Delhi: Crime
m (Pdewan moved page Crime in Delhi to Delhi: Crime without leaving a redirect) |
|||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
In a programme conducted by the Delhi police earlier this year, the principal judge JJB-II, Suchi Laler, had even asked the counsellors to find out the reason behind children resorting to crime and had called for educating the parents too. | In a programme conducted by the Delhi police earlier this year, the principal judge JJB-II, Suchi Laler, had even asked the counsellors to find out the reason behind children resorting to crime and had called for educating the parents too. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Crime in Delhi: 2014= | ||
| + | [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com//Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Roads-safer-10yr-low-in-accidents-03012015004008 ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jan 03 2015 | ||
| + | [[File: crime in delhi 2007 14.jpg|Crime in Delhi: 2007- 14|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | [[File: disciplinary and departmental action and seizure of arms some facts.jpg|Disciplinary and departmental actions and seizure of arms: some facts|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''' Roads are safer: 10year low in accidents ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Somreet Bhattacharya | ||
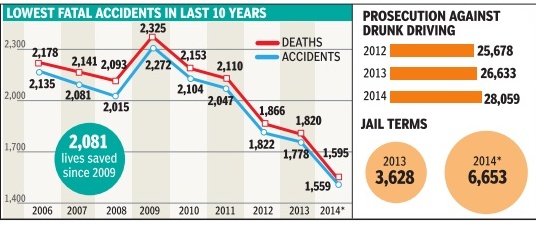
| + | Despite an increase in the number of vehicles, 2014 witnessed the lowest number of accidents in the past 10 years. In all, 1,595 deaths were reported in 1,559 accidents. During the previous year, 1,820 people had died in 1,778 accidents. | ||
| + | The police have attributed the decrease to steps like installing speedchecking equipment and conducting intensive drives against drunken driving and speeding which cause the maximum number of accidents in the city .Delhi Police commissioner B S Bassi blamed multimodal traffic, rapid unplanned commercialization along roads and an indifferent attitude towards road safety for the high rate of accidents. A special initiative was taken to identify high-speed corridors where traffic violations are rampant leading to deaths. The traffic police also formed a committee to analyse the cause, time and nature of every road accident that had taken place in 2014 and took corrective measures. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Out of the 7 lakh prosecutions by the traffic police last year, 1,23,676 vehicles were prosecuted for speeding as against 29,045 in 2013. The cops also introduced 11 high-speed interceptors that were deployed in areas where drivers tend to speed. A fleet of 50 highway patrol vehicles was deployed on the national highways passing through the city . | ||
| + | |||
| + | The traffic police cracked down on heavy vehicles plying without a rear under-run protection device, a bar that prevents smaller vehicles from slipping under the bigger one during a crash. This prevents fatalities and is a mandatory feature. Till mid-December, 21,514 heavy vehicles had been prosecuted. Delhi Police might also push for taking stricter action against heavy vehicle owners failing to comply with the prescribed standards. They booked 1,90,000 heavy vehicles for dangerous driving and impounded 1049 of them for failing to observe traffic norms. The cops also prosecuted 6653 drunk drivers this year which is nearly 50% more than 2013. Out of these, 17 were given a jail term ranging between one and three days, 21 four and five days, seven six and nine days and six for 10 days. The cops also counselled 38,224 traffic rule violators after challaning them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Drives were conducted against e-rickshaws which had been banned from plying in the city and 7038 were imponded. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Measures were also taken to increase traffic police presence past midnight resulting in a decrease in fatalities. The duty hours of the personnel were extended to 4am to carry out special drives and night checking. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The traffic cops issued all challans through the e-challan system which allows them to maintain a database of traffic violators. Repeat offenders were targeted and 707 licences cancelled for drunk driving. Action was taken on the basis of complaints found on the traffic police facebook page. | ||
Revision as of 10:33, 31 January 2015
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
2013
Juveniles, cyber crooks keep police on toes
Raj Shekhar & Somreet Bhattacharya New Delhi:
TNN
The Times of India Jul 02 2014
More Minors Involved In Rapes; Most Offenders Fall Under 16-18 Age Group
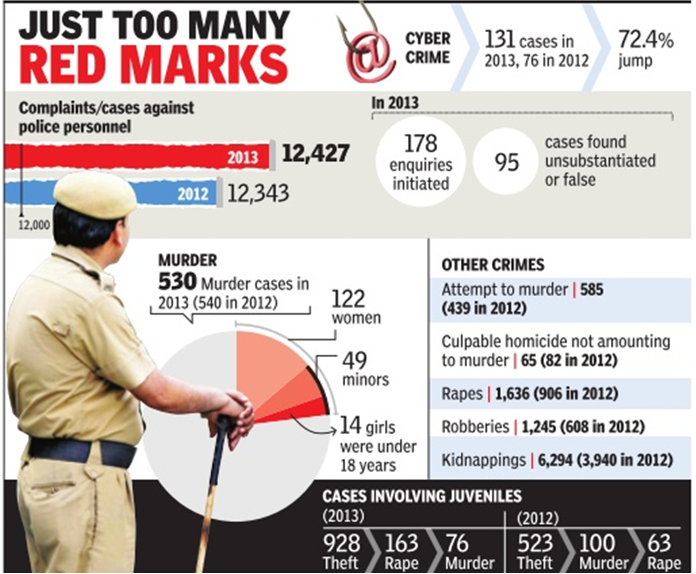
Cases involving juvenile offenders have increased by 28%--2,140 minors were tracked down in 1,590 criminal cases registered in 2013. In 2012, the figure was 1,541 against 523 cases.
In 2013, most juveniles were charged with theft as has been the trend. Unlike 2012, they were found to be involved in more rape cases than murders.
Of the 2,140 juveniles apprehended, 2,087 were found to be involved in cognizable offences; 697 were sent to home after admonition and advice, while 301 were released on probation. As many as 692 juveniles were sent to special homes, 17 faced fines and 149 were acquitted; 267 cases are pending.
Among those apprehended, 821 had dropped out of school at the higher secondary level; 599 were primary school dropouts, and 421 were illiterate.
As many as 1,774 were found to be also living with their parents, while 69 were homeless; 849 children were found to have a family income below Rs 25,000 a year, while 714 belonged to the in come group of Rs 25,001-Rs 50,000.
In 2013, juveniles were involved in 928 cases of theft, burglary or snatching, followed by 163 cases of rape and 76 murder cases.
In 2012, the figure was 1,144, of which 523 were involved in theft, followed by100 cases of murder and 63 of rape.
The NCRB statistics reinforce the need to bring down the juvenile age limit to 16, which Delhi Police has been demanding since the Nirbhaya case.
Out of 2,087 apprehended juveniles, 1,148 were in the age-group of 16-18. In 2012, this figure was 860. Nationally, 66.8% of the juveniles are in this age group.
Among the apprehended juveniles, 875 were boys between 12 and 16; the figure was 617 for 2012. The cops apprehended 23 girls of different ages for various crimes. In 2013 and 2012, juveniles were found to be involved in rapes, gruesome murders of elderly people and robberies.
Around a dozen escapes from correctional homes were reported in the last two years.
Delhi Police has requested juvenile justice boards and child welfare committees to put in place stronger rehabilitation programmes at correctional homes so that minors can be weaned away from criminal activities.
Senior police officers made this request to Child Welfare Committee officials during a sensitization programme.
In a programme conducted by the Delhi police earlier this year, the principal judge JJB-II, Suchi Laler, had even asked the counsellors to find out the reason behind children resorting to crime and had called for educating the parents too.
Crime in Delhi: 2014
Jan 03 2015
Roads are safer: 10year low in accidents
Somreet Bhattacharya Despite an increase in the number of vehicles, 2014 witnessed the lowest number of accidents in the past 10 years. In all, 1,595 deaths were reported in 1,559 accidents. During the previous year, 1,820 people had died in 1,778 accidents. The police have attributed the decrease to steps like installing speedchecking equipment and conducting intensive drives against drunken driving and speeding which cause the maximum number of accidents in the city .Delhi Police commissioner B S Bassi blamed multimodal traffic, rapid unplanned commercialization along roads and an indifferent attitude towards road safety for the high rate of accidents. A special initiative was taken to identify high-speed corridors where traffic violations are rampant leading to deaths. The traffic police also formed a committee to analyse the cause, time and nature of every road accident that had taken place in 2014 and took corrective measures.
Out of the 7 lakh prosecutions by the traffic police last year, 1,23,676 vehicles were prosecuted for speeding as against 29,045 in 2013. The cops also introduced 11 high-speed interceptors that were deployed in areas where drivers tend to speed. A fleet of 50 highway patrol vehicles was deployed on the national highways passing through the city .
The traffic police cracked down on heavy vehicles plying without a rear under-run protection device, a bar that prevents smaller vehicles from slipping under the bigger one during a crash. This prevents fatalities and is a mandatory feature. Till mid-December, 21,514 heavy vehicles had been prosecuted. Delhi Police might also push for taking stricter action against heavy vehicle owners failing to comply with the prescribed standards. They booked 1,90,000 heavy vehicles for dangerous driving and impounded 1049 of them for failing to observe traffic norms. The cops also prosecuted 6653 drunk drivers this year which is nearly 50% more than 2013. Out of these, 17 were given a jail term ranging between one and three days, 21 four and five days, seven six and nine days and six for 10 days. The cops also counselled 38,224 traffic rule violators after challaning them.
Drives were conducted against e-rickshaws which had been banned from plying in the city and 7038 were imponded.
Measures were also taken to increase traffic police presence past midnight resulting in a decrease in fatalities. The duty hours of the personnel were extended to 4am to carry out special drives and night checking.
The traffic cops issued all challans through the e-challan system which allows them to maintain a database of traffic violators. Repeat offenders were targeted and 707 licences cancelled for drunk driving. Action was taken on the basis of complaints found on the traffic police facebook page.