Labour: India
(→Commuting to work) |
(→2015: monthly wage adequate for unskilled worker with family) |
||
| Line 216: | Line 216: | ||
=Wages= | =Wages= | ||
==2015: monthly wage adequate for unskilled worker with family== | ==2015: monthly wage adequate for unskilled worker with family== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Trade-unions-eyed-Rs-15kmth-min-wage-as-04092015013025 ''The Times of India''], Sep 04 2015 | [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Trade-unions-eyed-Rs-15kmth-min-wage-as-04092015013025 ''The Times of India''], Sep 04 2015 | ||
Revision as of 10:50, 30 June 2018
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
Commuting to work
The Times of India, Nov 12 2015
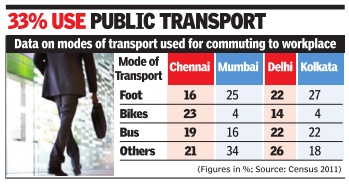
Sivakumar B
Long way to go: One in five Indians still walks to work
Well into the 21st century, more than one in five Indians walk to their work and less than 15% take public transportation. Some 33% use other modes of transport than buses and trains to reach their workplaces situated up to 20 km from their homes. Another 23% walk while 30% don't stir out of their houses but still work. These figures are based on recently released 2011 Census data on different modes of transport used by workers commuting to workplaces within 20km from their homes. Agricultural workers and domestic helps weren't considered in the survey . Of the nearly 20 crore workers surveyed, 4.5 crore walked to their workplace.
Most of those who work from home are in rural areas.“In urban areas, a large number of people who walk to work are poor. They often walk long distances in spite of inconvenient and dangerous conditions because they cannot afford any other form of transport,“ Institute of Transportation and Develop ment Policy regional director Shreya Gadepalli told TOI.
Experts see these figures as yet another reason for planners to take into account facilities for pedestrians.
In rural areas it is mainly lack of access to transport facilities that forces people to walk to work, Shreya said. The percentage of women who walk to work is even higher in urban areas.However, wide, continuous and shaded footpaths along with safe and frequent street-level crossings can entice higher-income people too to walk. Good footpaths also encourage the use of public transport,“ Shreya said. Only 11.4% workers in the country use buses and 3.5% of the workers have access to train, which includes Metro and MRTS in cities like Chennai. After foot and bicycle, the most preferred transport is twowheelers -more than 2.5 crore or 12.7% travel to their workplace by two-wheelers.
Of this, nearly 75% are in urban areas. Only 2.7% use car, jeep or van and 3% take an autorickshaw or a taxi.
“States must concentrate on developing better transport infrastructure in urban areas as a majority of workers are in cities and towns,“ said former Anna University urban engineering professor K P Subramanian. There should be better integration of multi-modal transport systems, he said. Urban authorities must discourage use of cars if there is proper connectivity between all modes of public transport, he aded.
Commuting by car
The Times of India, Nov 13 2015
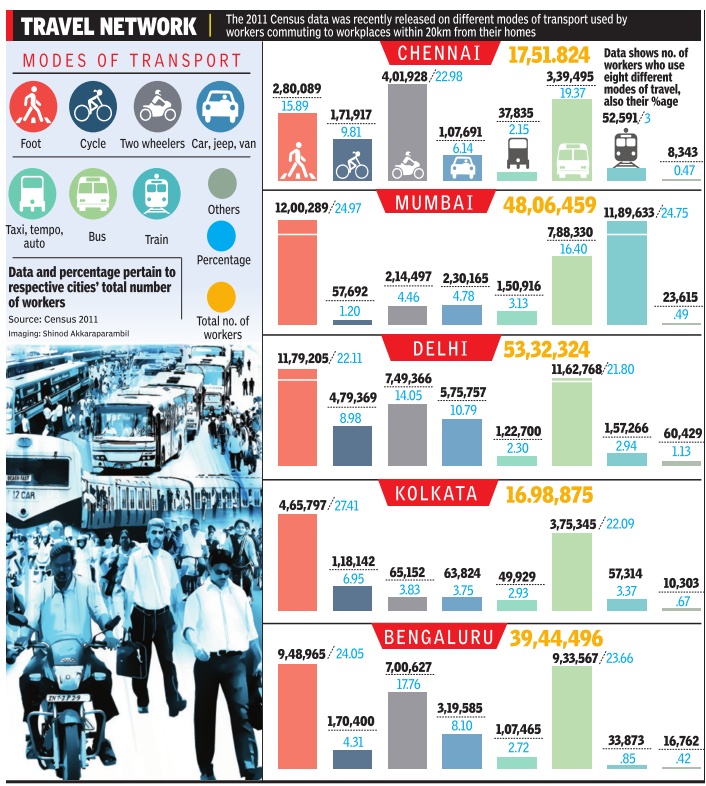
Meera Vankipuram
Delhi, Chennai top in car usage, reveals data T he 2011 Census data has revealed that Delhi has the highest number of workers in the country who commute by car, jeep or van at 10.79%. Chennai is in second place with 6.14%, while Mumbai is in third place at 4.78%. Kolkata (2.93%) and Bengaluru (2.72%) have the least number of commuters who take cars or vans to work, among the five metros.
According to transport ministry data, Delhi has the highest number of cars compared to any other metro city in India. While the highly efficient Delhi Metro helped ease traffic on city roads, of late, the burgeoning peak hour crowd has made it difficult for many Delhiites to use the Metro. Between 8am and 11am on weekdays, for example, the trains carry nearly 1 lakh passengers.
Dilip Singh, 49, a general manager with a private firm in New Delhi, prefers to use metro. Of late though, many commuters drive their cars to work due to overcrowding of trains during peak hours.“Metro is not equipped to handle the massive morning and evening traffic,“ he said. Also, many Delhiites view cars as a status symbol, he said.
In Chennai, poor connectivity of public transport systems force many working professionals to use cars and vans. Rajiv Balaram, 26, who is employed at an IT firm in Sholinganallur felt that that it is impossible to get to his office without using a car or auto.“Many of us who work on the IT corridor are able to use the trains or buses only upto a certain point. After that, we depend on shared autos, cabs or cars,“ he said.
Kolkata, where less than 3% of workers drive to work, has a robust transport network that includes the metro, buses, taxis, trams and autos.This network spares commuters the need to use personal vehicles.
The city also has a strong local railway network that carries 35 lakh commuters a day . The Kolkata Metro, which serves all the major office localities of Kolkata carries 5 lakh passengers daily .Taxis carry around 16 lakh commuters a day and trams still carry around 6-7% of the daily commuter load.
This is why Kolkata was chosen by World Bank as the city with most sustainable transport system in India, said chief traffic and transportation engineer Anup Chatterjee.
Commuting by bus, train
The Times of India, Nov 13 2015
Ayyappan V
Buses, first choice of many
Mumbai and Delhi have the largest number of people among cities in the country who use buses and trains to commute to work, data from the 2011 Census shows. The reason is simple: both cities have a good network of buses and trains. Of the working population in Mumbai, around 41.15% of the people use buses and trains to commute to their workplaces, while in Delhi it's 24.74%. In comparison, in Chennai, 19.37% of the workers took buses, while only 3% depended on trains to reach their work place. The share of public transport in a city should ideally be 60%.
This is why the Union ministry of urban transport has been pushing for mass rapid transit systems like metro rail and monorail in fast-growing urban cen tres.
In Mumbai, trains claim a share of 24.75% of all working people, while the share of buses is 16.4%.In Delhi, however, more people use buses because the suburban network is not convenient for residents and many of them have migrated to metro rail.
A senior railway official, who was involved in urban NOT AN EASY TRIP transit system planning, said the share of public transport had increased tremendously after metro rail extended its network across the national capital region.
Indian cities have to do a lot to make their public transport sys tems usable and reliable, especially by introducing intermodal connectivity so that people can switch from one mode of transport to another with ease during their trip from doorstep to workplace.
Binoy Mascarenhas of Embarq Mumbai, said, “Mumbai has a good track record of people using public transport. Majority of the trips for work are on public transport. Trains are the most popular while buses come second in preference.Metro rail will also have a good impact in boosting public trans port over the next 20 years when its entire network is ready.“
The reason for change in volume of patronage varies from city to city-from geography to poor capacity and poor connectivity . The choice of transport system depends on the nature of the city . Mumbai's linear geography makes trains the choice while that may not be the case with cities like Bengaluru and Delhi.
Mumbai tops list of train users
Though faster and cheaper, trains are not preferred much by people to travel to work in major cities in the country.Mumbai tops the list of cities where people use the services to travel to work among Delhi, Kolkata and Chennai. Among the four cities, Mumbai and Chennai have an efficient network of suburban trains. The 2011 Census statistics showed that among the metros, Mumbai tops the list with 24.75% workers using trains to their workplaces. This means that around 11,89,633 people prefer to use the suburban services. Delhi's trains are used by 2.94% of its work ing population. This includes people using long distance trains that come into the city to travel into the national capital for work. However, the number must have changed over the past few years because the region now has a substantial metro rail network. TNN
Contract workers
Entitled to 6-month maternity leave: HC
‘Contract workers can take 6-month maternity leave’ , March 20, 2018: The Times of India
Contract workers serving the government are entitled to six-month maternity leave, on a par with regular employees, the high court has held.
The ruling by Justice Anu Sivaraman came after considering two petitions filed by women working on contractual basis under the state. They were allowed maternity leave only for 90 days whereas regular employees were entitled to leave of six months.
A petition filed by Rakhi P V of Nayarambalam and four others was considered as the lead case by the court. The state government had contended that granting sixmonth leave to a woman employed on a one-year contract would obliterate the benefit of the employment.
Domestic help
2016:Rajasthan sets minimum wages
The Times of India Feb 01 2016
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
Enforcing labour reforms in the unorganised sector, the Rajasthan government has fixed minimum wages for domestic help and set limits to their working hours.
According to a recent notification by the state's labour department, the rate for chores for an entire day (defined as eight hours) including cooking, washing, baby sitting and other work has been fixed at a minimum of Rs 5,642 per month. The new salaries come into effect from January 1, 2016.
In case of overtime, employers will have to pay workers double the minimum fixed per hour for each hour beyond the mandated eight hours.
Domestic help hired for just washing dishes and laundry will have to be paid a mini mum Rs 705 per month for a household of four people. If the number of people exceeds four, the help would have to be paid 10% more than the minimum prescribed, per individual.
The Centre is also trying to prepare a national policy for domestic workers. On Au gust 17, 2015, TOI had reported that the Union labour ministry was seeking to ensure minimum salary of Rs 9,000 per month, compulsory paid leave of 15 days a year and maternity leave, apart from social security for domestic help. The minimum wage for domestic helps notified by the Rajasthan government is exclusive of food, clothes, accommodation or other perks that an employer may be providing.
Also, if an employer is paying more than the prescribed minimum wage, then he or she must continue paying the higher amount. Jaipur Servants Association spokesman Abdul Moin said, “This is a good step. Most people who work as domestic helps here are from other states like West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, and Jharkhand, and are unlettered. This will ensure they are paid their minimum amount. In fact, the government should raise the bar higher.“
Dhanraj Sharma, addi tional labour commissioner, said, “Domestic workers were included in Scheduled 27 of the Minimum Wages Act eight years ago. But, we have now fixed the number of working hours for them to ensure they are paid well.“
The department, to ensure implementation, will even press labour inspectors to carry out surprise checks in every district.
“Violators will be liable for prosecution, and domestic worker eligible for compensation as high as 10 times the difference between the minimum wage and the amount he or she was received,“ he added.
In the last couple of years, Rajasthan has emerged as a bellwether state as far as labour reforms are concerned
Informal labour
Data is scarce
Dipankar Gupta|Empire Of Numbers|Jul 15 2017: The Times of India (Delhi)
We have no interest in informal labour, as data on it is scarce What comes first, the question or the answer? If you believe in numbers, as many social statisticians do, the answer comes before the question. Hence, the chances are that only those issues will be raised which can be resolved through government, or quasi-government, statistics.Anything outside of this is over-spiced and bad for contemplation. It is this attitude that has kept our understanding of informal labour on a low calorie diet, though it gobbles up 93% of our economy. As information on this is sparse, even if the issue is so big, it is convenient to look the other way.This explains the administrative reluctance to bulk up on policies related to this subject. The system works best when answers predate and frame the questions, leaving little to chance. The stage is now set for the policy maker, as diviner, to deliver with a flourish.
This method actually resembles the way religious discourses are conducted. The Church opposed Galileo and Copernicus because they asked questions for which the sacred texts had no answers. As Joshua had bid, in the Old Testament, the sun to stand still and not the earth, therefore, Martin Luther concluded, Copernicus must be wrong. The Catholic establishment even accused Galileo of planting little figures in his telescope and passing them off as planets. Therefore, if the answer is not in the Bible or Quran or Gita ask not that question, admonish religious gurus.
Likewise, as there is very little that is reliable about informal labour, either in the Census, or in surveys (the equivalent of the Bible Quran Gita), it does not count. Information, such as is available, is scattered and sniggered at as `anecdotal'. Consequently, a big chunk of our society is deprived of attention. Numbers don't come easy in the informal sector, especially when commandeered from above and afar.However, our ignorance of these very vital issues does not disturb us too much.
For example, we rarely give any thought to strategising cottage industries, international competition, even worker-management relations, for they all include informal labour. When industrial strife is being discussed, figures tell us of a dramatic drop in strikes over the past three decades. This should mean that shop floors everywhere are buzzing with happy activity .Could it be that the sinister foreman, after a routine body check, swapped his old heart for new? Nor do we know how many unregistered units shut and open shop; or of workers who are routinely fired; or of wages unfairly held back.
As a result, we do not have a measure of what India needs to do to become a global power. If there are so many microenterprises, why are we still poor? Also, why don't graduates from vocational institutes find skilled jobs in the marketplace? When we laud our export earnings, the informal sector is rarely acknowledged, nor the millions who bent their backs night and day. We have not even spared a thought for the health of these units; what if they collapse? The ruling view is that if it ain't broke, and no emergency declared, why break the glass? Instead, we imagine ourselves lounging with the big boys, after elbowing the rat pack out.
The consumer price index falters at the sight of informal labour. Nevertheless, we continue to extrapolate from those figures, even if it hurts. As long as the tag says the size is right, who cares if the shoe pinches? Was demonetisation a success? By all accounts it was an electoral bonanza, yet so many questions remain unasked and unanswered. If livelihoods impact voting behaviour then we should know whether demonetisation affected workers differently. This is particularly so in the case of informal labour simply because of the many varieties they come in.
It is said that many lost their jobs, but who were they? Were those who were employed by the week, or month, worse off as high currency notes would be needed to pay them and these were now demonetised? Did daily wagers fare better, for they could be paid in small change? Or, perhaps it did not matter; they sank or swam randomly.
We can only guess the outcome, but where are the facts? Political analysts could have helped. But instead of asking tough questions on informal labour and voting behaviour, they are obsessed with caste. As many of them suffer from economist envy , they look out for issues where numbers tumble out.
Nor should one argue that precision does not count. It is a good idea when disciplinary questions and real world issues prompt the search for exactitude.When this route less travelled is taken, statistical exercises become legitimate. On the other hand, when it is independently pursued for its own sake, social science becomes a closed box; nothing new is found, nothing new is said. Have wages for informal workers kept pace with inflation? “But we don't have numbers on that,“ says the policy maker. How often have you heard that being said? This is what makes it an egg and chicken issue. As informal labour lacks ready numbers, you can eat it before it is born and after it is dead. Either ways, it does not stand a chance.
Online labour
India was the largest supplier/ 2016
India largest provider of online labour|Jul 20 2017 : The Times of India (Delhi)
Accounts For 24% Of Jobs, Tops In Software & Tech India is the largest supplier of online labour, says a recent report, analysing data from e-platforms connecting freelancers with employers. India is followed by Bangladesh, US, Pakistan, Philippines and the UK in what is being termed “digital gig work“ or freelance work offered online. Over half of the online work supplied out of India is dominated by software development and technology sector. Oxford Internet Institute of the University of Oxford published the report last week. It hosts the “iLabour project“ as part of which the Online Labour Index is produced. This report analysed data for the first week of July.
“The largest overall supplier of online labour according to the data is the traditional outsourcing destination India, which is home to 24% of the workers observed. India is followed by Bangladesh (16%) and US (12%). Different countries' workers focus on different occupations. The software development and technology category is dominated by workers from the Indian subcontinent, who command a 55% market share. The professional services category , which consists of services such as accounting, legal services, and business consulting, is led by UK-based workers with a 22% market share.“
While software and technology services was the top sector for India, creative and multimedia services came second, and sales and marketing support was the third most popular online labour sector for the country .
The report analyses data from four online platforms -Fiverr, Freelancer, Guru, and PeoplePerHour. “Based on traffic statistics, we can estimate that these four sites represent at least 40% of the global market for platform-based online work,“ says senior OII research fellow Vili Lehdonvirta.
Labour laws reform
2016: Rs 6,000cr textile package
The Times of India, Jun 23 2016
Govt brings in labour reforms via Rs 6,000cr textile package
The Union Cabinet introduced labour law changes while approving a Rs 6,000-crore package for the textile and apparel sectors. A key element is increase in overtime for workers which should not exceed 8 hours per week, translating into nearly 90 hours over three months. The current norm allows only 50 hours of overtime in three months. “It'll be advantageous for the industry as well as labour,“ said A Sakthivel, who represents industry lobby groups. The new cap on overtime, which meets ILO norms, would help increase earnings of workers, the Centre said. The cabinet on Wednesday approved the introduction of fixed-term em ployment, which was an industry demand to deal with the seasonal nature of demand. A fixed term workman will be considered on a par with a permanent workman in terms of working hours, wages, allowances and other statutory dues.While the move is unlikely to result in higher burden on companies, it provides flexibility in hiring to deal with seasonal rush, especially for exporters.
The government also announced a change in income tax laws to allow for deduction in case more permanent workers are hired by textile and garment units. Instead of the current provision of the benefit accruing if workers are hired for 240 days, the government has now lowered the floor to 150 days. Industry players said this would provide greater flexibility. In what could also become the template for other industries, the government has made it optional for textile industry workers earning less than Rs 15,000 a month to contribute to the Employees' Provident Fund. “The announcement will bring relief for the garment sector where a large number of employees work shortterm and prefer to take full wages without deduction,“ said M Senthil Kumar, chairman of the South India Mills Association.
The move is also significant since the finance ministry has been trying to wean away employees from EPF to the National Pension Scheme. The government said it would bear the entire 12% of the employer's contribution of the EPF scheme for new garment industry employees who are earning less than Rs 15,000 per month, for their first three years of employment.
At present, 8.33% of the employer's contribution is being provided by the government under the Pradhan Mantri Rozgar Protsahan Yojana (PMRPY). The textiles ministry will provide the additional 3.67% of the employer's contri bution, amounting to Rs. 1,170 crores over the next three years. If successful, the labour related changes could become the template for other sectors.Although the government is keen on ushering in reforms in this crucial segment of the economy , it is going slow given the pressure from trade unions, including BMS, which is affiliated to BJP .
The government said a majority of new jobs are likely to go to women as they acount for nearly 70% of the garment industry's workforce. The textile ministry said with policy support, Indian exports could again regain their leadership position. In recent years, apparel exports from Bangladesh and Vietnam have overtaken India's exports. The slowdown in China presents an opportu nity to India to ramp up its shipments in the world market.
India Inc cheered the labour law changes in the sector and said it would help the industry to scale up.
“Flexible labour reforms are critical for the sector as the industry is highly labour intensive and India needs to increase productivity to put up with the growing competition,“ said B K Goenka, chairman, Welspun group and co-chairman of CII national committee on textiles.
Additional incentives under the amended technology upgradation fund scheme were also approved. “The package breaks new ground in moving from input to outcome based incentives by increasing subsidy under the Amended-TUFS from 15% to 25% for the garment sector as a boost to em ployment generation,“ said a government statement. It said a unique feature of the scheme will be to disburse the subsidy after expected jobs are created.
The cabinet also approved enhanced duty drawback coverage. A new scheme will be introduced to refund the state levies which were not refunded so far. The move is expected to cost the exchequer Rs 5500 crore but will boost competitiveness of Indian exports.
Literacy/ educational levels of workers, non-workers
2011
The Times of India, Nov 07 2015
Over 130m of workforce below matric level in India In freshly-released census data on literacy status and educational levels of various types of workers and non-workers in the country , Census 2011 has found nearly 130.2 million of the total 362.6 million main workers to be literate but below matricsecondary level. The census data released on Friday -which gives the distribution of main workers by educational level and age groups -further shows that 104.3 million (28.8%) main workers are illiterates and 71.5 million (19.7%) matriculatesecondary but below graduate level.
Of about 55.5 million marginal workers seekingavailable for work in India, the majority of 21.9 million (39.4%) are illiterates followed by 20.9 million (37.6%) literates but below matricsecondary and 8 million (14.5%) matricsecondary but below graduate.
However, among 60.7 million non-workers seeking available for work in India, the major share is constituted by literates but below matricsecondary (33.6%) followed by matricsecondary but below graduate (31.1%) and illiterate (17.2%).
The decade 2001-11 exhibited 59.2 million increase in literate main workers out of which maximum increase of 20.5 million was reported under the category matricsecondary but below graduate followed by 16.2 million as below matricsecondary and 11 million as graduate and above other than technical degree.
As per overall data, only 4.5% of the country's population is educated up to the level of graduate or above while a majority 32.6% population is not even educated till the primary school level.
Those educated till primary level are 25.2%, middle school 15.7%, matric 11.1%, higher secondary 8.6% and graduate and above 4.5%.
During the decade 200111, improvement was observed at middle and above educational levels even as there was decline in percentage share at lower levels (below-primary and primary).
Wages
2015: monthly wage adequate for unskilled worker with family
The Times of India, Sep 04 2015

The break up justifying this figure Intercontinental Almaty as above; Graphic courtesy: The Times of India, Sep 04 2015
A labour ministry document argued that by current norms, prices and calorific needs, Rs 6330 per month is the monthly wage adequate for an unskilled worker with a wife and two small children.
The Times of India adds: How did the government calculate their proposal? A look at the fine print shows a slew of gross under-estimations and the use of an archaic formula first spelled out way back in 1957. Some of the food items' prices are far from reality . For instance dal is costed at Rs 65 but only one of the various dals in the market -chana or gram dal comes in this range. Arhar (tur) is Rs 135 per kg, urad is Rs 117.5, masur is Rs 95. All these current retail prices are from the consumer affairs ministry's price monitoring data spanning 81 cities and towns.
See also
Labour: India

