Income Tax India: Expert advice
(Created page with "{| class="wikitable" |- |colspan="0"|<div style="font-size:100%"> This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content.<br/>You can help by converting...") |
(→Choosing an e-filing portal) |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
==Choosing an e-filing portal== | ==Choosing an e-filing portal== | ||
| − | + | Charges should not be the only reason for choosing a portal. Here are some other factors that you should consider. | |
===Is it comprehensive? === | ===Is it comprehensive? === | ||
The more details sought, the better it is. If the return uses only Form 16, you might lose out on deductions you were eligible for, but didn’t claim. | The more details sought, the better it is. If the return uses only Form 16, you might lose out on deductions you were eligible for, but didn’t claim. | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
Does the portal help even after the uploading? Some alert you if you forget the ITR V. Others send it to the CPC in Bangalore on your behalf. | Does the portal help even after the uploading? Some alert you if you forget the ITR V. Others send it to the CPC in Bangalore on your behalf. | ||
===Privacy policy === | ===Privacy policy === | ||
| − | The data in your tax return form is priceless for financial services companies. If it goes out, you will be inundated with calls and spam mail. | + | The data in your tax return form is priceless for financial services companies. If it goes out, you will be inundated with calls and spam mail. |
=Five tax filing mistakes= | =Five tax filing mistakes= | ||
Revision as of 12:46, 19 July 2013
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Contents |
Filing tax returns
New rules of filing tax returns (2013)
The tax authorities have introduced several new guidelines for filing returns this year. Find out how these changes are likely to impact you
The Times of India 2013/07/15
First they made it compulsory for businesses to e-file their tax returns. Then they made it mandatory for taxpayers with incomes of over 10 lakh to take the online route. This year, the income tax authorities have cast a wider net and made e-filing compulsory if your taxable income is above 5 lakh a year.
The lowered threshold represents one of the key changes in the tax filing rules this year. Some of these are mere tweaks, such as mentioning your bank’s IFSC number, instead of the MICR code, in the return. However, some of these variations are tectonic, such as the mandatory e-filing for incomes above 5 lakh a year. In the following pages, ET Wealth explains the new rules and how they will affect the way you file your tax return this year.
E-filing tax returns
E-filing of tax returns has grown tenfold since its introduction in 2006. Less than 8% of the 3.37 crore taxpayers efiled their returns in 2007-8. Last year, 45% of the 5 crore taxpayers took the online route. That’s a big jump and the figure is expected to go up significantly this year.
The change has spawned a massive opportunity for tax e-filing portals. These websites charge individual taxpayers between 200 and 4,000 for uploading their tax returns. You can also do it for free on the official website of the Income Tax Department. However, private tax filing portals hand-hold the taxpayer through the process. They guide you while filling the form and even correct you if you make a mistake.
Filing tax returns online is easy. The average taxpayer won’t take more than 30-40 minutes to enter all the details and upload the return. However, the average taxpayer also harbours several misconceptions about e-filing. Mumbai-based Harshad Doshi has fallen in and out of love with online filing during the past three-four years. Doshi started e-filing in 2008, but when he got a scrutiny notice in 2010, he was advised by a relative to desist from the online route. The next year, he reverted to physical returns, but still got a notice. This year, Doshi has no choice but to e-file his returns because his annual income is above 5 lakh. “I have realised that one can get a tax notice, irrespective of whether one files his return online or offline,” he says wryly.
He’s right. Tax returns are picked up for scrutiny through a computerassisted selection procedure that has no human intervention. If the computer detects certain discrepancies in the return, it raises the red flag and the individual gets a notice. In fact, there is a greater probability that a return filed offline will get picked up for scrutiny. The information in your physical return is ultimately fed to the computer by operators. A typing error at this stage can introduce a discrepancy in the return, leading to a notice being sent to you.
This problem can be avoided when you file online because the chances of going wrong are lesser. The e-filing portals further reduce the risk of errors by calculating the tax as you fill in the form. Some e-filing companies, such as Taxspanner, even verify your return for a small fee. If you are ready to shell out 200, the portal will check if you have entered correct information and alert you when you are going wrong. Tax professionals go through your return form, tallying the numbers and cross-checking the information before it is uploaded.
Choose the right form
The online filing data reveals that more than 32% of the 2 crore individual taxpayers used the basic ITR 1, also known as Sahaj, to file their returns last year. Only 11% used the more complicated ITR 2. These statistics indicate that a lot of taxpayers who should have used ITR 2 filed their returns using the simpler Sahaj form. The income level does not matter; what is important is the source of income. For instance, if one had made capital gains or earned rent from more than one house, he should have used ITR 2.
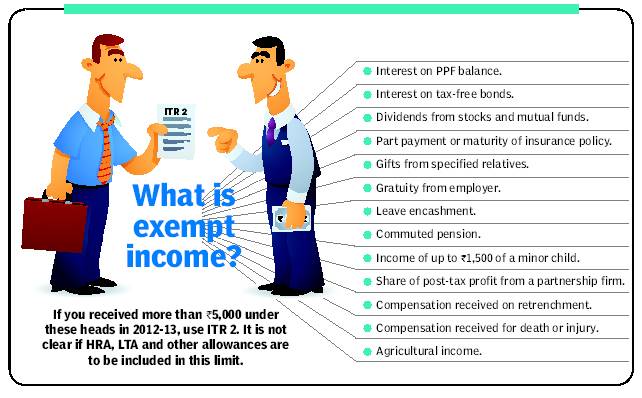
Whether the popularity of ITR 1 was out of ignorance or a deliberate attempt to conceal income is not clear. However, the government has now changed the rules to capture a better picture of the income of taxpayers. If you received more than 5,000 tax-exempt income during 2012-13, you will have to use the ITR 2 for filing your return this year. Exempt income includes tax-free sources of income, such as the interest on PPF, tax-free bonds and dividends (see table). Also, a taxpayer is is not supposed to use ITR 1 if he has foreign assets or has claimed tax relief under any double taxation avoidance treaty.
Experts are divided over the interpretation of exempt income in this regard. “This change will have a big impact on the salaried taxpayers because HRA, LTA or conveyance allowance are commonly availed of by most of them,” warns Kuldip Kumar, executive director of PriceWaterhouse Coopers. This effectively means that a vast majority of salaried taxpayers will have to use ITR 2 this year. Even if they don’t claim HRA exemption, they get LTA, or at least 800 conveyance allowance per month, which is tax free.
However, other experts believe that the 5,000 limit for exempt income does not include HRA, LTA and other allowances that a taxpayer receives from an employer as part of the salary package. More clarity is needed on this aspect.
The stress on disclosure demonstrates the tax department’s resolve to plug the leakages in tax collection. The direct tax collection of 5.58 lakh crore in 2012-13 fell short of the revised target by 7,000 crore. Addressing a meeting of tax officials in May, Finance Minister P Chidambaram exhorted them to “target non-filers and stop-filers to widen the tax base”. Almost 12.5 lakh such “non-compliant” taxpayers have been identified by the Central Board of Direct Taxes, and almost 2 lakh notices are already on their way. The taxpayers who have not filed or s t o p p e d f i l i n g would do well to take heed of the warning. If you have not filed your return for last year as well, you can do so now. A return filed after the due date is a delayed return. If you file your delayed return before you get a notice, you have a better chance of getting away lightly. The taxman will not take you to task for not filing your returns, just give you a mild rap for waking up late.
Automatic choice for e-filers
For some online tax filers, choosing the right form is not an issue. “A taxpayer has to just enter what he has earned under different heads of income and the portal automatically chooses the applicable form,” says Sudhir Kaushik, co-founder and CFO of Taxspanner.com. For instance, if the person has only income from salary and no exempt income, his return will be filed using ITR 1, but if he made some capital gains, has rental income from more than one house or his exempt income exceeds 5,000, ITR 2 will have to be used.
However, taxpayers who upload their returns through the official Income Tax Department website will have to be more careful about the form they use. Delhi-based Kuldip Kaushik used the ITR 1 last year, but since he had dividend income of over 5,000 for the year 2012-13, he will have to use ITR 2 this year.
If a taxpayer uses the wrong form and the mistake is discovered by the tax authorities, the return may be rejected. Every year, thousands of defective returns are sent back to taxpayers. A defective return is not an earth shattering matter. If you get a notice, you will have to file a revised return within 15 days. If you meet the deadline, the return is treated as valid. Get delayed and your return will become invalid and you will have to file afresh.
“If you discover on your own that you have made a mistake in the return or used the incorrect form, you can file a revised return to rectify the mistake,” says Vineet Agrawal, director KPMG. Your new return will overule the previous one if the assessment has not been completed.
Check your TDS details
Before you sit down to file your returns this year, spend a few minutes to check whether the tax you paid for last year has been correctly credited to your name. The Form 26AS has details of the tax deducted on behalf of the taxpayer and can be easily checked online. Noida-based Brijendra Singh wishes he had done so last year. The former army officer got a tax notice because of a clerical error by his bank. The TDS paid on his income from fixed deposits was credited to another PAN by mistake. Though he was eventually given credit for his TDS, Singh is not taking any chances this year. He has diligently matched all his TDS details with his Form 26AS online.
Checking your tax credit details online is child’s play if you have a Net banking account with any of the 35 banks that offer this facility. Otherwise you can go to the official website of the Income Tax Department and click on ‘View Your Tax Credit’. First-time users will have to register but it takes less than five minutes before you can log on and view your details. “It is necessary that taxpayers check their TDS when they file their returns,” says Kuldip Kumar of PwC.
Forms seek more information
If salaried people are feeling jittery about using the more detailed ITR 2, imagine what partners in firms and businessmen are going though. In an attempt to dig deeper for undisclosed income, the government has made it mandatory for partners, professionals and businessmen with an income of over 25 lakh to furnish details of their assets and liabilities. There is a new ‘Schedule AL’ in the ITR 3 and ITR 4. If the taxpayer’s income exceeds 25 lakh during the year, he will have to declare his assets and liabilities.
Don’t forget the ITR V
The most important form in the whole process is the ITR V. This is the acknowledgement of your return. If you file offline, this form has to be submitted along with the ITR. If you file online without digital signature, this form has to be sent to the CPC in Bangalore by snail mail within 120 days of uploading the return. This also means that for a vast majority of efiling taxpayers, the process is not fully online. The CBDT is considering a proposal that will do away with the physical posting of the ITR V. However, till then you will have to send it by ordinary post.
Others feel that the cost of digital signature should be brought down and its usage expanded to cover other areas as well. “If e-filing has been made mandatory, the government should also make the use of digital signatures mandatory,” says Delhibased chartered accountant Minal Agrawal Jain.
Choosing an e-filing portal
Charges should not be the only reason for choosing a portal. Here are some other factors that you should consider.
Is it comprehensive?
The more details sought, the better it is. If the return uses only Form 16, you might lose out on deductions you were eligible for, but didn’t claim.
Assistance in filing
For a small charge some portals guide you in the process to ensure there are no mistakes. Others pick up documents from your office or residence.
Follow-up services
Does the portal help even after the uploading? Some alert you if you forget the ITR V. Others send it to the CPC in Bangalore on your behalf.
Privacy policy
The data in your tax return form is priceless for financial services companies. If it goes out, you will be inundated with calls and spam mail.
Five tax filing mistakes
Five tax filing mistakes to avoid this year
Here’s how to ensure you don’t commit errors and receive a tax notice
The Times of India 2013/07/15
1 Availing of deduction twice
This is a common error that many salaried taxpayers commit. If you had switched jobs during the previous financial year, you might have got the Form 16 from both employers. While the first company may have deducted the tax correctly, the second might have deducted very little. It would have considered only the income for the rest of the year and given you the basic exemption of 2 lakh, as also the deduction under Section 80C. However, these must have already been factored in by the previous company. “You might have to pay additional tax in such a situation,” says Sudhir Kaushik, co-founder of tax filing portal, Taxspanner.com. Don’t think you can escape by ignoring the previous income in your tax return. The computerised scrutiny will immediately detect the discrepancy. There will also be a mismatch in your TDS details because the previous employer would have deposited the TDS on your behalf, along with your PAN and other details. 2
Not mentioning exempt income
Dividends are tax-free. So are longterm capital gains from stocks and equity funds, as well as the interest on your PPF investments and taxfree bonds. There is also no tax to be paid on agricultural income and gifts from specified relatives. Even though these are tax-free, all exempt incomes must be mentioned in the tax return. Ignore this at your peril. The new rules for tax filing announced this year state that if the total exempt income during the year exceeded 5,000, you will have to use ITR 2 to file your return.
3 Not including interest
2012’s budget had introduced a new Section 80TTA, which gives a deduction of up to 10,000 on interest earned on your balance in the savings bank account. Many taxpayers think this deduction also includes the interest earned on bank deposits. The interest earned on fixed deposits and recurring deposits is fully taxable at the normal rate. You have to mention it under the head ‘Income from other sources’ in your tax return. Tax is payable even if the TDS has been deducted. TDS is only 10% (20% if you haven’t submitted your PAN details), and if you are in the 20-30% bracket, you need to pay additional tax. The interest on NSCs is also taxable.
4 Not checking TDS details
Before you file your returns, check whether the tax you had paid for last year has been correctly credited to your name. The Form 26AS has details of the tax deducted on behalf of the taxpayer and can be easily checked online. It is easier if you have a Net banking account with any of the 35 banks that offer this facility. Otherwise, you can go to the official website of the Income Tax Department and click on ‘View your tax credit’. First-time users will have to register, but it takes less than 5 minutes to log on and view your details.
5 Not mailing ITR V in time
The ITR V is the acknowledgment of your tax return. It is to be submitted along with your return if you file offline. If you have e-filed your return without a digital signature, you need to take a print of the ITR V, sign it and send it to the CPC in Bangalore by ordinary mail. This should be done within 120 days of uploading your return. The filing process is complete only after the ITR V is received at the CPC. You can check the status of your ITR V on the official website of the Income Tax Department. If it has not been recieved within 7-10 days of mailing, call up the Ayakar Sampark Kendra or send another copy.