Manipur (Home page)
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Contents |
The source of this article
INDIA 2012
A REFERENCE ANNUAL
Compiled by
RESEARCH, REFERENCE AND TRAINING DIVISION
PUBLICATIONS DIVISION
MINISTRY OF INFORMATION AND BROADCASTING
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
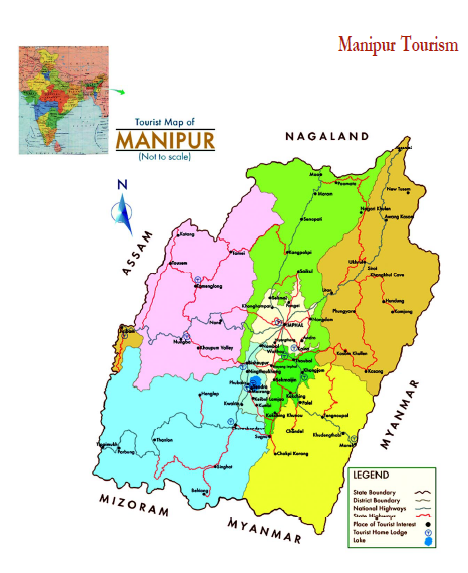
MANIPUR
Area : 22,327 sq km
Population : 22,93,896 (2001 Census)
Capital : Imphal
Principal Language : Manipuri
HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY
Manipur has a long and glorious history from before the beginning of the Christian era. The political history of Manipur started from 33 A.D. with the coronation of Nongda Lairen Pakhangba. After Pakhangba a number of kings ruled over the kingdom of Manipur. The independence and sovereignty of Manipur remained uninterrupted until the Burmese invaded and occupied it for approximately seven years in the first quarter of the 19th century (1819-1826). Then, Manipur came under British Rule on 27 April 1891.
Manipur regained its independence in 1947 and merged into Indian Union on 15th October 1950. Thus, it became a Part C State under a Chief Commissioner. During 1950-51, an Advisory form of Government was introduced and in 1957 this was replaced by a Territorial Council of 30 elected and 2 nominated members. Later, in 1963 a Territorial Assembly of 30 elected and 3 nominated members was established under the Government of Union Territories Act, 1963.
The status of administrator was raised from that of a Chief Commissioner to that of a Lt. Governor in December 1969. Manipur became a full-fledged State on 21st January 1972 with a Legislative Assembly of 60 members of whom 19 are reserved for Scheduled Tribes and one for Scheduled Castes. The State is represented in the Lok Sabha by two members and by one member in the Rajya Sabha.
Manipur is situated in the extreme north-eastern border of India. It is bounded on the east by upper Myanmar, on the north by Nagaland, on the west by Cochar District of Assam and on the south by Chin Hills of Myanmar and Mizoram. Manipur has a total border line of about 854 kms. of which about 352 kms. are international boundary line with Myanmar on the east and south-east. This State can claim a geographically unique position, since it virtually is the meeting point between India and South-East Asia. Manipur lies between 23.800 N and 25.680 N latitude and between 93.030 E and 94.780 E longitude.
The State has a total area of 22,327 sq. kms. There is a small oval shaped plain in the central part. This central plain known as Imphal Valley is at a height of about 790 metres above MSL. This valley is surrounded by hills on all sides. The hill covers about 9/10 of the total area of the State. The hill ranges are higher on the north and gradually diminish in height towards the south. The valley itself slopes down towards the south.
AGRICULTURE
Agriculture and allied activities are the only mainstay of the State’s economy where about 70 per cent of the population depends on it. The State has two topographical zones — valley and hills. The valley is known as the 'Rice Bowl' of the State. The valley has sub-tropical to tropical to sub-temperate climate. The hills have subtemperate to temperate climate with an average altitude of 3000 metres above MSL.
The State has distinct winter, warm, humid and rainy summer. The average rainfall covering the State is 1436 mm. It occurs mainly during June to September when the State is under the spell of South West Monsoon. The growth of agriculture in the State has been quite uneven and unsatisfactory for the reason that its production still depends on seasonal rainfall.
FORESTS
According to the State Forest Report, 2009 prepared by Forest Survey of India, Dehradun, the forest cover in the State is 17,280 sq. km, which is 77.40% of the State's geographical area. In terms of forest canopy density classes, the State has 701 sq. km. very dense forests, 5474 sq. km. moderately dense forests and 11.105 sq. km. open forests. Comparison of the current forest cover with the previous assessment in 2005 shows an overall increase in forest cover of 328 sq. km. This overall increase in forest cover is mainly due to regeneration in abandoned jhum areas.
IRRIGATION
Major and Medium lrrigation had been introduced in the State since 1980. So far 8 (eight) Major and Medium Irrigation & Multipurpose Projects have been taken up of which 5 (five) projects viz. Loktak Lift Irrigation Project, Khoupum Dam Project, Imphal Barrage Project, Sekmai Barrage Project and Singda Multipurpose Project were completed by the end of 8th Plan. By the end of Eighth Plan period, only about 67,546 ha. has been brought under irrigation of which Major and Medium irrigation projects contributed 28,150 ha. and Minor Irrigation contributed 39,396 ha.
COMMERCE & INDUSTRIES
The Handloom industry is by far the largest and most important cottage industry in Manipur. As per National Handloom Census, 1995-96 report conducted by the National Council for Applied Economic Research, New Delhi, Manipur has 4.62 lakh handloom workers which is 2nd position among the States, 2.81 lakh looms which is 4th position, consuming 12.196 lakh kg of yarn per month which is 7th position and produced 96.07 lakh metres of handloom fabrics which is also 7th among States of the country.
POWER
Power Supply in Manipur is fully dependent on the Central Generating Stations situated in the North Eastern Region (NER). Peak demands for night and day are of the order of 150 & 100 MW in summer and 170 & 110 MW in winter. As the generating stations in the NER are mainly of hydel in nature, during lean period there is a shortfall in generation and therefore the available share of Manipur reduces drastically.
ART AND CULTURE
Its own art-forms and cultural expressions and ramifications distinctly showcase Manipur to the world. Its famous classical dance remains unique in all Manipuri dance-forms whether it is folk, classical or modern and has different style and gesture of movement.
TRANSPORT
Roads: Road Transport is the only means of communication for development of the State as there are no inland Waterways, Railways or Ropeways. All development activities depend entirely on the road transport facilities.
The total length of roads in Manipur by 2009 including National Highways, NEC, BRTF and Roads under Rural Development, was 12618 km. Out of the total road length, the surfaced length in 5443 km.
3 National Highways : i) NH-39, ii) NH-53 and iii) NH-150 criss-cross the State connecting all Districts. Imphal the capital of Manipur is joined by NH-39 with Nagaland on the north and Myanmar on the east, on the west with Assam by NH-53 and Mizoram on the south by NH-150.
Aviation: Imphal Airport is the second largest airport in the North Eastern Region. Imphal is connected to Aizwal, Guwahati, Kolkata, Silchar, Bangaluru and New Delhi by Air India, JetLite, Indigo and Kingfisher Airlines.
Imphal Airport is being upgraded to international status. The Construction of infrastructure for Night Landing Facility at Imphal airport has been completed and Air India has started Night Flights to and from Imphal.
Railways: The State is included in the railway map of India with the opening of a rail head at Jiribam in May 1990. It is 225 km from Imphal. Dimapur (Nagaland), 215 km from Imphal is the nearest rail-head.
The Jiribam - Tupul - Imphal Railway line has been declared as a National Project. Construction of the Line is in good progress and is targeted for completion by 2014 (upto Tupul) and 2016 (upto Imphal).
FESTIVALS
A year in Manipur represents a cycle of festivals. Hardly a month passes by without a festival which to the Manipuris is a symbol of their social, cultural and religious aspirations. Important festivals of the State are : Lai Haraoba, Rasa Leela, Cheiraoba, Ningol Chak-Kouba, Rath-Jatra, Idul Fitre, Imoinu Iratpa, Gaan-Ngai, Lui-Ngai- Ni, Idul Zuha. Yaoshang (Holi), Durga Pujah, Mera Houchongba, Diwali, Kut, Christmas, etc.
TOURIST CENTRES
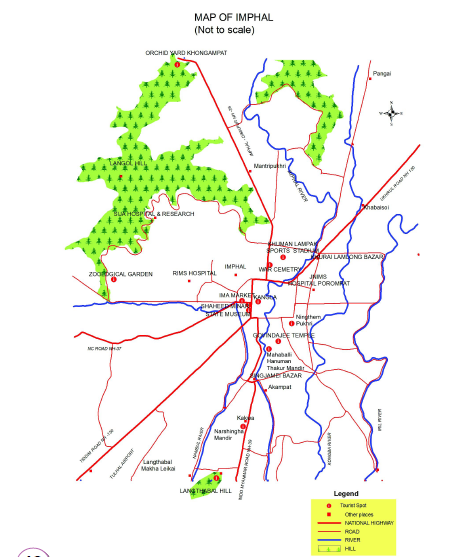
Manipur is not only the gateway of the North Eastern region but is also a fascinating destination for discerning tourists. Blessed with a salubrious climate, natural beauty and scenic splendour, the state extends to the tourists a warm welcome. Some important tourist centres in the State are : Kangla, Shree Shree Govindajee Temple, Khwalramband Bazar (Ima Keithel), War Cemeteries, Shaheed Minar, Nupi Lan (Women's War) Memorial Complex, Khonghampat Orchidarium, INA Memorial (Moirang), Loktak Lake, Keibul Lamjao National Park, Sendra, Moreh, Siroy Hills, Dzuko Valley, State Museum, Kaina Tourist Home, Khongjom War Memorial Complex, India Peace Memorial (Red Hill) etc.
GOVERNMENT
Governor : Shri Gurbachan Jagat
Chief Secretary : Shri D.S. Poonia, IAS
Chief Minister : Shri O. Ibobi Singh
Jurisdiction of High Court: A permanent bench of the Guwahati High Court, Imphal Bench started functioning from 14th March 1992. The Chief Justice of India laid foundation stone for construction of a new High Court Complex on 30th April 2006 and construction of the complex is in good progress & targeted to be completed within this year.
AREA, POPULATION AND HEADQUARTERS OF DISTRICTS
S.N. District Area Population Headquarters (Census 2001)
1. Senapati 3,271 2,83,621 Senapati
2. Ukhrul 4,544 1,40,778 Ukhrul
3. Chandel 3,313 1,18,327 Chandel
4. Churachandpur 4,570 2,27,905 Churachandpur
5. Tamenglong 4,391 1,11,499 Tamenglong
6. Imphal (West) 519 4,44,382 Lamphelpat
7. Imphal (East) 709 3,94,876 Porompat
8. Thoubal 514 3,64,140 Thoubalpat
9. Bishnupur 496 2,08,368 Bishnupur
Total 22,327 22,93,896
PLACES OPEN IN RESTRICTED/PROTECTED AREA
VISIT PERMITTED TO
Lohtak Lake, Imphal, Moirang INA Memorial, Keibul Deer Sanctuary and Waithe Lake Kongiam War Memorial
AUTHORITY
All Indian Missions abroad All FRROs & MHA State Government of Manipur
REMARKS
Individual tourists not permitted, 6 days allowed Calcutta to Imphal by air only Foreigners allowed only in groups of 4 or more. 10 days. Entry by road allowed on NH39 & NH53 for Dimapur-Kohima-Imphal-Jiribam-Silichar
ADDITIONAL AREAS OPENED UP
Imphal-Bishnupur-Phubala-Moirang-Sendra-Keibul-Lamjao-Imphal Imphal-Moirang Lake-Keibul-Lamjao-Chur-Chanderpur-Khuga-Imphal Imphal-Litan-Ukhral-Shiroy-Sangsak-Imphal Imphal-Thoubal-Waithou Lake-Khongjam-Kakching-Thongjao-Waikhong-Sugnu-Imphal Imphal-Khonghampat-Kanglatombi-Kangpokpi-Senapati-Karong-Mao Gate-Imphal Imphal-Nonoh-Khongsang-Nungba-Jiribam-Imphal