Monsoons: India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Contents |
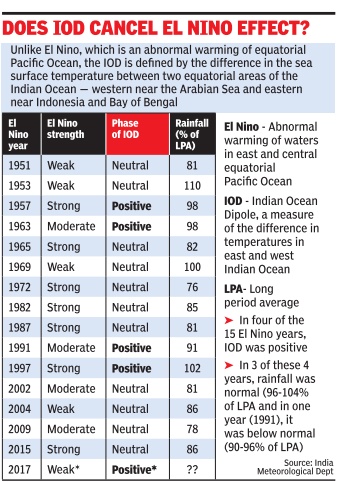
The El Niño effect
Vs. IOD: 1951-2017
See graphic.
How the monsoons control our destiny
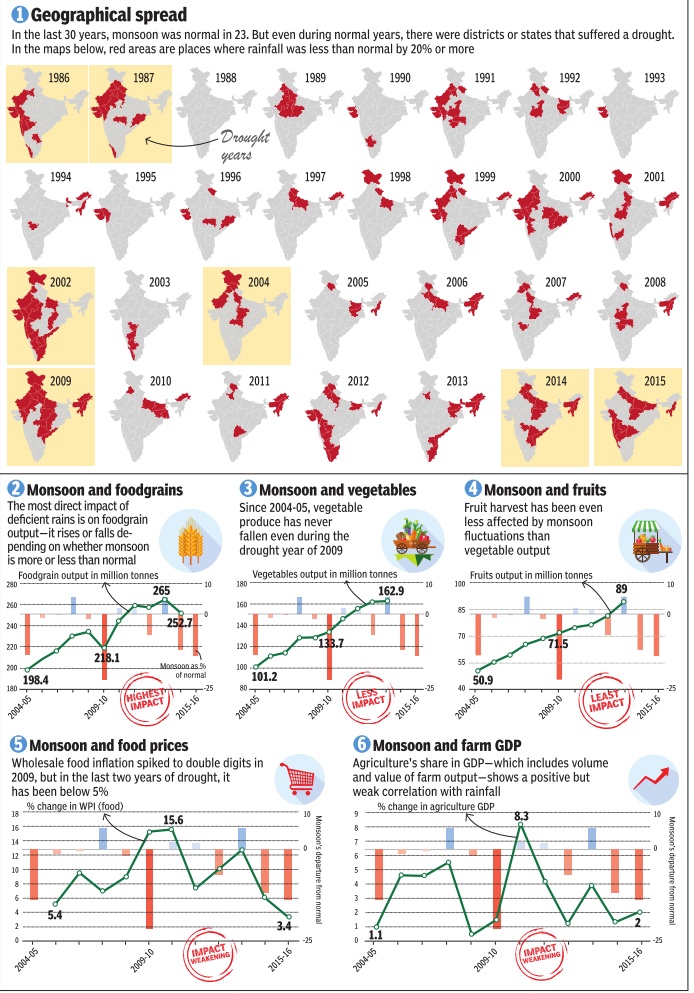
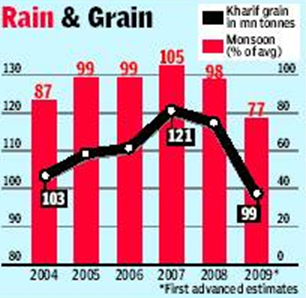
Monsoon and agriculture
See the graphics
Monsoons: India
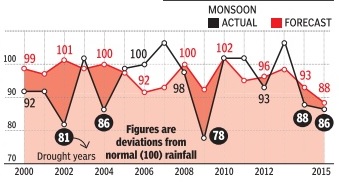
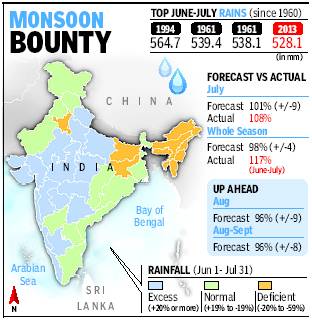
Monsoon going strong, hopes soar
Rains Set To Cross 100% Of Long-Period Average, Record Rice Output Likely
Neha Lalchandani TNN
The Times of India 2013/08/02
A bountiful monsoon normally benefit the kharif crop and augurs good rice production with the area under sowing touching 196 lakh hectares in 2013, a 16 lakh hectare increase over 2012.
Monsoons that crossed the 100% mark
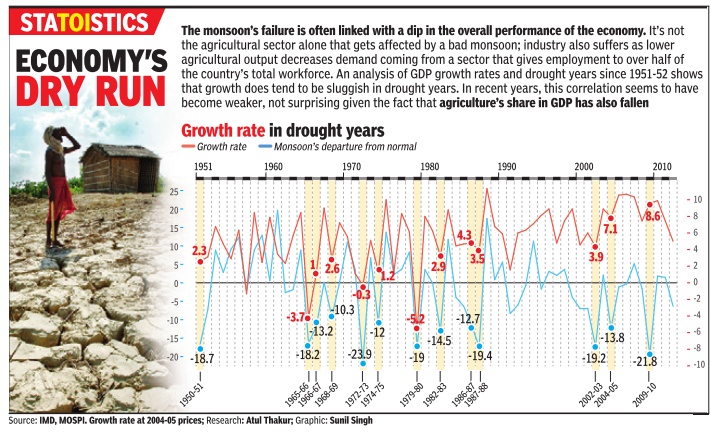
Since 1901, there have been 59 years when the monsoon has crossed 100% of the LPA. Since 2000, there have been only four years when monsoon crossed the 100% mark. These are 2003, 2007, 2010 and 2011. The projection is welcome news for the government as a stuttering monsoon can cast a long shadow on its political fortunes with growth slipping below 5% and high food inflation — prices for consumers rose 11.84% in June — proving a sizeable thorn in the side for UPA-2.
The government hopes the farm sector significantly improves on 2012’s 1.8% growth with R Rangarajan, chairman of the PM’s economic advisory council, saying a normal monsoon could even yield a 3.4% growth.
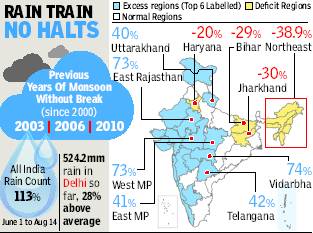
Monsoons without a break
Non-stop monsoon marches on
Amit Bhattacharya TNN
The Times of India 2013/08/16
One or two periods of a break in monsoon — defined as three straight days of very low rain activity across central India — are common during the rainy season. Since 2000, there have only been three years when there was no monsoon break. And all three years coincided with plentiful rains.
“Two months of monsoon activity without a break is rather rare. It’s an indication of agood monsoon,” said M Rajeevan, senior weather scientist at the earth sciences ministry.
At least four factors have worked in favour of the monsoon in 2013. The first good sign was an absence of El Nino — an anomalous rise in ocean surface temperatures in the east Pacific that is linked to monsoon failure in India.
Currently, weak La Nina conditions exist in the Pacific, which is the opposite of El Nino and is known to help the monsoon here.
“Then, typhoons breaking out over the south Pacific this season have also helped because these have generally moved in a direction that reinforces the Indian monsoon. This is consistent with the weak La Nina conditions,” said Rajeevan.
More importantly, what has helped sustain the rains — and distribute it more or less evenly across the region — has been a series of low pressure formations over the Bay of Bengal that have travelled westwards at regular intervals.
“There have been an unusually high number of low pressure systems, along with cyclonic circulation over land. These have nurtured the monsoon this year, especially in the interior regions of south and central India,” said Pai.
Lastly, Pai said a strong Arabian Sea branch of the monsoon first helped accelerate the rain coverage over the country, and also brought good rains over the west coast.
2015: Monsoons in India
The Times of India, May 30 2015
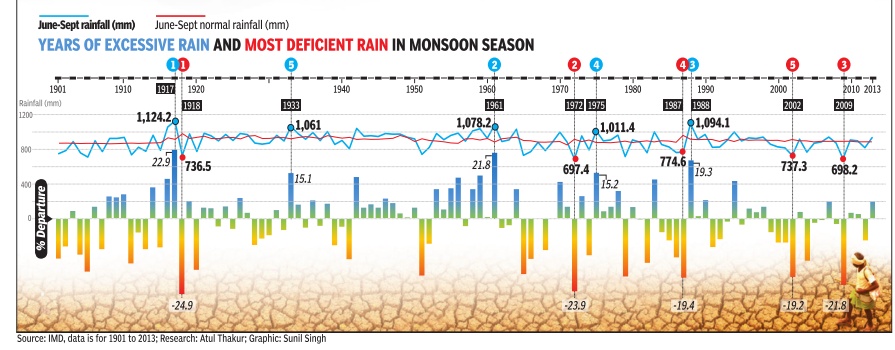
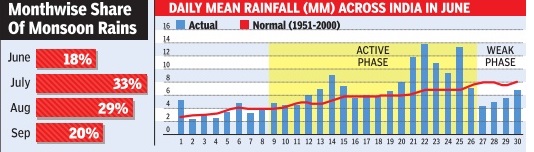
India receives most of the rainfall in four monsoonal months-June, July, August and September. The Met department defines normal monsoon to be 96 to 104% of the long period average, usually the average monsoon over 30 years. If the rainfall deficiency is more than 10%, it would typically be called a drought year. Last year's monsoon was deficient by 12%. This year's monsoon rainfall is predicted to be 93% of the average. If this year's monsoon deficiency crosses 10%, it will be one more year of drought, making it two successive years of drought, an event that has happened only three times in the past 113 years (1904-05, 1965-66 and 1986-87). In 1917, monsoon exceeded normal by the highest percentage (22.9) in 113 years. In 1918, monsoon was deficient by 24.9%, the highest deficiency for this period
2015
The Times of India, Aug 02 2015
Amit Bhattacharya, Vishwa Mohan & Neha Madaan
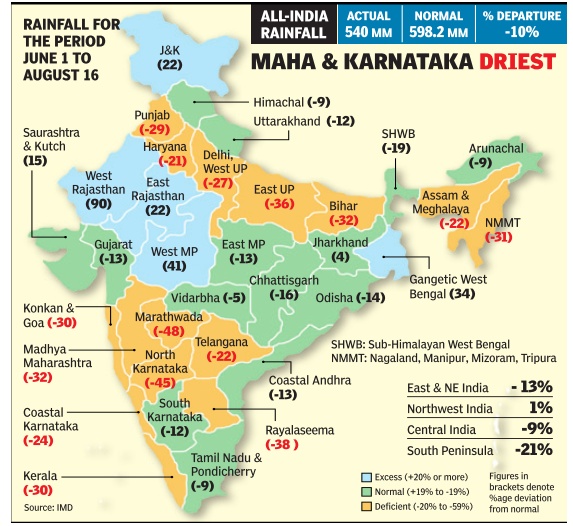
Dry days: 17% rain deficit in July
After a wet June, when other systems had countered the adverse effects of El Nino, monsoon took a drier turn in July and the month ended with a countrywide rain deficit of 17%. However, kharif sowing remained robust, boost ed by good rain spells in sev eral parts of the country . With the dip in rains monsoon's performance in the first half of the season -June 1 to July 31 -was 5% below the long term average June had a monsoon surplus of 16%.
Heavy rains in Gujarat Rajasthan, West Bengal Jharkhand and parts of cen tral India masked the fact that July this year was the driest since 2002 in terms of average rainfall across the country . The month started on a weak note and rains re mained below par till July 19, except for a brief four day period from the 9th.
But there were several redeeming features. “The rainfall, although weak, has been fairly well distributed across most parts of the country ,“ said D Sivananda Pai, head of India Meteoro logical Department's long range forecasting section.
However, some distress zones of low rainfall have started emerging. Rains were consistently weak through July in south India as well as subdivisions such as Marath wada and Madhya Maharash tra. From July 1 till 29, the southern peninsula recorded the highest rainfall deficien cy in the country , at 46%.
“We had forecast an 8% rainfall deficit for July , but it has turned out to be more. A typical feature this year has been that most rain-causing disturbances have been com ing from the east. Indian Ocean's monsoon circulation has been weak, which means that the monsoon pulses are not progressing from the south, which has caused a significant rainfall deficiency in the southern parts,“ a Met department official said.
However, rains in the north, most parts of central India and many regions of the east were close to normal.This is reflected in the kharif crop sowing figures. The overall sown area has, so far, been far ahead of the corresponding figures last year, which was a bad monsoon year.
The area under kharif as on Friday (July 31) was still less than what was reported at this time in 2013, when rains were plentiful in the monsoon months. As compared to 819.99 lakh hectares as on August 2, 2013, the kharif sown area this year was 764.28 lakh hectares as on July 31.
The monsoon is predicted to be active through the first week of August, raising hopes that the net sown area would grow in the coming days.
Several agencies, howev er, have predicted a relatively dry period in the country after the first week of August when the monsoon could go into a break, increasing the overall rain deficit.
In its monsoon update in June, IMD had forecast a 10% rain deficit in August. The department will issue another update for the second half of the season in a day or two. It had in June predicted a drought year, with overall seasonal rains at 12% below normal. Meanwhile, private forecaster Skymet downgraded its prediction for the season from 102% to 98%, still staying within the normal range.
PM explores ways on sugar exports
M Modi called for renewed P efforts to raise ethanol blending of fuel and exploring all possibilities for sugar exports as he brainstormed with key ministers and officials to resolve the problems faced by the sector.He reviewed the progress with regard to the Rs 6000 crore incentive package approved by the Centre in June and emphasized that the farmers' interest be kept foremost at all times.
Monsoon: floods
Every monsoon means flood of bad news
Shobhan Saxena | TNN 2010
In the great plains of India, there is nothing romantic about the monsoon. People’s fate depends on the monsoon’s mood swings. If it fails to keep its date with the country, there is drought. If it’s over generous, the floods cause death and destruction. Even when it’s “normal”, some river somewhere exceeds the danger mark and kills a few hundred people. After the skies clear and the water recedes, armies of mosquitoes and bugs launch attacks. Millions fall prey with chills, cramps, fever. In this part of the world, drought, deluge and death are as much an annual phenomenon as the monsoon.
Bangladesh may be famous for its notorious floods, but India is not far behind. Every year, the monsoon floods leave a trail of destruction in India. Roughly 20% of deaths caused by flooding worldwide occur here; some 30 million people are evacuated every year. Every year witnesses an “unprecedented flood”. Every other year the “worst flood in living memory” leaves scores dead. Is India becoming ever more vulnerable to monsoon fury?
No, say Vinod K Sharma and A D Kaushik of the National Centre for Disaster Management in a recent paper on floods in India. They argue that states did not appear quite as vulnerable as before because there was less developmental activity and population pressure. “However, in the present time, unabated population and high rate of developmental activities forced on the occupation of flood plains has made the society highly vulnerable to flood losses,” they wrote.
In 2009, the monsoon was weak and deficient but it caused floods, deaths and displacement in Orissa, Kerala, Karnataka, Gujarat and the north-eastern states. In 2008, the monsoon was normal, but Bihar faced the worst flood crisis ever as the Kosi breached its embankment, changed course and deluged several districts, leaving hundreds dead and three million homeless.
Monsoon/ water cycle
Let’s respect the water cycle
Amit Bhattacharya | TNN 2010
Think of water and chances are you wouldn’t picture a farmer digging a tubewell. Most urban Indians can’t think beyond their own water woes — dry taps; waking up at odd hours to tank up for the day. Yet, 80% of all the water India uses goes into agriculture. But even so, 60% of our farmlands remain dependent on the rains. Just as water evaporates, it seems, so do the resources that go into water management in the countryside.
The scale of this ‘evaporation’ is so massive it is surprising the issue hasn’t generated more public debate. Nothing illustrates this better than the money spent on canals. In the 15 year-period from 1991-92 to 2006-07, the government spent Rs 1.3 lakh crore on major and medium irrigation projects without achieving any net increase in the irrigated area!
If anything, India’s total canalirrigated area has decreased from 17,791,000 hectares in 1991-91, to 16,531,000 hectares in 2007-08, according to provisional figures released by the agriculture ministry. The story behind this dubious feat encapsulates almost everything that’s wrong with water planning and use in agriculture.
Himanshu Thakkar, coordinator for South Asia Network on Dams, Rivers and People, should know. Last year, he co-authored a paper that contained exactly those startling statistics. He says it’s not about too few new canals but about “many old ones have stopped functioning, at least partially, due to siltation, lack of maintenance and faulty assumptions of water use. Then there are water management and sharing issues. Often there’s intensive water use in upstream areas which leaves no water at the tail-ends.”
Thakkar says it boils down to bad investment decisions. “The government keeps pushing for big irrigation projects without taking care of the existing ones, which in itself is a huge task. According to a 2005 World Bank report, the annual maintenance bill for India’s canal network comes to around Rs 17,000 crore. Less than 10% of that money is available,” he says.
Experts lament that new irrigation projects often fail to take into account the larger hydrological processes they would affect. They also pay little attention to water-use patterns. This has led to river basins such as the Krishna becoming over-irrigated.
Planning Commission member Mihir Shah calls such policy practices “hydroschizophrenia (or) a schizophrenic view of an indivisible resource like water, failing to recognize the unity and integrity of the hydrologic cycle.”
Shah elaborates: “It’s a strange situation. Water management in villages comes under two ministries — rural development ministry and ministry of water resources. Often the left hand doesn’t know what the right hand is doing.”
Both Shah and Thakkar say the first step in dealing with the crisis is accepting ground realities. “While huge amounts are spent on canal systems, groundwater has emerged as the dominant method of irrigation,” says Thakkar. The latest official figures show that more than 60% of India’s 62 million irrigated hectares is fed by groundwater.
With no regulation, this has obvious perils. In August, two independent studies used satellite data from GRACE or the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment to show that northern India was losing more groundwater than anywhere else in the world except for the Arctic ice sheets. One of the studies put the annual net groundwater loss in Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan at 109 cubic km, which is roughly equivalent to 109 billion tonnes. The water table has dropped dramatically in many areas and this is one of main problems Indian agriculture faces today.
Thakkar identifies four urgent policy measures: “Ensure that our old water recharge systems are sustained and enhanced, develop new recharge systems and harvest water where it falls, regulate groundwater use and, lastly, massively promote conservation methods like drip irrigation and rice intensification.”
Shah, who has been asked by the Prime Minister to write a paper for the National Development Council on a holistic water policy, says it's possible for agriculture to grow even as water use falls. “In Australia, water consumption in agriculture has reduced by 30% in the past 20 years. If they can do it, so can we,” he says.
But for that to happen, water policy has to become participatory. “The irrigation department, which is managed by civil engineers, needs to recruit people managers who understand local needs and sentiments,” concludes Shah.
It will make all the difference to a thirsty nation and parched fields.
TOTAL AREA IRRIGATED BY CANALS 1991-92: 17.8 mn hectares 2006-07: 16.8 mn hectares Amount spent on irrigation projects from 1991-92 to 2006-07: Rs 1.3 lakh crore
INFLATION IN IRRIGATION Nagarjunasagar project (AP) Original cost (pre-fifth Plan):
Rs 91.12cr Latest estimates*: Rs 1,184cr Increase: 1299%
Western Kosi canal (Bihar) Original cost: Rs 13.49cr Latest estimates: Rs 904cr Increase: 6701%
Barnar (Bihar) Original cost (in seventh Plan): Rs 8.03cr Latest estimates*: Rs 216.23cr Increase: 2689%
- All ‘latest estimates’ as on 2003, according to Planning Commission document
Monsoon cycle
The Times of India , Jun 02 2015
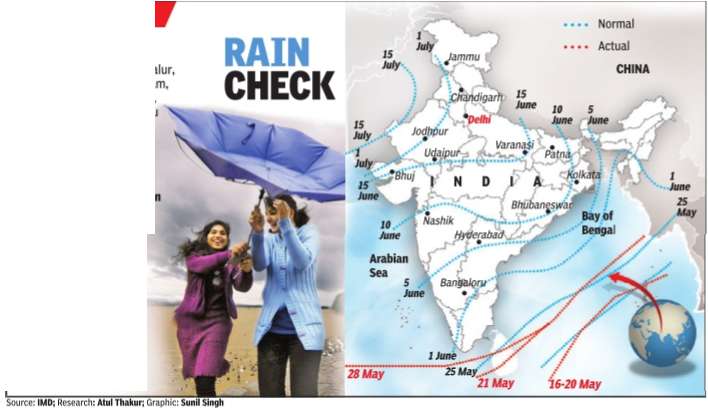
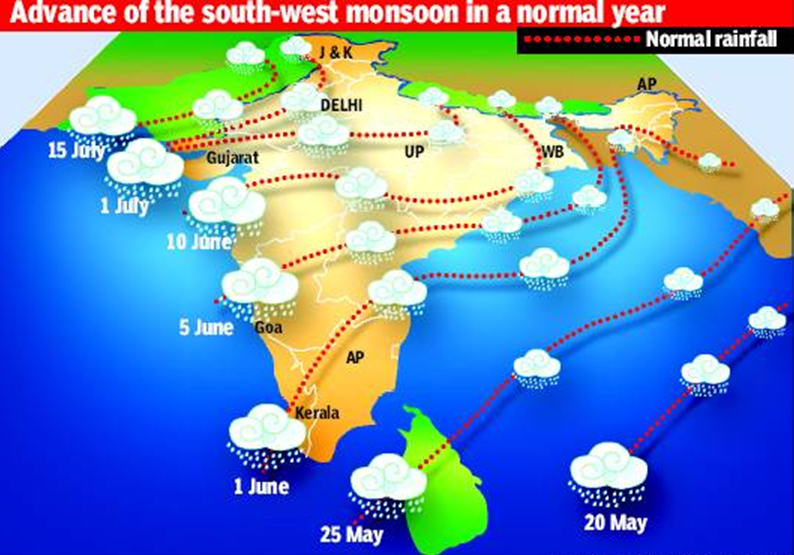
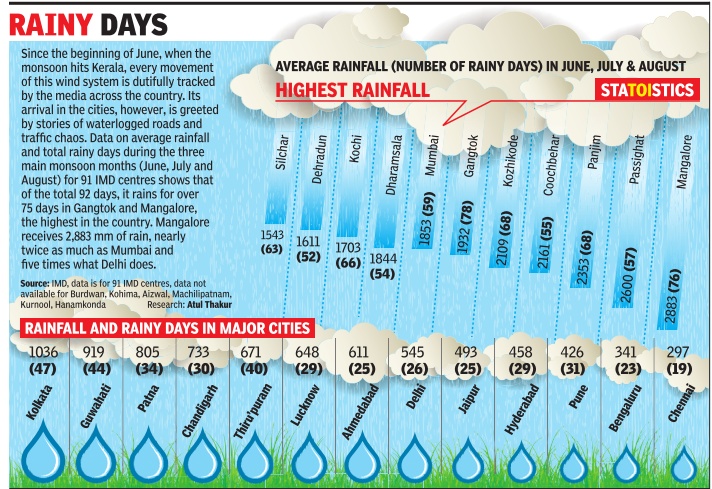
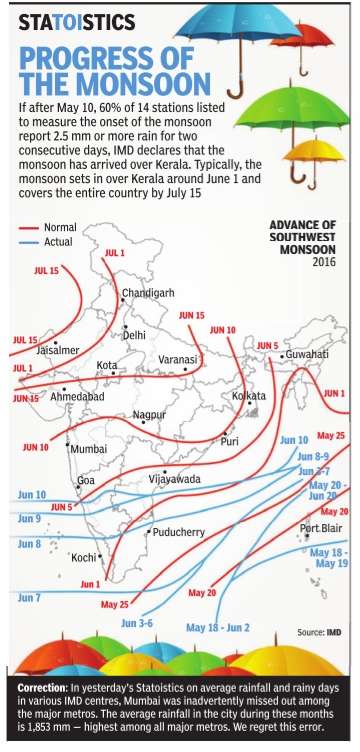
If after May 10, 60% of 14 stations -Minicoy, Amini, Thiruvananthapuram, Punalur, Kollam, Allapuzha, Kottayam, Kochi, Thrissur, Kozhikode, Thalassery, Kannur, Kudulu and Mangalore -report rainfall of 2.5 mm or more for two consecutive days, the onset of the monsoon is declared on the second day. Normally, the monsoon sets in over Kerala around June 1 and then advances northwards. By June 5, it goes past half of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh and crosses Maharashtra by the 10th.It covers significant portions of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh by June 15 and the entire country by June-end.
Monsoon break
A monsoon break — a period when rain activity comes to a stop in most of central India, the region where the monsoon trough is formed — is a common occurrence during the season. “The monsoon has been active without a break since mid-June. This does not happen often and is a reason why the rains were higher than the predicted 101% of LPA for July,” said D Sivananda Pai, IMD’s lead monsoon forecaster. (By Amit Bhattacharya)
Monsoons: date of arrival in various parts of India
See accompanying chart for Delhi
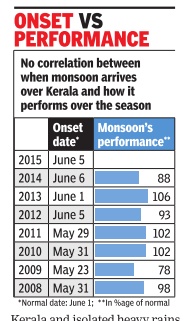
Years in which the monsoon arrived early
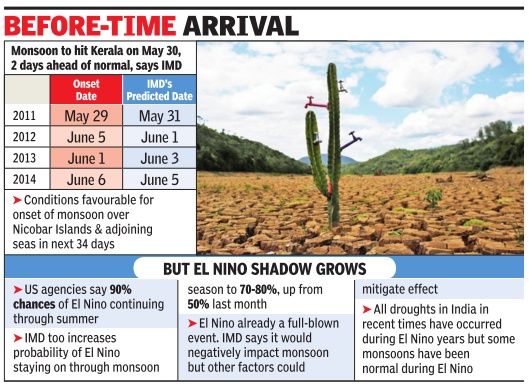

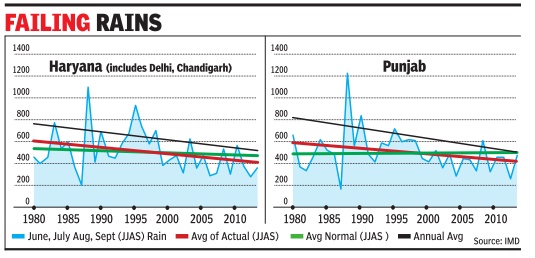
Monsoons in Punjab, Haryana
16-year trend of poor monsoon in Punjab, Haryana
Amit Bhattacharya New Delhi The Times of India Sep 22 2014
India's bread basket states of Punjab and Haryana received just around half the normal rainfall this monsoon season. But more worryingly , this year's rain deficit is not an isolated event. The two key agricultural states have been getting below par rainfall for the past 16 years.
Met department figures reveal Punjab has seen above normal monsoon rainfall in just two years since 1999. The last time that happened was seven monsoons ago, in 2008.The stats are similar for Haryana, where rains have been above normal in just four of the last 16 monsoons.
Experts are divided over why rains have been consistently failing in the region but the trend has dire implications for agriculture, which relies heavily on groundwater. The two states are among the most exploited regions in the world for groundwater.
Deficient rains add another dimension to the crisis.Groundwater mainly de pends on rainfall for recharge. So, less rain means less groundwater availability .A failed monsoon also means farmers draw more ground water to irrigate their crops, particularly paddy , accelerating the fall of the water table.
At TOI's request, Prof Krishna AchutaRao from IIT Delhi's Centre for Atmospheric Sciences plotted the annual and seasonal rainfall in the two states since 1980.The rain stats were obtained from the India Meteorological Department. A linear graph reveals a disturbing trend of decreasing rains in the bread basket of India. It shows average annual rainfall in Punjab falling during this period from just over 800mm in 1980 to less than 600mm in 2014 — a drop of roughly 200mm. Haryana’s annual average shows a similar drop, from around 780mm in 1980 to less than 580mm at present.
For monsoon season rainfall, Punjab has seen a drop of nearly 120mm, from an average of around 600mm in 1980 to roughly 480mm this year.
In Haryana, it’s down from more than 600mm to around 470mm during the same 35year period.
“The long term decrease in rainfall is apparent from the graph,” says AchutaRao, “although the rain statistics for the 1980s show very high variation.” But what’s not so apparent is the cause of the decline.
D Sivananda Pai, head of long range forecasting at IMD Pune, believes the drop is part of natural variability which will get reversed in time.
“Indian monsoon is passing through a low rainfall epoch since the 1990s. The drop in rainfall in this region could be part of that phenom enon,“ says Pai.
The story may not be that straightforward, says AchutaRao, who is coordinating multi-agency research into the Indian monsoon.
2016
June 2016: 11% Monsoon deficit
The Times of India, July 01, 2016
Amit Bhattacharya
11% monsoon deficit in June
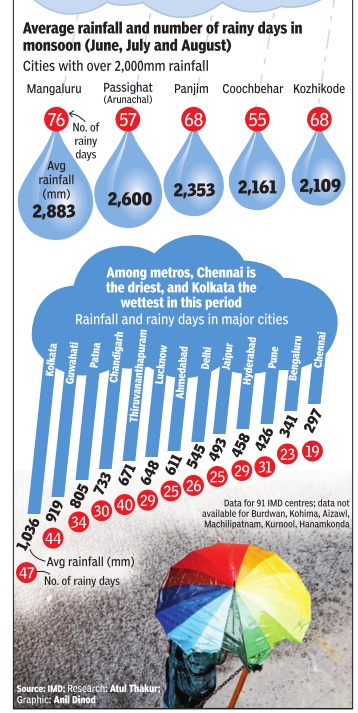
Monsoon remained slightly below expectations in the first month of the rainy season as June ended with a countrywide deficit of 11%, mainly on account of a delayed onset. Despite the deficit, however, rains have been in the normal to excess range in around two-thirds of India's 36 meteorological subdivisions. “The deficit in June was mainly due to the eight-day delay in monsoon's onset. It progressed well after that but did not perform as expected in central India.But the shortfall should be made up in July ,“ said D Sivananda Pai, lead monsoon forecaster at the India Meteorological Department.
The Met department expects rains to pick up in July , the most crucial month of the season for kharif sowing.Monsoon's performance in July is also important for water recharge as it accounts for almost a third of the total seasonal rainfall. By contrast, June normally gets only around 18% of the total monsoon rains.
“The monsoon hit the country only on June 8. So, we have got just about three weeks of monsoon rains so far. By that measure, an 11% shortfall is well within range,“ said B P Yadav, director, IMD. Among the meteorological regions of the country , south India received the best rain bounty , with 22% excess rains in June.Although the monsoon is yet to arrive in many parts of northwest India, the region had just a2.4% rain shortfall because of fairly good pre-monsoon showers in states such as Punjab.
The highest shortfall was in east and northeast India, where June ended with a 27.3% deficit. The performance wasn't totally unexpected because the region is predicted to receive less rains this year.
The region where monsoon has been more or less disappointing is central India, which had an 18.2% deficit in June. Except for Konkan and Goa, Marathwada and west Madhya Pradesh, rainfall has been less than average in all subdivisions of the region.
While Odisha and east MP are expected to get rains in the next days, other subdivisions in the region where the deficit is high -Gujarat and Madhya Maharashtra -may have to wait a few more days for good rainfall, Met officials said.These areas too would get good monsoon showers in July , they added. “In the next few days, monsoon activity is likely to be concentrated in northwest India and adjoining parts of central India. We expect monsoon to hit Delhi, Haryana, Punjab and more parts of UP and Rajasthan in the next two-three days,“ said Yadav.
Deficit hampers kharif sowing
The Times of India, Jul 02 2016
Vishwa Mohan
Deficit rainfall hampers kharif sowing in June 2016
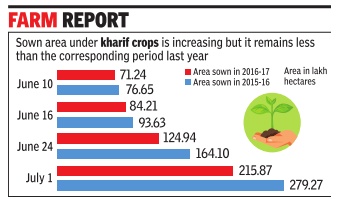
Deficit monsoon rains in June has affected the overall kharif sowing operation in the month, keeping the sown area low as compared to the corresponding period last year but the area under paddy has shown improvement for the first time this season as compared to 2015-16. Kharif sown area data, released by the agriculture ministry on Friday , put the total area at 215.87 lakh hectare as on July 1 as compared to 279.27 lakh hectare at this time last year. However, the paddy recorded marginal increase by covering 47.77 lakh hectare so far this year as compared to 47.62 lakh hectare in 2015-16.
Sowing operations, which remained sluggish during the first three weeks after the onset of monsoon, picked up pace in the past one week due to good rains in south India -covering over 90 lakh hectare under various crops in the past seven days.
“Though the area under kharif crops, including pulses, oilseeds and cotton, is still less than the area during the corresponding period last year due to 11% of deficit rainfall in June, the sowing operation will further pick up in July and hopefully cross the last year's sown area by the end of this month“, said an official.
Areas under pulses and oilseeds will, however, continue to be a major concern.Sown area under oilseeds stands at merely 28.71 lakh hectare as on Friday as compared to 54.24 lakh hectare at this time last year. Similarly, cotton too recorded poor sowing as its sown area stands at 30.59 lakh hectare as compared to 60.16 lakh hectare in the 2015-16.
The availability of water in the country's 91 major reservoirs has marginally increased from 23.20 billion cubic meter (BCM) on June 23 to 23.94 BCM as on June 30 despite constant withdrawal of water from them.
According to the Central Water Commission, Rajasthan, Tripura and Andhra Pradesh have better storage in 2016 than the corresponding period in 2015.
See also
India Meteorological Department