory website published in early 2017, Jethva also analysed normalised difference vegetation index (NDVI) — a measure for greenness that can indicate crop or vegetation cover.
“There seems to be a oneon-one relationship in NDVI measured by the MODIS sensor prior to harvest (September) and the total number of fire hotspots observed during the harvest season (October and November). This suggest that the increase in the number of fires is likely related to increasing crop production,” the blog says.
Jethva also refers to data from the Directorate of Economics and Statistics, department of agriculture, which says post-monsoon, rice crop production has increased at a linear rate of 0.18 million tonnes from 2002 to 2016 in Punjab. On November 5 last year, Delhi had suffered its worst smog episode in 17 years with average PM2.5 levels 14 times the 24-hour standard. In October-November last year, there were nearly 18,000 crop fires in Punjab and Haryana put together — the highest since 2002. The number of fires reduced in 2017 — to a little more than 12,000 — but still had a huge impact on air quality in NCR, according to experts.
The impact of crop fires on air quality is accentuated by hostile meteorological conditions. During this smog episode, for example, ground wind speed was very low on most days, but wind direction was from north and northwest through Punjab and Haryana where crop stubble is being burnt over large stretches.
IMD said mixing heights (also called boundary conditions) — the levels at which ground level winds mix with the higher winds and allow dispersion — has been extremely low, leading to a high concentration of pollution particles. But crop fires are also ruining soil health and depleting groundwater resources massively in these states. According to Ramanjaneyulu G V, executive director at Centre for Sustainable Agriculture, burning also leads to an immediate decline in the bacterial and fungal population in the top 2.5cm of the soil.
Repeated burning permanently diminishes the bacterial population by more than 50%, increasing farmers’ dependence on fertlisers and pesticides. He added that the problem of crop stubble burning started increasing since 2002. “The depletion of groundwater levels made Punjab come up with a law in 2009, which makes sowing of paddy before June 15 a criminal offence. The law allows agriculture department officers to destroy the nursery or transplanted paddy. The uprooting costs are to be borne by farmers. The Act levies a penalty of Rs10,000 per hectare per month on the farmers who contravene it. It even allows field officers to disconnect power supply to a farmer’s field till the notified date if the farmer is found violating the law repeatedly. This left a very small window for farmers between kharif harvest and rabi sowing, forcing them to resort to burn off,” Ramanjaneyulu said. He added: “The prices of paddy have not increased in the last 10 years. As a result, farmers also felt spending more amount on removal of stubbles is not economically viable … so they burn off.”
Farmers from various farmer groups, including the Bharatiya Kisan Union, say an important factor could be increasing labour costs, which have led to more farmers taking up mechanised harvesting by using combines to harvest both paddy and wheat.
Many farmers say they want to give up paddy cultivation, but can’t — because procurement prices for other crops are not fair.
“Solutions lie in finding uses for the stubble and assigning real economic value to it, so that burning is an economic loss to the farmer. Solutions are well known, in terms of infield use as manure to reduce fertilizer cost or generate power, or make fuel and material. But there is no clear strategy to build business cases around these solutions to scale or provide support to farmers to use this as manure,” said Anumita Roy Chowdhury, head of Centre for Science and Environment’s clean air campaign.
2016> 18: 41% decline in northwest India
August 13, 2019: The Times of India
Paddy stubble burning declines 41% in Punjab, Haryana, UP, Delhi-NCR
NEW DELHI: Burning of paddy crop residue, one of the major causes of air pollution, declined by 41 per cent last year over 2016-level in Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Delhi-NCR with the help of a Rs 1,151 crore central scheme, the government said on Tuesday.
Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) Director General Trilochan Mohapatra highlighted the considerable reduction in crop residue burning incidents in 2018 and said the country has demonstrated through coordinated public and private efforts that such challenges can be addressed effectively.
"...through the various efforts under the Central Sector Scheme on 'Promotion of Agricultural Mechanization for In-Situ Management of Crop Residue in the State of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and NCT of Delhi' then paddy residue burning events have reduced by 15 per cent and 41 per cent in 2018 as compared to that in 2017 and 2016, respectively in all these States as per the satellite data," Mohapatra said in an official statement.
He expressed confidence that crop burning would further reduce this year.
Mohapatra said more than 4,500 villages in Punjab and Haryana were declared as zero stubble burning villages during 2018 as not a single crop burning incident was reported from these villages during the year.
Crop residue burning in northwest India contributes to air pollution, health hazards, disruption of transportation, school closures and soil degradation.
ICAR said in a statement that 23 million tonnes of rice residue were being burnt in rice-wheat cropping system (around 4.1 million ha) to clear the field for conventional wheat sowing because of the narrow window (about 10-20 days) between rice harvesting and wheat sowing.
"Considering the findings of the SCIENCE article as well as reports from thousands of participatory validation trials by KVKs, our efforts have resulted in an additional direct farmer benefit of Rs 900 crore compared to a burning option," ICAR said.
Mohapatra said that the central sector scheme was launched with a total outgo of Rs 1,151.80 crore for the period from 2018-19 to 2019-20 to tackle air pollution and to subsidize machinery required for in-situ management of crop residue in Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and national capital territory of Delhi.
Within one year of its implementation utilising an amount of Rs 500 crore, the happy seeder/zero tillage technology was adopted in 8 lakh hectares of land in the northwestern India.
"During 2018-19, the funds amounting to Rs 269.38 crores, Rs 137.84 crores and Rs 148.60 crore have been released to the Governments of Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh, respectively, for distribution of in-situ crop residue management machinery to the farmers on subsidy, establishment of Custom Hiring Centres (CHCs) of in-situ crop residue management machinery and undertaking Information, Education and Communication (IEC) activities for creating awareness among farmers," it said.
During 2019-20, funds amounting to Rs 273.80 crore, Rs 192.06 crore and Rs 105.29 crore have also been released so far to Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh, respectively.
ICAR is implementing the scheme through 60 Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) of Punjab (22), Haryana (14), Delhi (1) and UP (23).
2018: the 4 worst offending districts of Punjab
Amit Bhattacharya, November 17, 2018: The Times of India
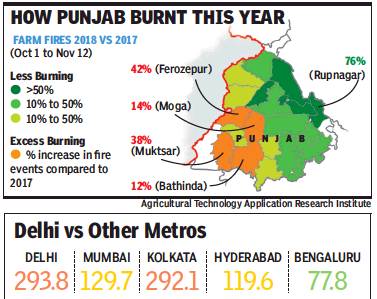
From: Amit Bhattacharya, November 17, 2018: The Times of India
Stubble-burning in Punjab was higher in 2018 than in 2017, Nasa satellites show, but the real story lies in the detail.
Just four districts in the state recorded an almost 30% rise in crop fires while all the rest of the districts registered a decrease, eight districts by more than 25%, according to Indian satellite data with the gover nment.
The high number of crop fires — 57,756 as per Nasa data till November 15 in Punjab and Haryana this year as compared with 55,404 last year — suggests the PM’s Rs 1,151-crore package for management of paddy residues failed to make a dent this year.
At the same time, the large variation in stubble-burning incidents, particularly within Punjab, indicates that several factors were in play, some that led to a spurt in burning as well as others that worked in reducing fires.
The four districts where burning increased this year are Ferozepur (up 42%), Muktsar (38%), Moga (14%) and Bathinda (12%), as per figures collated till November 12 by the Agricultural Technology Application Research Institute (ATARI), Ludhiana.
Together, these four districts alone accounted for 40% of fire events in the state, up from 29% last year.
Time factor played big part in fuelling farm fires in Punjab
All four districts are in the western Malwa region of the state where kisan unions are strong. The unions have been demanding cash compensation of Rs 200 per acre to farmers for not burning stubble. In many areas, the unions ensured that farmers burned stubble in support of the demand,” said a state agriculture department official.
Political factors can’t be ruled out as some of these areas are Akali strongholds, the official added.
Time too played a big part in fuelling fires across Punjab. Rice sowing started late and harvesting was delayed by rains in October, leaving many farmers with a very small window to prepare the fields for the rabi (winter) crop.
“Each day’s delay in sowing of wheat after November 15 decreases yields by an average of 30kg per hectare. Pressed for time, many farmers opted to burn the paddy residue,” said M L Jat from the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Centre (CIMMYT), an international research organisation that promotes sustainable agriculture in the region in collaboration with the Indian Council for Agricultural Research and other bodies.
TOI travelled through Karnal (in Haryana) and Ludhiana, and farmers in both districts said the respective state governments did not crack down on stubble-burning by imposing challans, particularly when the fires were peaking in November.
In the midst of these failures, there was heartening news as well. Outside of the four Punjab districts and Sirsa in Haryana, all places reported a reduction in crop-burning, as per data released by ATARI.
Among areas that see heavy stubble-burning, Kapurthala (down 53%), Ludhiana (46%), Jalandhar (37%) and Karnal (45%) saw impressive reduction in fires. In many of these areas, in-situ residue management techniques like the use of happy seeders have been increasing in the past two years.
In Taraori village in Karnal, for instance, farmers said roughly 100 acres out of 2,000 saw burning this year. The village has farmers such as Vikas Chaudhry and Manoj Kumar who have been using happy seeders for the past six years.
“Farmers from the village and neighbouring areas have been coming to us to look at how in situ management works and have seen the results. Most of them have now adopted these techniques,” said Chaudhry.
Punjab agriculture commissioner B S Sidhu agreed that large-scale demonstration of in situ techniques was needed, along with training for personnel to handhold farmers making the transition to burning-free agriculture.
“We plan to take up these activities on a wide scale in the coming year. We are sure we will reduce stubble-burning significantly next year,” Sidhu said.
Meanwhile, this year’s burning season is expected to end in a few days, with just around 10-15% of rice harvesting yet to be done, officials said.
As in 2020
Jasjeev Gandhiok & Mohammad Ibrar, October 5, 2020: The Times of India
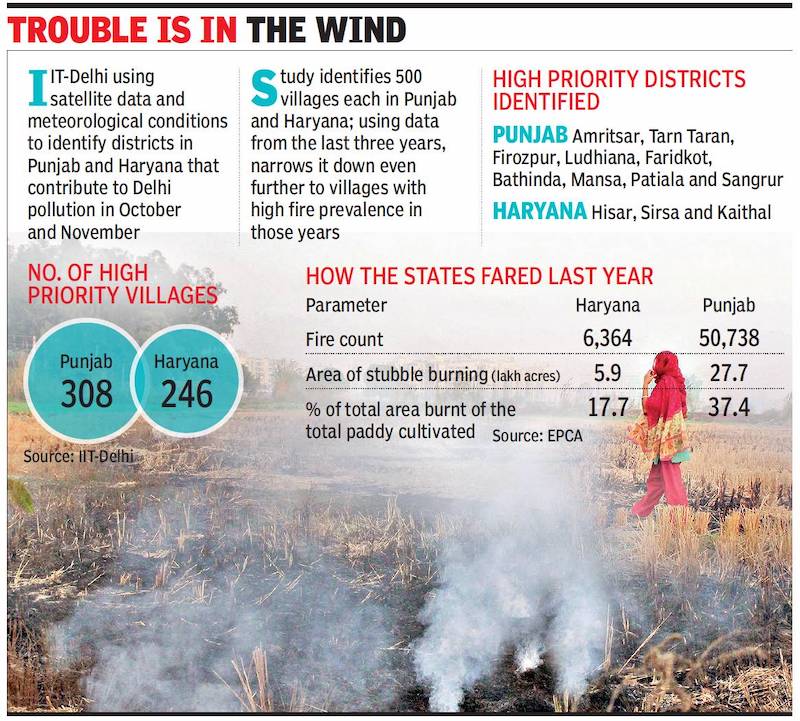
From: Jasjeev Gandhiok & Mohammad Ibrar, October 5, 2020: The Times of India
Ahead of the crop stubble-burning season, a study by IIT-Delhi has identified which districts in the neighbouring states of Punjab and Haryana contribute the most to Delhi’s air pollution in October and November. The study — based on wind direction, intensity of farm fires and their proximity to the capital — stated that Amritsar, Tarn Taran, Firozpur, Ludhiana, Faridkot, Bathinda, Mansa, Patiala and Sangrur in Punjab and Hisar, Sirsa and Kaithal in Haryana were the biggest contributors.
The team at IIT-Delhi’s Centre for Excellence for Research on Clean Air (CERCA) used multi-year satellite data from VIIRS and SUOMI-NPP at a resolution of 375m, integrating it with meteorological data to not only track open biomass burning in districts, but the route taken towards the capital to spike the pollution level.
Sagnik Dey, associate professor at IIT-Delhi’s Centre for Atmospheric Sciences and coordinator at CERCA, said the study began at the district level. However, as it was a large geographical area, they needed to narrow it down to the village level to make it easier to curb stubble burning.
“We have prepared a detailed report so that the situation doesn’t turn bad this year and preventive action can be taken. The report has been shared with the state governments of Punjab and Haryana, as well as NITI Aayog,” Dey claimed, adding that most farmers were helpless and unaware of alternative technologies and methods available.
To facilitate ground-level action, the researchers identified 500 villages each in both Punjab and Haryana, based on higher prevalence of burning and its contribution to the NCR’s air. This was then narrowed down to 246 villages in Haryana and 308 villages in Punjab, which were found having high fire counts consistently over the past three years.
“We have recommended strict monitoring in these villages this year as they have emerged as problem areas over the past three years. Consistent stubble burning has been recorded in the identified 554 villages,” Dey said.
Delhi’s air quality has been deteriorating and is forecast to touch the poor category over the next few days as early stubble burning has been recorded in both Punjab and Haryana from the second week of September.
“The overall AQI in Delhi is at the higher end of the moderate category and a marginal improvement is forecast for Monday. AQI is likely to stay in the moderate range for the next two days. An increase in stubble burning was observed on Saturday in Punjab and Haryana and bordering regions, which is likely to start impacting Delhi’s air in the coming days,” said System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting And Research (SAFAR).
Historical data recorded on satellite imagery, however, showed there had been a steady improvement in reduction of farms fires. Data from Council on Energy, Environment and Water for October and November from 2017 onward showed there were 56,758 fire counts in Punjab, which increased slightly to 56,835 in 2018 before dropping to 44,076 in 2019.
Similarly, according to Nasa’s VIIRS satellite system, Haryana recorded 10,970 fire counts in October and November in 2017, 8,827 in 2018 and 5,900 in 2019.
Data submitted by both Punjab and Haryana to EPCA showed that 37.4% and 17.7% of paddy cultivated area was burnt last year, but both states said this was a drop from the previous year. Punjab stated that the area under paddy cultivation was also coming down, dropping to around 27 lakh hectares compared with 31.3 lakh hectares in 2018.
See also
Crop stubble burning: India
Fire accidents (accidental fires): IndiaThis page includes data on all categories of fires, including forest fires and the burning of crop residue