Non-governmental organisations (NGOs): India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Contents |
An overview
Only 2% NGOs registered with govt
PTI | Mar 23, 2014
NEW DELHI: Despite voluntary organizations receiving over Rs 11,500 crore of foreign funds annually, only two per cent of the 20 lakh odd NGOs operating in the country have been registered, raising eyebrows in the home ministry.
According to a home ministry report, although there is no centralized database on the number of NGOs in the country and the quantum of finance involved in their operations, unofficial figures indicate that there are over 20 lakh NGOs registered under Societies' Registration Act, Trust Act etc.
However, the number of NGOs registered under Foreign Contribution Regulation Act would be less than 2 per cent of the total number of NGOs.
"Though, the number of associations reporting receipt and utilization of foreign contribution is increasing; yet, it is a matter of concern that a large number of registered associations still do not submit their statutory annual returns mandated by the law," the latest Home Ministry report on receipt and utilization of foreign contribution by voluntary associations said.
A total of 43,527 NGOs were registered under the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act up to March 31, 2012. During the year 2011-12, a total of 22,702 NGOs reported receipt of foreign contribution amounting to Rs 11,546.29 crore.
Altogether 9,509 NGOs have reported 'Nil' receipt of foreign contribution while many have not filed their returns.
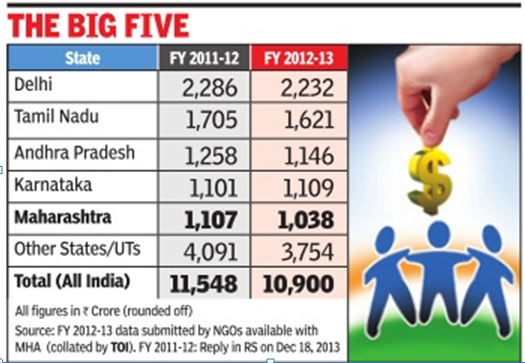
Top four recipient states
Among all states and Union Territories, Delhi received highest amount of foreign contributions in 2011-12.
While Rs 2285.75 crore of foreign contribution has been received by 1482 NGOs in the national capital, 3341 NGOs in Tamil Nadu received Rs 1704.76 crore, 2527 NGOs in Andhra Pradesh received Rs 1258.52 crore and 2056 voluntary organizations in Maharashtra received Rs 1107.39 crore.
State-wise foreign receipts
Delhi NGOs get most foreign donations
Lubna Kably Mumbai
TNN
The Times of India Jul 01 2014
Actual Receipts Could Be Higher Than Reported
Non-government organizations (NGOs) in India received Rs 10,900 crore as foreign donations during financial year 2012-13.
This is a slight decline from the previous year’s figure of Rs 11,548 crore.
Going by past trends, it is safe to assume that only 3040% of NGOs comply with reporting requirements. Thus the actual receipts of foreign donations could be much higher for both these years.
Foreign donations over the past few years, starting from FY 2006-07, have been in the range of Rs 10,000-11,000 crore. This is a steep rise of more than 100% if compared with foreign donation inflows of just Rs 4,872 crore during FY 2001-02.
NGOs registered in Delhi reported the highest receipts of foreign donations at Rs 2,232 crore during FY 2012-13, followed by Tamil Nadu at Rs 1,621 crore and Andhra Pradesh at Rs 1,146 crore.
Karnataka unseated Maharashtra as the fourth ranking territory in terms of foreign donations to its registered NGOs. The receipts by NGOs in Karnataka and Maharashtra were Rs 1,109 crore and Rs 1,038 crore, respectively . The top ten states/UTs, which include Kerala, WB, Gujarat, UP and Orissa, account for 87% of total foreign donation inflows.
The aggregate data for the financial year 2012-13 was collated by TOI based on the information available with the home ministry as of June 18.
A Rajya Sabha reply dated December 18, 2013 had indicated that of 41,844 NGOs registered under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), 16,756 have not yet filed their annual returns for the year 2011-12. TOI also analysed the key activities of the top recipient NGO in each of the top 10 states/UTs. Tamil Nadu-registered World Vision of India got the maximum quantum of foreign donations of Rs 251 crore (Rs 233 crore during 2011-12). These funds were primarily utilized for AIDS awareness and treatment and its key overseas donors were World Vision USA and Coca Cola.
Among the list of the top recipient NGOs in each state/UT during 2012-13, only a few utilized all or most of their foreign donations for religious activities. These included The Indian Society of Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (foreign donations of Rs 193 crore), Believers Church (foreign donations of Rs 67 crore) and Bochasanwasi Akshar Purushottam Swaminarayan Sanstha (foreign donations of Rs 50 crore). MHA 's December 2013 report also shows that key specific activities for which foreign funds have been utilized in the past include rural development, children welfare and education.
The recent report by the Intelligence Bureau, alleging that a few NGOs carried out activities aimed at stalling India's projects has created ripples among foreign donors.
“NGOs across the world compete for getting increased funding each year--be it from parent associations or other foundations. The fear that their welfare activities--such as medical relief--could be construed as having a devious motive is likely to have an ad verse impact in the coming f years. No foreign donor would like to be dragged into a contro versy ,“ said a US-based non profit consultant The central government is l also empowered to ban receipt of foreign donations by an NGO or permit such donations only with prior permis sion, if such receipts are likely to prejudicially impact `public interest', `sovereignty and integrity of the nation', `harmo. ny between religious groups' to name a few instances. Some of these widely defined terms are also causing anxiety among NGOs and their overseas donors.
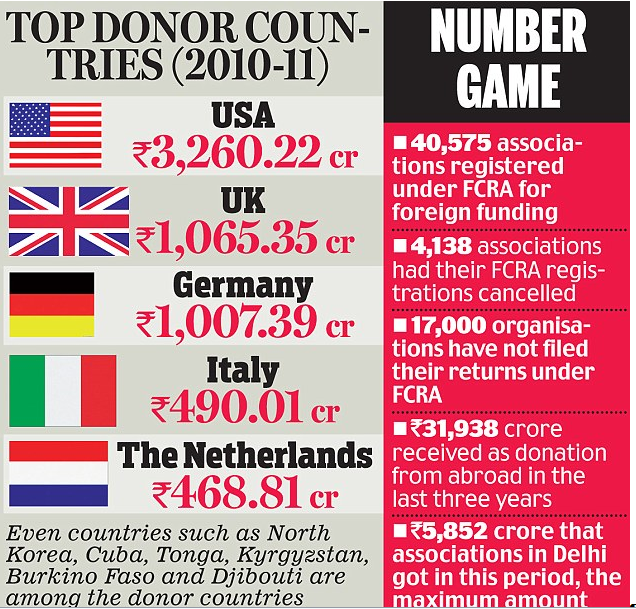
Top five donor countries
The five major donor countries are the US (Rs 3838.23 crore), the UK (Rs 1219.02 crore), Germany (Rs 1096.01 crore), Italy (Rs 528.88 crore) and the Netherlands (Rs 418.37 crore).
2012: Government’s reply in Lok Sabha
UPA too talked of NGOs' role in anti-India activities in '12
The Times of India Jun 15 2014 Deeptiman Tiwary New Delhi:
TNN
Docu Said Bodies In Delhi, TN Got `10k Cr In 3 Yrs
The UPA-commissioned Intelligence Bureau report on NGOs, that surfaced days after the new government took over, has kicked up a ruckus but the assertion that some of these organizations were engaged in “anti-national activities” was made way back in 2012 by the government in Parliament.
In reply to a question in Lok Sabha, the Congres-led UPA had then said, “There were reports that certain NGOs were engaged in antinational and political activities.” The statement had come amid raging protests against the Kundankulam nuclear power project in Tamil Nadu. The government had even presented a document showing that NGOs in
Tamil Nadu and Delhi had received foreign contributions to the tune of over Rs 10,000 crore between 2008 and 2011.
It said Tamil Nadu-based NGOs received 10,119 contributions in that period, adding up to Rs 4,800 crore. Delhi based NGOs, the government said, received 4,297 contributions amounting to Rs 5,800 crore. The contributions came from around 160 countries, the government had informed the House.
A recently leaked IB report, submitted to the Narendra Modi government on June 3, has also called into question the role of NGOs involved in the Kudankulam
protests and gives details of foreign contributions received by them.
The report says that eight out of 11 NGOs involved in the protests were primarily funded by Europe-based donors who allegedly pumped in Rs 80 crore between 200506 and 2010-11.
Of this, Rs 43 crore flowed into Tuticorin Multipurpose Social Service and Rs 20 crore to Tuticorin Diocesan Association.
In the 2012 document, the government said one of the NGOs involved in Kundankulam protests was facing a CBI inquiry for contributions received by it and that 30% of the 3000-odd foreign contributions in the period had been cornered by Tamil Nadu.
The outfit under CBI inquiry — Coimbatore-based Tamil Nadu Muslim Muneetra Kazagham (TNMMK) — had supported the anti-Kudankulam protests and some of its members were arrested during an agitation in September 2012. Other NGOs under investigation by the Tamil Nadu Police include AID India (Chennai), Saccer (Nagercoil) and Centre for Promotion of Social Concern.
Following vociferous protests by NGOs, the government had alleged the Kudankulam stir was being funded from abroad by vested interests and put 77 NGOs under the scanner for funding. The document also named some other states where NGOs had received a large number of contributions.
These included Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Kerala and Maharashtra with 4,500-6,000 contributions during the period.
Foreign-funded NGOs with malign agendas
Foreign-funded NGOs stalling devpt: IB report
The Times of India Jun 12 2014
To Muzzle Dissent, Say Activists An Intelligence Bureau report has accused “foreign-funded” NGOs such as Greenpeace, Cordaid, Amnesty and ActionAid of “serving as tools for foreign policy interests of western governments” by sponsoring agitations against nuclear and coal-fired power plants across the country.
The NGOs, said to be working through a network of local organizations such as PUCL and Narmada Bachao Andolan, have negatively impacted GDP growth by 2-3%, claims the IB report sent to the PMO and other government agencies.
Environmental activists joined Greenpeace in rubbishing the IB report. Greenpeace said it was a conscious attempt by the country’s premier intelligence agency to crush and stifle opposing voices in civil society. The organization also wrote to the home minister, requesting him to share a copy of the report “to know and understand impacts of this labeling”.
As far as the source of funding is concerned, the NGO said, “Greenpeace India is funded by individual supporters in India. Greenpeace does not accept any donation from corporate or government entities.” Environmentalist Ramesh Agrawal, who recently won the Goldman Environmental Prize for resisting destruction of forests by private mining companies in Chhatisgarh, said the report was an attempt to muzzle dissent. “Environmentalists working on the ground have always been branded as anti-development.
At a time when global warming is threatening us and air pollution is the most serious
public health problem, why is the government suppressing voices of dissent?“ he asked.
The IB report -addressed to PMO, heads of joint intelligence committee and R&AW , national security council secretariat (NSCS), coal and power secretaries, home minister, finance minister and Cabinet secretary , and signed by IB joint director Safi A Rizvi -alleges that the “areas of action“ of these NGOs include anti-nuclear, anti-coal and anti-genetically modified organisms protests. Apart from stalling mega industrial projects, including those floated by Posco and Vedanta, these NGOs have also been working to the detriment of mining, dam and oil drilling projects in north-eastern India, it adds.
According to the report dated June 3, these NGOs are allegedly the influence behind “Praful Bidwais and Medha Patkars“. The document, the details of which were accessed by TOI, accuses Greenpeace of having expanded its activities to oppose coal-fired power plants and coal mining and receiving Rs 45 crore from abroad in the last seven years.
“It is using foreign funds to create protest movements under `Coal Network' umbrella at prominent coal block and coal-fired power plant locations in India,“ alleged the IB report.
Since 2013, Greenpeace has undertaken protests in five project-affected villages of Mahaan (in MP) coal block allocated to Essar and Hindalco under the banner of Mahaan Sangarsh Samiti. Its activists have been targeting mining companies, specifically Coal India, Hindalco, Aditya Birla group and Essar as they “stand in their way“, the report alleged.
The report has also raised questions over nearly $40,000 deposited in two bank accounts of S P Udayakumar, convenor of People's Movement against Nuclear Energy that has been at the forefront of the agitation against the Kudankulam N-plant. The money was supposedly transferred by Ohio University for sending in resources and articles in the field of Kudankulam.
Some well-funded NGOs
Government cracks down on NGOs which scoop Rs 10,000 crore a year in foreign donations... but don't bother to file returns
By ABHISHEK BHALLA
31 July 2013 |
Missionaries of Charity in West Bengal recieved funding of Rs 62.29 crore
The foreign hand is rocking quite a few cradles in India.
It's been believed for long that that Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs) get a major part of their funding from overseas.
Now it's all come together in a government file, tabulated and troubling. What's really set alarm bells ringing is that an average Rs 10,000 crore pours into the country every year in form of donations to NGOs from organisations across the world.
Getting foreign funding is no crime; flouting guidelines under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act 2010 that governs such transfers is.
The government is warier of NGOs in the wake of persistent allegations about their role in recent agitations like the one against the Kudankulam nuclear plant, or those sparked by Delhi's December 16 gang-rape, or even those led by Anna Hazare.
Sample this: In the last two years, Chennai- based NGO World Vision of India has received Rs 442.68 crore, making it the highest paid organisation consecutively in 2009-10 and 2010-11.
Despite being the highest paid, the NGO has not filed its returns under FCRA.
It is a Christian charity organisation focused on children's well being and humanitarian efforts following disasters.
Another NGO, the Oxfam Trust, Delhi, got Rs 71 crore - and did not file returns. Bal Raksha Bharat, also Delhi-based, got Rs 67.57 crore but filed no returns.
NGOs and institutes in the Capital account for the larger part of foreign contributions; many FCRA defaulters are also from here.
There are close to 700 defaulting NGOs for the financial year 2011-12 in Delhi. Andhra Pradesh has the highest number of such defaulters at 2,453.
All are under the home ministry scanner now.
In the last three years, the home ministry has cancelled the FCRA registration of more than 4,000 institutes; over 17,000 regular defaulters are under scrutiny.
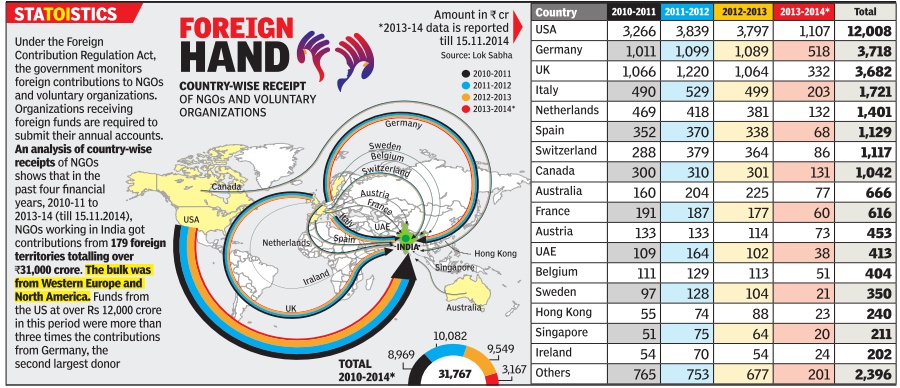
The US continues to be the highest donor country, followed by the UK and Germany. While huge amounts are pouring in from developed countries, countries like North Korea, Syria, Cuba, Tonga, Kyrgyzstan, Burkino Faso, Djibouti are also among the donor countries.
Over the last three years more than Rs 30,000 crore has been received by organisations across the country.
Institutes in Delhi have amassed the highest amount touching Rs 6,000 crore. The number of organisations and entities receiving funds from abroad has been going up steadily.
According to the latest home ministry report on FCRA in 2010-11 the number of institutes that received foreign funding was 22,735-a jump from the previous years.
In 2009-10 this number was 21,508 and in 2008-09 it was 20,088. In the last decade the number of associations registered under FCRA has doubled.
The number was 21,244 in 1999-2000 and it is 40,575 in 2010-11. Intelligence agencies are maintaining a strong vigil on the donations being made from associations abroad.
"There are several organisations that are under scanner and action would be taken if any wrongdoing is found," said a home ministry official.
Sources said it is feared that the foreign aid can be misused and diverted for purposes other than mentioned.
Fearing this misuse and money laundering the FCRA Act of 2010 has made the procedure for foreign funding stringent. Action against the dubious organisations is being taken.
While 72 organisations have been prohibited from getting funds from abroad, accounts of 32 NGOs have been frozen, and 24 cases referred to the CBI.
In some cases, state police forces are probing illegalities committed by these organisations. In many cases the government has put the organisations on notice for not filing their returns.
Sources said the defaulters are required to a pay a penalty, and if they don't, cancellation of FCRA registration is the likely outcome. It's not just NGOs that have been added to the list of defaulters by MHA for not filing their returns.
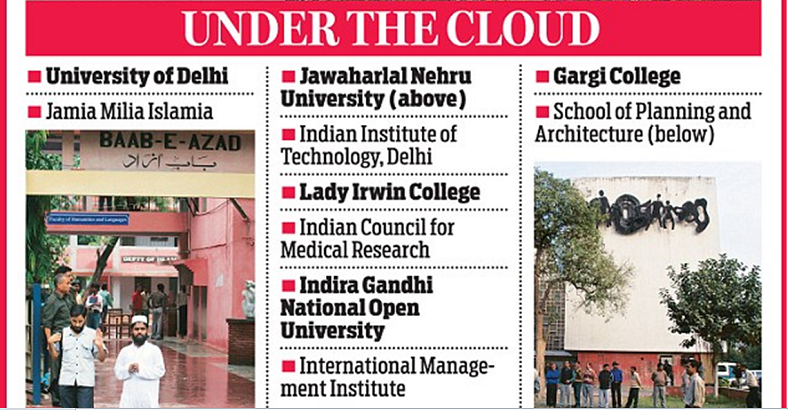
The list shows that top educational institutes in the national capital have also flouted the guidelines by not filing their returns in the previous two years.
The University of Delhi, Jawaharlal Nehru University, Jamia Millia Islamia, Indian Institute of Technology, Lady Irwin College, Indian Council for Medical Research, School of Planning and Architecture, Indira Gandhi Open National Open University, International Management Institute and Gargi College are among the 693 organisations in Delhi that have not filed their returns under FCRA.
The home ministry report indicates that most of the funds are meant for establishment expenses, rural development, welfare of children, construction and maintenance of schools and colleges, grant of stipend and scholarships, AIDS awareness, research, awareness campaigns, welfare and maintenance of religious functionaries and schools, welfare of women and construction of hostel for poor students.
Holland's CORDAID and oil drilling in Manipur
IB: Dutch-funded NGO bid to stall oil drilling in NE
Bharti Jain New Delhi:
TNN
The Times of India Jun 14 2014
The Dutch government-funded CORDAID and its associate outfits had organized an elaborate training session for northeastern NGO activists in Shillong last year, teaching them how to use GPS tracking to map oil wells, mines, dams, forests and habitation for an updated GIS platform on extractives in the region.
The database would be used to facilitate targeted local protests and international activism against extractive industries like oil drilling in Manipur, according to an Intelligence Bureau report on the impact of foreign-funded NGOs' activism on India's GDP growth.
The trainers at the session, two Dutch and an American, constantly told the participants that oil reserves in the northeast were as large as those in the entire Gulf region and that the resources must be preserved by the local tribals for their own use. They alleged that the government of India was, in collaboration with MNCs, “stealing the resources of the region and refusing to remove the Armed Forces Special Powers Act (from Manipur) as it needed the Indian Army to extract those resources“.
The trainers insisted that until the rights of communities over their land and resources were recognized, Jubilant Energy , engaged in oil drilling in Manipur, and the government should stop all petroleum and drilling activity in Manipur.
According to the IB report, CORDAID has added `extractive industries in the northeast' as one of the focal points for its interventions in India.
Greenpeace and coal plants
`Anti-coal stir picked up after Turkey meet'
Deeptiman Tiwary New Delhi: TNN
The Times of India Jun 14 2014
The leaked Intelligence Bureau report on NGOs has detailed how Greenpeace sent its activists to Istanbul for a coal conference where an elaborate plan to “stop new coal build (plant) and to retire existing coal plants“ was mooted.
According to the report, though Greenpeace had begun expanding its anti-CFPP (coal fired power plant) activity in 2010-11, the real push came following the Istanbul conference held in July 2012.
The report said, “Starting 2012, Greenpeace activists have been financed to attend international coal conferences, such as the Istanbul Coal Strategy Conference (July 2012). This conference was held to discuss `people-centric' protests in order `to stop new coal build (plant) and to retire existing coal plants'.“
The report said at the conference, the US-based Climate Works Foundation presented a paper that highlighted India as the primary target for CFPP activism.
2015: 69 NGOs blacklisted
Of 69 blacklisted NGOs, 30 work for minorities
Deeptiman Tiwary The Times of India Mar 05 2015
Prohibited From Getting Foreign Funds
The government has banned 30 NGOs, ostensibly engaged in welfare of minorities, from receiving foreign funds after adverse reports about their activities from intelligence agencies.These are part of 69 NGOs which have been prohibited by the government from receiving foreign funds under the Foreign Contributions Regulation Act (FCRA). Andhra Pradesh accounted for most of these “dubious“ NGOs followed by Tamil Nadu and Gujarat. Of the 14 NGOs blacklisted by the home ministry in Andhra Pradesh, eight are engaged in minority welfare. While seven of these are Christian institutions, one is an Islamic education association.
Of the 12 NGOs banned in Tamil Nadu, four are Christian organizations while one is Islamic. In Gujarat, of the five organizations banned, all except one is engaged in Muslim welfare.
Across the country , 15 organizations each engaged in Muslim and Christian welfare have been banned from receiving foreign funds.
The information was shared by minister of state for home Kiren Rijiju in reply to a question in Lok Sabha on Tuesday . Home ministry regularly reviews and audits flow of funds in NGOs from abroad and issues notices to those not filing their returns properly. It also initiates action against those not following the FCRA regulations while receiving foreign funds and blacklists those suspected to be working against the interests of the country . NGOs in India receive foreign donations in excess of Rs 10,000 crore annually from over 150 countries with the US and Europe being top donors apart from United Arab Emirates.
Registrations of 4,138 associations under the FCRA were cancelled for non-submission of annual returns from 2006-07 to 2008-09. Among these, Tamil Nadu accounted for the maximum NGOs (794) followed by Andhra Pradesh (670) and Kerala (450).
Recently , over 31,000 NGOs were served notices for not filing annual returns on their foreign donations. In 2011-12, notices were sent to 21,493 associations which had not submitted annual returns under the FCRA for the years 2006-07, 2007-08 and 2008-09. In 2014, notices were issued to 10,343 associations which had not filed annual re turns from 2009-10 to 2011-12.
Rijiju had earlier informed Parliament that adverse reports were received from intelligence agencies against NGOs such as Tuticorin Diocesan Association; East Coast Research and Development Trust, Thoothukudi; Centre for Promotion and Social Concerns, Madurai and Greenpeace India Society , Chennai.
“Based on inspectionsinvestigations, the FCRA registration of Tuticorin Diocesan Association and Centre for Promotion and Social Concerns were suspended and their bank accounts frozen. The FCRA registration of East Coast Research and Development Trust was cancelled,“ he had said.
The Modi government has mounted greater scrutiny on the activities of NGOs and their funding. In a report leaked last year, IB claimed a host of NGOs, including Greenpeace India, were working against the interests of the nation at the behest of foreign powers and that their activities had cost the country 2-3% of GDP .
The government recently prevented Greenpeace activist Priya Pillai from flying to London to address a gathering.
The complete list of the 69 NGOs blacklisted in 2015
1. Society for People’s Action for Development, 11-4-5, Donica Road, Chenchupet, Tenali, District – Guntur, Andhra Pradesh
2. Action for Welfare and Awakening in Rural Environment(Aware), Administrative Office, 5-9-24/78, Lake Hill Road, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh-500463.
3. Agape Helping Ministries, 80-24-4/1, Jayasri Gardens, A.V.A. road, Rajahmundry, West Godavari, Andhra Pradesh
4. Anjumane Hussamia Educational Association, 22-6-785, Hussamia Manzil, Panjeshah, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh
5. Aware (India) Foundation (AIF) H. 8-2-703/A/C/B 5, Banjara Hills Road No. 12, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh
6. Christ’s Helping Hand Children’s Home, Near B.G.R. High School, Alcot, Gardens, Rajahmundry, Andhra Pradesh,
7. Christian Outreach Centre, Rayadupalem, Kakinada-5, Andhra Pradesh
8. Christian Outreach Ministries Properties Trust, H. No. 11-6-23, Laximpur, Warangal, Andhra Pradesh
9. Christian Outreach Ministries, H. No. 11-6-23, Laximpur, Warangal, Andhra Pradesh
10. Good Samaritan Evangelical and Social Welfare Association, Sathyavedu, Krishna Dt.-517-588 Andhra Pradesh
11. John Abraham Memorial Bethany Home, TANDUA, P.O.Bag NO.3, TANDUA-501141, Rangareddy Distt. Andhra Pradesh
12. John Abraham Memorial Bethany Home, House No.6-19, Plot No. 342, Vivekanagar Colony, Kukatpally, PO, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh-500072.
13. Matsyagandhi Mahila Welfare Association, Appu Ghar Fishermans Colony, Visakhapatnam (U), Andhra Pradesh
14. Andhra Pradesh Pragati Orphen Home, Pagati Nagar, Old Town, Tanuku- 534211 Andhra Pradesh
15. Chandigarh Apostolic Christian Assembly, Chandigarh Ministry,123/1 Sector- 55,Chandigarh
16. Bhartiya Cattle Resource Development, D-37, South Extension, Part- II, New Delhi
17. IGEP Foundation, C 3A/86C, Janakpuri, New Delhi
18. Saraswati Charitable Trust, M-109, Greater Kailash-II, New Delhi- 110048
19. Gujarat Gujarat Idar-E-Talimate Islamia, (Darul-Ulm Shahe-Alam), Jamalpur Road, Ahmedabad, Gujarat- 380001
20. Jameah Rashidiyah Trust, Surat- Via-Kim At/PO Nani Naroli, Surat, Gujarat- 394110
21. Madrasa Jamiyad Ravatul-e-Hat, Porbandar Bye Pass Road, New Micro Town, District-Mongrol, Junagadh-362225, Gujarat
22. Samadhan Foundation, Chilakota Block No. 1564 D, Khadda Colony, Dahod, Gujarat-389160
23. Samast Muslim Khalifa Sunnatwal Jamat Navsari, 1/1057, Char Pul Road, Navsari, Gujarat- 396445
24. Haryana Organisation for Progress and Ecology (HOPE) H. No.1592, Sector – 15, Sonepat, Haryana- 131001
25. Jammu & Kashmir Akandar Tryst C/o Muslim Augaf Trust, MujahidManjil, Srinagar Jammu & Kashmir
26. Public Relief Trust C/o Prof Yunus-Al-Umar, Islamic Study Circle, Augaf Building, Badshah Chowk, Srinagar, Jammu & Kashmir
27. Falah – e- Aam Trust C/o G.M. Butt, Village Lathishah, Sapore, Baramula, Jammu & Kashmir
28. J & K Muslim Conference Wazirabad, H. NO. 114, Sardar Manzil, Srinagar, Jammu & Kashmir
29. Asian Aid Organisation Welfare Trust, No. 55, Kodandaramn Garden, 2nd Stage, Coxtown, Jeevanahalli, Bangalore, Karnataka 560005
30. Tibetan Culture & Education Foundation, C-10, Devetha Plaza, Residency Road, Bangalore, Karnataka
31. Action for people’s Participation and Environmental Care, A-62, Ashoka Marine Drive, Ernakulam, Cochin, Kerala
32. Islamiya College kuttiadi, Calicut Distt. Kerala
33. Social Action Movement of Idukki, Pulianmela- 685565 District Idukki, Kerala
34. Society for Action with the Poor, H. No. 126, Ward No. V, Manglath, Pannivizha, Adoor PO, Pathanamthitta Dt. Kerala Pin- 591523
35. Evangelical Lutheran Church in Madhya Pradesh, Luther Bhawan, Post Box No. 30, Chhindwara, Madhya Pradesh-48000
36. Reach Valley View Academy, 21/B Shreeram Nagar, Indore, Madhya Pradesh
37. Iqra Education Society, Haji Gulam Nagar, Mehrun Jalgaon, Maharashtra -425135
38. Khair-e-Ummat Trust (KEUT), 51-55, B.I.T. Chawl, 2nd floor, Immamwada, Compound, Kambekar Street, Mumbai, Maharashtra- 400009
39. Watch Tower Bible & Tract Society H- 58, Old Khandala Road, Lonavla, Maharashtra –410401
40. M. A. Wahab Islamic Public School Usmanganj, Lilong, Manipur 795130
41. Adima Jati Seva Samiti (AJSS), Circular Road, Phulbani Sahi, Kandhamal, Orissa- 762002
42. Health Education Development Society, A-6, Tribeni, Sahidnagar, Bhubaneswar, Khurda, Orissa
43. Society for Development Action (SODA), Iindapahi, PB No.16, Baripada, Dt. Mayurbhanj, Orissa
44. The Association, Society for Awareness of Human Society & RuralAdvancement (SAHARA), Kalahandi, P.O. Numper Vis M. Rampur Kalahandi, Orissa- 766102
45. Vikash Parishad Gandhi Nagar, Korsput-764020 Distt. Koraput, Orissa
46. Harpawat Charitable Trust, 30 C, Madhuban, Behind Bhartiya Lok Kala Mandal, Udaipur, Rajasthan
47. Harvest Ministries, Door No. 4/56, Arul Illam 5th Cross Street, Shanthi Nagar, Palayamkottai, Thirunelveli, Tamil Nadu-627002/ Door No. 15C, Opposite to World Gymn, Ratnada Subji Mandi, Jaipur, Rajasthan-342011
48. New Life Community Development Society, Mubarak Bagh, Ajmer Road, Jaipur, Rajasthan- 302006
49. Aid India, Chennai, Tamil Nadu
50. Association Madras Church of Christ, No. 11, Shenoy Road, Nungambakkam, Madras, Tamil Nadu- 600034
51. Nadu Church of Christ Trust, Carmel Nagar, Siluvathur, Dindigul, Tamil Nadu
52. Community Service Society, S/83, Keelaperuvilltai, Asaripallam 629 201, Nagercoil, Kanyakumari, Tamil Nadu
53. Development Organisation for Women (DOW), P.O. Batlagundu Distt. Dindigul, Tamil Nadu
54. Good Vision, Kanyakumari, Tamil Nadu
55. Mount View Academy, Madurai and Reach International Education and Social Welfare Trust, Kodimangalam, Madurai, Tamil Nadu
56. Muslim Munnetra Kazhagam (TMMK) No. 6, Vadaraikayyaar, Street, Chennai. Tamil Nadu
57. Reach in the Nilgiris, Plot No. 99, Sai Deep Apartments, VGP Saravanan Nagar, Madambakkam, Chennai, Tamil Nadui-600073
58. Saccer, Nagercoil, Tamil Nadu
59. Trust for Rural Uplift and Education, Tirunelveli, Tamil Nadu
60. Tuticorin Diocese Association, Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu
61. Heritage Foundation, Village- Badhwar, Bye pass Road, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh
62. Jamai Atul Falah, Bilariganj, Azamgarh, Uttar Pradesh
63. Khwaja Khushal Charitable Trust, Vill-Bihargarh, PO-Morna, Muzaffarnagar, Uttar Pradesh-251316
64. Maa Research Foundation, 31/10, Siddantha Colony, Arya Samaj Road, Muzaffarnagar, Uttar Pradesh – 251 002
65. Dhe Chen Chokhor Kagyupa Monastery, Clement Town, Dehradun, Uttrakhand
66. Shrimati Jashoda Devi Foundation Society, Pauri Garwal, Uttrakhand
67. Calcutta Urban Service, 14/2, 1st Floor, Sudder Street, Kolkata, West Bengal-700016
68. Children’s Development Communities India, 134, S.N. Banerjee Road, Calcutta, West Bengal
69. Congregation of the Daughters of St. Anne, St. Anne Convent, Assammore, P.O. Mohit Nagar, Jalpaigiri, West Bengal- 735101