Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary (Delhi/ Haryana)
Note: The Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary is in Delhi as well as Haryana

Sohail Madan/ Jasjeev Gandhiok, The Times of India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents[hide] |
Buffer zone
The Times of India, Apr 22 2016

Haryana creates Asola buffer zone
Bagish Jha
Proposes 100m Radius Around Sanctuary In Gurgaon, 1km In Faridabad The Haryana government has forwarded the final draft of the demarcation of the eco-sensitive zone (ESZ) on its side of Asola Bhatti wildlife sanctuary for approval to Union ministry of environment, forests and climate change (MoEFCC). The state government had proposed a 100m radius around the boundary of the sanctuary as the ESZ in Gurgaon, and a 1km radius around it in Faridabad.
The ESZ details were released in a reply to an RTI filed by advocate Sanjeev Aliawadi in January 2016.
To protect developers from ESZ regulations, the state has recommended excluding areas for which change of land use (CLU) has already been granted for residential and commercial projects, and where projects are on-going.“In the absence of a notified ESZ, a 10 km-radius ESZ is applicable, in line with the 2006 Supreme Court order. But that will affect developmental work already underway ,“ read the final ESZ proposal sent to MoEFCC. On behalf of the state government, it was submitted by P P Bhojvaid, the state's additional principal chief conservator of forest and chi ef wildlife warden (CWW).
The demarcation of ESZ was initiated after a December 4, 2006 Supreme Court direction to all states, over a PIL filed by Goa Foundation, asking them to declare ESZs around protected areas. Based on this, MoEFCC issued a guideline on how ESZs could be demar cated, on February 9, 2011.
Spread over 32.71 sq km along south-eastern Delhi bordering Gurgaon and Faridabad in Haryana, Asola Bhatti is the only protected area in the National Capital Territory (NCT). The Asola Bhatti ESZ includes parts of Gwalpahari, Balola, Bandhwari and Kha rak in Gurgaon district, and Mangar, Gothra, Mohabbatabad, Pali, Bhankri, Anangpur, Ankhir, Meola Maharajpur, Surajkund and Badkhal in Faridabad district.
On June 20, 2015, the Haryana CWW had constituted a committee, consisting of Gurgaon's divisional wildlife and forest officers, and the deputy conservator of forest in Faridabad, to suggest the extent of ESZ on the Haryana side. The committee submitted its report in October 2015, recommending a kilometre of ESZ along the sanctuary boundary .
At a meeting to demarcate the ESZ in December 2015, chaired by principal secretary of forests Amit Jha, the deputy commissioners of Gurgaon and Faridabad, along with the Haryana director general of mines and geology and the department of town and country planning (DTCP), together submitted their objections to the suggestion of a kilometrewide area as ESZ.
DTCP suggested that those areas in Gwalpahari and Faridabad that can be urbanised, and areas for which licenses to develop residential and commercial complexes have already been given, be exempted and kept outside the ESZ.
The Gurgaon deputy commissioner said the ESZ should not be over 100m from the sanctuary boundary .
“The 100m area is where there is no existing road or physical structure,“ said deputy commissioner T L Satyaprakash. For Faridabad, it was proposed that the ESZ be restricted to 1km from the boundary .
The animals
Hyena
The Times of India, Jul 12 2015

Asola-Bhatti can be NCR's hyena habitat
Delhi's depleting scrub forests and the Aravalis around it may be home to the threatened striped hyena.While the forest department believes there may be a fairly healthy population, they will confirm it by camera trapping in a couple of months.
Hyenas may not be as charismatic as the tiger or leopard but, if nurtured, Delhi's Asola Bhatti Sanctuary can be made to stand out as a habitat for the animal. The department had conducted a camera trapping exercise way back in 2000 and officials claim a pack was seen often in those days.
There is no dearth of prey or food for hyenas in the sanctuary . Experts say they can thrive on dead cattle, dead dogs or monkeys or even hunt for food. There is a dumping ground for dead animals near the Haryana border, too, which hyenas may be foraging on.
A book, “An Introduction to Delhi Ridge”, edited by G N Sinha, former additional principal chief conservator of forests, mentions “a pack of striped hyenas is also spotted occasionally in the Bhatti area“.
Asola Bhatti sanctuary is a small area of 4,707 acres in Maidan Garhi, notified in 1986, and about 2,167 acres in Bhatti, notified in 1991. But it shares a border with the Faridabad frontier of the Aravalis, making it an important wildlife corridor. The department is in talks with the Haryana government to secure an eco-sensitive zone shared between the two states.
Monkeys
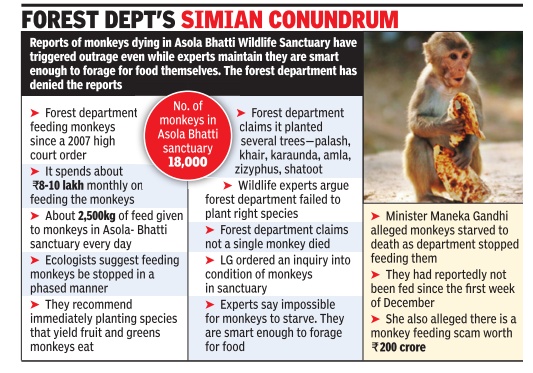
Jan 05 2015
Asola monkeys must be weaned off feed: Experts
The forest department in Delhi spends most of its funds not on protecting endangered species or on reviving the leopard populationbut on feeding monkeys. It's a perplexing problem, but, following a high court order, the department sends 2,500kg of fruits and vegetables to feed over 18,000 monkeys every day which were moved from the city to Asola Bhatti sanctuary in 2007. The department reportedly stopped feeding monkeys in the wildlife sanctuary for a few days when prices of vegetables and fruits went up but what ensued was more baffling. Many animal lovers claimed monkeys were starving to death. In fear of retaliation, the department resumed feeding them.
But primatologists and wildlife experts say monkeys are too smart to starve. They are extremely adaptable mammals who will leave the sanctuary to forage in neighboring villages or just come back to the city. All the department needs to do is to plant the species that monkeys love and stop feeding them.
“The department should have prepared the sanctuary before releasing monkeys in it. I had given them a list of species, including bansa, gram, banana and sugarcane, but those were not planted. I have seen how much food the department is just wasting on the pretext of feeding mon keys,“ said Iqbal Malik, a veteran primatologist.
Even forest officials jest that the wildlife sanctuary is gradually turning into a Rhesus monkey sanctuary .“There are 18,000 of them. It's not possible to care for so many and they are multiplying exponentially . Sterilization is not being considered because animal rights activists will protest. We have no option but to feed them. None of them are starving. In fact, the problem is that the place has lost its ecological balance. We don't have many predators feeding on monkeys. On the other hand, the carrying capacity of our sanctuary is not suited for such a large monkey population,“ said a senior official. The lieutenant governor recently ordered a probe into whether monkeys were starving in the sanctuary .
CR Babu, DU professor emeritus and chairman of a state-level experts appraisal committee, is also of the view that monkeys should be gradually weaned off the habit of being fed. “There are people who believe feeding birds, monkeys and other animals is a great service. But we are destroying their natural immunity and survival skills. They should forage on their own.That can be done by planting the species they feed on. Why is Pongemia and neem being planted by the department when animals don't eat them?” he said.
Experts say the department can turn the situation around in five years--if they slowly stop food supply and plant the right species.
2017, Leopards

Officials Say Pugmarks Sighted On Regular Basis For 30 Days
Months after a leopard was spotted in Yamuna Biodiversity Park, a whole leopard family has been sighted in the Asola Wildlife Sanctuary . According to forest officials, they have been seeing pugmarks of leopards on a regular basis for the past 30 days.
A big cat was spotted almost a month ago but it was difficult to identify the animal then. A week later, more pugmarks surfaced in the sanctuary . “Two of the pugmarks were of fully grown adults and we could see footprints of a suspected cub as its size was smaller than that of other two. The pugmarks also confirmed that they belong to leopards,“ said a wildlife and ecological task-force official.
Another member of the family was spotted a few weeks ago. While the adult male and female are suspected to be around five years old, the cub may be between 4 and 6 months.
“Pugmarks are being seen on a regular basis. The leopards have been sighted by the eco-task force. This is a good sign as it shows that the habitat has improved and there is a soild prey base for them. The terrain at Asola and old pits there provide a safe habitat for them. It is also away from any human settlement,“ said A K Shukla, chief conservator of forests and chief wildlife warden.
According to Shukla, there is a high possibility that the family has been staying at Asola for a long period of time. “There is enough food for them inside and they also have a cub, so there is no sense of insecurity . The possibility of attacking someone is higher when they are under stress and alone,“ said Shukla.
In November last year, a leopard was spotted at the Yamuna Biodiversity Park in north Delhi. However, the animal had to be shifted out of the the city as it may have posed a threat to the locals living nearby . The forest department, however, feels there is no such risk attached to the leopards here as there are no human settlements in the vicinity. The forest department plans to place camera traps inside Asola from next month onwards to determine the animal species that are currently present at the sanctuary. In addition, pugmarks of the animals will be collected by making soft-sand beds.“The camera traps will not only give us an update on the big cat, but also other animals living in the sanctuary .Extensive data will be collected for all species,“ Shukla added.
See also
Delhi: Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary