Alcohol and the Indian physique
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 32: | Line 31: | ||
Dr Ambuj Roy, assistant professor of cardiology at AIIMS, told TOI, “Benefits of moderate alcohol consumption have been found among southern European populations from the Mediterranean region and Caucasians in Europe and North America. However, in Indians, it clearly causes harm just like in African Americans.” | Dr Ambuj Roy, assistant professor of cardiology at AIIMS, told TOI, “Benefits of moderate alcohol consumption have been found among southern European populations from the Mediterranean region and Caucasians in Europe and North America. However, in Indians, it clearly causes harm just like in African Americans.” | ||
| − | = | + | == No. 1 cause of liver failure== |
| − | [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com | + | [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Alcohol-now-No-1-cause-of-liver-failure-20042017007026 DurgeshNandan Jha, Alcohol now No. 1 cause of liver failure, April 20, 2017: The Times of India] |
| − | + | [[File: Cause of liver failure and reasons for mortality.jpg|Cause of liver failure and reasons for mortality; [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Alcohol-now-No-1-cause-of-liver-failure-20042017007026 DurgeshNandan Jha, Alcohol now No. 1 cause of liver failure, April 20, 2017: The Times of India]|frame|500px]] | |
| − | ''' | + | '''More People Are Dying Of It Than Hepatitis B, Reveals AIIMS Study''' |
| − | + | There has been a sharp rise in the number of patients visiting AIIMS with alcohol-related liver failure.More alarmingly , the institute says, death rate among these patients is 64% -much higher than mortality from liver failure by hepatitis B virus, a common cause of infection in the organ in the country . | |
| − | + | AIIMS admitted 150 patients with alcohol-related liver failure from 2011 to 2015. Of this, the study said, 96 died within 10 days despite all possible medical intervention. | |
| − | + | Follow-up of the rest of the patients who were discharged when their condition got stable revealed that nearly 20% died within three to four months and another 20% in a year.“Once you have got acute-onchronic liver failure due to alcohol, survival is rare. Transplant, the only life-saving treatment option, is not possible immediately because three months of abstinence from alcohol is required,“ said Dr Shalimar, associate professor of gastroenterology at AIIMS. | |
| − | + | He added that medicines can treat liver infection caused by most hepatitis viruses and even autoimmune hepatitis flare-up can be controlled with medicines, but there is no medicine for alcoholism. “ Abstinence is the only way to prevent liver failure and deaths caused by that. The government needs to create awareness to prevent excessive drinking,“ the AIIMS doctor said. | |
| − | + | A recent survey published in Global Heart, a repu ted medical journal, showed alcohol use has gone up from 16.1% to 25.6% among urban dwellers in Delhi in the past 20 years. The increase in alcohol use in rural areas in the corresponding period is nearly four times -from 8% to 33.2% -the survey found. | |
| − | + | Dr Shalimar, who led a research published in Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology , said not only mortality rate, but also incidence of liver diseases due to alcohol has gone up significantly . “We admitted 427 patients with acute-onchronic liver failure from 2011 to 2015 at the hospital. Of this, a maximum 150 (40.8%) cases were alcohol-related, followed by hepatitis B virus infection (71, 19.3%), hepatitis E (45, 12.2%), autoimmune hepatitis flare-up (17, 4.6%), anti-tuberculosis drugs (16, 4.3%) and hepatitis A (2, 0.5%). In 67 patients (18.2%), the cause of acute liver failure couldn't be ascertained,“ he said. | |
| − | The | + | The AIIMS doctor added alcohol-related liver failure cases have poorer prognosis.“Most of them required ventilator support, their blood was thinner and brain damage was higher too,“ he added. Dr S K Sarin, director of the Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS), said most alcoholics are calorie-deprived. “Most infections cause leaky bowel.But in case of alcoholics, this problem is severe. Due to this, bacteria easily gets into liver from the small intestine, thus aggravating organ failure status,“ he added. |
| + | |||
| + | ILBS is experimenting with several therapies, including stool transplant, plasma exchange and liver dialysis, to increase survival rates in alcohol-related liver failure, Dr Sarin said. He, however, stressed on the need to create awareness about harmful effects of binge drinking. Dr Subhash Gupta, liver transplant surgeon at Max Hospital, Saket, said liver failure due to alcoholism “is a totally preventable disaster“. | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Safe drinking limit= | ||
| + | ==India vis-à-vis other countries== | ||
| + | [http://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2017%2F12%2F23&entity=Ar00401&sk=499F4461&mode=text December 23, 2017: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: Maximum units of alcohol per week in India and other countries; Top 10 countries for per capita alcohol consumption.jpg|Maximum units of alcohol per week in India and other countries; Top 10 countries for per capita alcohol consumption <br/> From: [http://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2017%2F12%2F23&entity=Ar00401&sk=499F4461&mode=text December 23, 2017: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | It’s the festive season, the countdown to New Year’s, and celebrations are in order. But while you reach for that bottle of wine you may want to make a note of the prescribed drinking level for the week of partying. Turns out different countries have different levels of safe drinking prescribed by their national health bodies. In India, that’s between five to 10 glasses for women and between 10 to 15 glasses for men per week. Mind, these are just recommended drinking limits; end-of-year parties are something of a time for going over the top, so don’t be surprised if you find you’ve had a drink or two more. In any case, there’s always the New Year to make a resolution that you will drink within limits. Here, a look at drinking-level recommendations of selected countries | ||
| + | |||
| + | =See also= | ||
| + | [[Alcohol: India ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Alcohol and the Indian physique]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Prohibition: India]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Prohibition: Mizoram]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:42, 24 December 2017
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Contents |
[edit] Alcohol and the Indian physique
Drinking good for you? Not if you’re an Indian
Kounteya Sinha
New Delhi: Did you think a peg or two would do wonders for your heart? Unfortunately, not if you’re Indian. The largest-ever study to investigate the link between alcohol consumption and heart disease among Indians has made an interesting revelation — even small amounts of alcohol consumption harms Indians.
The study covering 4,400 drinkers and an almost equal number of non-drinkers in 10 cities by doctors from AIIMS, Centre for Chronic Diseases, Public Health Foundation of India and Madras Diabetes Research Foundation has challenged the much touted cardiac benefits of alcohol and warned of potential harm to Indians due to drinking.
The study categorized drinkers in three brackets —heavy drinkers (who consumed more than 28 grams per day), moderate drinkers (14-28 grams per day) and light drinkers (less than 14 grams a day. While light drinkers had a 40% greater risk of CHD compared to non-drinkers, the chances were as high as 60% among moderate drinkers and nearly 100% in heavy drinkers. One drink was equivalent to 14 grams of alcohol (equivalent to 120 ml of wine, 285 ml of beer and 30 ml of spirits).
Dr Ambuj Roy, assistant professor of cardiology at AIIMS, told TOI, “Benefits of moderate alcohol consumption have been found among southern European populations from the Mediterranean region and Caucasians in Europe and North America. However, in Indians, it clearly causes harm just like in African Americans.”
[edit] No. 1 cause of liver failure
DurgeshNandan Jha, Alcohol now No. 1 cause of liver failure, April 20, 2017: The Times of India
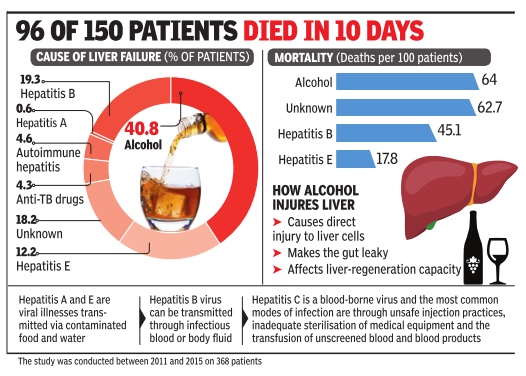
More People Are Dying Of It Than Hepatitis B, Reveals AIIMS Study
There has been a sharp rise in the number of patients visiting AIIMS with alcohol-related liver failure.More alarmingly , the institute says, death rate among these patients is 64% -much higher than mortality from liver failure by hepatitis B virus, a common cause of infection in the organ in the country . AIIMS admitted 150 patients with alcohol-related liver failure from 2011 to 2015. Of this, the study said, 96 died within 10 days despite all possible medical intervention.
Follow-up of the rest of the patients who were discharged when their condition got stable revealed that nearly 20% died within three to four months and another 20% in a year.“Once you have got acute-onchronic liver failure due to alcohol, survival is rare. Transplant, the only life-saving treatment option, is not possible immediately because three months of abstinence from alcohol is required,“ said Dr Shalimar, associate professor of gastroenterology at AIIMS.
He added that medicines can treat liver infection caused by most hepatitis viruses and even autoimmune hepatitis flare-up can be controlled with medicines, but there is no medicine for alcoholism. “ Abstinence is the only way to prevent liver failure and deaths caused by that. The government needs to create awareness to prevent excessive drinking,“ the AIIMS doctor said.
A recent survey published in Global Heart, a repu ted medical journal, showed alcohol use has gone up from 16.1% to 25.6% among urban dwellers in Delhi in the past 20 years. The increase in alcohol use in rural areas in the corresponding period is nearly four times -from 8% to 33.2% -the survey found.
Dr Shalimar, who led a research published in Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology , said not only mortality rate, but also incidence of liver diseases due to alcohol has gone up significantly . “We admitted 427 patients with acute-onchronic liver failure from 2011 to 2015 at the hospital. Of this, a maximum 150 (40.8%) cases were alcohol-related, followed by hepatitis B virus infection (71, 19.3%), hepatitis E (45, 12.2%), autoimmune hepatitis flare-up (17, 4.6%), anti-tuberculosis drugs (16, 4.3%) and hepatitis A (2, 0.5%). In 67 patients (18.2%), the cause of acute liver failure couldn't be ascertained,“ he said.
The AIIMS doctor added alcohol-related liver failure cases have poorer prognosis.“Most of them required ventilator support, their blood was thinner and brain damage was higher too,“ he added. Dr S K Sarin, director of the Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS), said most alcoholics are calorie-deprived. “Most infections cause leaky bowel.But in case of alcoholics, this problem is severe. Due to this, bacteria easily gets into liver from the small intestine, thus aggravating organ failure status,“ he added.
ILBS is experimenting with several therapies, including stool transplant, plasma exchange and liver dialysis, to increase survival rates in alcohol-related liver failure, Dr Sarin said. He, however, stressed on the need to create awareness about harmful effects of binge drinking. Dr Subhash Gupta, liver transplant surgeon at Max Hospital, Saket, said liver failure due to alcoholism “is a totally preventable disaster“.
[edit] Safe drinking limit
[edit] India vis-à-vis other countries
December 23, 2017: The Times of India

From: December 23, 2017: The Times of India
It’s the festive season, the countdown to New Year’s, and celebrations are in order. But while you reach for that bottle of wine you may want to make a note of the prescribed drinking level for the week of partying. Turns out different countries have different levels of safe drinking prescribed by their national health bodies. In India, that’s between five to 10 glasses for women and between 10 to 15 glasses for men per week. Mind, these are just recommended drinking limits; end-of-year parties are something of a time for going over the top, so don’t be surprised if you find you’ve had a drink or two more. In any case, there’s always the New Year to make a resolution that you will drink within limits. Here, a look at drinking-level recommendations of selected countries
[edit] See also
Alcohol and the Indian physique