Civil Aviation, India/ 2: ministry data
All non-ministry data from this page has been shifted to Civil Aviation, India/ 1
This article has been sourced from an authoritative, official readers who wish to update or add further details can do so on a ‘Part II’ of this article. |
The source of this article
INDIA 2012
A REFERENCE ANNUAL
Compiled by
RESEARCH, REFERENCE AND TRAINING DIVISION
PUBLICATIONS DIVISION
MINISTRY OF INFORMATION AND BROADCASTING
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
Civil Aviation:India
The Ministry of Civil Aviation is responsible for the formulation of national policies and programmes for development and regulation of civil aviation and for devising and implementing schemes for orderly growth and expansion of civil air transport. Its functions also extend to overseeing the provision of airport facilities, air traffic services, carriage of passengers and goods by air, safeguarding civil aviation operations, regulation of air transport services, licensing of aerodromes, air carriers, pilots and aircraft maintenance engineers. The Ministry also administratively controls the institution of Commission of Railway Safety, which is responsible for the safety in rail travel and operations in terms of provisions of the Railways Act. India has been a member of the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) and is also on the Council of ICAO since its inception. The civil aviation sector has three main functional divisions--regulatory, infrastructural and operational. The civil aviation sector in India has seen an unprecedented growth in the recent years. As on date, there are a large number of companies providing passenger transport and cargo handling services in the country. The Air Transport Companies are both in the public sector and in the private sector. In the public sector, there is the Air India Limited, and its subsidiaries, viz., Alliance Air, Air India Charters Ltd, (Air India Express) etc.
Apart from Air India and its subsidiaries, there are at present 06 private scheduled operators, viz., Jet Airways (India) Ltd., Jetlite Airlines, Go Airlines (India)
Pvt. Ltd., Kingfisher Airlines, Spicejet Ltd., and Inter Globe Aviation Ltd. (IndiGO) operating on the domestic sector providing a wide choice of flights and connectivity to various parts of India.
Three cargo airlines viz., Blue Aviation Pvt. Ltd., Deccan Cargo and Express Logistics (Pvt.) Ltd. are operating scheduled cargo services in the country. A total number of 298.1 lakh passengers were carried by the domestic scheduled operators between January to June, 2011 as against 253.33 lakhs during he corresponding period of year 2010 thereby registering a growth of +17.7%. In addition to the above mentioned scheduled airlines, there are at present 130 companies (as on 19.05.2011) holding non-scheduled air transport operators permit. Amendments of Air Services Agreements (ASAs) with foreign countries Keeping in view the recent developments in the civil aviation sector, and with a view to modernize and update the existing Air Service Agreements with foreign countries as per the ICAO templates, bilateral air services consultations were held in 2010 with foreign countries, viz., Zimbabwe, Indonesia, Ireland, Brazil, UK and Iran and the respective ASAs have been amended and finalized.
Also, Bilateral Air Sevices Agreements were formally signed with Bhutan, Iceland, Nepal, Bosnia and Herzegovina, South Africa and Iran. Apart from these, new Air Services Agreements have been initialled with Senegal, Barbados and Rwanda.
Technical Co-operation Agreements with Nepal and Afghanistan Technical co-operation agreements were signed by the Director General of Civil Aviation and Airports Authority of India with the Nepalese and Afghan Civil Aviation authorities in order to provide active technical support including training of personnel to these countries by India to promote and develop civil aviation sector. A draft Arrangement between India and Bhutan foro the cooperation on search and rescue services (ASAR) was negotiated and finalized between the AAI and the Bhutanese side.
Indo-US High Technology Co-operation Group (HTCG)
Under the India-US High Technology Co-operation Group, the Civil Aviation subcommittee was set up in March 2010 at Washington. The HTCG will focus on the Airport infrastructure, security, ATC modernization/technological cooperation, environment/promotion of alternative fuels and capacity building. Following up on the recommendations from that meeting, an Airport Infrastructure Working Group has been set up for which the first meeting was held in September, 2010 in New Delhi. In this meeting, The Terms of Reference of the India-US Airport Infrastructure Working Group were adopted.
India-France Civil Aviation Co-operation
Signing of MoUs
Three MoUs were signed on 11th February, 2010 between DGCA of India and BEA of France relating to Aircraft Accident and Incident Investigations, between Airports Authority of India and French Civil Aviation Authority and between DGCA of India and DGAC of France in order to pave the way for India-France civil aviation technical co-operation. The first India-France Steering Committee meeting was held on 28-29 April, 2011 and future course of action in order to initiate further action for India - France civil aviation co-operations under these MoUs have been discussed and agreed.
India-EU Civil Aviation Co-operation Programme
Under the Joint Action Plan, a Civil Aviation Co-operation Project - II has been agreed to. The project called "Institutional Capacity Building in the Civil Aviation sector in India (ICAA)" is under way.
16th World Route Development (RDG) Forum
The 16th World Route Development (RDG) Forum was held on 19-21 September, 2010 in the Vancouver Centre, Vancouver (Canada). 3000 delegates from 130 countries participated in the event including 400 airlines. A prominent delegation from India also participated, which included representative(s) of Ministries of Civil Aviation and Tourism, Airports Authority of India, GMR, GVK, besides representatives from Air India, Kingfisher, Jet Airways, Indigo, etc. An Indian pavilion was set up in the Networking Village, which provided one platform for stakeholders to meet and discuss possible opportunities on Tourism and Aviation sectors in India.
DIRECTORATE GENERAL OF CIVILAVIATION
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is the regulatory body in the field of civil aviation. It is responsible for:- (i) Regulation of air transport services to/from and within India in accordance with the provisions of the Aircraft Rules, 1937; (ii) Licensing of pilots, aircraft maintenance engineers and monitoring of flight crew standards; (iii) Registration of civil aircraft; (iv) Laying down airworthiness requirements for civil aircraft registered in India and grant of certificate of airworthiness to such aircraft; (v) Coordination of the work relating to International Civil Aviation Organization; (vi) Investigation of minor air accidents and incidents and rendering technical assistance to the Courts / Committees of Inquiry appointed by the Government; (vii) Supervision of Training activities of Flying/Gliding Clubs, (viii) Licensing of aerodromes and air carriers; (ix) Safety oversight and surveillance of air carriers and aerodromes; (x) Rendering advice to Government on matters pertaining to air transport including bilateral air services agreements with foreign countries; (xi) Processing amendments to the Aircraft Act, 1934 and the Aircraft Rules 1937, and other Acts relating to aviation, with a view to implementing in India the provisions of the Chicago Convention and annexes thereto and other international conventions relating to aviation; (xii) Type certification of aircraft.
BUREAU OF CIVILAVIATION SECURITY
The Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS) was initially set up as a cell in the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) in January 1978 on the recommendation of the Pandey Committee constituted in the wake of the hijacking of an Indian Airlines flight on 10th September, 1976. The role of the Cell was to coordinate, monitor, inspect and train personnel in Civil Aviation Security matters.
The BCAS was reorganized into an independent department on 1st April, 1987 under the Ministry of Civil Aviation following the Kanishka Tragedy in June 1985. The main responsibility of BCAS is to lay down standards and measures in respect of security of Civil flight at international and domestic airports in India.
INDIRA GANDHI RASHTRIYA URAN AKADEMI
The Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Uran Akademi was set up at Fursatganj, Raebaraeli (Uttar Pradesh) to bring about a quantum improvement in the standards of flying and ground training of Commercial Pilots in the country. The Akademi is equipped with most modern and sophisticated trainer aircraft, up-to-date audio-visual training aids and other facilities for effective ground training. It employs qualified flying and ground instructors, with long experience in the field of aviation and flying training. The aim at IGRUA is not only to train to make a pilot but also to make him an effective systems manager in aeronautics. The flying trainees of the Akademi acquire the standards required for their transit with ease into the cockpits of the airlines.
The Akademi has made remarkable expansion of its existing infrastructure, viz. doubling the capacity of hostel from 72 fully furnished rooms to 144 including a 20 room girls' hostel and renovation of hostel rooms, construction of additional 'C' & 'D' type Residential Quarters, renovation of all the existing residential quarters, institutional block & Engineering office buildings, re-carpeting of roads, installation of Solar Water Heating System in hostels, installation of Air-conditioning plant having capacity of 60 TR X 3, laying of additional bore well to meet the enhanced requirement, new water supply lines, renovations of Sports Complex, Recreation Centre, Mess Kitchen, etc. are the other major infrastructure upgradations carried out in the institutional area. In the airport side, runway re-carpeting, taxitract recarpetting, installation of new runway lights, renovation of two existing old
hangars, expansion of Apron, installation of high mast lighting, etc. were also carried out. The Akademi's infrastructure, such as exclusive Runway & ATC, Night Flying facilities including Nav Aids like Instrument Landing System (ILS) & Precision Approach Path Indicator (PAPI) are the hallmarks of a flying training institution that matches contemporary international standards.
IGRUA is managed by the Global Aviation Giant - CAE, Canada to scale up the standards at par with international standards since 1st March 2008 in pursuance to the management contract between the Ministry of Civil Aviation and CAE, Canada.
The objective of the Akademi is to conduct airline oriented flying training courses to the level of contemporary international standards. The courses offered are:
TRAINING
Commercial Pilot's Licence (CPL) Course: This is the main activity of the Akademi. This course is offered to Ab-initio trainees and pilots holding Private Pilot's Licence. Training for Commercial Pilots Licence with multiengine endorsement and instrument rating is imparted to the trainees along with training on Simulator, as per DGCA norms.
GROUND TRAINING
(a)Basic Training On arrival at the Akademi, the students undergo ground training in basic aviation science subjects and also specific to Zlin, TB-20 aircraft, DA 40, DA42, and King Air Aircrafts. Ground Training in Aviation a subject comprises of 576 hours of class room lectures. It sets a sound foundation for Line oriented Flying Training (LOFT) and prepares the pilot trainees for adaptation of fast developing needs of aviation industry. Flying training commences after about 20-24 weeks.
(b)Audio visual Aids To impart ground training effectively, the Akademi has modern audio-visual aids including a large number of video training films and slides, working and schematic models of various aircraft components and systems, computer Based training (CBT) system and Pilot Aptitude Test trainer (WOMBAT).
(a)Flying Training Flying training is carried out by experienced flying instructors. Group briefing on important exercises is carried out over and above through personal briefing and debriefing prior to and after each flight.
(b)Simulator Training
The Akademi has two single engine TB-20 flight simulators with visual system for initial flying training and instrument rating exercises. The akademi also has King Air C-90A/B-200 full flight simulator with visual system and six axis motion system for giving extensive training to pilots in normal and emergency procedures and for instrument flying exercise. Akademi has touch panel trainers (TPT) for King Air C-90A and Boeing 737 aircrafts.
Akademi has also acquired two single engine Diamond DA-40 flight simulators and one simulator for multiengine Diamond DA42. These are fixed base FNPT (Flight and Navigational Procedure Trainers) with CAE visual system having 180 degree field of view. Akademi will train pilots on these simulators for newly acquired single engine DA40 and multiengine DA 42 Diamonds fleet. Flight training at IGRUA is managed through a web-based training management system called TALON. It is a system which offers unprecedented tools for managing scheduling, curriculum, security, student records, resources, planning tools, flight following/operations and more. (d) AIRCRAFT (i) the Akademi has recently inducted 14 DA 40 aircraft equipped with glass cockpit and two multiengine DA42 aircraft. (ii) In addition, the Akademi has 05 Zlin Z242L aircraft. It is a piston single engine aircraft with fixed undercarriage and is equipped with modern Navigational Aids. The Aircraft is ideal for Line Oriented Flying Training (LOFT) and instrument flying training. (iii) The Akademi also has 05 Trinidad TB-20 Aircraft for intermediate stage of flying training. TB-20 aircraft is a piston single engine aircraft with variable pitch propeller, retractable undercarriage and is equipped with modern Navigational Aids. (iv) The Akademi has two king Air C-90A aircraft. The final stage of training is carried out on this aircraft. This is a twin-engine turbo prop aircraft with pressurized cabin. The aircraft is equipped with modern and sophisticated radio and navigational aids. Particular attention is paid to Line Oriented Flying Training. The students graduate with multi-engine endorsement and instrument rating on their Commercial Pilot Licence. These aircraft are being replaced by multi engine aircraft.
(e) FLYING TRAINING SYLLABI For Ab-initio to CPL trainees Single Engine: 20:00 hrs. training on Cockpit Procedure Trainer 40:00 hrs. flying on Zlin Z242L aircraft 150:00 hrs. flying TB-20 & DA 40 aircraft (or) 190:00 hrs. flying DA 40/TB-20 aircraft Training: The trainees are graduated with CPL, Instrument Rating along Multiengine rating endorsement on King Air C-90A or Diamond DA42 type of aircraft.
MAIN ACHIEVEMENTS
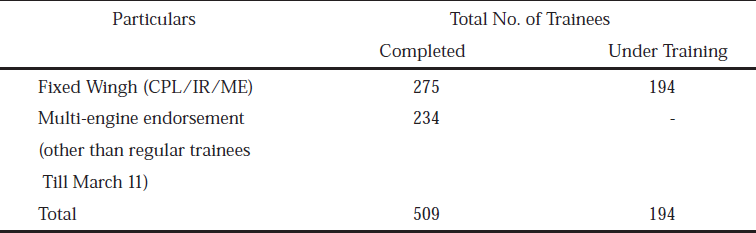
(a) The details of pilots trained and the number of trainees undergoing training at IGRUA are as follows:
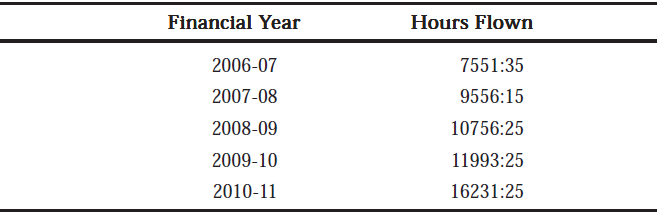
Flying training of -0906, 0909, 0912, 1003, 1006, 1009, 1012 and courses for Afghan trainees are also in progress. (b) Number of Hours flown during last five years: Financial Year Hours Flown
The standard achieved by the students during their training at the Akademi is comparable to international standards. The performance of the graduates of the Akademi, who have joined Air India, Indian Airlines and other private Airlines has been appreciated by their respective employers.
(c) Internet/LAN facility
In order to improve the communication facility as well as to keep updating all aviation related matters which could be a part of training curriculum, IGRUA has provided internet facility in almost all important official location and the facility of training data sharing is also provided through the Local Area Networking (LAN). (d) Web Camera To facilitate better management of the man and machinery by improving the surveillance/safety over the different functional areas in the Akademi,
web cameras are installed at all important locations like Aircraft Tarmac and aircraft maintenance workshop, Class Rooms, Flight Operations, Messing Area, Airport/Institutional exit areas, etc. (e) Pollution Control Maintenance of aircraft and its equipments/spares is being done in the Akademi, which does not involve any production/manufacture. However, the following steps are taken in the Akademi for pollution control: Control of Ambient Air Pollution (i) Vehicle engines are properly maintained within the prescribed limits of emission. (ii) Solid waste is burnt in a manner as to cause minimum fumes. (iii) Forestation is actively pursued to maintain a green environment in the Akademi.
Waste Water Disposal
The Akadimi has proper underground drainage and an efficient sewage plant to ensure that the water sources are not polluted in any manner. Control of pollution from Chemical and other waste The Akademi does not possess such plants/machinery which produce chemical and other waste. Solid-waste-Management through Vermiculture Garbage collection at the Akademi is done door to door with the biodegradable and non-bio-Garbage collection separately from the source itself. The bio-degradable is then converted to high quality manure with vermiculture. This manure is used to green the surroundings.
CNS/ATM Modernization
In addition to the ground based airport infrastructure, AAI has taken many a strides in modernizing its CNS/ATM facilities, wherein, AAI has drawn up the Master Plan for implementation of FANS (Future Air Navigation System). This includes shift from Voice Communication to Digital Data Communication and from Ground Based navigation to Satellite Based Navigation (i.e. GAGAN-Indian SBAS), Modern Radar coverage with ADS-B, Multilateration etc. The implementation of the CNSATM Master Plan will put India amongst the elite group of countries having an efficient ATM System supported by a strong, and robust CNS infrastructure consisting of Digital Data Unit, Integrated ATM automation network, SWIM (System Wide Information Management) Separation Management System, the aim being to provide safe, efficient & cost-effective environment-friendly ATM services, applying Gate to Gate approach and to achieve a "Collaborative and Co-ordinated Global Approach" to ensure harmonization and adoptation of the technological solutions. GAGAN (GPS Aided Geo-Augmented Navigation system) is a satellite based navigation system being developed by AAI & ISRO, to deploy and certify an operational SBAS for the Indian Flight Information Region, with expansion capability to neighbouring FIRs. When commissioned, GAGAN will provide a civil aeronautical navigation signal in consonance with the dictates laid down by ICAO Standards, and Recommended Practices (SARPS) as established by the Global Navigation Satellite System Panel (GNSSP).
GAGAN after its final operational phase completion will be compatible with other SBAS systems such as the Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) of USA, the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) of European Union (EU) and the Multifunctional Satellite Augmentation System (MSAS) of Japan and will provide seamless air navigation service across regional boundaries, thus making India proud, being 4th in the world to have developed such a system.
Rajiv Gandhi National Flying Training Institute, Gondia
AAI in collaboration with CAE, Canada has set up a Joint Venture Company in the name of National Flying Training Institute (NFTI). This Institute is located at Gondia in Maharashtra. AAI holds 49% equity share capital while CAE holds 51% share capital in this Joint Venture Company. The Institute has been aptly named Rajiv Gandhi National Flying Training Institute (RGNFTI) after our Late Prime Minister, Rajiv Gandhi, who himself was an ace pilot of the Indian Aviation fraternity. The Institute became operational in September 2008. The aim of the setting up of this Institute was to train civil pilots, so as to meet the requirements of Indian
Civil Aviation which is in the expansion phase with the induction of new aircraftand new airline operators.
At present, there are eighty nine Flight Cadets (FC) undergoing training at RGNFTI for become commercial pilots. Fifteen FC's have got Commercial Pilot License of which fourteen have been absorbed into various Domestic/International Airlines as pilots. Eight FC's are on the threshold of getting their Commercial Pilot
License from DGCA.
On 13rd February, 2011 RGNFTI has also made a formal announcement for ab initio Helicopter Training. With this, the Institute will soon impart pilot training for rotary wing along with ongoing fixed wing aircraft training. Civil Aviation Sector in India has resumed the path of higher trajectory of growth emerging out of the adverse impact of global financial crisis. India's Air traffic has grown by about 18% per year since 2004. Potential for higher levels of growth in future is also very high. Forecasts by the industry suggest that India would be the fastest growing civil aviation market in the world by 2020 with about 420 million passengers being handled by the Indian Airport system as against 140 million passengers in 2010. Such growth prospects pose a number of challenges on many fronts. Growth has to be inclusive and sustainable. There are issues relating to appropriate models for achieving affordable air connectivity to remote and underserved areas without hurting any section of the stakeholders and within the shortest possible time. In the process of growth, protection of consumer interest is of paramount importance.
Further, liberalization of internationalization of air services is another priority area. At this critical juncture, it has become necessary to broadbase the engagement with stakeholders so that a competitively sustainable industry is developed that supports an inclusive growth process. Keeping in view the pace of developments in this area and to draw upon the expertise available outside the system to address issues that are predominantly economic in content, the Civil Aviation Economic Advisory Council (CAEAC) has been set up under the chairmanship of Secretary, Civil Aviation with experts drawn from different subsegments of the industry and from other related fields.
The CAEAC met once in
December, 2010 and once in January, 2011 and is scheduled to meet periodically at
regular intervals and advise the Ministry in charting out a framework of analysis
for addressing issues facing Civil Aviation sector that are predominantly economic
in content.
Protection of interests of Air Travellers
In order to ensure appropriate protection for the air travelers in the event of flight disruptions involving flight cancellation and delays without due notice to passengers, airlines have been mandated to provide compensation in addition to the refunding of ticket prices for the inconvenience caused. Additionally, if boarding is denied to passengers (who have confirmed bookings) against their will, the airlines have been mandated to compensate such passengers in accordance with the Civil Aviation Requirements dated 6th August, 2010 in addition to refund of air ticket. As a further measure of promoting transparency in the Air transport market, DGCA has issued a Civil Aviation Requirement, Section 3-Air Transport Series 'M' Part III issue I, dated 31st July, 2010 in order to promote fair competition in the airline sector and to ensure that consumers do not receive inaccurate or misleading information on airline services. Tariff Monitoring Unit set up in DGCA continues to
monitor the passenger fares offered by scheduled domestic Airlines to ensure that the competition in the market is fair and transparent.
Outstanding Issues
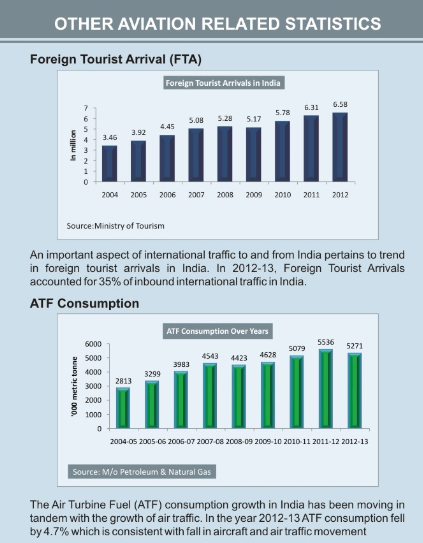
The Indian carriers operate in an exceptionally high cost environment. The single largest element contributing to the airline costs is cost of Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) which accounts for 40% of the operating cost of Indian carriers, as against a figure of only 20% for international carriers. ATF on an average in India is priced almost 60% higher compared to international benchmarks in the region. The future of India's aviation growth is critically linked to the health of the airline industry. India's domestic airlines have fuelled growth and connectivity in the country in a major way.
The highly competitive Indian airline industry has encouraged many
first time fliers and rail travellers to take to the skies-cutting down their travel time
and fuelling access and economic activity. The widening differential in ATF price
charged in India and its huge negative impact on airline balance sheets are eroding
their competitiveness. In the backdrop of the oil-crude prices at higher level, there
is a severe risk of dampening of the passenger market growth by quickly making
air travel out of reach for a significant portion of the market, which was fuelling its
growth.
The losses being registered by some large Indian carriers may result in reduced connectivity thereby affecting the growth in this sector. The moderation of the rate of sales tax imposed on ATF and by bringing it down to the 'declared goods' rate of 4% would help to ensure that our airlines remain viable and functional to achieve the larger and resultant goal of building aviation industry as a key driver of the economy.
Safety violations
By flight crew, 2014-16
The Times of India, Aug 15 2016

Saurabh Sinha
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) has found that safety violations by airline crews are on the rise. In 2015, DGCA took action against 275 crew members, including 204 suspensions for safety violations and for being drunk on duty .
Till August, 2016 has seen about 280 violations, with the regulatory body suspending 150 crew members, mostly pilots.
Maximum safety violations were seen in the general election year of 2014, with the regulator taking as many as 391 (205 suspensions, 71 derostering and 115 warnings) enforcement actions, of which 77 (27 suspensions; 12 de-rostering and 38 warnings) were against the crew of charter plane operators and private planes. The rise in 2014 can be atributed to the DGCA launching a special surveillance during the poll period when small planes are used extensively as charters. Despite a miniscule number of flights operated by charters and private planes in the campaigning period, compared to regular flights, almost 20% of onefifth of violations were by the crew of these flights.
An official of DGCA's flight safety division said, “We are stepping up surveillance. To curb the menace of crew reporting to fly in an inebriated state, we have started asking airlines to file police complaints so the fear of being jailed, apart from the mandatory licence suspension, acts as a deterrent.“
The year 2015 saw 275 en forcement actions against the crew, pilots being the majority among them, with 204 suspensions, 27 de-rostering and 44 warnings. The figures for 2016 showed a sharp rise in July as the regulator had taken 169 enforcement actions till June 30 and the number rose to 280 before mid-August.
However, in 2015 and half of 2016 the share of actions against charters and private planes dropped as these expensive birds take to the skies more frequently in poll period. In 2015 and up to June 30, 2016, airline crews accounted for 24 and 20 of the total 275 and 169 actions taken, respectively.
AIR INDIA LIMITED
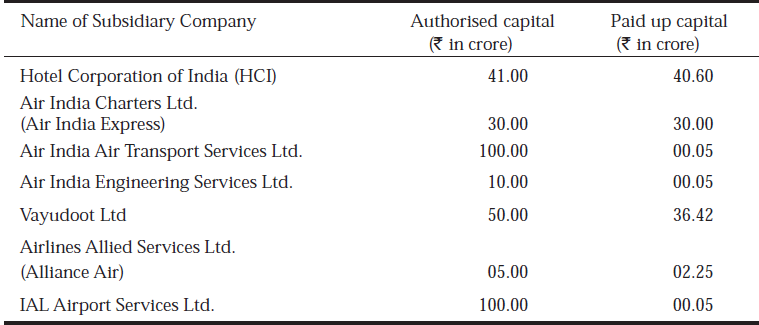
Air India and Indian Airlines merger attained its official status on the formation of National Aviation Company of India Ltd. (Air India) on 27 August 2007. Post merger the new entity is known as Air India while its mascot is retained as 'Maharajah'. The new company has the following subsidiaries under its control:
HCI : The Hotel Corporation of India Limited (HCI) is a Public Limited Company wholly owned by Air India Limited and was incorporated on July 8, 1971 under the Companies Act, 1956 when Air India decided to enter the Hotel Industry in keeping with the then prevalent trend among world airlines. The objective was to offer to the passengers a better product, both at the International Airport and at other places of tourist interest, thereby also increasing tourism to India. However, in 2002-03, three properties of HCI, viz, Indo-Hokke Hotel Limited (Centaur Hotel, Rajgir), Centaur Hotel, Juhu Beach and Centaur Hotel, Mumbai airport were sold off. The remaining units of HCI are Centaur Hotel, Delhi Airport, Centaur Hotel Lakeview, Srinagar and Flight Kitchens at Delhi and Mumbai.
Air India Express
Air India Express has a fleet of four leased and seven owned B737-800 aircrafts. Commencing with 26 Kerala/Gulf flights, Air India Express operations have grown and new routes have been added to the network. Currently, 188 flight are operated per week on different routes. Air India Express currently operates from 12 domestic sectors viz., Kozhikode, Kochi, Thiruvananthapuram, Mangalore, Chennai, Tiruchirapalli, Mumbai, Pune, Jaipur, Lucknow, Amritsar and Kolkata to 13 destinations across Gulf and South East Asia.
Alliance Air
Historically Alliance Air was set up on 15.04.1996 as a separate company envisioned to function as profit centre of erstwhile Indian Airlines Limited to effectively utilize the Boeing 737 aircraft fleet and to improve productivity and profitability of Indian Airlines Ltd. At present, Alliance Air has taken a lease on 4 ATR-42 aircraft and commenced scheduled operations in the North-East Region with effect from 2.01.2003. These aircraft have been deployed exclusively in the 1110 India 2012 North-East region in terms of MOU with the North-Eastern Council. In return, a budgetary support of Rs.175 crore is being provided over a period of five years (annual budget of r.35 crores) by the NEC during the 10th Five Year Plan. Throughout the period of the MOU, North-Eastern Council is required to facilitate Alliance Air in obtaining concessions on ATF, Landing RNFC rates, etc. whenever available. The MOU was effective from the financial year 2002-03 for a period of five years, which has been extended for another one year, i.e., December 2008 and has now been extended upto the year 2010 and 2011. As on 1st July 2011, the operational fleet strength of Air India (Including Air India Express and Alliance Air) are 162. As a part of fleet augmention, an order for the purchase of 111 new aircraft (50 for erstwhile Air India, 18 for Air India Express and 43 for erstwhile Indian Airlines) has been placed by Air India. Development of Facilities l CFM56 engine shop and Test Cell set up at JEOC, Delhi.
l Universal Hydraulic Test Rig at Mumbai.
l Fuel and Oil components servicing facility at Kolkata.
l Pneumatic Components servicing facility at Kolkata.
l ATEC (Automatic Test Equipment Complex) series 6, Commissioned at Delhi is being used in testing of all A320 family aircraft computers along with ATEC series 5.
l Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) of New A 320 family & B737-800 aircraft to be developed at Kolkata.
IT initiatives
Air India has embarked on several IT initiatives during the year which have either been implemented or are in the process of being implemented. Some of the major projects currently undertaken are:- l ERP: SAP ERP is being implemented across Air India and its subsidiaries to bring about operational efficiencies and cost reduction. M/s IBM are implementing this program. It is likely to be rolled out by end of 2012. l Passenger Services System (PSS):- During the year, a PSS which comprises of Reservations, Departure Control System, Internet Booking Engine and Baggage Reconciliation System was cutover in February, 2011. This is the first step towards integration of the two erstwhile entities - Air India and Indian Airlines.
This provides seamless booking of passengers on its network. The state-of-the art Internet Booking Engine has brought in a quantum jump in the bookings made by the prospective passengers directly using this portal. It is expected that by end of 2012, 20% of the total bookings made will be through the Internet Booking Engine, which will save the GDS cost of Air India. l MRO IT - This solution is expected to be cutover towards end of 2012. The contract has been awarded to M/s Ramco. The system will improve the aircraft availability through proper maintenance schedule besides bringing in savings in terms of material, planning procurement and storage. l IOCC - This system has been introduced to avoid inconvenience to passengers in case of distruptions. Corrective action can be initiated in case any disruption
is visualized. The Crew Management System, which is a part of this system is expected to be cutover in March, 2012 and will ensure optimum utilization of the crew-both cockpit and cabin. M/s Sabre are implementing this solution. l New Hanger at Hyderabad Airport-5 acres of land has been taken on lease for the construction of new Hanger and other Engineering facilities at New Greenfield airport at Shamshabad, Hyderabad. Lease rental is j 7 lakh per month. Project is nearing completion.
Besides the above, there are several other initiatives on Flight Planning, Document Management System, Improving fuel efficiency, Cargo automation which are at various stages of implementation. All these are expected to bring in increased transparency and cost reduction.
With the growing increase in the usage of the web, Air India officers its passengers the facility of making bookings and purchasing the tickets through the internet. Currently, around 90% of the domestic tickets issued are e-tickets. For round the clock access to NACIL reservations, a toll free number has been arranged to enable passengers to get the services of booking of seats / obtaining information regarding flight arrivals / departures etc. from NACIL. NACIL Call Centres have been established at Belapur in Mumbai, and Gurgoan in New Delhi to cater to the needs of the passengers.
Appreciation of the Services of Air India Limited
In appreciation of the services of Air India Limited, the following awards have been received by Air India in the recent years:
l Adjudged as the Best Airlines MRO in India during expo MRO 2011 organized jointly by India Aviation and State Trade Times for having ensured maximum availability of airworthy aircraft without compromising on safety.
l Air India has been ranked as number 3 in the awareness and perception index amongst 25 top Indian companies in the latest Penn Schoen Berland (PSB) survey published recently.
l Voted the most trusted brand in the country's aviation sector in the Economic Times Brand Equity Survey 2010. l Won the Reader's Digest Trusted Brand Gold Award 2010 for the fifth consecutive year.
l Air India also achieved a milestone when it became the first airline, providing ground services in India, to earn the IATA Safety Audit for Ground Operations (ISAGO) recognition. ISAGO recognition reiterates the airline's commitment to achieve excellence in safety and quality standards in all spheres of aviation.
l All nine Air Indians were amongst the Medal Winners in the recent Commonwealth Games held in Delhi. Five Air Indians were in the Indian Hockey team that played the finals.
l Four Air Indians - Capt. Mahender Singh Dhoni, Suresh Raina, Harbhajan Singh and Yuvraj Singh were members of the Indian Cricket Team which won the World Cup 2011.
l Voted Best Airlines - Central and South Asia/India by readers of Global Traveler magazine - a prestigious US business travel publication.
l Award in recognition of Air India's role in promotion of domestic tourism by the Association of Domestic Tour Operators of India.
Air India was invited to join Star Alliance
Air India was invited to join Star
Alliance in 2007 (the global leading airline network, with 27 member airlines and maximum market share (25.8%). Star Alliance members operate 21,200 daily flights to more than 1,172 airports in 181 countries with a fleet of 4,022 aircraft). Being a Star Alliance member will enable Air India frequent flyer cooperation with other members (reciprocal earn, burn, upgrade etc.), get global publicity with the Star brand, offer harmonized product with other Star carriers and offer exclusive benefits (lounge access, connection centres, one stop booking of multi-carrier ininerary etc.). Membership of Star Alliance will enhance Air India's image and also traffic feed and revenues.
HAJ
For Haj 2010, it was decided to go for a competitive bidding process through sealed tender inviting qualified Air Operators to fly between India and Saudi Arabia as per bilateral agreements.
During the year 2010, a total 878 Haj Charters flights were operated by Saudi Arabian Airlines, NAS Air and AI-Wafeer carrying approx. 1,26,018 pilgrims.
PAWAN HANS HELICOPTERS LIMITED
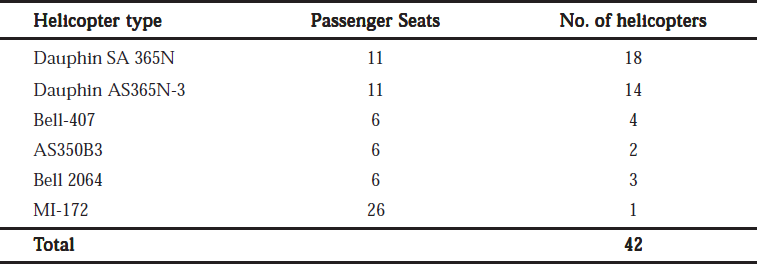
Pawan Hans Helicopters Limited (PHHL) was incorporated in October, 1985 (under the name of Helicopter Corporation of India Limited) as a Government company under the Companies Act, 1956 with the primary objective of providing helicopter support services to the oil sector in offshore exploration, operate in hilly and inaccessible areas and make available charter flights for promotion of trave and tourism. The Registered Office of the Company is located at Safdarjung Airport, New Delhi, Corporate Office at Nodia and its Regional Offices are at Mumbai and New Delhi. The Company's authorized capital has been increased from r 120 crores to r 250 crores on 3.12.2010. The paid up share capital of the Company is now r 245.616 crores comprising of j 125, 266 crores in the name of President of India and r120.35 crores in the name of ONGC Ltd. ONGC has converted loan amounting to r 95.85 crores into equity and equity shares allotted on 14.2.2011. Government has conferred the status of "Mini Ratna-I" for PHHL on 11th April 2011. Fleet Profile PHHL has emerged as one of Asia's largest helicopter operators having a wellbalanced own operational fleet of 42 helicopters. The Company's operational fleet profile is as follows:-
Operational Milestones
l Pawan Hans has transited from its Quality Management Systems under ISO 9001-2008 standards to ISO 14001 and 18001 certification which is known as Integrated Management System covering Environment and Safety aspects. The Company achieved flying of more than 5.13 lakh hours and 19 lakhs landings on its fleet since its formation. l Operations for ONGC Since October, 1986, Pawan Hans has been providing helicopter support for offshore operations of ONGC for carrying its men and vital supplies round the clock to drilling rigs situated in Bombay Off-shore platforms. PHHL operates at ONGC's Rigs (mother platforms and drilling rigs) and production platforms (wells) within a radius of 130 nm. from the main land at Mumbai. At present, 15 Dauphin N and N3 helicopters are on contract with ONGC out of which 2 Dauphins are stationed overnight at the main platforms in addition to a dedicated Night Ambulance to meet any emergency evacuation.
l Other Customers
PHHL provides helicopter support services to several State Governments, namely, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Tripura and Sikkim. The Company is also providing three Dauphin helicopters to the Administration of Andaman & Nicobar Islands and two Dauphin helicopters to Lakshadweep. It is also providing helicopter services to Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) at Guwahati, Oil India Limited and GAIL. PHHL runs the helicopter services from Phata to the Holy Shrine of Kedarnath during the May-June and September-October seasons every years.
The Company was able to achieve record revenue from operations at Phata during two seasons, namely May-June 2010 and September-October, 2010 by carrying 19182 passengers. PHHL has also been awarded contract by Shri Amarnath Shrine Board for operating "Helicopter services for the Shri Amarnathji Yatra 2010 and 2011" on Baltala- Panjtarni-Baltala sector. Pawan Hans started helicopter passenger services at Baltala- Panjtarni sector w.e.f. 1 July 2010 with 2 Bell 407 helicopter. The Company has been successfully operating helicopter services at Mata Vaishno Deviji from Katra to Sanjhichat under competitive conditions and has carried 1.90 lakhs passengers in 2010-11, 2.05 lakhs passengers during financial year 2009-10 as and 1.24 lakhs passengers in the financial year 2008-09. The Company has been awarded contract for next 3 years by the Shrine Board of Mata Vaishnodeviji w.e.f. 1st April 2011 under significant competitive environment after being declared the lowest bidder. l The Company had undertaken a project for M/s. Power Grid Corporation of India Ltd. for Hotline Washing of insulators of the power transmission lines for 5 months in 2008 and for 3 months in 2009.
l The Company has been awarded contract by M/s Gujarat State Petroleum Corpn. Ltd. for charter hire of one Dauphin N3 helicopter for 3 years w.e.f. 26 Nov. 2010.
l The Company has carried out operations for Border Road Organization at Arunachal Pradesh w.e.f. 18 Nov 2010 for 8 months with one Mi-172 helicopter taken on lease.
l First time in India, the Company had provided 4 nos. helicopters (Dauphin and AS 350 B3 helicopters) for live coverage of CWG 2010 events for Doordarshan.
Operations & Maintenance Contracts
The Company has got Operation & Maintenance Contract of 01 Dauphin N3 helicopter of Government of Gujarat, 2 Dhruv helicopters owned by ONGC and 4 Dhruv helicopters owned by BSF (MHA) in 2009 with M/s HAL. Further, the Company has signed in December 2010 another contract with Hal for operation & maintenance of 4 more Dhruv helicopters of BSF and 2 nos. Cheetah and Chetaks of BSF.
Heliport/Helipad in Delhi
DDA on 1st June, 2009 has allotted 25 acres land near Rohini in the name of Ministry of Civil Aviation for construction of first integrated Heliport in the country. Further, DDA has earmarked one hectare land for construction of helipad at Commonwealth Games Village site and PHHL completed the Helipad in October, 2010. PHHL has also created basic infrastructure facilities/Parking and Helipad at Rohini. Environmental Impact Assessment Study Report for Rohini Heliport has been completed by M/S RITES and Final report submitted onward to DPCC and other local authorities. Public Hearing was carried out on 19 Feb 2011 at 11.00 AM.
Further,
Expression of Interest (EOI) for selection of consultant for Heliport designing,
planning & operations was floated and under technical evaluation.
l PHHL is planning to develop a Helicopter Training Academy cum Heliport at
the existing Gliding Centre at Hadapsar, Pune which is owned by DGCA.
Project has been approved by Ministry of Civil Aviation and the DGCA has released an amount of j 10 crores as GBS for the purpose. PHHL signed MOU with DGCA on 17th May, 2010 and DGCA has authorized it to use land and other infrastructural facilities for this purpose at the Gliding Centre, Pune on behelf of Government of India comprising of 30 acres of open area adjacent to the existing hangars/building, two hangars for initial operation, 3 staff quarters and 3 rooms in the existing office building for housing, classes and instructors. l PHHL has signed MOU on 23.7.2010 with HAL for setting up a joint venture for operation & maintenance of ALH Dhruv and Chetak 7 Cheetah helicopters of Defence Forces. The Boards of HAL and PHHL have given in-principle approval for setting up of the said JV of 50:50 and further discussions are in progress.
Funding for Acquisition of Dauphin Fleet
The Company has signed agreement with ONGC on 13.08.2010 for term loan upto r 275 crores, being 80% of the estimated cost for purchase of 07 new Dauphin N3 helicopters at the rate of interest based on SBI base rate plus 150 basis points. The loan is repayable in 60 monthly installments from the date of drawal of loan for each helicopter. Further, the Company has also signed MOU with NTPC for long term lease of a new Dauphin N3 helicopter for 10 years. Till the delivery of new Dauphin N3, one Dauphin N helicopter has been provided to NTPC on wet lease basis.
Mid-Life upgrade programme of Dauphin Fleet
With a view to meet the requirements of DGCA and ONGC contract for Aviation Standard-4 (AS-4) compliant helicopters, Retrofit programme for the Dauphin fleet is being undertaken in a phased manner. This retrofit programme has been undertaken for better safety and improved serviceability of Dauphin fleet in view
of on-time monitoring of all dynamic components and engines by the technical personnel of the Company. Presently, 18 nos. AS-4 compliant Dauphin helicopters after upgrade programme are available. The Company has a team of dedicated, highly motivated and skilled manpower comprising of pilots, engineers, executives, technicians and support staff. The total staff strength of regular and contractual employees was 989 as on 31st March, 2011.
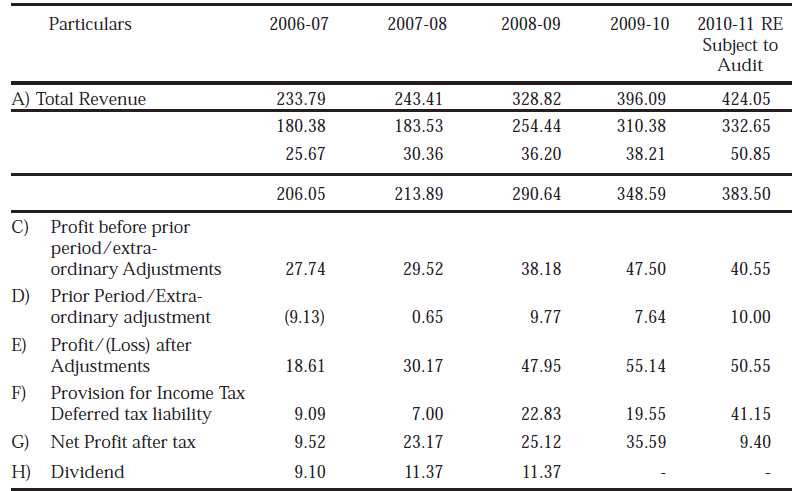
Since the financial year 1991-92, Pawan Hans has been continuously making profit. The financial performance during the period from 2006-07 to 2009-10 is as under:- (r in crores) Particulars 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 RE Subject to Audit
PHHL prides itself on being an extremely self-contained organization; with workshops covering different requirements (instruments, electrical, safety equipment, synthetic panel, component repair shop, spectrometric Oil Analysis Procedure Lab and radio including Full Test Data Checks) are available on site at Mumbai. All periodic inspections as well as overhaul is carried out in-house. The operating and maintenance standards of Pawan Hans are one of the highest in the world. All aircrew must pass proficiency tests every six months.
Maintenance
crew undergo regular refresher courses. Meticulous maintenance checks on helicopters are carried out and extensive workshops with in-house facilities provide the back up. Maintenance capability has been upgraded to carry out major 'G' inspections (Airframe overhaul) totally in-house without any foreign assistance. PHHL has laid a strong foundation in terms of trained manpower and excellent safety standards. The Company looks forward to a bright future.
Statistics, year-wise
Civil Aviation Statistics 2012- 2013
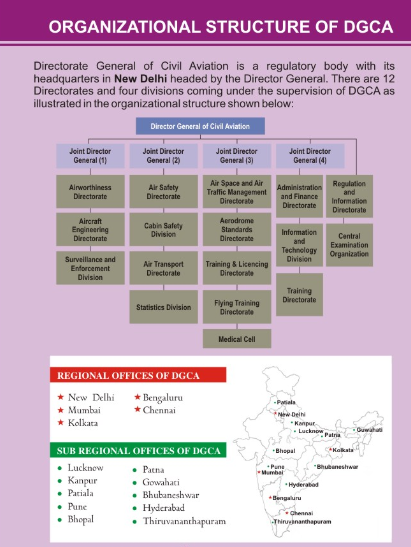
Organizational Structure of Dgca
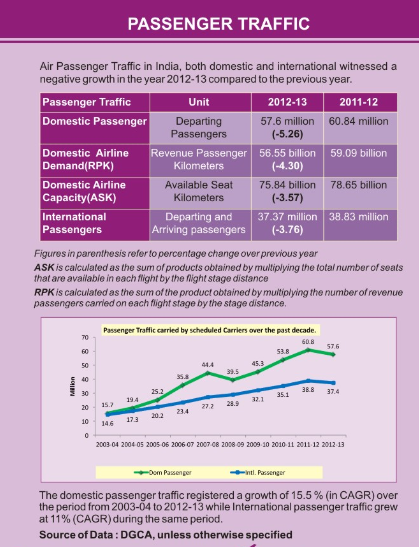
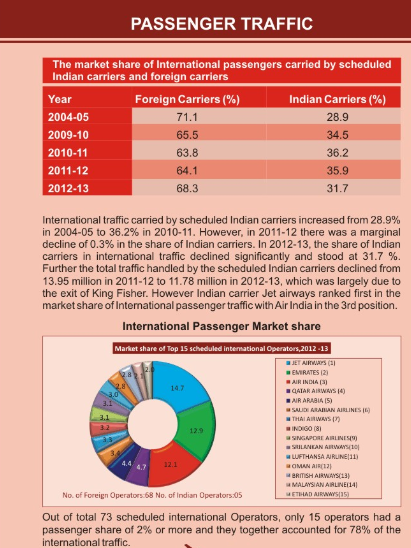
Passenger Traffic
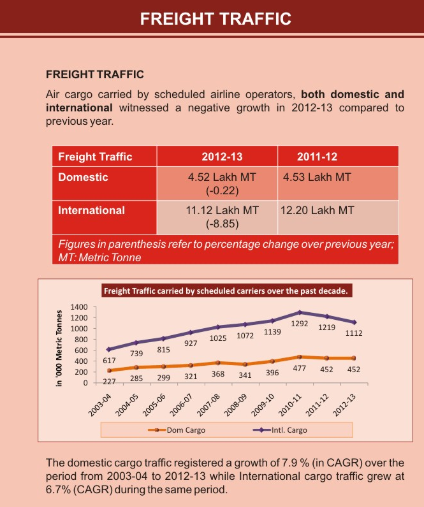
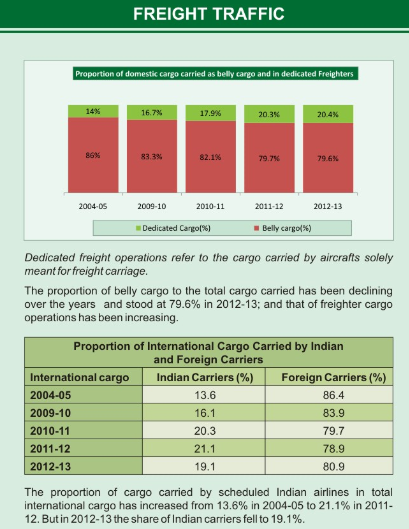
Freight Traffic
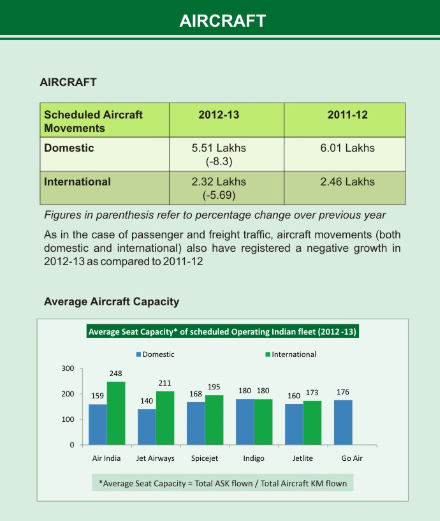
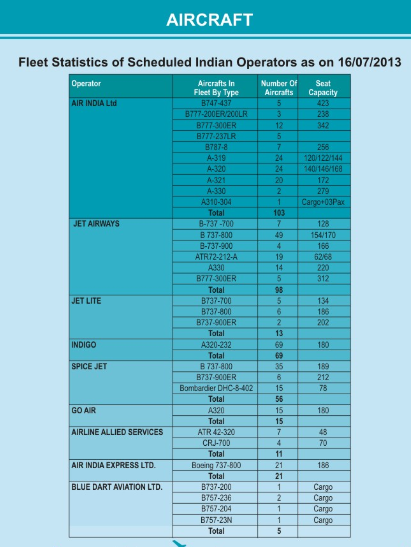
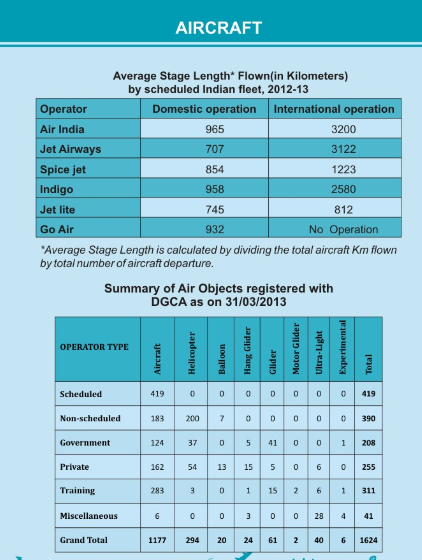
Aircraft
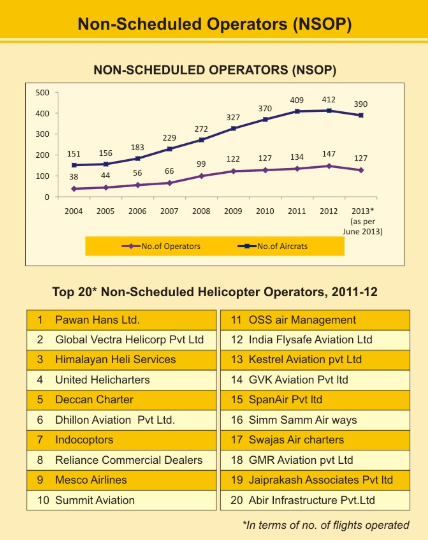
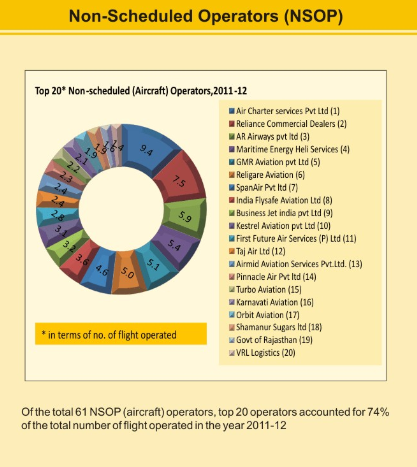
Non-Scheduled Operators (NSOP)
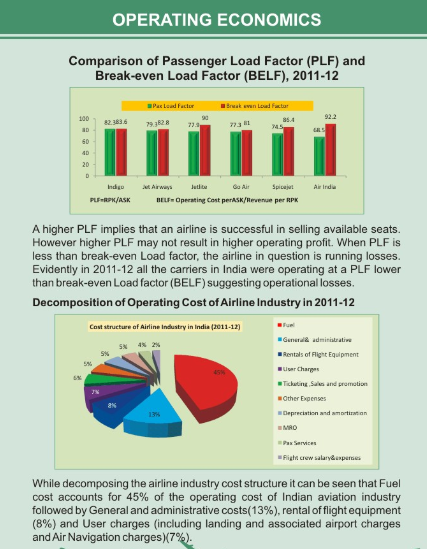
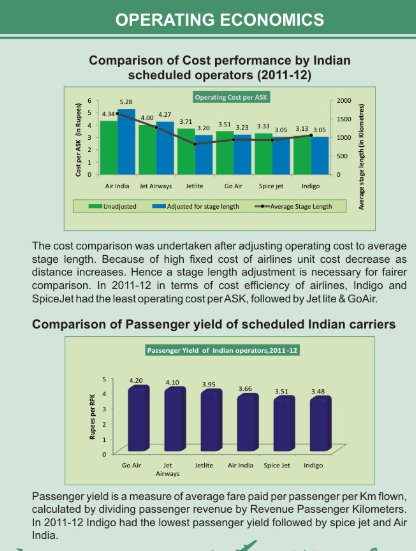
Operating Economics
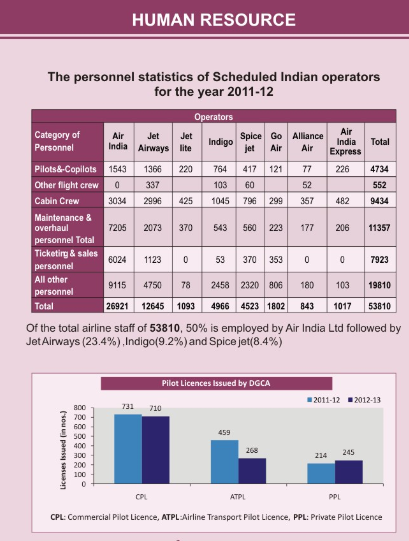
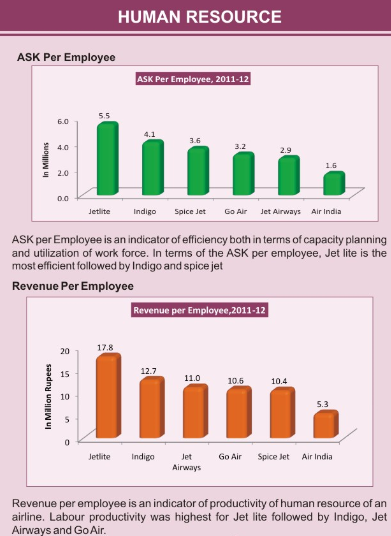
Human Resource
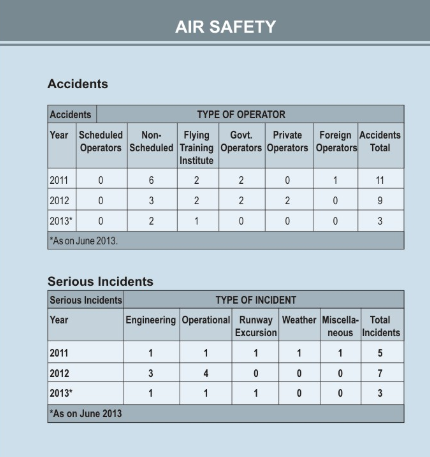
Air Safety
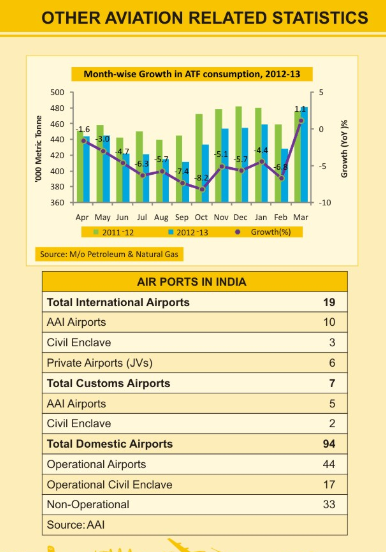
Other Aviation Related Statistics
Civil Aviation, statistics: 2016-17
Passenger traffic
See graphic
International and domestic passenger traffic in India, Jan-Sept 2016

See also
Civil Aviation, India/ 2: ministry data