Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content.
|
Contents |
Milestones
Hits and misses of Isro
Chethan Kumar,TNN The Times of India | Sep 24, 2014
Times of India tracks the journey of India’s space agency, the Indian Space Research Organization (Isro):
1: The sounding rocket might have been launched from Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) as early as 1963, with Vikram Sarabhai being the visionary mind behind Indian space programme, but the Indian Space Research Organisation (Isro) was officially created on Aug 15, 1969. A new campus at Veli, Thiruvananthapuram was set up in the same year.
2: Just about 6 years from creation of Isro, the launch of the first Indian satellite, Aryabhata, happens on April 19, 1975. Several other landmarks like operationalising SHAR Centre in Sriharikota (1971) rechristened as Satish Dhawan Space Centre in October 2003; establishment of the Department of Space (DOS) on June 1, 1972 with Satish Dhawan as the Secretary, and, establishment of the Isro Satellite Centre in Bangalore (1972).
3: Four years after Aryabhata, Isro launches Bhaskara, an experimental satellite for earth observations on June 7, 1979, and the first experimental launch of SLV-3 (launch vehicle) was done on August 10 the same year. But the satellite failed to reach the orbit. Many experiments including multiple attempts of launching SLV-3 and other satellites happened over the next eight years, including the launch of the first INSAT system on August 30, 1983.
4: Basking in the glory of the achievements, Isro experimented with the launch of ASLV, an advanced version of SLV-3 on March 24, 1987. But the satellite (SROSS-1) failed to reach the orbit. This was followed by a successful launch of INSAT-1D on June 12, 1990, which preceded the launch of the second operational Remote Sensing Satellite on August 29, 1991.
5: 1993: First developmental launch of what is today called Isro's workhorse launch platform, the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) began. Even the PSLV's first attempt to put a satellite into orbit failed on September 20, 1993 This was followed by many communication and remote sensing satellites in the 90s. Isro saw success with PSLV, even began development of the Geo-synchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV). GSLV, in fact, placed GSAT-1 satellite in orbit on April 18, 2001.
6: 2008: Isro launches a record Cartosat-2A and IMS-1 along with eight nano satellites (DELFI-C3 for the Netherlands; CUTE-1.7 and SEEDS for Japan; CAN-X2 and NLS-5 for Canada; AAUSAT-II for Denmark; COMPASS-I and RUBIN for Germany). Landmark project Chandrayaan also saw its launch on October 22, 2008 aboard the PSLV-C11.
7: November 5, 2013, Isro sent a probe to Mars at a cost of Rs 450-crore.
8: As India gears up for her date with the Red Planet, Isro's first interplanetary mission, the space agency holds the credit of having put in place the largest (civilian) constellation of remote sensing satellites, with 10 of them currently working in space.
9: September 24, 2014: Mars Orbiter Mission to be inserted into the Martian Orbit.
1981: Apple and other early successes
The Times of India, Jun 21 2016
Chethan Kumar How an `Apple' on a bullock cart took Isro to stars
The Indian Space Research Organisation (Isro) has become one of the first picks for countries looking to launch satellites. The situation was not always like this.Thirty-five years ago, on June 19, 1981, Isro successfully launched its first communication satellite, Ariane Passenger PayLoad Experiment (Apple), on Ariane-1 from Kourou, French Guiana. This was a major milestone in India's space programme as Apple was used for several communication experiments, including relay of television programmes and radio networking. Incidentally , this satellite was transported on a bullock cart, captured for pos terity in an unforgettable photograph. It had only been six years since Aryabhatta, Isro's first satellite, and the agency was still in its infancy much like the country's infrastruc ture. Isro had been trying launch technology through its SLV class of launchers and the Satellite Telecommunication Experiments Project had been launched.
Bhaskara and Rohini had been successes before Apple.But Apple laid the foundation for indigenous development of operational communication satellites which grew into a very large constellation of satellites in Insat and Gsat series that spurred the country's technological and economic growth. Newer applications like tele-education, telemedicine, Village Resource Centre, Disaster Management System etc were enabled through space technology.
According to the book `Fishing Hamlet to Red Planet', although the satellite was laun ched through Ariane, Apple was boosted into Geo-Synchronous Orbit by Isro's own apogee motor derived from the fourth stage motor of the SLV-3. It kicked off Isro's impeccable record with deadlines. While the agency is known to have built the Mars Orbiter Mission in 18 months, it continued a long tradition and the agency had designed and built Apple in just two years with limited infrastructure in industrial sheds. Meanwhile, the final 48hour countdown to Isro's record-breaking mission, which will place 20 satellites -17 from abroad -in the same orbit, kicked off on Monday . The launch of the PSLV C-34 Cartosat-2 series satellite mission is slated for June 22 at Sriharikota.
Manned mission
Crew module test
The Times of India, Nov 30 2014
Binoy Valsan
Scientists at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota were busy integrating a brown bucket-like structure with a black lid mounted on a pedestal.Some day soon, they believe, an improved version of this would carry people to space. Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) took baby steps towards sending man to space, with an experimental flight of a GSLV-Mark III all set to carry this `crew module' as the payload in the sec ond week of December. While the manned mission is at least 10 years away , a full-fledged flight of GSLV-MIII is also a couple of years away . The biggest rocket to be made by ISRO, it can carry payloads up to four tonne-a necessity in the coming days of heavy satellites. Scientists are testing indigenously developed cryogenic engine at Isro's Mahendragiri facility.
The unmanned module to be used in Crew Module Atmospheric Re-entry Experiment (CARE) is to test its ability to re-enter the atmosphere with thermal resistance, parachute deployment in cluster formation, aero braking system and apex cover separation procedures.
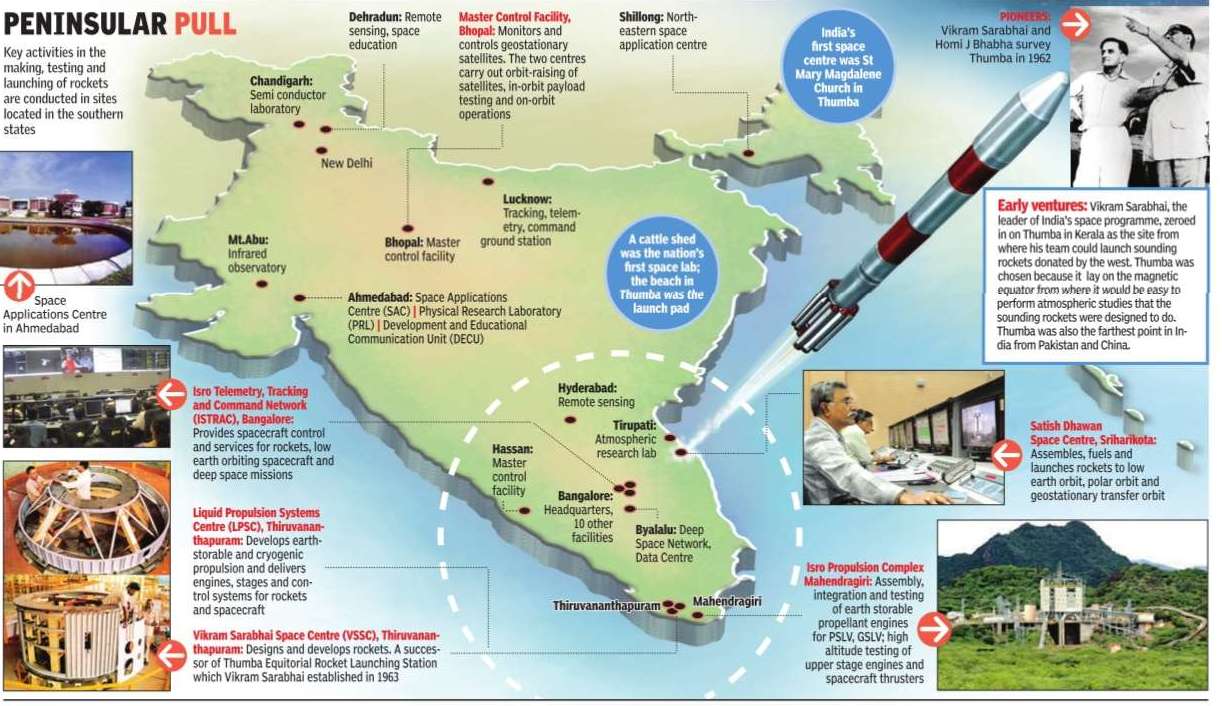
Major ISRO centres
Feb 20 2015 Arun Ram
Geography, history and logistics have necessitated the positioning of 14 of 20 major ISRO centres in the region
In the 1960s, when children of coastal Thiruvananthapuram remained outdoors even after nightfall, mothers employed a scare: “Get in, Maadan would be flying now.“ Maadan, the not-so-friendly local god would fly with a mace at night, spewing fire and threatening to knock down those who disobeyed parents. For those disbelieving kids, the women would point to the night sky and show the occasional ball of fire that disappeared in seconds. Later in high school, science teachers called the mothers' bluff. The fire ball, they told the students, was the flare of sounding rockets fired from the neighbouring Thumba Equitorial Rocket Launching Station. The 30kg-something rockets would go up to an altitude of 60km, and the tiny payloads, before plunging into the Arabian Sea, would do some atmospheric studies.
From flying tiny sounding rockets gifted by the US, the USSR and France in the 1960s to launching satellites weighing up to a couple of tonnes into geosynchronous transfer orbits from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, India has come a long way . With that has grown the Indian Space Research Organisation (Isro) that today has centres across the country . But the southern peninsula remains the hub of India's rocket-making, testing, flying and tracking.
Sample this: Out of the 20 major Isro centres, 14 are situated in the southern states . While a large majority of these centres handle strategic operations, the others are mostly involved in research, education, training and analysis.
So why this geographical dichotomy? The answer lies not in parochialism, but in a combination of science, history and logistics. To know this concentration of Isro branches, we should look at the roots of India's space programme.
When Jawaharlal Nehru, on the advice of Homi J Bhabha, formed the Indian National Committee for Space Research (Incospar) in 1962, its leader Vikram Sarabhai's first assignment was to identify a place from where India could launch borrowed sounding rockets.
To carry out atmospheric stud ies, the best place would be somewhere near the magnetic equator of the Earth which ran close to the southern tip of the country. And this led Sarabhai and Bhabha to Kerala, where they zeroed in on Thumba, then a sleepy fishing village. There was not even a proper building in Thumba, but Sarabhai was in a hurry . In 1963, he moved his small team that included H G S Murthy ,D Eswar Das, M R Kurup and A P J Abdul Kalam to the St Mary Magdalene's Church.
Murthy, who headed the team, had an office in the Bishop's house. The remaining scientists, later joined by S Nambinarayanan, put together four tables in the church building to mount their drawing boards. A cattle shed doubled up as their laboratory , the coconut palmfringed beach their test pad.
After experimenting with foreign sounding rockets, when Incospar became Isro in 1969, it was time for indigenous rocket launches. And it needed a bigger launch pad on the eastern coast, for future satellite launches would need an eastward launch to go against the Earth's spin.Sriharikota, 100km north of Chen nai, on the Andhra Pradesh side was identified. The island had Bay of Bengal on one side and the Pulicat lagoon on the other three. This meant that even if a rocket went out of control, it could be destroyed above the sea, with minimum risk to people.
Soon, a liquid propulsion centre came up in Thiruvananthapuram and, after Sarabhai's untimely death in 1971, all the facilities in the Kerala capital became the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC). When Isro wanted a facility to test its rocket engines made in Thiruvananthapuram, Mahendragiri in neigh bouring Tamil Nadu became a natural choice because of the proximity and the hilly topography.
For administrative purposes, Bangalore had become the Isro headquarters, and being equidistant from VSSC and Sriharikota helped. This also led to many auxiliary offices cropping up around Bangalore, including the Isro Telemetry Tracking and Command Network headquarters and the Isro Satellite Centre.When India needed a deep space tracking centre, Byalalu, a remote place in Karnataka was chosen for its sparse population and the result ant low electromagnetic interference.Hyderabad became the nerve centre of remote sensing, probably for its central location.
Isro centres in the northern states provide basic research and payloads. Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad, does high-end studies in astrophysics, while Space Applications Centre in the same city makes satellites and other payloads.Once the satellite is in space, north and south equally count, and hence the regional remote sensing centres and tracking centres across the country . For controlling geostation ary satellites, Isro has a master control facility each in Hassan, in Karnataka, and Bhopal.
Still, as India's rockets continue to be made, tested and fired in the south, there remains an open secret that Isro scientists don't tell you. In 1962, when Vikram Sarabhai's search for the perfect place near the Earth's magnetic equator took him to Thumba, the great man wouldn't have suppressed a smile when he realized it was also the farthest point from Pakistan and China.
Maadan, obviously, posed a much lesser risk.
Antrix, ISRO's commercial arm
Devas contract, its scrapping and Rs 4,435cr fine
The Times of India, Oct 01 2015
Int'l tribunal slaps Rs 4,435cr fine on Antrix
Isro Arm Had Aborted Devas Deal In 2011 Antrix and Devas had signed a contract to launch two satellites and use spectrum. However, after a controversy over procedural lapses led to blacklisting of four Isro scientists, including ex-Isro chief Madhavan Nair (above), the govt had scrapped the deal Isro's commercial arm, Antrix, has termed the international arbitration court ruling asking Isro to pay Rs 4,435 crore ($672 million) in damages to Bengaluru-based Devas Multimedia as shocking. “Antrix, with the support of the department of space, is preparing to file in court its application for remedy ,“ said an Antrix statement.
The tribunal's ruling on Tuesday is not yet binding on the Indian space agency , as Devas would require to get the ruling enforced by an Indian court. In a statement, Devas Multimedia said: “Devas Multimedia and its shareholders, including highly regarded international investors, are pleased that the ICC Tribunal unanimously ruled in its favour and found that Antrix is liable for unlawfully terminating the Devas-Antrix Agreement in February 2011.“
It said that Devas is hopeful that Antrix will now live up to its legal obligations and pay the award so that this dispute that arose during the prior government can be brought to a swift closure.
The contract signed between Devas and Antrix was to launch two operating satellites and use spectrum that is licensed to the firm.
However, following a controversy of lapse in procedures that led to blacklisting of four Isro scientists, including ex-chairman Madhavan Nair, the government scrapped this deal. This prompted Devas to take the legal course.
Devas was to lease 70 MHz of S-band spectrum from two satellites that were to be launched by Isro and pay $300 million for the rights.
2016: Indiainches closer to its own GPS
The Times of India, Jan 21 2016
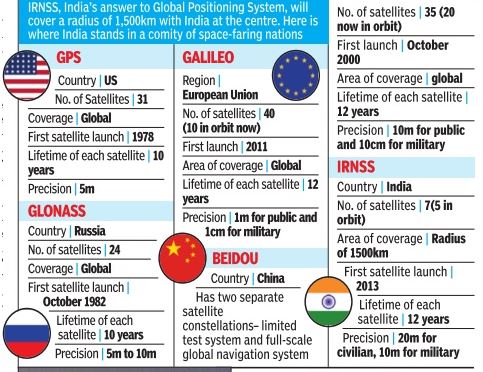
U Tejonmayam
SEVEN-SAT SYSTEM - 5th navigation sat takes India closer to `desi GPS' Indian Space Research Organisation (Isro) has started 2016 with a bang, launching the fifth (IRNSS-1E) naviga tion satellite in the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) constellation that will function as an alternative to the US-owned Global Positioning System (GPS).
An XL version of a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C31) placed in orbit the satellite 19.36 minutes after liftoff from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
IRNSS will provide navigation and positioning services in areas that require high precision for aviation, marine navigation, rail transport and military applications.In six-months, Isro expects the system to be integrated with smartphones.
2016
April 2016: PSLV C33
The Hindu, April 29, 2016
Avinash Bhat
ISRO’s workhorse PSLV C33, carrying India's seventh navigation satellite IRNSS-1G, soars into the sky after its launch from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota near Chennai on Thursday. Photo: K. Pichumani The Hindu ISRO’s workhorse PSLV C33, carrying India's seventh navigation satellite IRNSS-1G, soars into the sky after its launch from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota near Chennai.
A regional navigation satellite system with just seven spacecraft and in civil domain is unique to India.
India’s own navigational system, the set-up for which was completed on Thursday with the launch of the seventh and final satellite, will be called NAVIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation), Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced after the launch.
The seventh and final satellite of the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System, the IRNSS 1G, was launched into a sub geosynchronous transfer orbit with a perigree (nearest point to earth) of 284 km and an apogee (farthest point to earth) of 20,657 km. The satellite was launched on board the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), which took off from the Sriharikota launch pad at 12.50 p.m.
With this launch, the IRNSS constellation of seven satellites is now complete. This will allow the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to focus on the process of designing front end chips which will receive the navigational signals sent out by the satellites. The system will be similar to the Global Positioning System (GPS) operated by the United States with 24 satellites and the Glonass, Galileo and BeiDou systems of Russia, Europe and China respectively.
All satellites will undergo stabilisation testing and verification of their performance over the next few months before being pushed into use, according to ISRO officials.
An area of 1,500 km from Indian boundaries will be covered under the navigational system. The Prime Minister invited other countries to make use of this system as well. “We have seven neighbours who rely on technology provided by other countries. They can use Indian services if they want,” he said in a video message addressed to ISRO engineers.
With an accuracy of better than 20 m being claimed by ISRO, the navigation system will be offered as an open or Standard Positioning Service and a superior, coded military Restricted Service.
“We are now one of five countries with our own navigational system. Today we are free of dependence on other countries for navigation. Our planes will be able to land with ease and accuracy, we can plan disaster relief better and with our own technology,” a proud Mr. Modi said.
Explaining the name NAVIC, Mr. Modi said the system was dedicated to India’s mariners and fishermen who have been navigating using the sun and stars as waypoints for hundreds of years. “They have shown strength and determination in venturing out to sea for so many years. We have named this system for them, the ‘naviks’ (mariners),” he said.
June 2016
Inject a record 20 satellites at a time into orbit
The Times of India, Jun 23 2016
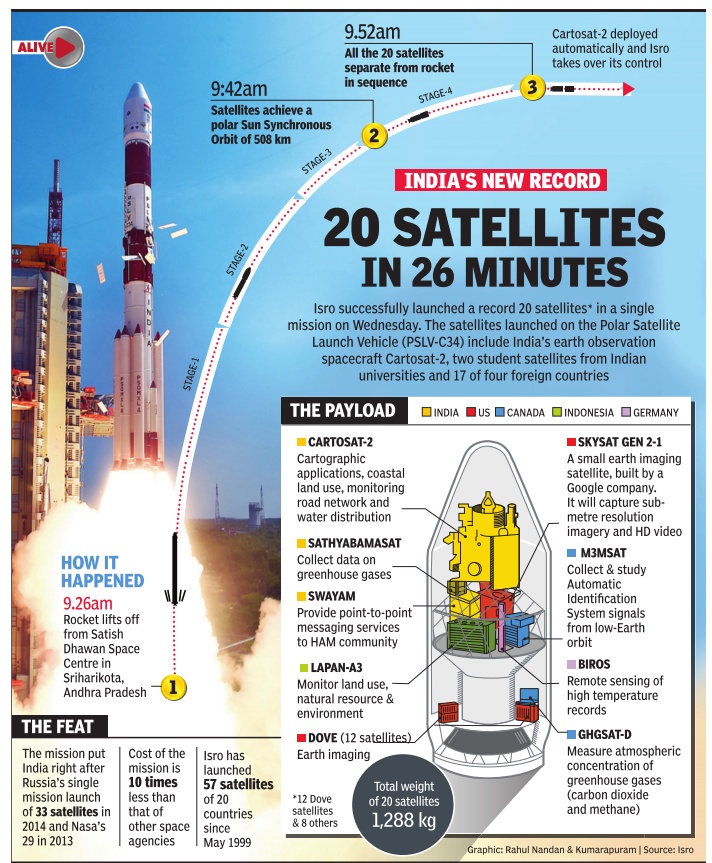
U Tejonmayam
Isro record: 20 satellites take off at one go India's PSLVC34 rocket circled the earth in about 90 minutes, at 7.7km per second, to inject a record 20 satellites into orbit and demonstrate its capability to reach another orbit in the same mission. The `XL' version of the 320-tonne spacecraft lifted off from Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota with payloads weighing 1,288kg at 9.26am. India's remote sensing satellite Cartosat-2C, weighing 727.5kg, sat on the top part of the PSLV's nose cone; riding piggyback were two Indian student satellites and 17 earth observation satellites from the US, Canada, Germany and Indonesia. Prime Minister Narend ra Modi called it a mo numental accomplishment. “20 satellites in a go! @isro continues to break new barriers. Hearty congratulations to our scientists on the monumental accomplishment,“ he tweeted. “PSLV has done its job again,“ said Isro chairman A S Kiran Kumar.
About 17 minutes after lift-off, the rocket began injecting satellites, starting with its Cartosat-2C. In the next 10 minutes, PSLV made several manoeuvres to inject all the satellites in a single orbit in different inclinations and with varying velocity, in the process travelling halfway around the earth.
Isro also used the occasion to test its capability to launch multiple satellites into different orbits.
About 50 minutes after launching all the satellites, the fourth stage reignited for five seconds before travelling around the earth for 45 minutes, completing a full circle.
The demonstration was conducted for Isro's next mission, when it plans to launch five satellites in two different orbits.
Mission director B Jayakumar said that multiple launches in a single mission required complex technology and Isro is working on resolving certain problems that may arise during such launches. “Initially we were a little hesitant to take 20 satellites in one go. But we soon resolved the problems,“ he said.
“What we have achieved today shows we have the expertise to take up complex missions,“ Jayakumar said.
Isro set a world record for the highest number of satellites launched in a single mission when it placed 10 satellites in a PSLV on April 28, 2008.Nasa in 2013 placed 29 satellites in a single mission and Russia in 2014 launched 33 satellites in one launch.