Migration: India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
Attacks on migrants, normally workers
1960s-2018 (brief history)
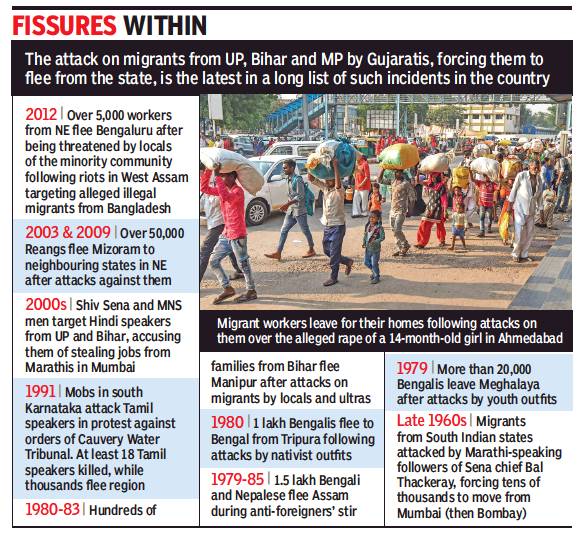
From: October 9, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
1960s-2018: Attacks on migrants, normally workers, a brief history
HNW individuals’ migration
How The Rich Buy New Nationalities; 2017 figures
How The Rich Buy A New Nationality, July 30, 2018: The Times of India
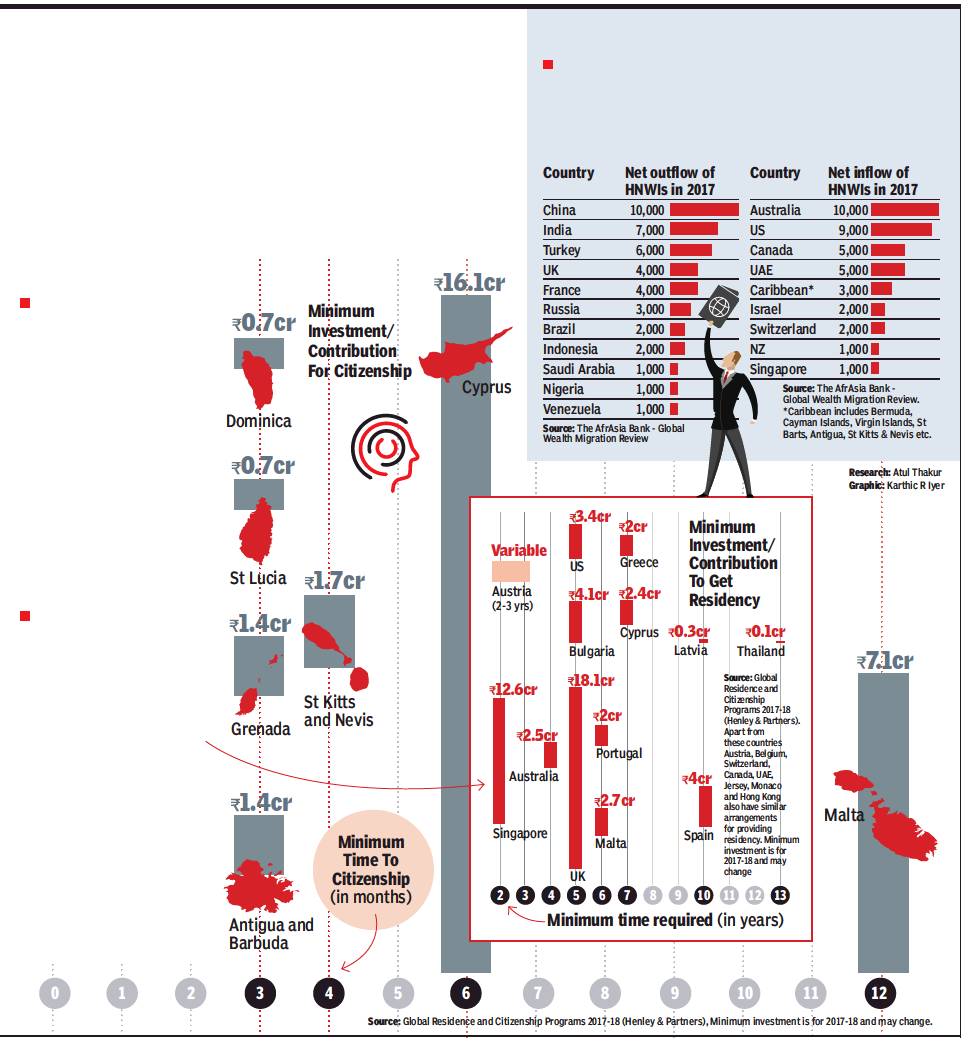
ii) THE countries that they migrate to.
From: How The Rich Buy A New Nationality, July 30, 2018: The Times of India
Fugitive Mehul Choksi bought Antiguan citizenship, and his new passport allows him visa-free entry to over 130 countries. TOI takes a look at how the rich can buy their way to new citizenship and residency
Can citizenship be acquired by investing?
Acquiring citizenship need not be a long-drawn process. Not all nations need you to prove years of residency. Many countries offer the wealthy citizenship-by-investment programmes. This method of granting citizenship was seen as controversial when Caribbean island St Kitts and Nevis pioneered the idea in 1984. But today many countries have followed suit to offer citizenship to well-heeled individuals who donate a fixed amount to the government of their new home or invest over a certain level.
Can permanent residency be acquired by investing?
Many countries that don’t provide citizenship but grant residency to the wealthy if they invest above a certain amount in the local economy. Residency provides unlimited stay and rights enjoyed by locals. These may include benefits like healthcare coverage and the right to work or study. Such residents cannot vote and are not issued passports of their new home nation. Indians, for instance, can apply for Tier 1 (Investor) visa of UK if they are willing to invest GBP 2 million (INR 18.1 cr). Similarly, the process for a US Green Card can be expedited for an individual who invests USD 1 million (or USD 500,000 in rural areas with few jobs) and creates at least 10 new full-time jobs.
Where are the super-rich going and which countries are the biggest losers?
South Africa-based New World Wealth, a global market research group that specialises in wealth statistics, found China followed by India witnessed the highest migration of high net worth individuals (HNWIs) — people with net assets of US$1 million (Rs 6.9cr) or more. The largest recipient of these super rich migrants are Australia, US and Canada.
Immigration (into India)
2010, 2017: Migrants in India

From: February 5, 2019: The Times of India
See graphic:
2010, 2017: Immigrants living in India, China and major countries'
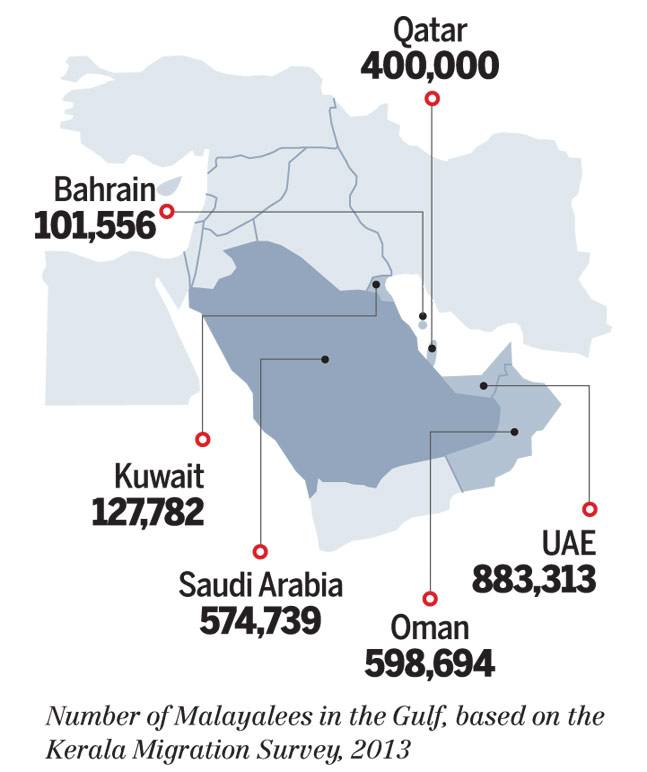
Gulf, Migration to
2013: Malayalis in the Gulf
See graphic:
No. of Malayalees in the Gulf
2014> 2018: Migration to Gulf for jobs drops 62%
Lubna Kably, January 12, 2019: The Times of India
Lubna Kably, UAE is top Gulf workplace for Indians, January 12, 2019: The Times of India
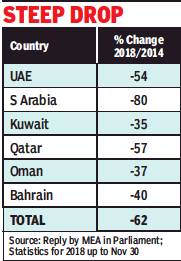
From: Lubna Kably, January 12, 2019: The Times of India
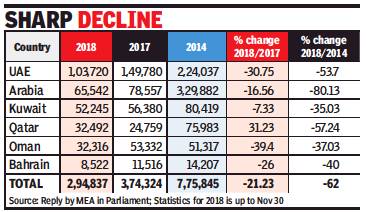
From: Lubna Kably, UAE is top Gulf workplace for Indians, January 12, 2019: The Times of India
The total number of emigration clearances granted to Indians headed to the Gulf, for employment, has dropped by 21% to stand at about 3 lakh during the 11-month period ended November 30, 2018, compared with the year 2017.
Over the past five years, during 2014, the outflow of Indian workers to Gulf was the highest at about 7.8 lakh. Compared with this figure, the decline in 2018 is as high as 62%. These statistics are drawn from the e-Migrate emigration clearance data, which captures the emigration clearances issued to workers holding ECR (emigration check required) passports.
Among all the Gulf nations, the largest outflow of Indian workers in 2018 was to UAE, with about 1 lakh (or 35%) of the total workers being granted emigration clearances. It was followed by Saudi Arabia and Kuwait with 65,000-odd and 52,000-odd workers headed to these countries.
In 2017, Saudi Arabia had relinquished its position as being the most attractive destination among Gulf countries for Indian workers. In its edition dated August 22, 2017, TOI had analysed the Nitaqat scheme for protection of local workers — the decline in expat workers, including from India is attributed to this scheme and the economic conditions.
Qatar stands out by being the only country in the Gulf region, where the number of workers shows an increase in 2018 as compared to the previous year. Nearly 32,500 workers headed to Qatar were granted emigration clearances, as compared to close to 25,000 in 2017, which is a rise of 31%.
“This could be because of increased labour requirement as the country prepares to host the World Cup, 2022” says a Mumbai based labour recruiter. However, there have been some reports of non-payment to Indian workers by unscrupulous employers, an instance of a construction agency not paying nearly 600 workers was recently in the spotlight. Washington headquartered think-tank, The Middle East Institute, says there are an estimated 6 to 7.50 lakh Indian migrant workers in Qatar, constituting the largest expatriate community and nearly double the number of native Qataris.
According to a reply given by the ministry of external affairs in Lok Sabha last December, there are several reasons for the decrease in numbers. “Prominent among them is that the Gulf countries are passing through a period of economic slowdown primarily because of the slump in oil prices.”
Illegal migration
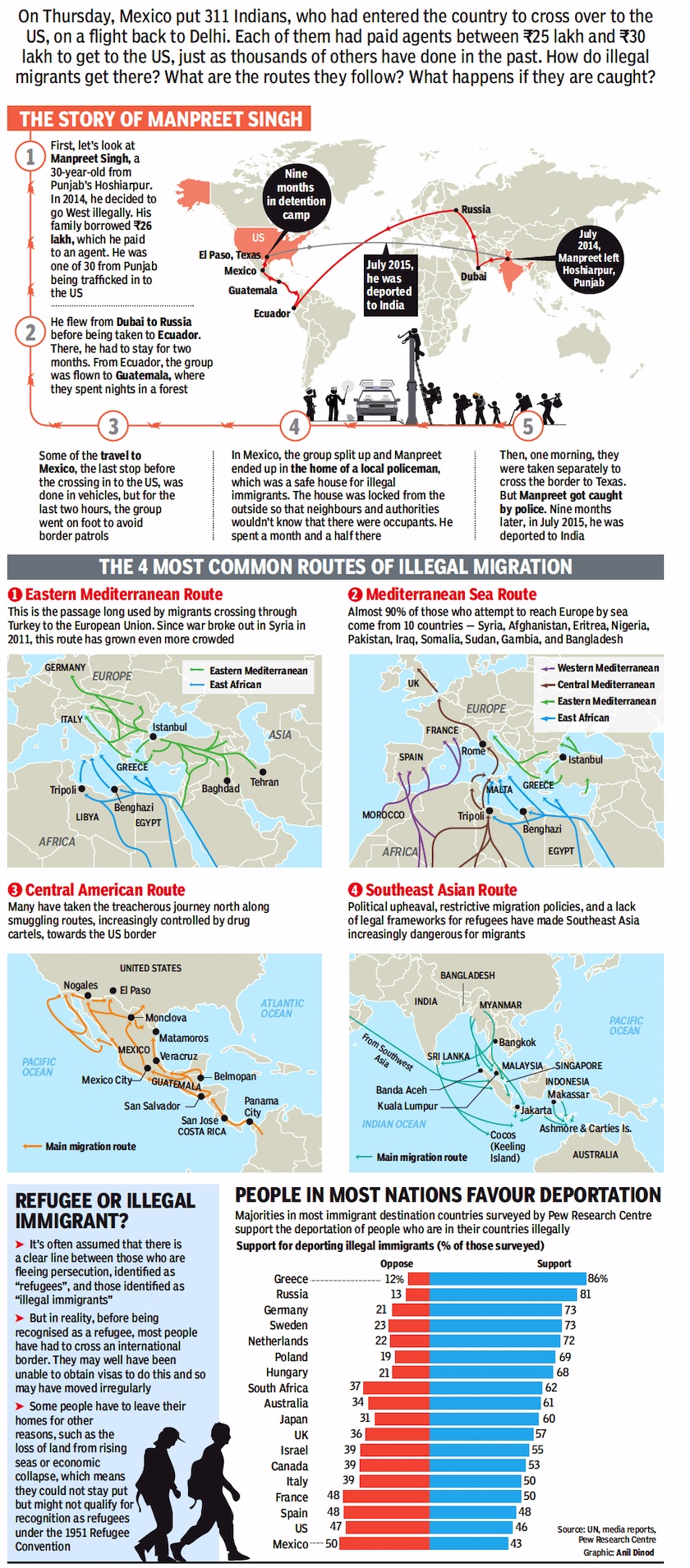
From: Oct 19, 2019: The Times of India
See graphic:
Some of the routes that Illegal Immigrants Take To Go West
Through Mexico
2019: Mexico deports 311 Indians
Oct 18, 2019: The Times of India
In a transatlantic deportation without precedent, Mexico has put 311 Indians caught illegally entering the country and trying to cross over to the US on a Boeing 747-400 charter scheduled to touch down at Delhi airport.
Mexico’s National Migration Institute (INM) said in a release that the deportees, who are being escorted back home by 60 federal migration agents, had been found to have entered the country without valid documents for “regular stay” over the past few months.
The mass deportation revived memories of the tragedy that befell a family from Punjab in June, when a six-year-old girl died of a heat stroke in the Arizona desert on the US-Mexico border after her mother went in search of water during their illegal border crossing. The body of Gurpreet Kaur was found after two Indian women apprehended by US border patrol revealed that a mother and her two children had been with them until a few hours earlier.
Sources said each member of the group possibly paid Rs 25-30 lakh to the agents who arranged their travel to Mexico and promised to help them illegally cross over to the United States.
Trump’s tariff threat on Mexican imports triggered deportation
The cost apparently included airfare, accommodation in Mexico and meals. The agents had purportedly cited a week to a month’s time to arrange their entry into the US, the sources said.
According to the Mexico’s National Migration Institute release, they were caught in Mexico without “papers for regular stay” and produced before immigration authorities in the states of Oaxaca, Baja California, Veracruz, Chiapas, Sonora, Mexico City, Durango and Tabasco. US President Donald Trump’s threat to impose tariffs on all Mexican imports if the country did not put a check on people illegally entering US through the porous borders forced its hand, sources said.
A source said the Boeing 747-400 that took off from Mexico’s Toluca City International Airport with 311 deportees was expected to land in Delhi at 5.45am on Friday.
“This operation was carried out thanks to the excellent communication and coordination with the embassy of that Asian country (Indian) with which the recognition and return of these citizens was worked under strict adherence to the migration law and its regulations,” the INM statement said.
The deportees were issued an “emergency certificate” each, which is a oneway travel document that allows an Indian citizen to enter India in an emergency. Such papers are issued to individuals who lose, damage or have no valid passports. INM said never before had Mexico carried out a deportation exercise of this scale.
Loans for migration
==‘Dollariyo Pradesh’ in north and central Gujarat== Bharat Yagnik & Ashish Chauhan, February 3, 2022: The Times of India
Ahmedabad: Immigrating abroad is not easy, and if you must take a loan to achieve your dream, the process turns into a great burden. Yet, there’s a region in Gujarat where people planning to immigrate legally or even illegally cannot only avail themselves of a loan worth lakhs at 0% interest but also are under no obligation to return the money. While the beneficiaries do not have to pay EMIs, most of them usually pay much more than they received back to the community.
Ankit Patel, 21, from Kalol in Gandhinagar district wanted to go to the US but did not have the financial means to take a loan. He approached a local trust that pooled money from the community to finance youngsters who want to study abroad.
Within a week, the money was arranged. Once Ankit settled down in Pennsylvania, US, he returned double the amount he had taken as a loan back to the trust.
There are various such trusts in the region called ‘Dollariyo Pradesh’ in north and central Gujarat that financially help young men and women to pursue their desire to settle in foreign countries. According to locals, these trusts are informal and mainly run by local communities.
Bhavin Patel (42) is a resident of Dingucha, Gandhinagar, that recently came into the limelight after a family of four from the village froze to death while trying to illegally cross into the US from Canada. He said every family has at least one member in the US, Canada, or Australia. “This doesn’t mean everyone has the money to send their family members abroad. We have a trust in the village which collects money solely for sending people abroad,” said Bhavin.
Outward migration from India
2017, 2018: to OECD countries
Lubna Kably, October 20, 2020: The Times of India
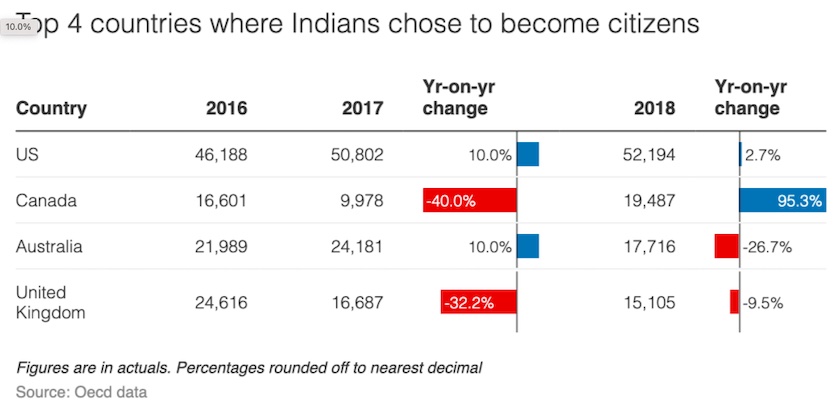
From: Lubna Kably, October 20, 2020: The Times of India
India world No. 2 in migrations to OECD nations, getting citizenships
MUMBAI: India has emerged as the second largest source country both in terms of the “total” inflow of new migrants to OECD countries during 2018 and also as regards the number of Indians acquiring citizenship of these countries. While China continued to retain its top slot as the largest source country, India replaced Romania to emerge as the second largest source. During 2018, about 4.3 lakh Chinese migrated to OECD countries, accounting for nearly 6.5% of the total migration inflows.
However, there was a slight decline of 1% as compared to the previous year. On the other hand, migration from India to OECD countries increased sharply by 10% and reached 3.3 lakh. Migration from India represents about 5% of the overall migration to OECD countries. While Canada saw a huge spike in numbers, others such as Germany and Italy also saw more arrivals as compared to the previous year.
Collation of country-wise data shows that the “total” inflow of new migrants to OECD countries was 66 lakh, a slight rise of 3.8% over the previous year. Data on migra tion flows by nationality may include temporary migration for some destination countries, clarifies OECD. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is an association of 37 member countries, such as European countries, US, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and Japan.
As these are well-developed economies, they attract a large share of immigrants, be it for work, studies or even asylum. Before the pandemic, permanent migration flows to OECD countries (bar Colombia and Turkey that have hosted a large number of humanitarian migrants in recent years) was 53 lakh in 2019, with similar figures for 2017 and 2018. Permanent migration flows do not include temporary labour migration or international students.
While releasing the “International Migration Outlook 2020” at a virtual press conference on Monday, Angel Gurría, secretary general at OECD, said Covid-19 has redrawn the international mi gration map. Following the onset of Covid-19, almost all OECD countries restricted admission to foreigners. Issuances of new visas in these countries plummeted by 46% in first half of 2020 compared with the same period in 2019. This is the largest drop ever recorded. In the second quarter, the decline was 72%. The secretary general said migration would continue to play a key role for economic growth and innovation, and in responding to rapidly changing labour markets.
2015-16: Educated migrants
November 28, 2020: The Times of India
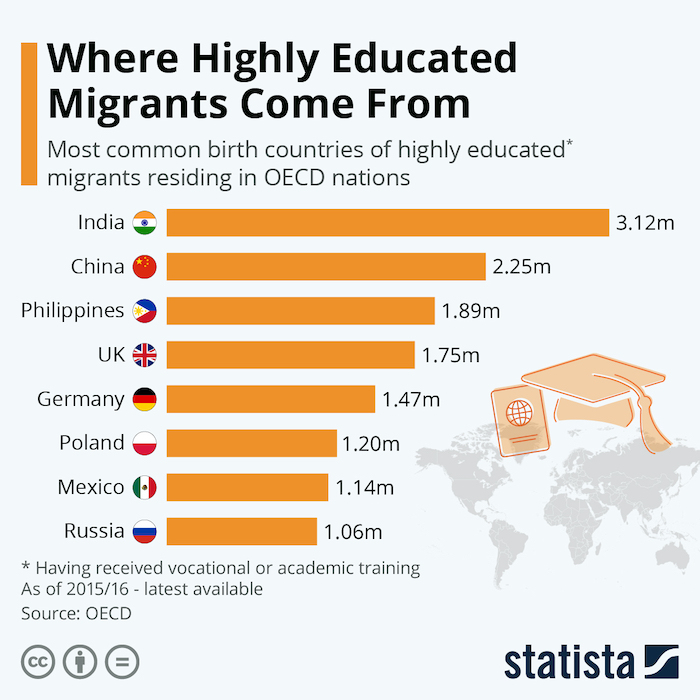
From: November 28, 2020: The Times of India
Indians top the list of educated migrants in rich countries OECD data reveals that there are around 120 million migrants living in OECD member countries. 30 to 35 percent of these migrants are considered highly educated, meaning they have received vocational or academic training. Among the most common birth countries for highly educated migrants, these shares are a lot higher, however.
For India, which topped the list as of 2015/16 with more than three million highly educated migrants in the OECD, the share of those considered of high education status was nearly 65 per cent. China had a rate of 48.6 percent highly educated migrants in the OECD – or 2.25 million.
The Philippines come in rank 3, behind the world’s two biggest countries and ahead of a list of OECD nations, naturally trading highly educated personnel back and forth with each other, especially within Europe. 53.3 percent of Filipino immigrants to the OECD are considered highly educated, which brings the total to almost 1.9 million for a country of just over 100 million inhabitants. In a paper on the Philippines, the International Labor Organization finds that many of those high skilled migrants - to OECD countries and elsewhere – were health care professionals, especially nurses. Because of the coronavirus pandemic, the Philippines government has put a stop to this brain drain at least temporarily by capping the deployment of newly hired nurses at 5,000 per year.
Around half of Filipino migrants in the OECD chose the United States, forming one of the most important migration corridors identified by the OECD, behind Mexican and Indian immigration to the United States and ahead of Polish immigration to Germany.
Migration, outward, to all countries
1990-2019: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Pakistan
Sep 23, 2019: The Times of India
Source: UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs; Graphic: Karthic R Iyer
From: Sep 19, 2019: The Times of India
See graphic:
1990-2019: Outward migration from Afghanistan, Bangladesh, China, India, Pakistan and other countries.
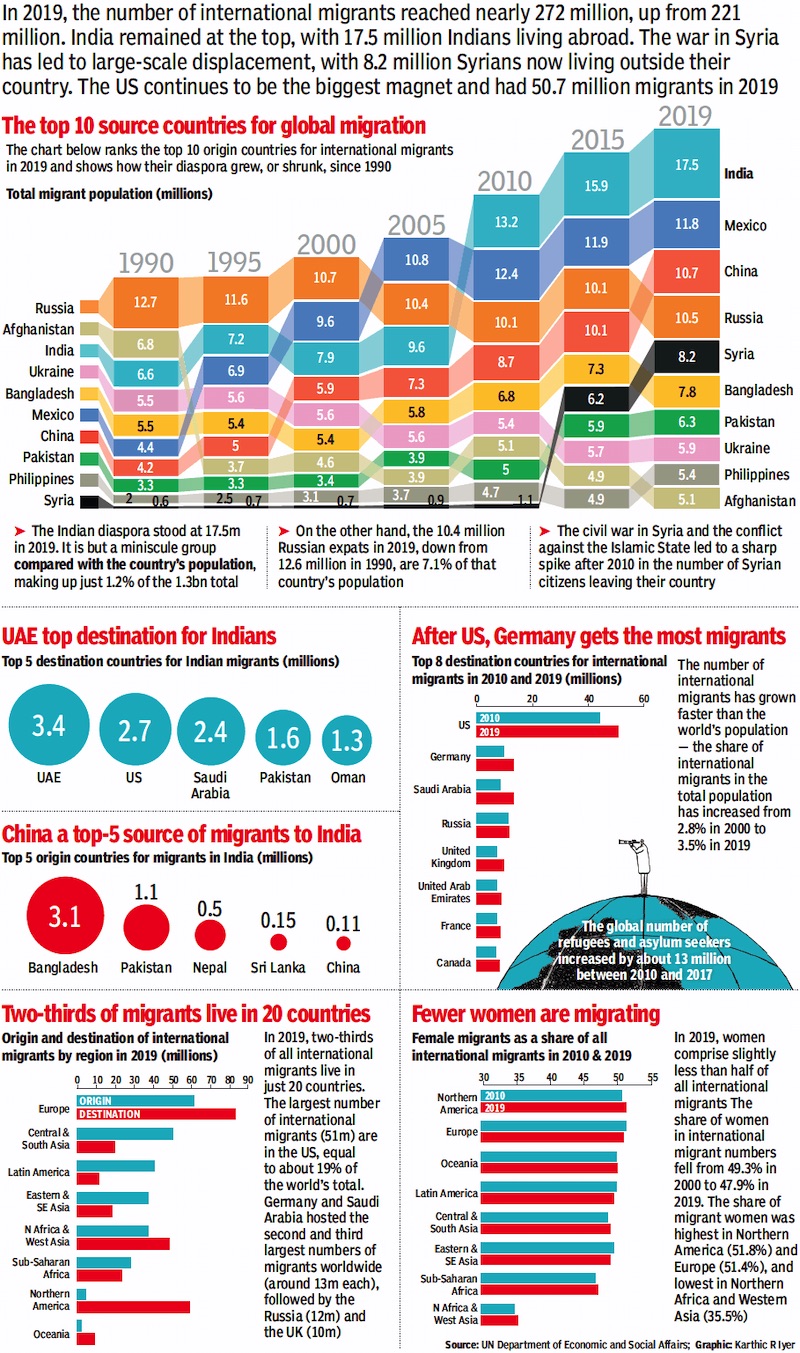
In 2019, the number of international migrants reached nearly 272 million, up from 221 million in 2010, an increase of 51 million people or 23%. That's more global migrants than the number of children born each year. India remained at the top, with 17.5 million Indians living abroad.
The US continues to be the main magnet, hosting 50.7 million migrants in 2019, including a sizable and affluent Indian-American community — one of the reasons why US President Donald Trump attended Prime Minister Narendra Modi's 'Howdy Modi' mega rally in Houston, Texas, which witnessed an over 50,000-strong crowd. Not just Trump, other lawmakers — both Republican and Democrat — were also present, a sign that the Indian diaspora's vote in the 2020 US presidential election is important for both sides.
INDIA TOP ORIGIN COUNTRY FOR MIGRATION
But although India ranks at the top with a 17.5 million diaspora worldwide, it is only a minuscule group compared with the country's population, making up just 1.2% of the total 1.3 billion population. On the other hand, the 10.4 million Russian expats in 2019, down from 12.6 million in 1990, are 7.1% of that country's population.
In recent years, Syria has witnessed large-scale displacement owing to the civil war and the conflict against the Islamic State, leading to a sharp spike in migration after 2010 with 8.2 million Syrians now living outside their country.
The chart below ranks the top 10 origin countries for international migrants in 2019 and shows how their diaspora grew, or shrunk, since 1990.
UAE TOP DESTINATION FOR INDIANS
While the US has a large Indian diaspora, it is not the top destination for Indians who want to settle abroad. Gulf countries, particularly the UAE, continue to have a high concentration of Indians, although in recent years they've lost some of their drawing power due to nationalisation programmes, economic recession and the rise in living costs there.
CHINA A TOP-5 SOURCE OF MIGRANTS TO INDIA
India, meanwhile, hosted 5.1 million migrants this year. International migrants as a share of total population remained steady at about 0.4% from 2010 to 2019. China also made it to the top-5 list. But the maximum migrants to India came from Bangladesh. even as concerns over illegal migration from across the India-Bangladesh border persist.
AFTER US, GERMANY GETS THE MOST MIGRANTS
The number of international migrants grew faster than the world’s population in 2019 — the share of international migrants in the total population increased from 2.8% in 2000 to 3.5% this year. The US hosted the largest number of migrants at 51 million, equal to about 19% of the world's total, followed by Germany and Saudi Arabia (13 million each), Russia (12 million) UK (10 million) and UAE (9 million). Three out of every four international migrants are in the 20-64-year age group, a sign that the majority moved countries for better work opportunities.
TWO-THIRDS OF MIGRANTS LIVE IN 20 COUNTRIES
In 2019, two-thirds of all international migrants live in just 20 countries. Europe and North America absorbed the largest share — 82 million migrants live in Europe and 59 million in North America in 2019.
FEWER WOMEN ARE MIGRATING
Women comprised slightly less than half of all international migrants this year. The share of women in international migrant numbers fell from 49.3% in 2000 to 47.9% in 2019. The share of migrant women was highest in Northern America (51.8%) and Europe (51.4%), and lowest in Northern Africa and Western Asia (35.5%).
Women migrating abroad
2010
Changing times: More women go abroad to work
Divya A |
June 2010
Deepa Gupta, 22, a mathematics graduate from Ludhiana, thought it a great opportunity to go to a postgraduate course in Michigan University. Two years down the line, she is settled in the US and has been joined by her widowed mother.
Gupta represents a trend — that of Indian women increasingly leaving home turf for professional, rather than personal reasons. The World Bank’s report on ‘Gender, Poverty Reduction and Migration’ says more women from developing countries such as India are migrating to the West independently rather than as dependents. It also says that female migration indirectly helps alleviate poverty.
Neelam Soni, executive with an overseas placement agency in Delhi says women in nursing, teaching, social and voluntary work, the hospitality industry, data-entry operations, sales and even housework are able to migrate to foreign shores.
Social scientist Mala Kapur Shankardass says that even though a large proportion of female migration can still be explained away by marriage (estimates say 80%) it is significant that 20% of all women migrants leave for professional reasons. A decade ago, less than 5% of women migrants worked She says that earlier, male migrants used to belong to the ‘Employed’ category and female to the ‘Not in the Labour Force’. This is changing. Shankardass.
But Shankardass cautions that Indian female contribution to forex remittances is still not properly documented. Official data largely focuses on male remittances.
See also
Migration: India