Restaurants: India
Contents |
S.Pelligrino’s Asian top 50, 2013
7 Indian restaurants among Asia’s top 50 By ANI, Feb 27, 2013 ANI
Seven restaurants in India were included in S.Pelligrino’s list of the top 50 restaurants of Asia for the year 2013. These restaurants, with their ranks, are:
17. Dum Pukht (New Delhi)
20. Wasabi by Morimoto (Mumbai)
26. Bukhara (New Delhi)
28. Indigo (Mumbai)
30. Varq (New Delhi)
41. Indian Accent (New Delhi)
44. Karavalli (Bangalore, India)
Regional and other demographic preferences
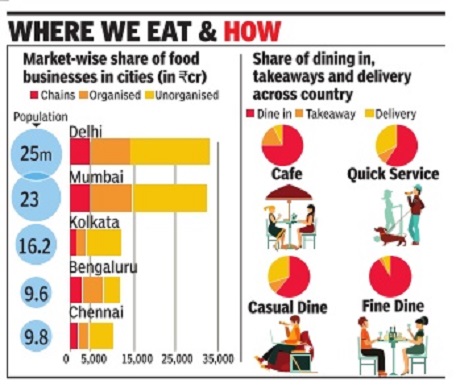
Delhi: fast food chains; Mumbai: restaurants
Eating out is arguably the biggest social activi ty today for Indians across metros, but their choice of venue varies depending on the city . Delhiites spend more money at fast food chains, cafes and street food stalls while Mumbaikars show a preference for restaurants, both standalone and inside hotels.
The bulk of the food business in India is still in the unorganised sector, according to a survey done by the National Restaurants Association of India (NRAI), but the urge to experience novel cuisines is driving different formats in the organised sector at a brisk pace.
Mumbai has the highest share in the organised market -which mainly accounts for standalone restaurants -followed by Delhi, Bengaluru and Pune (see graphic). For all other formats ranging from quick service restaurants (QSRs) such as McDonald's and Subway , to casual dine restaurants (CDRs) like Pizza Hut and Barbeque Nation and fine dining chains, it is the na tional capital region that provides the maximum patronage. In the unorganised segment too, Delhi comes first, followed by Mumbai, Kolkata, Hyderabad and Chennai respectively. In Bengaluru, notably , or ganized outlets such as chains and restaurants enjoy a bigger slice of the overall pie as compared to the unorganized sector. But in Kolkata, business from streetside stalls and households is more than twice as big as the organized segment. Clearly , eating out in the City of Joy is an experience far different from the one in the Silicon Valley of India.
These are the findings in the India Food Service Report 2016, considered the most comprehensive study done on the trade in recent years. Among tier-II cities, it says, Jaipur, Lucknow, Surat, Nagpur, Kanpur, Indore and Goa have the highest market shares.
Currently , the Indian food market is worth Rs 3,09,110 crore in all and is expected to reach Rs 4,98,130 crore by 2021. While share of restaurants (organized) and chains such as Domino's, Café Coffee Day , McDonald's and Barbeque Nation will go up over the next five years, the share of the unorganised sector will decline.
The one unappetizing fact that stands out though is that the per capita spend on food services by India's urban population is still less than one-tenth of the US and less than one-seventh of that in China. Speaking of the food industry's concerns, Riyaaz Amlani, President, NRAI said the sector needed more incentives and deregulation to thrive. “We have to go to several departments for paperwork and get a plethora of licenses and NOCs issued.“
Corporatised street food, traditional snacks

The Times of India, Nov 13 2015 Anand J, Shalina Pillai & Ranjani Ayyar I
First-gen foodpreneurs pack OLD VADA IN NEW PAV
Barring a Haldiram or a Bikanervala, most desi snacks and beverages have stayed in the unorganized sector, sold by vendors using ancient, unstandardized methods.
Several entrepreneurs are trying to change that by using global practices to sell Indian street food
Green mangoes are hard.
And no one knows this better than Neeraj Kakkar, co-founder of Paperboat.
Hector Beverages, the makers of Paperboat, has been selling its aam panna drink (green mango juice flavoured with roasted masalas) for a while. Green mangoes are notoriously hard to process because they are tough, and Kakkar says his team had to innovate extensively to make Paperboat's aam panna flavour taste like its fresh, home-made version.
“So our biggest challenge is today our biggest advantage. Nobody has done this kind of thing before and it is difficult to replicate,“ says Kakkar. Paperboat now boasts an array of 10 distinct beverages including jaljeera, golgappe, kokum and chilled rasam. Many more innovative products are under development including coconut water and the juice of purple carrots. The company, which opened its biggest factory in Mysuru a few months ago, works with agricultural universities and farmers across the country to figure out best practices, as they break new ground on products.
Across the country , entrepreneurs are picking up traditional Indian food and beverage products to challenge Western imports like colas and burgers. In some cases they are reimagining the products and offering innovative variants. Mr & Mrs Idli and Idli Factory offer exotic stuff like Idli Manchurian, Kanchivaram Idli and Punjabi Idli. Faaso's, with funding from Sequoia and Lightbox, and Kaati Zone do a variety of Indian rolls, including Cheesy Corn Salsa and Chicken Mushroom.
In other cases, they are using technology to make the products at scale and sell them around the country , the way McDon ald's and KFC do. Ammi's Biryani, with funding from Saif Partners, is doing that with biryani, as is the Hyderabad-based chain Paradise which is opening outlets in cities like Bengaluru at a fast clip. At Paradise, the self-service counter is clearly modelled after the McDonald's and Burger Kings of the world, with combos and packages and easy-to-select options.Similarly, Jumboking pioneered the organized vada pav business, and was quickly followed by Goli Vada Pav, which has received funds from Ventureast.
Dheeraj Gupta of Mumbai initially dabbled in the Indian mithai (sweet) market. But the technology needed to keep sweets fresh was expensive and since the venture wasn't very profitable, Gupta was finding the going difficult. He looked at India's streets and realized how disorganized the vada pav business was. “Vada pav was the largest selling snack in Mumbai but no one had thought of organizing that segment,“ he says. He borrowed Rs 2 lakh from his father and founded Jumboking.The venture is about to open its 100th store and is present across the top eight cities in the country. The company charges a 30% premium on vada pavs compared to the street pavs. It also focussed on the bread size, weight and size of the patty and eliminated wastage. The patties needed instant quick freezing at minus 18 degrees centigrade, and with hygiene a priority for Gupta, he invested in the required technology .
Hygiene is a big focus for most, because for many middle class Indians today, that's the concern they have about food offerings from the unorganized segment. “Tea is available in all corners of this country but our focus is the white collar corporate employee in the top seven cities who are conscious about cleanliness and consistency,“ says Amuleek Singh Bijral, founder of Chai Point.
Most tea joints in India end up being smoking joints, which discourages nonsmoking customers. Chai Point does not allow smoking and so enjoys a broader clientele. The average price of a glass of tea at Chai Point is less than Rs 20, less than a fourth of the price at leading cafe chains, and is designed to drive volumes.The company's 50 outlets sells more than three million glasses a month.
Hygiene, comfort and innovation is also the focus of Chennai's Idli Factory .“My biggest driver is to create food for travelling, which means comfort food that is well-packaged and easy to carry,“ says R U Srinivas. The company's flagship product is its `Madras bars' which are idlis shaped like bars coated with powders such as milagai podi, garlic podi and curry leaf podi. Srinivas researched and tested 300 different batters before arriving at the best combination of rices and dal to create idlis that would remain soft and fresh even after they are cold.
Arvind Singhal, chairman and MD of retail consultancy Technopak, says native food offers great opportunity in terms of revenue. “Indian food has long been neglected,“ he says, and appreciates startups like Chaayos and Chai Point that have leveraged Indian tea rather than going after coffee, like many others.
Singhal also notes that many Indian startups in this space fail because they complicate their menus by adding too many different items. Keeping it simple helps with handling the supply chain, quality assurance and faster service across all outlets, and in keeping prices low.
Bijral of Chai Point agrees. While expanding his food variety option looks enticing -currently it contributes 25% of topline -Bijral wants to reduce it to 20% and focus even more on tea. “Let others sell food,“ he says. Idli Factory also has a skeletal menu, and Srinivas intends to keep it that way. So does Jumboking's Gupta, who notes that multinational food chains too stick to a narrow menu but offer different versions of that menu. “Once this mindset (to complicate menus) changes, it will benefit a lot of entrepreneurs,“ he says.
But that strategy could have its limitations too. When Mohan Kumar, partner with Norwest Venture Partners, received a request from a food startup for investment, he analysed a number of companies in the space. He found that some 25 companies in the space had touched revenues of Rs 200-300 crore, but then stopped growing. “Probably there aren't enough categories to scale up and these companies tend to get acquired by bigger ones. Big Indian players like ITC and Marico understand the market well. Some of the MNC competition too could catch up,“ he says.
Jacob Kurian, partner at private equity fund New Silk Route, which has invested in Bengaluru-based Vasudev Adigas, a south Indian food retail chain, feels that Indian food businesses tend not to grow beyond the local area as the promoters tend to be contented at a certain size.One exception, he notes, is Haldiram.“The skill set needed to grow till Rs 200 crore and to grow beyond that are different,“ he says.
Kurian also notes that unlike the earlier family-owned Indian businesses, those like Paperboat and Chai Point are not family businesses and don't have legacy issues. “Let these guys reach around Rs 200 crore and then we will see,“ he says. That could happen if the brands can go into smaller towns or even global. Paperboat's Kakkar is not sure if his drinks can be as popular as Coke in small towns. But he notes with some satisfaction: “Cola sales are declining globally.“
Service charge
Restaurants take advantage of non-binding rules
Despite the government's repeated stand that service charge is optional, the fact that eateries across India include this fee in bills of consumers has exposed why central advisories lack bite. Advisories are not binding on the stakeholders and states hardly pay heed to such stands of the Centre.
While consumer affairs ministry officials admit to their advisories falling in deaf ears, they have no other option but to create awareness. “In western countries, customers are asked how much service charge they would like to pay since it's a tip. But here, the eateries neither ask nor do they mention how this optional charge is linked to the quality of service. ,“ said an official.
The official said that tho ugh the eateries' associations agree with the Centre's stance, none of their members display prominently this provision in their menu.
Consumer activists said that rather than completing formalities by issuing advisories, the government must come out with practical solutions. “Why can't they make it mandatory that eateries leave the service charge section blank thereby giving the option to customers to pay or not? At present, consumers have only option of taking such cases to consumer forums, which is a lengthy process,“ asked Amit Agrawal, an activist.
TOI on November 30 had first reported that the consumer affairs ministry had informed the Parliament that paying service charge was optional and levying such an amount without the knowledge of consumers was “unfair trade practice“. An official said they were hopeful of the state labour department swinging to action since in many cases the service charge collected by eateries might not be even passed on to their workers.