Deputy Chief Ministers: India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
History
As in 2018

From: December 20, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Deputy Chief Ministers in Indian states, As in 2018
The legal position of Deputy PM/ CM
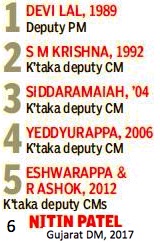
From: Dhananjay Mahapatra, Dy CM: Not in Constitution, yet a post with a long history, December 27, 2017: The Times of India
Nitin Patel’s oath as Gujarat deputy chief minister, a post not mentioned in the Constitution, has revived the old controversy whether the oath was constitutionally valid and whether the post gave him part responsibility as CM.
The controversy arose in 1989 when Devi Lal took oath as deputy PM in the V P Singh government, audaciously altering the oath for Cabinet minister being administered by then President R Venkataraman.
A book ‘Commissions and Omissions of Indian Presidents’ quoted Venkataraman: “I asked my secretary to convey to V P Singh that Devi Lal could be sworn in as a minister and designated later as deputy PM. But before anything could be finalised, the swearing-in ceremony commenced and V P Singh was sworn in as PM. Then Devi Lal was presented and when I administered oath as ‘mantri’, he insisted on reading it as ‘upa pradhan mantri’. I corrected him saying ‘mantri’ again but the second time too he read it as ‘upa pradhan mantri’. It was fully displayed in the live telecast of the proceedings. I did not want to create an ugly scene and therefore allowed Devi Lal to proceed as he wished.”
Though Devi Lal made it appear as if he took oath as deputy PM, the post was held earlier by Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, Morarji Desai, Choudhary Charan Singh and Jagjivan Ram without taking oath as such. In 1989, Devi Lal’s oath was challenged in the Supreme Court by one K M Sharma alleging that the Haryana leader had not taken oath as prescribed in the Third Schedule of the Constitution.
Then attorney general Soli J Sorabjee told the SC that since the PM was also a member of the council of ministers, he took the same oath as the other ministers, the only difference being the word PM in place of minister. He said, “Describing Devi Lal as deputy PM is descriptive only and for all purposes, he is a minister and there is no constitutional sanction for a deputy PM.”
The SC on January 9, 1990, accepted the argument and said since the AG had termed Devi Lal to be just a minister though he was described as deputy PM, “the post did not confer on him (Devi Lal) any powers of the PM”. So, even though Nitin Patel took oath as deputy CM, he will function only as a minister.
The trend of creating the post of ‘deputy’ CM caught the political imagination after Devi Lal’s act and Karnataka took the lead. In 1992, the state had a deputy CM in S M Krishna (Congress). In 1994, it was J H Patel (Janata Dal). In 2004, a coalition under N Dharam Singh took the reins and Siddaramaiah was appointed deputy CM. In the succeeding coalition led by H D Kumaraswamy, B S Yeddyurappa was deputy CM. In 2012, two deputy CMs — K S Eshwarappa and R Ashok — took oath. Deputy CMs came to be a feature in most states thereafter.