Mumbai: Wildlife (fauna)
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Mammals
2019?: 96% mammalian species show decline
Vaishnavi Chandrashekhar, November 15, 2020: The Times of India
From: Vaishnavi Chandrashekhar, November 15, 2020: The Times of India
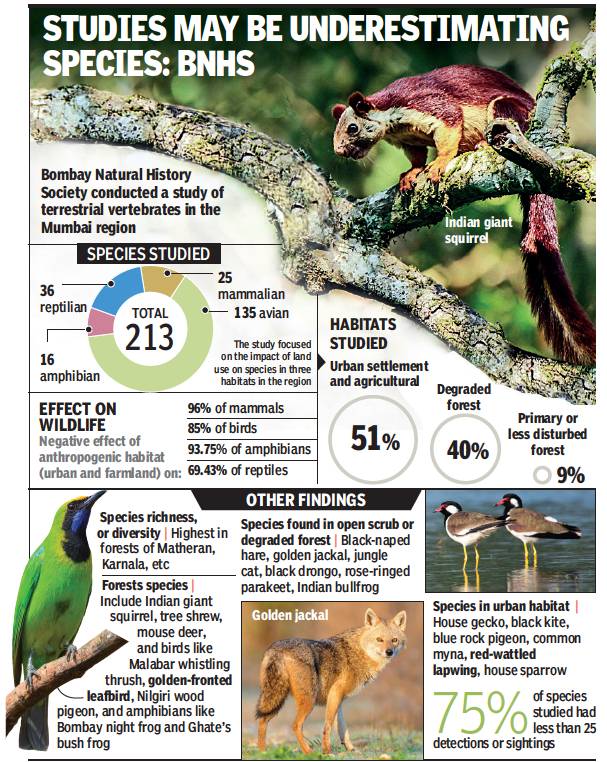
New research from the Bombay Natural History Society highlights the adverse impact of urbanisation on wildlife in the Mumbai Metropolitan Region (MMR), while also suggesting that previous studies may have underestimated species numbers.
Of 213 species studied in the region, researchers found that among animals, 96% of mammals, 85% of birds, 93.75% of amphibians, and 69.43% of reptiles showed a decline with urban and agricultural land cover, compared to scrub and forest habitats.
Still, the region holds “astonishing” species diversity that needs to be preserved, the study said. Researchers used a model to estimate species richness and abundance and compared them to studies on the ground.
The estimates were higher than the numbers from the ground sampling, especially for reptiles and birds. That is because sightings are often dependent on environmental conditions such as time of day and weather. Factoring in “detection probability”, as this study did, is thus important for species monitoring and conservation management, said researchers. “A lot of studies may be underestimating species,” said Sameer Bajaru, assistant curator at BNHS, who conducted the study with senior scientist Deepak Apte and others. The study focused on the impact of land use on mammals, birds, amphibians, and reptiles in three habitats in the region: urban and agriculture; scrub and degraded forest; and intact forest. Not surprisingly, they found species diversity was highest in forest tracts like Matheran and Karnala and lowest in urban settlements.
Interestingly, species prevalence was also high in scrub and degraded forest areas that lie between city and forest (such as the hilly areas near Khargar or the fringes of the Karnala sanctuary). This is because some species are “generalists” that can eat a variety of food, and thus adapt to a more disturbed habitat, said researchers. They include mammals like the golden jackal, birds like the black drongo, and reptiles like Murray’s house gecko. “These species are tolerant to human disturbances,” said Bajaru.
Another reason: scrub and degraded forest comprise a large part of MMR now. “High prevalence of species preferring degraded forest cover may indicate the degraded nature of this landscape,” the study said.
Even the forests of Matheran, for instance, have deteriorated over the centuries. Timber extraction in the 17th and 18th centuries followed by development of the hill station transformed the area from a semi-evergreen and moist deciduous forest into a scrubby, dry deciduous and fire-prone forest landscape, researchers noted. “Priority should be given to the conservation of remaining primary habitats such as Prabalgad, Malanggad, Manikad, Karnala, and Matheran, as well as restoring degraded habitats with the help of local people,” said Bajaru.