Rape in India: longer- term statistics, analyses
Contents |
Rapes in India
This is a collection of newspaper articles selected for the excellence of their content. |
‘Stranger rape’
(Rapes committed by men who were strangers to the victim)
‘Stranger rape’ goes over 10%
Rukmini Shrinivasan TIG 2013/06/15
New Delhi: Was 2012 the most dangerous year for women in the capital in the recent past? One statistic would seem to suggest so: the proportion of rapes committed by men who were strangers to the victim rose above 2% for the first time in five years to cross 10%.
‘Stranger rape’ of the type that occurred in Delhi on December 16 last year tends to form the basis for women’s perceptions of public safety, but is relatively rare. Rape in India, as in the rest of the world, remains overwhelmingly a crime committed by persons known to the victim. Atthe all-India level,lessthan 2% – 453 in all — of the nearly 25,000 rapes registered during the year 2012 were committed by strangers, data released on Wednesday by the National Crime Records Bureau show. In Madhya Pradesh, the state that consistently records the largest number of rapes, all of the 3,425 assaultswereby persons known to the victim.
In Delhi too, the proportion of stranger rapes has hovered close to the 2% mark over the last five years. However 2012 NCRB data for Delhi show that 63 of the 585 rapes that were committed in 2012, or nearly 11%,wereby strangers to the victim.
While data for Delhi have been stable over the previous years, large swings between years for a few other cities raise some doubts over the accuracy of NCRB data. Bangalore is the most extreme example of this: the proportion of ‘stranger rapes’ in the southern city swung from 77% to 0% between two consecutive years, 2009 and 2010. Karnataka’s crime statistics chief hadearlier toldTOIthat it was probably a problem with the numbers. “In Bangalore and Karnataka, as in the rest of the country, rape by strangers is a very small part of total rapes,’ Praveen Sood, additional DGP, Karnataka State Crime Records Bureau, had told TOI. A spokesperson for the Delhi police said he could not comment without the exact numbers in front of him.
It’s too soon to draw conclusions based on one year’s data, agreedKalpana Vishwanath of the Delhi-based women’s rights organization Jagori. “It’s undoubtedly a fact that there is crime against women, but there also seems to be some slight increase in the last six months. There is greater family and community supportto girlswhowantto speak out, and a little less of blaming the victim,” Vishwanath said.
Victims of rape also tend to be younger in cities than in the rest of the India, more so in Delhi. In the cities for which NCRB provides data, justover half the rape victims were aged 18 or less. The corresponding all-India figure was just 36.5%. In Delhi, 329 of the 585 victimes, or about 56.2% were aged 18 or less.
Rapes in India's 5 biggest cities
More rapes in Delhi in 2012 than 4 metros put together
Dwaipayan Ghosh TNN 2013/06/14
New Delhi: Delhi’s shame continues. The National Crime Records Bureau’s report for 2012 iterates through statistics what every woman in the city knows by experience — that it remains the most unsafe for women among 88 important cities of India.
With 5,959 cases of crime against women registered last year, Delhi accounted for a staggering 14.88% of all women-related crimes reported from these 88 cities. No other city even came close to matching Delhi’s notorious record.
Bangalore was a distant second, with a share of 6.18% of all crimes against women in urban India. Next came Kolkata (5.66%) and then Mumbai (4.86%).
No crime reveals Delhi’s violence towards women better than rape. The number of rapes in the capital last year (706) was more than those reported in four other metros — Mumbai, Kolkata, Bangalore and Chennai (484) — put together. The staggeringly high figure can’t be explained by the capital’s sprawl. For, the female population of Delhi is 75.76 lakh, lower than Mumbai (85.20 lakh) and not much higher than Kolkata (67.93 lakh).
Child rapes/ Sexual assault on children
‘336% spurt in child rape cases’
By TIMES NEWS NETWORK, The Times of India , 22 April 2013 The Times of India
Even as the national Capital protests against the heinous nature of the five-year-old child’s rape, an independent report, based on National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) figures, shows that India is no country for children.
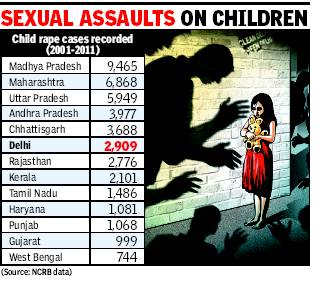
The report says a total of 48,338 child rape cases was recorded between 2001 and 2011, and the nation saw an increase of 336% of such cases from 2001 (2,113) to 2011 (7,112).
The report by the Asian Centre for Human Rights (ACHR), however, warns that this is only the “tip of the iceberg” as the large majority of child rape cases are not reported to police while children regularly become victims of other forms of sexual assault too. Madhya Pradesh recorded the highest number of child rape cases with 9,465 cases between 2001 and 2011, followed by Maharashtra (6,868), Uttar Pradesh (5,949) and Andhra Pradesh (3,977). Delhi, which reported 2,909 cases, ranked sixth on the list.
The report, “India’s Hell Holes: Child Sexual Assault in Juvenile Justice Homes”, which has been submitted to the UN Special Rapporteur on Violence against Women, says that many of the cases take place in juvenile homes.
“It will not be an understatement to state that juvenile justice homes, established to provide care and protection as well as reintegration, rehabilitation and restoration of the juveniles in conflict with law and children in need of care and protection, have become India’s hell holes where inmates are subjected to sexual assault and exploitation, torture and ill-treatment apart from being forced to live in inhuman conditions. The girls remain the most vulnerable. It matters little whether the juvenile justice homes are situated in Delhi or in mofussil towns,” said Suhas Chakma, director, ACHR.
The 56-page report also highlights 39 cases of systematic and often repeated sexual assault on children in juvenile justice homes. Out of the 39 cases, 11 were reported from governmentrun juvenile justice homes, while in one case a CWC member was accused of sexual harassment during counselling sessions.
The remaining 27 cases were reported from private or NGO-run juvenile justice homes.
Compensation for rape victims
‘Compensate rape victims’
TIMES NEWS NETWORK 25/04/2013
New Delhi:Victims of sexual assault need a completely different treatment than what is meted out to them by society and state authorities, the Supreme Court has said and ordered all states to implement its 18-year-old directive.
The 1995 judgment of the apex court had directed setting up of Criminal Injuries Compensation Board and said it could take up the task of determining the amount to be paid by the offender to rape victims who incur huge financial loss apart from carrying the unwarranted stigma.
“The board shall take into account the pain, suffering and shock as well as loss of earnings due to pregnancy and the expenses of child birth if this occurred as a result of rape,” the court has said in Delhi Domestic Working Women’s Forum case.
Reiterating the guidelines, a bench of Justices B S Chauhan and F M I Kaliffulla said, “Undoubtedly any direction issued by this court is binding on all the courts and all civil authorities within the territory of India.” While dealing with a rape case from Madhya Pradesh, the bench accepted arguments of Vibha Datta Makhija and upheld the HC’s decision to reverse the acquittal of one Dilip who was accused of rape.
The lack of sensitivity shown towards the rape victim by the prosecution and the trial court anguished the bench and said that the 18-year-old directive asking the prosecution and states and Justices Chauhan and Kalifulla decided to add more norms to the guidelines.