Road accidents: India
(→Soldiers: Road accidents: Peacetime killer among soldiers) |
(→Two-wheelers, accidents involving) |
||
| Line 325: | Line 325: | ||
Two-wheelers claim 94 lives a day while trucks and lorries account for 66 fatalities, according to the NCRB report for 2013. Though overall, there is marginal reduction in total number of people killed on roads last year in comparison to 2012, these two indicators signal how there is little regulation or enforcement of road safety measures. | Two-wheelers claim 94 lives a day while trucks and lorries account for 66 fatalities, according to the NCRB report for 2013. Though overall, there is marginal reduction in total number of people killed on roads last year in comparison to 2012, these two indicators signal how there is little regulation or enforcement of road safety measures. | ||
| − | + | ==Unlicensed drivers, accidents by: 2012-14: rise of 54%== | |
[[File: road accidents .jpg| Unlicensed and underage Indian drivers in 2012-14; Graphic courtesy: [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Accidents-by-licence-less-drivers-jumped-54-in-21122015001055 ''The Times of India''] Dec 21 2015|frame|500px]] | [[File: road accidents .jpg| Unlicensed and underage Indian drivers in 2012-14; Graphic courtesy: [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Accidents-by-licence-less-drivers-jumped-54-in-21122015001055 ''The Times of India''] Dec 21 2015|frame|500px]] | ||
| Line 345: | Line 345: | ||
Interestingly, details sub mitted by the road transport ministry to Parliament last week said Delhi traffic police did not provide details on either count. | Interestingly, details sub mitted by the road transport ministry to Parliament last week said Delhi traffic police did not provide details on either count. | ||
| − | + | ==Women drivers== | |
[http://epaper.timesofindia.com/Default/welcome.asp?skin=pastissues2&QS=skin%3Dpastissues2%26enter%3DLowLevel The Times of India] | [http://epaper.timesofindia.com/Default/welcome.asp?skin=pastissues2&QS=skin%3Dpastissues2%26enter%3DLowLevel The Times of India] | ||
| Line 388: | Line 388: | ||
Bihar, meanwhile, accounted for the most number of arrests of women for causing death due to negligence (52) in 2014. Uttar Pradesh is second with 49 arrests, followed by West Bengal (42), Tamil Nadu (24) and Karnataka (21). This is the first time rash driving cases have been classified separately in the NCRB's report. NCRB director general Archana Ramasundaram, in her cover note for the 2014 report, stated that like the earlier editions, this report contains detailed information on cognisable crimes, and disposal of crimes by police and courts, etc, but has more chapters. Mumbai joint commis sioner of police (traffic) Milind Bharambe said most accidents caused by reckless driving can be prevented simply by following rules. | Bihar, meanwhile, accounted for the most number of arrests of women for causing death due to negligence (52) in 2014. Uttar Pradesh is second with 49 arrests, followed by West Bengal (42), Tamil Nadu (24) and Karnataka (21). This is the first time rash driving cases have been classified separately in the NCRB's report. NCRB director general Archana Ramasundaram, in her cover note for the 2014 report, stated that like the earlier editions, this report contains detailed information on cognisable crimes, and disposal of crimes by police and courts, etc, but has more chapters. Mumbai joint commis sioner of police (traffic) Milind Bharambe said most accidents caused by reckless driving can be prevented simply by following rules. | ||
| + | |||
=Drunk driving= | =Drunk driving= | ||
==Bar the drunk from driving: Bombay HC== | ==Bar the drunk from driving: Bombay HC== | ||
Revision as of 10:19, 7 October 2016

This is a collection of newspaper articles selected for the excellence of their content. |
Good Samaritans
Good Samaritan SOPs
The Times of India, Jan 27 2016
Centre finally notifies good Samaritan SOPs for cops
The government has notified a standard operating procedure (SOP) on how to `respectfully' deal with good Samaritans and bystanders who rush road crash victims to hospitals or inform police. The SOP says no such person must be asked to reveal personal details, including full name, address and phone number unless he she volunteers to become an eyewitness. “In case a good Samaritan chooses to be a witness, his examination by the investigating officer shall, as far as possible, be conducted at a time and place of his conveni ence such as his place of residence r business, and the investigation officer shall be dressed in plain clothes, unless the good Samaritan chooses to visit the police station,“ says the SOP notified by the road transport ministry . On January 10, TOI was the first to report that the ministry had decided to notify the norms within a fortnight following the Supreme Court direction to the Centre to submit the steps taken to protect the good Samaritans.
The SOP also specifies that in case a good Samaritan choses to visit the police station, he shall be examined in a single sitting in a “reasonable and time-bound manner“.Even it will be the responsibility of the investigating officer to arrange for an interpreter to interact with the person, if he speaks a language the IO doesn't understand.
SOPs after Supreme Court’s 2016 order
Dipak Dash, Samaritan witness can be quizzed only once, Oct 06 2016 : The Times of India
Police can call a good Samaritan for examination only once if he opts to be a witness in a road accident. In a recent notification, the road transport ministry has said in case a statement is to be recorded, it should be done in a single examination.
Complying with the direction of the Supreme Court order of March, the ministry has added the new provision in the standard operating procedures (SOP) for dealing with those who either inform police about road crashes or rush the injured to hospital. “The affidavit of good Samaritan, if filed, shall be treated as complete statement by police while conducting the investigation,“ the notification said. On an average, 400 people lost their lives in road crashes every day in 2015. According to the government's own estimates, half of these deaths can be prevented by providing quick medical care within the first hour of a crash. A study by Save Life Foundation had flagged how nearly threefourth of bystanders are unlikely to help road crash victims and almost nine of 10 would cite fear of legal hassles and repeated questioning by police. A ministry official said this provision will help end the fear of bystanders.
The extent and nature of the problem
Accidents, road: all India
1 death every 4.5 min in road accidents ‘In 2008, Country Witnessed 4.85L Road Accidents In Which 1.2L People Died’ Dipak Kumar Dash | TNN
New Delhi: Indian roads witness one road mishap every minute and one death in accidents every four and a half minutes, according to the latest report of the road, transport and highways ministry.
The report, which was released this week by the transport research wing of the ministry, said that in 2008, the country witnessed 4.85 lakh road accidents in which 1.2 lakh people lost their lives. And more than half of the road accident victims are in the age group of 25 and 65 years, the ‘key wage earning and child raising age group’.
Similarly, the report estimates that these road accidents left 5.2 lakh people injured.
The annual road accident document also points to high fatalities — almost 65% of the all road deaths — on national and state highways in comparison to other roads. In 2008, while 42,670 persons died on NHs, the state highways claimed 34,081 lives. ‘‘The deaths are on rise despite the ministry spending more on road safety in the last six years. We are not analyzing the actual reasons behind road accidents. Had technical people with road safety expertise been in-charge of the affairs, the situation would not have slipped to this alarming level,’’ said a senior ministry official.
While in 2004-05, the ministry spent Rs 35 crore out of the allocated fund of Rs 39.7 crores, in 2008-09 it shot to Rs 54.8 crore. The report singles out fault of the drivers as the major reason of road deaths. This claimed 89,360 persons in 2008. Fault of cyclists, pedestrians, motor vehicles and bad road and weather conditions were also identified as some of the factors for fatalities on roads across the country.
However, ministry sources said that in the absence of proper investigation of road mishaps, local police put the onus of these accidents on the drivers. ‘‘The report is silent on how the governments’ failure to regulate the issuance of driving licences and lack of proper training of drivers are contributing to this high occurrence of road mishaps,’’ officials said on condition of anonymity.
Meanwhile, the ministry has set an ambitious target to bring down road deaths by 50% in the next two years. For this purpose, the budget estimate for 2010-11 has been increased to Rs 180 crore from Rs 74 crores in the previous year. RISKY ROADS Total road deaths in 2008: 1,06,591 persons Share of national highways: 42,670 persons Share of state highways: 34,081 persons People who died due to drivers’ fault: 89,360
The cost of road accidents to the nation
The Times of India, Dec 01 2015
Dipak Dash
Road crashes costing India Rs 55,000cr a yr
The cost of over nearly 4.9 lakh road traffic crashes annually in India is close to Rs 55,000 crore, road transport minister Nitin Gadkari said on Monday , while launching a joint road safety campaign by the government and a major car maker along with Bollywood actor Shah Rukh Khan. The actor called for an intense campaign like that of anti-polio or the family planning drive to reduce road crashes and fatalities. Officials said the actual cost of road traffic crashes, fatalities and injuries could be much more since no fresh study has been conducted to estimate the loss; particularly considering the fact that over 50% of dead are in the age bracket of 15 and 39. In 2014, about 1.4 lakh died in road crashes and another 4.9 lakh people were left injured.
Causes
Roads, signals (physical factors)
2015: bad roads and potholes increase deaths
The Times of India, Aug 01 2016

Dipak Dash
Bad roads killed over 10k people in 2015; 3,416 deaths due to potholes
In 2015, 10,727 people were killed in crashes caused by potholes, speed breakers and roads under repair or being constructed.Though fatalities under these categories had come down marginally from 2014, the number of people killed due to potholes rose to 3,416, from 3,039 in the previous year. Deaths caused by potholes rose seven-fold in Maharashtra, according to the surface transport ministry's road accidents report. A rise in such fatalities indicates fai lure of road-owning agencies to maintain stretches.
UP, known for its bad roads, reported an almost 50% reduction in pothole deaths compared to 2014. In Delhi, where a biker died after getting stuck in a pothole on Saturday , there were only two pothole deaths in 2015. According to data compiled by the road trans port ministry, 10,876 accidents were reported last year due to potholes across the country. “The number could be higher as we don't have a scientific data collection mechanism. Many accidents go unreported and there is no detailed investigation into causes of road deaths,“ said Ashish Kumar, former chief of the transport research wing.
Top road engineers working with government departments said until the drainage system was improved, roads would keep de veloping potholes. “Every city and town has a multiplicity of authorities and in most cases, both the sewerage and storm water drainage system are inadequate and inefficient. Drains have been covered with unauthorised construction. Any amount of repair won't work if you have stagnant water and overloaded vehicles plying on such stretches,“ a state public works department official said.
To make road owning agencies and traffic police accountable for failure on their part, the road transport ministry has finalised the Rules of Road Regulation.
2014: Deaths caused by potholes, speed breakers and humps on roads
The Times of India, Sep 14 2015

Dipak Dash
Over 11,000 killed by potholes, humps & speed breakers in 2014
4,000 died on roads under construction
Potholes and badly designed speed breakers don't just irritate drivers and damage vehicles. They actually kill. For the first time, the government recorded deaths caused by potholes, speed breakers and humps on roads. Last year, about 11,400 people died in such cases with Uttar Pradesh topping the list. Another 4,100 people were killed in crashes on stretches under repair or under construction. UP alone saw 4,455 lives being lost due to bad roads.
Other states with a high number of fatalities on these counts included Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and West Bengal.
Maharashtra registered 368 deaths in crashes due to potholes, humps and speed breakers while another 224 died on roads under repair or under construction. According to the Road Accident Report (2014), while 4,726 lives were lost in crashes due to humps, 6,672 people died in accidents caused due to potholes and speed breakers. Sources said the actual figure could be much higher since the data was not properly captured by local police while registering accidents and in many cases these are recorded as any other crash.
UP had the largest share with 4,455 lives lost in such accidents. In MP , 915 people died in crashes caused due to bad road conditions and in Bihar, the fatalities stood at 867. In a first, the government's transport research wing has used data detailing about a dozen road conditions to classify crashes, fatalities and injuries.
While poor maintenance by road-owning agencies is the main reason behind potholes, experts said there was lack of uniformity and no standard design for speed breakers on most roads. Director of Indian Academy of Highway Engineers and former director general (roads) V L Patankar said most speed breakers on internal roads were “hugely dangerous“.“None follow design, curvature and location when constructing speed breakers. In most cases, locals put up speed breakers,“ he said.
2014: Junctions with blinkers more prone to accidents than places with signals

The Times of India, Sep 06 2015
Dipak Dash
`Junctions with blinkers more prone to accidents than places with signals'
Road crashes at traffic junctions with blinker or flash lights are more fatal in comparison to similar incidences at other such intersections, including ones with no traffic signals. According to the Road Accident report on 2014, at least three persons are killed in every 10 crashes at crossings with blinkers and the number of persons injured was higher than the total number of accidents. The latest road accident report shows that though the total share of crashes at `uncontrolled' intersections is over 76%, the fatalities are less than 20%. Similarly at crossings having traffic signals and are controlled by police, the rate of fatalities is around 20%.
The trend was similar in 2013 when 4,740 persons died in 14,690 crashes at crossings with blinkers. These accidents had left 17,411 injured.According to Delhi traffic police officials, commuters hardly follow norms at crossings with blinkers, which are primarily meant for warning the drivers at a crossing to slow down and move cautiously .
The death of former rural development minister Gopinath Munde in a road crash at a crossing which was on blinker mode had prompted the Delhi traffic police to turn some of the major signals around Lutyens' Delhi into signal mode past midnight. Since May this year, they have also de ployed over 50 traffic police men from 9pm to 6am at these crossings.
Traffic safety experts said that unfortunately even road owning agencies don't follow norms while installing blink ers at crossings or merging points. In most cases, the traf fic lights are even found to be non-functional. “There is no specific data of how many permanent traffic lights are pu on blinker mode in cities and towns during the day . We have yet to go a long way to get ade quate data to find out the exact reasons behind crashes and fatalities,“ said one of them.
The report also flags the point that traffic junctions are the most accident-prone areas as about 57% of tota accidents took place at junc tions in 2014.
Other causes
Cell-/ mobile- phones
The Times of India, Aug 07 2016
Somreet Bhattacharya
Most drivers in dark about SC rule on phone use
More than threefourth of the drivers who were issued challans for talking over phone while driving were unaware of the Supreme Court ruling against it and the rest hoped they would escape the cops eye.
Seizing licences hardly acts as a deterrent for drivers who frequently abuse the ru le, the police said. According to a traffic police study , most people use headsets or call facilities in cars, which makes it difficult to catch defaulters.In the past one week, cops have seized 41 licences from around Connaught Place alone.
Talking while driving leads to most accidents on roads. Thursday's incident where Chhawla, a woman who lost control while driving, is one such case that happens on road almost every other day , the police said.
The police have planned to approach schools and colle ges in the next few weeks to sensitise teachers and students about the hazards of driving while using a mobile phone.
Since December 2015, the traffic police have issued challans to 3,899 drivers and have seized their licences. South Delhi reported maximum violations. Areas around Josip Tito Marg, Mathura Road and South Extension saw most violations. The police have seized 900 licences from areas around ITO crossing and Delhi Gate during the same period.
Sources said the use of echallan machines have made the job a little easier for the men on duty . These machines automatically issue a note for cancellation of licence when the nature of offence is punched in.
Earlier a penalty of Rs 1,000 was imposed under Section 184 of Motor Vehicles Act 1988, besides under Rule 17 (i & ii) of Rules of Road Regulations 1989, punishable under Section 177 MV Act 1988, since the offence is an act of dangerous driving. In extreme cases, Section 279 IPC (rash and negligent act) is imposed leading to arrest and seizure of vehicles, the police said.
A Supreme Court committee on road safety has recommended jail terms for reckless driving or Driving under the influence( DUI).
2014: 'Overtaking’ is the leading cause
The Times of India, Sep 05 2015
Overtaking led to max crashes in 2014
Dipak Dash
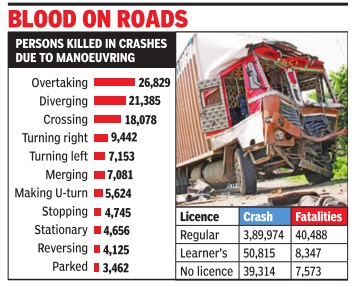
Better be alert every time you try to overtake or any other driver is speeding past your vehicle on the roads. Numbers show that maximum crashes and deaths on roads took place in 2014 when drivers were overtaking and the second highest cases of fatalities happened while “diverging“ or when jumping lanes. According to the latest report on country's road accidents and deaths, over 48,000 people died in crashes caused due to overtaking and `diverging' during 2014. “These accidents are also directly linked to speeding. There are two ways to address this concern. Either drivers must be sensitized or there has to be strict enforcement of traffic laws. Unfortunately, our drivers have no sense of how to change lanes, which is also main reason for such accidents,“ said an official of the transport research wing, which has prepared the report after compiling data from the local police from across the country .
The report also points to how most of the drivers with valid licenses have little training or knowledge of how to drive safely . It mentions how drivers with valid licenses were involved in crashes killing about 40,500 persons.
A recent analysis of people having driving licenses had revealed how 13% of such licenses are either fake or duplicate in India.
The report by National Informatics Centre (NIC) had found around 74 lakh licenses out of the total six crore may be duplicate ones, indicating the systemic flaws when doling out such licences.
Overtaking: 30,000 deaths in 2015
The Times of India, June 7, 2016
Dipak Dash
Rash overtaking led to 30,000 deaths in 2015
It is better to be alert when overtaking or letting any other vehicle overtake you on the road. Numbers show how dangerous and risky overtaking is on Indian roads. Last year, over 30,000 lives were lost in road crashes caused due to overtaking, says a road traffic accident report by the transport ministry . It also shows how diverging and merging resulted in nearly 32,000 fatalities on roads while stationary and other parked vehicles were involved in nearly 26,000 crashes that claimed 7,280 lives in 2015.
“Overtaking is a menace across all roads because neither the road users nor the enforcement agencies are aware of the right of way . The rules clearly say that you can't overtake at crossings, junctions, bend or wherever you can't see the traffic clearly,“ said road safety expert Rohit Baluja.
In fact, two-lane roads without dividers are more dangerous so far overtaking is concerned. What makes it worse is either no or little enforcement. “The danger is more on hilly areas and vehicles from outside these states violate the law. There is none to enforce.So, all these make the roads more unsafe,“ Baluja added.
Experts said poor traffic engineering is responsible for increasing cases of crashes and fatalities due to diverging and merging traffic. They said every road should be audited and the necessary changes must be made to make them safer. “We also have high number of deaths caused due to stationary vehicles on road. It simply points to how there is hardly any enforcement and patrolling to prevent such crashes. State police have no adequate force to patrol the highways and the highway managers don't wake up until a few lives are lost,“ said S P Singh of IFTRT, a think tank on transport issues.
2014: Rash driving and road rage
The Times of India, Aug 20 2015

Kochi, T'puram top rash driving & road rage cases
Dipak Dash
Two major cities in Kerala Kochi and Thiruvananthapuram -have reported maximum number of “rash driving road rage“ cases leaving 22,300 injured while Chennai and Delhi have registered third and fourth highest number of such cases. The compilation data based on cases registered by state police departments in the 53 major cities show that a total of 96,648 such cases were reported across the country and at least 99,822 people were left injured.This is almost one fifth of the total injury reported in 2014 involving road crash cases.
Among these cities, the rate of such rash driving and road rage cases per one lakh population is also highest with 634 recorded in Kochi and Thiruvananthapuram recording 522 cases per lakh population.The national average was little over 60.
Sources said the main reasons behind high rate of rash driving and road rage cases in Kerala include high volume of vehicles and less road space with little expansion of highways happening in the recent years. They added these two are also the main commercial cities and Kochi has emerged as a cosmopolitan city .
Interestingly , even Indore in Madhya Pradesh recorded over 4,100 such incidences which left equal number of people injured in the crashes.
According to the NCRB report, at all India level a total of 4.09 lakh rash driving and road rage cases were reported and at least 4.79 lakh people were left injured. Kerala registered high number of these cases at 1.09 lakh, Lakshadweep reported only one such incident.
Trends
2014: Age profile, regions worst affected
The Times of India, Sep 03 2015

Dipak Dash
75,000 youngsters killed in road crashes in 2014
Delhi tops list of deadly cities with 1,671 dying in 2014
India's killer roads claimed the lives of 75,000 people aged between 15 and 34 years last year. Over 82% of these victims were males, according to the Road Accident Report for 2014 prepared by the road transport and highways ministry .
PM Narendra Modi too made an appeal on the issue to elders of families in a recent radio address.
According to the report prepared by the ministry's transport research wing (TRW), the total number of road crashes has increased marginally from 4.86 lakh in 2013 to 4.89 lakh in 2014. The number of fatalities has also gone up by about 1.5%. Thirteen states -Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, West Bengal, Bihar, Punjab and Haryana -account for about 83.2% of the deaths.
It says about 12% of the fatalities happened in 50 cities with populations of over a million each, Delhi leading with 1,671 deaths and Chennai registering the second highest number at 1,118.
2014-15: poor and young people worst impacted
The Times of India, June 20, 2016
Dipak Dash
Poor, young worst-hit in road crashes: Report
The poor and the young (in the age-group of 15 to 30 years) are the worst impacted in road crashes, an evaluation of India's first cashless scheme for accident victims has revealed. According to the interim report, nearly 75% of the crash victims on Gurgaon-Jaipur stretch of NH-8 were the poorest.
The evaluation carried out by the PGI, Chandigarh has revealed how the number of crashes recorded or registered by police are far less than the actual numbers. The difference in number of crashes as recorded by police and insurance companies for claims between September 2014 and September 2015 has been found to be more than five times in some months.
“Data collection is very poor in our country . There is a concrete finding to suggest how we need to have a robust compilation of road crash details,“ a transport ministry official said. In fact, World Health Organisation had estimated the total fatalities in road crashes in India at around 2.07 lakh while government data put it at 1.37 lakh in 2013.
After rolling out the first scheme to provide first 48 hours' free medical care costing up to Rs 30,000 on the Gurgaon-Jaipur stretch, the road transport ministry had implemented this on Mumbai-Vadodara and Ranchi-Mahulia stretches. While 13,252 road crash victims were provided medical help on the GurgaonFaridabad stretch, in case of the Mumbai-Vadodara stretch there were 2,238 beneficiaries . There were 1,318 beneficiaries in the case of the Ranchi-Mahulia stretch. The average cost per beneficiary was around Rs 14,381.
The transport ministry has proposed to extend the cashless scheme to the entire Golden Quadrilateral and East-West and North-South corridors, which will cost around Rs 254 crore annually .
2014: Age of vehicle and accidents
The Times of India, Sep 03 2015

Dipak Dash
Newer vehicles involved in bulk of accidents
Contrary to the general belief that old vehicles are likely to be involved in more crashes, particularly fatal ones, the latest official data shows that it's 1-6-yearold vehicles that are involved in the largest chunk of such cases. Vehicles ranging from 2-4 years old accounted for the highest numbers of both crashes (86,956) and deaths (24,494), the national road accidents report shows. This is for the first time the report prepared by the government's transport research wing has incorporated such details. “This data itself can be used to analyze why young fleets are involved in more cases. However, it's quite clear that the human beings behind the wheel are mainly responsible for crashes and fatalities.Speeding could be one of the key reasons. But so far, no scientific study has been done to establish the reason,“ said a government official.
In fact, the report mentions that 78.8% of crashes are caused due to “driver's fault“ and more than 56% of the total deaths were due to speeding. Across the globe, speeding, driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs and not wearing helmets and seatbelts have been identified as the main factors behind crashes and high fatalities.All these relate to the behaviour of drivers.
The carelessness of drivers is also established from the data, which shows that the share of fatalities in rural areas is higher since commuters have little fear of getting caught because of almost no presence of traffic police personnel.
No Accident Day, UP: 2015
The Times of India, Jul 02 2015
UP's `No Accident Day' a hit as no mishap in three big cities
UP's ambitious `No Accidents Day' saw something close to a miracle. No road mishaps in three of its biggest cities -Meerut, Agra and Bareilly -were reported on July 1 till late in the evening. To make the campaign successful, police had been deployed at high-accident `grey' and `black' spots across the state.At many places they conducted eye check-ups. The state reported 16,287 deaths from traffic accidents and 22,337 injuries in 2014.According to traffic officials, 70% of road mishaps occur due to negligence, while 10% occur because of snags.
Seasons: Traffic accidents: highest in May, lowest in monsoons
STATOISTICS - RAIN-FALL
The Times of India Aug 02 2014
The monsoon might mean waterlogged roads, flooding of low-lying areas, overflowing of gutters and ditches -complete traffic chaos in a nutshell. An analysis of NCRB data on traffic accidents in the past ten years shows the positive side of this turmoil. At the all-India level, July, August and September witness the lowest number of accidents. May, on the other hand, is the month that sees the most accidents. Experts link this to clear weather during the month in most of the country and the fact that truckers' working hours increase also because goods are being transported before the rains make it more difficult to do so. Because engines tend to heat up during the day in the summer, commercial transport seeks to maximize the night. With visibility also good, average speeds tend to rise too, hence the larger number of accidents in May. The monsoon, in contrast, increases caution and reduces speed and volume of traffic. A state-wise analysis shows variations from this all-India trend. But these can also be linked to the local climate and terrain. For instance, accidents spike in Delhi, Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh during the winters, perhaps due to the dense fog often seen in these months
Soldiers: Road accidents: Peacetime killer among soldiers

The Times of India Apr 21 2015
Rajat Pandit
At least 300 jawans die every year
Without going to war the Army has lost well over 6,500 soldiers in peacetime since the 1999 Kargil conflict. Around half that the number of soldiers were killed in each of the three wars fought in 1962 1965 and 1971.
It includes around 4,700 “battle casualties” occurring due to enemyterrorist ac tion and extreme weather natural disasters in high-alti tude areas as well as different kinds of on-duty mishaps, in cluding road accidents.
Over these numbers, sui cides constitute a major chunk of “non-operational“ deaths. Around 100 soldiers take their own lives in the Army's highly-disciplined environs every year despite successive governments holding several measures have been taken to reduce stress in the 1.17 million-strong force. Just since 2010, over 520 soldiers have committed suicide.
But the toll in counter-ter rorism operations has largely been brought under control over the last several years, even though soldiers are still not properly equipped with basic protection gear like light-weight modular bulletproof jackets and ballistic helmets. The annual counter-terror casualty rate is now down to below 50 from around 300 just over a decade ago.
The Army may have gained “ascendancy“ over militancy but it's finding it difficult to tackle the biggest peace-time killer among its ranks. Consider this: 313 soldiers were killed in road accidents in 2003, 315 in 2004 and 295 in 2005. A decade later, the numbers still stand at 306 (2012), 297 (2013) and 284 (2014), as per data collected by TOI.
The ongoing Army commanders' conference in New Delhi would do well to focus on concrete measures to reduce road accidents in the force.These could range from more rigorous training for drivers and proper pre-induction training before deployment in treacherous terrain as well as stricter overall monitoring and phasing out of old vehicles.
A senior officer, however, contended the number of deaths was “not much“ compared to the “sheer volume“ of the Army's vehicular movement across the country . Take just the infantry , which has 382 battalions with 800-900 soldiers each. There are around 40 vehicles, from motorcycles to heavy-duty ALS 5-tonne trucks, in each battalion.
“Yes, there are many cases of negligent driving. But our drivers also have to drive in snow-bound mountains, deserts, jungles or marshes. If one truck goes down a valley , 20 soldiers could be killed in one go,“ said another officer.
There is also the “fatigue factor“ in long convoys, which carry troops, ammunition and other supplies, to different areas. “Proper maintenance of vehicles is also carried out, with older ones like the famous Shaktiman trucks being phased out,“ he said.
State Road Transport Corporations/ Undertakings
Delhi Transport Corporation’s accidents
The Times of India, Nov 26 2015 Rumu Banerjee
Most DTC bus mishaps due to rash driving: Study
At a time when the Delhi government is making serious efforts to promote public transport, an internal study by Delhi Transport Corporation has revealed shocking facts about the state of the bus agency . An analysis of data till July 2014 and 2015 has shown that a significant number of accidents involving DTC buses were due to “rash and negligent“ driving. While 16.66% of accidents took place due to a fault of DTC drivers, 5.56% were due to fault of “others“. According to data by the traffic police, DTC has had fi ve fatal accidents in the past two months, three in October and two in September. The transport utility , meanwhile says there have been 18 fata accidents involving DTC bu ses between January and Ju ly this year. The internal stu dy, which looks at accident fi gures from January to July compares the accident figu res of 2015 with 2014.
In the same period last ye ar, there were 18 fatal acci dents but none due to rash and negligent driving. There are also figures for accidents due to other reasons, clubbed as “miscellaneous“ and stand at 66.66%. This sub-he ad, said officials, were for accidents caused due to external factors. In 2014, all the 18 accidents had happe ned under this category .
Interestingly, there is also a sub-head for accidents caused due to “alighting of passengers“. This consists of one accident or 5.56% of passengers “alighting“ from the front gate while another accident is due to boarding of passengers from rear gate.
While DTC claims accident rates have “come down“, the traffic police have a different story to tell. According to the cops, speeding is a common complaint, one that has elicited remarks about DTC and cluster buses “going the Blueline way“.And though DTC officials say that speed governors have been installed on buses, the reality is that few of them work.As a result, most drivers still drive at a high speed on cong ested roads leading to accidents. Said a senior government official, “The fact is that almost none of the buses of DTC has a working GPS, nor speed governors. Checking speed or route thus is difficult.“
DTC has 12,196 drivers on its rolls, with roughly 4,000 being contractual. Drivers involved in accidents are chargesheeted to which they respond within a given period. If accepted, they get back on duty . The rest are suspended and go through an inquiry committee, which decides on the quantum of punishment. After that, they are put back on duty .
Two-wheelers, accidents involving
Two-wheelers claim 94 lives every day
Dipak Kumar Dash
Two-wheelers claim 94 lives a day while trucks and lorries account for 66 fatalities, according to the NCRB report for 2013. Though overall, there is marginal reduction in total number of people killed on roads last year in comparison to 2012, these two indicators signal how there is little regulation or enforcement of road safety measures.
Unlicensed drivers, accidents by: 2012-14: rise of 54%

The Times of India Dec 21 2015
Dipak Dash
Accidents caused by drivers without licences increased by 54% between 2012 and 2014, according to data provided by the police departments of all states and Union Territories. In abso ute numbers, the accident count went up from 25,463 to 39,314. In the same period, drivers younger than 18 caused between 19,000 and 21,500 accidents.
Though the official count s evidently much less than actual numbers, it reflects the ree run such drivers seem to enjoy and the need to bring them to book. Transport ministry officials said local police hardly ever book such offenders or the owners of vehicles as they treat these as petty offences.
Global studies suggest drivers in the age group of 1619 are four times more likely to cause accidents compared to older drivers. Teenagers are also more likely to speed, jump traffic lights, take wrong turns and drive after consuming alcohol or drugs.Usually, no one favours taking action against young boys and girls, including their parents, transport ministry officials added.
“The actual number of vio ations, including under-age driving and without licence, is much higher as there is hardly any detection of such drivers in rural areas and small towns. We don't get proper data that can help us plan better and map the gaps. What we al so need is to educate parents and schoolgoing children,“ K K Kapila, chief of International Road Federation, said.
Interestingly, details sub mitted by the road transport ministry to Parliament last week said Delhi traffic police did not provide details on either count.
Women drivers
Women are safer drivers, says police study Indrani Basu TNN
The Times of India, Oct 17, 2011
New Delhi: Busting the stereotype about women being bad drivers, a report compiled by Delhi Traffic Police reveals that woman drivers cause less
than 2% of all fatal road mishaps in the city and their involvement in accidents has dropped in the past few years despite more women taking the wheel.
Till September 15 this year, 12 fatal accidents were caused by women in Delhi, against 724 by men, the report said. Woman drivers were involved in 53 accidents causing injury while the number for men was 2,524. Even in accidents which did not cause injuries, the male-female ratio was 284:4.
“The data does not support the popular impression that women are poor drivers,” said joint CP (traffic) Satyendra Garg. Women smash stereotype, more cautious behind wheel
New Delhi: A report compiled by the Delhi Traffic Police has debunked the age-old stereotype about women being bad drivers as they are found to be involved in less than 2% of all fatal road mishaps in the city. They are believed to be more cautious and therefore responsible for fewer accidents.
“The number of women drivers is just a fraction of the number of men who drive. But even proportionately, women are involved in far fewer accidents and incidents of rash driving than their male counterparts,” said joint commissioner of police (traffic) Satyendra Garg.
“Our impression is women are far safer drivers, with a tendency to follow traffic rules. This disproves the contention that women cannot drive,” he added.
The report is in sharp contrast to the findings of a recent “perception-based” survey by an industry chamber which said women were more aggressive drivers and caused more road fatalities.
Overall, 5,432 road accident cases were reported in the city till September 15, of which woman drivers were found to be responsible for 69 – just over 1% of the total.
The report said over the years, the involvement of woman drivers in accidents has also decreased. While in 2008 women were found to be involved in 107 road accidents, the figure dropped to 101 and then 72 in 2009 and 2010 respectively. Despite stringent checks by the traffic police, women have not been found driving drunk.
Driving school instructors too rubbish perceptions of women having poor motor skills. “More number of women have started driving. Though they are predominantly young girls in the age group of 18-20 years, women of all ages, including between 55 and 60 years, also come to us for learning how to drive. Women are more diligent students and are interested in learning traffic rules carefully. They are perhaps more hesitant and cautious but that is better than rash driving,” said Gaurav Kaghait, senior instructor at New Star Motor Driving College in Kalkaji.
2014: Rash driving arrests among women
The Times of India, Nov 10 2015
V Narayan
Kerala, Maha women lead in arrests for rash driving
Women drivers of Maharashtra and Kerala have beaten their counterparts across the country to emerge as the worst offenders when it comes to rash driving or road rage. According to National Crime Records Bureau data, of the 1,355 women arrested in 2014 for the offence, 263 or 19.4% were in Kerala, and 183 or 15.6% in Maharashtra. With 141 arrests, Gujarat was third in the list. Delhi was much further down with 97 arrests.
Bihar, meanwhile, accounted for the most number of arrests of women for causing death due to negligence (52) in 2014. Uttar Pradesh is second with 49 arrests, followed by West Bengal (42), Tamil Nadu (24) and Karnataka (21). This is the first time rash driving cases have been classified separately in the NCRB's report. NCRB director general Archana Ramasundaram, in her cover note for the 2014 report, stated that like the earlier editions, this report contains detailed information on cognisable crimes, and disposal of crimes by police and courts, etc, but has more chapters. Mumbai joint commis sioner of police (traffic) Milind Bharambe said most accidents caused by reckless driving can be prevented simply by following rules.
Drunk driving
Bar the drunk from driving: Bombay HC
The Times of India Jan 08 2016
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
The Bombay high court directed the Centre to consider adopting a “zero tolerance policy“ towards drunk driving and make appropriate changes in the law.
Observing that “too many lives had been lost“ to the “lethal cocktail“ of drinking and driving, a division bench of Justices Abhay Oka and Gautam Patel recommended action against those driving under the influence irrespective of the amount of alcohol in blood. At present, motorists with alcohol exceeding 30mg per 100ml of blood are liable to be charged under Section 185 of the Motor Vehicles Act.
“We find nothing to suggest that some quantity of alcohol in the blood can be considered `safe',“ said the judges, adding that there was no fundamental right to drink. The HC also asked the state government to direct the police and transport authorities to immediately suspend driving licences of persons against whom DUI cases are registered. Driving licences are being suspended for three months for drunk driving since January 1 in the city.
Calling the permissible alcohol limits prescribed in the law as theoretical, the judges added: “There is, in fact, no reason why any person who has had any amount to drink should be permitted to drive at all. Given the alternatives available, and having regard to the manifest risks especially to third parties, we would strenuously urge the adoption by the Central government of a zero tolerance policy toward drunk driving.“
The high court said there was no fundamental right to drink, “let alone to drink any amount and then get behind the wheel of a motor car or on to a two-wheeler. Even the most minute impairment caused by alcohol intake might have the most disastrous consequences“.
Cases of drunk driving accidents decline
The continuous decline in accidents caused due to intake of alcohol/drugs in the past three years has come as a breather for the government. While in 2010 such violation caused 31,000 accidents, the number of such mishaps reduced to 23,979 last year. Even the fatalities have fallen from 9,976 in 2010 to 7,835 in 2012. Uttar Pradesh reported maximum fall in fatalities in this category from 4,635 in 2011 to 2,400 last year. TNN
Legal aspects
Fatal Accidents Act, 1855
Dhananjay Mahapatra TNN
The Times of India, July 9, 2011
SC: Mughal-era legislation still governs road accident relief
Apart from the penal laws punishing drunk drivers running over people, the offender can be sued by the victim’s relatives for compensation under a law that was enacted when the last Mughal Emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar, was the titular head of the throne at Delhi.
Taking note of this, the Supreme Court has asked the Centre to immediately commence work to draft a new law to replace the archaic legislation. It expressed serious concerns over the extreme inadequacies in the law governing suits for damage filed by relatives to claim compensation for death due to rash and negligent act, including drunken driving cases. It rapped the government for not taking note of a 20-year-old apex court judgment recommending drastic change in the 1855 law or a new legislation to meet the present-day challenges.
A bench of Justices Aftab Alam and R M Lodha said, “We are constrained to observe that a suit for damages for a murder of a person, like the present one, is filed under the Fatal Accidents Act, 1855. As the year of enactment shows, the Act dates back to the period when the greater part of the country was under the control of East India Company with the last Mughal ‘Emperor’, Bahadur Shah Zafar, as the ineffective, though titular monarch on the throne at Delhi.”
The Act was enacted to provide compensation to families for loss occasioned by the death of a person caused by actionable wrong. “It is a matter of grave concern that such sensitive matters like payment of compensation and damages for death resulting from a wrongful or negligent act are governed by a law which is more than one and a half centuries old,” said Justice Alam, who wrote the judgment for the bench.
With anguish it remembered that a constitution bench of the Supreme Court in a 1990 judgment had said: “The Fatal Accidents Act, on account of its limited and restrictive application, is hardly suited to meet such challenge. We are, therefore, of the opinion that the old antiquated Act should be drastically amended or fresh legislation should be enacted which should contain appropriate provisions for various exigencies.” Justice Alam said: “It is unfortunate that the observations of the SC have so far gone completely unheeded.”
Compensation a right of mishap victims: HC
Shibu Thomas, TNN | Aug 29, 2013
MUMBAI: Victims of road accidents and their next of kin have a right under law to claim compensation, the Bombay high court has ruled. Twenty-three years after a Yavatmal-based bank officer lost his life in a road accident involving an MSRTC bus, Justice A P Bhangale ordered the state transport undertaking to pay Rs 6.51 lakh, along with interest, to his wife and three children.
The judge threw out the MSRTC's contention that the deceased bank officer, Mukundrao Dongre (38), could not be categorized as a third party eligible for compensation under the third-party risk insurance rule.
"I find it difficult to accept the submission that the victim was a person 'other than third party'," said the judge. "The Motor Vehicle Act provides for mandatory third-party insurance, which is compulsory for any motor vehicle owner. The objective of the act is to ensure that the third party receives just and fair compensation from the owner of the offending motor vehicle and receives compensation."
The court said the law protects victims of road accidents. "The right of the victim of a road accident to claim compensation is statutory. The legislature in its wisdom enacted the (law) to protect the victims of road accidents, who may be travelling in the vehicle or using the road, and thereby made it obligatory that no motor vehicle shall be used unless the vehicle is compulsorily insured against third-party risk."
The court said the MSRTC could not escape paying compensation by claiming that the other vehicle was responsible for the accident. "If liability is denied, it is for the MSRTC to plead and prove rashness and negligence on the part of the driver of the jeep if according to it the jeep was the offending motor vehicle... Mere allegation is not enough."
Mere absence of or fake or invalid driving license or disqualification of the driver for driving at the relevant time are not in themselves defences available to the MSRTC against the third parties."
Financial aid to victim
Mar 03 2015
Amit Choudhary
Increases compensation in HP case
SC: States must aid accident victim's kin if accused is poor
If death is caused by rash and negligent driving and the driver is unable to pay adequate compensation to the victim's family because of his poor financial status, the state government must step in and pay the amount, the Supreme Court has ruled. “We are of the view that where the accused is unable to pay adequate compensation, the court ought to have awarded compensation under Section 357A from the funds available under the Victim Compensation Scheme framed under the said section,“ a bench of Justices T S Thakur and A K Goel said.
It increased the amount of compensation awarded by the Himachal Pradesh high court to family members of a girl who died in a road accident from Rs 40,000 to Rs 4 lakh. Considering the poor financial condition of the convicted truck driver, the bench directed him to pay Rs 1 lakh and asked the state government to pay the remaining Rs 3 lakh.
The bench said if the driver failed to pay the amount, he had to undergo a six months' jail term and in that case the entire compensation of Rs 4 lakh would have to be paid by the state government.
“We modify the impugned order passed by the high court and enhance the compensation to be paid by the driver to Rs1 lakh to be paid within four months failing which the sentence awarded by the court of sessions shall stand revived,“ it said.
“In addition, we direct the state of Himachal Pradesh to pay an interim compensation of Rs 3 lakh. In case the driver fails to pay any part of the compensation, that part of compensation will also be paid by the state so that the heirs of the victim get total sum of Rs 4 lakh towards compensation. The amount already paid may be adjusted,“ the bench said.
Death of foetus in mishap
Rs 2.5L relief for unborn child’s death in mishap
HC Compares Dead Foetus With Minor Child
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
From the archives of The Times of India 2007, 2009
2010
New Delhi: In an important ruling, the Delhi High Court has held that an unborn dead foetus can be considered on par with a minor child while fixing compensation. It directed an insurance company to pay extra compensation of Rs 2.5 lakh to a man who lost his pregnant wife in a road accident in 2008.
HC allowed an appeal filed by one Prakash seeking compensation for his unborn child as his plea was ignored by the Motor Accident Claim Tribunal (MACT). The court, however, made it clear that the dead foetus cannot be compared with a grown-up child, because by then a child’s presence in the life of his or her parents has created enough memories for them to feel greater pain at the loss of their child. This pain will be lesser were an unborn child to die as in that case there will be no memories to cherish.
‘‘This court holds that an unborn child — aged five months onwards in mother’s womb till its birth — is treated as equal to a child... the foetus is another life in a woman and loss of foetus is actually loss of child in the offing,’’ HC reasoned, while allowing the appeal and the compensation of Rs 2.5 lakh along with an interest rate of 7.5 per annum to Prakash.
While the MACT had already awarded Rs 6.11 lakh to the petitioner for the accident in which his wife died with sevenmonth-old foetus in her womb, the tribunal had not taken into account the death of foetus as a factor.
HC directed the insurance company to deposit Rs 2 lakh with the UCO bank as fixed deposit within a month and release rest of the amount to the victim’s family.
On his part, the petitioner argued that the MACT Tribunal had ignored the plea on a ground that post-mortem report has not mentioned anything about the presence of foetus. The counsel argued the road accident took place on June 8, 2008 and the foetus was removed from the woman’s womb on June 17 and the mother died on August 14.
Clarifying that the foetus was absent at the time of the victim’s death, the lawyer submitted the statements of doctors from Shushruta Trauma Centre and LNJP who treated the woman soon after the accident and removed the foetus after the unborn baby died in the womb due to the accident.
toireporter@timesgroup.com
Regions
2004-2013: road accidents, state-wise figures
See graphic

Regions: India's highest road fatalities 2008 to 2013 were in Delhi
Delhi sees most road deaths in India
New Delhi
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
The Times of India Jun 24 2014
About 40 busloads of citizens die on the capital’s roads every year. From 2008 to 2013, more than 12,300 people died in road accidents here. Last year alone, there were a total of 1,820 deaths.
An assessment of road accidents done by the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) reveals that not only does Delhi have the most dangerous roads in the country but pedestrians and bikers are at the greatest risk on them. On average, five people die in road accidents every day, and four of them are either pedestrians or twowheeler riders.
The traffic police have identified 128 accident hotspots — places where three or more fatal accidents, or 10 accidents have occurred in a year -and the CSE assessment shows that northwest and southwest Delhi have the most such spots. Taken design-wise, signal-free arterial roads are the most dangerous.
Ironically, roads that have received the maximum government attention and resources for widening and signal-free movement have the highest accident rates.
“These features have, in fact, turned arterial roads into death traps. Especially dangerous are spots where flyovers begin, such as Dhaula Kuan, AIIMS, Sarita Vihar, Mahipalpur, Rajokri, ITO or IP, and Moti Bagh,” says the report released on Monday.
Eight key arterial roads, designed to be high-speed corridors, record nearly 75% of all deaths in Delhi alone.
For nearly a decade now, road infrastructure in Delhi has received a lot of attention but despite having the best roads in the country, the city leads in terms of traffic fatalities. Mumbai records far more accidents—25,000 in 2012—but the number of deaths is around 500. Even Chennai, with 9,000 accidents annually has 1,350 fatalities. However, Delhi has the highest percentage of fatal accidents. Last year, 1,820 persons died in 7,566 accidents.
Traffic experts say violation of rules is rampant in Delhi, and speeding is a common offence due to the better road conditions. This year, more than 3 lakh motorists have been challaned for jumping signals and 45,158 for speeding.
Also, more than 14,000 cases of drunken driving have been detected.
Anil Shukla, additional commissioner of police (traffic), said policies on road safety are framed in fits and starts. “Our roads should be so designed that they are forgiving of the mistakes drivers make,” he said. At the same time, existing laws are not strong enough to deter traffic violations. For instance, the fine for many serious offences is a meagre Rs 100.
Shukla gave the example of a traffic junction, where 1.3 lakh violations were detected in a month, and a man who was challaned 144 times in three months but did not correct his ways. “About 15% are court challans. Most wait for Lok Adalat hearings where cases are settled by paying a fine of Rs 10 or Rs 20. For a person who can afford a Rs 45-lakh car, does a fine of Rs 100 matter?” Half of the road casualties (dead and injured) in Delhi are pedestrians (44%) and cyclists (6%), while nationally, the numbers are 9% and 5%, respectively. Till May this year, 325 people had died in accidents at night and 332 during daytime. An IIT Delhi study of AIIMS Flyover showed that after the cloverleaf was opened, speeds increased by 21.5%, 22.6%, 15% and 31.6% for heavy vehicles, cars, three wheelers and two wheelers, respectively.
Yet, nearly 22% of pedestrians continued to cross the road at ‘grade’ level although a pedestrian underpass is provided.
Regions in 2010-12
Roads in Punjab most fatal in India
Dipak Kumar Dash | TNN
The Times of India 2013/08/16
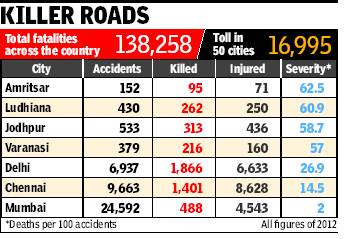
New Delhi: Chances of getting killed in a road accident is the highest in Amritsar and in the country’s Mercedes capital Ludhiana.
Latest data on road fatalities shows that at least six people died in every 10 road crashes in these two cities in 2012 against only three in Delhi, which recorded maximum fatalities in 2012. Though Mumbai recorded the highest number of accidents among 50 million-plus cities, the fatality rate was only 2%.
The ‘Road Accidents in India’ report prepared by the transport research wing of the road ministry also shows that roads in Punjab are proving to be fatal for commuters. The severity of accident – deaths per 100 mishaps – in the state has been increasing in the past four years. While it was 65.9% in 2009, this increased to 76% in 2012.
“Ludhiana and Amritsar are the worst examples. But the state as a whole is also losing over 4,800 lives in road accidents. We have heterogeneous traffic, little enforcement of noentry timings and huge problem of drink driving,” said Dr Kamalzit Singh Soi, vice-chairman of Punjab Road Safety Council.
The industrial city of Ludhiana has around 1.4 million vehicles for its 3.5 million people, of whom 20-30% are migrant labourers. Soi said traffic coming from six districts passed through the city and almost 23 km of the under-expansion Panipat-Jalandhar highway runs through the urban area.
“On top of this, annually around 35 crore bottles of liquor are sold in the state that has a population of only 2.7 crore. Out of this, around 1.49 crore are women. So, we can make out how many times and how many people drive in a drunken state,” he said.
Regions: 2012
Delhi is the road death capital too
Dipak Kumar Dash TNN 2013/06/25
New Delhi: New Delhi besides being the capital of the country holds the dubious distinction of being the road death capital. In the year 2012, the city recorded 1,527 deaths in accidents.
Latest data on accidental deaths released by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) shows that India’s overall record deteriorated further, with the toll crossing 1.39 lakh during 2012 in comparison to little over 1.36 lakh in the previous year. Chennai seems to be moving closer to the national capital registering 1,401 road fatalities in 2012.
“While Delhi has witnessed high growth of vehicles resulting in slowing down of traffic, the situation is different in Chennai. Roads have become better and the speed of vehicles has increased,” said a road transport ministry official.
The data shows that at all India level, Tamil Nadu has overtaken Uttar Pradesh registering 16,175 deaths during 2012. UP reported 15,109 deaths while Andhra recorded 15,000 fatalities and Maharashtra ranked four among the states with 13,936 deaths
Dipak Kumar Dash
Remedies
Fixing black spots brings deaths down
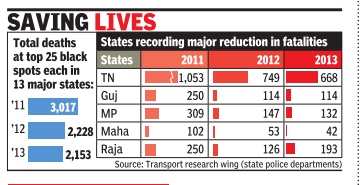
Casualties reduced: 2011-13 Dipak Dash The Times of India Feb 02 2015 New Delhi
Road Casualties Dip By 28% In 2 Yrs: Report Showing that efforts to fix black spots can help reduce road fatalities, the first-ever comparative analysis of trends from the top 25 black spots in 13 states has shown deaths coming down by over 28% in two years. While the number of such deaths was 3,017 in 2011, it came down to 2,153 in 2013. Black spots are locations which report abnormally high number of road crashes. The road transport ministry had flagged off identifying black spots on roads for the first time in 2011 and had also pushed for treatment of such zones.
The 13 states, including Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Kerala, Gujarat, Bihar and West Bengal, together account for 88.4% of the total road crashes in the country . According to the data compiled by the transport research wing of the ministry , the maximum reduction in fatalities at such spots was reported in Tamil Nadu. In absolute numbers, the decline was 385 fatalities between 2011 and 2013.
Madhya Pradesh registered almost 60% reduction in fatalities at such high-risk spots on its roads.
But some other states, including Haryana and West Bengal, reported a minor increase in fatalities. “States where there is no reduction in fatalities are a greater concern for us. The steps taken there are not proving to be adequate. Even in other states, the effort has to achieve zero fatalities at such spots since the agencies are now aware of the causes of crashes and what they need to do to rectify those factors,“ a transport ministry official said.
Officials and road safety experts said certain points or stretches have become black spots because of inadequate facilities to road users, bad road design such as blind turns, lack of traffic signals or narrow junctions.
As per a government report, the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI), which is responsible for fixing 203 of the 322 identified black spots, has completed short-term measures at 159 spots. It has completed longterm remedial measures at 57 spots and work is in progress at another 125 spots.
“But what we are now observing is that new black spots are being identified, once the old ones are fixed.So, we are going to carry out a detailed study of black spots in five states -UP, Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan, Jharkhand and Delhi -to identify the steps that need to be taken,“ a ministry official said.
Part II: the year-wise position
2014: road accidents

2014: Road accidents, Delhi

The Times of India, Jul 19 2015

Dipak Dash
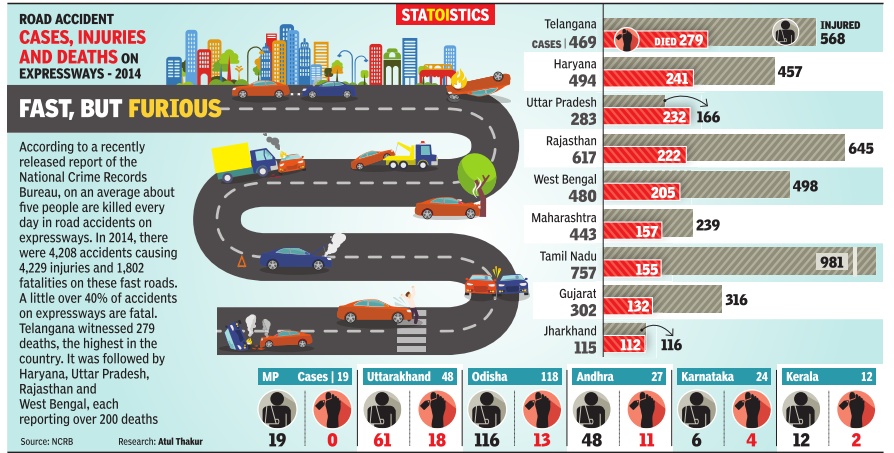
16 lives lost every hour, India's roads deadliest ever in 2014
Delhi had the worst record among cities32% died on roads, 7% in ops: NCRB
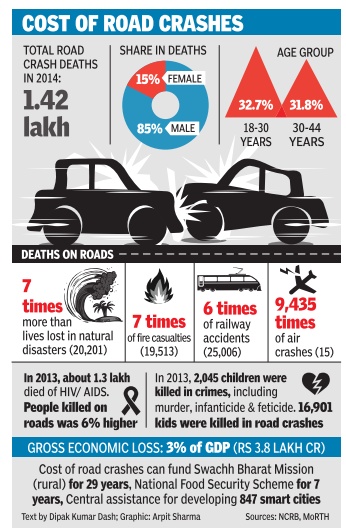
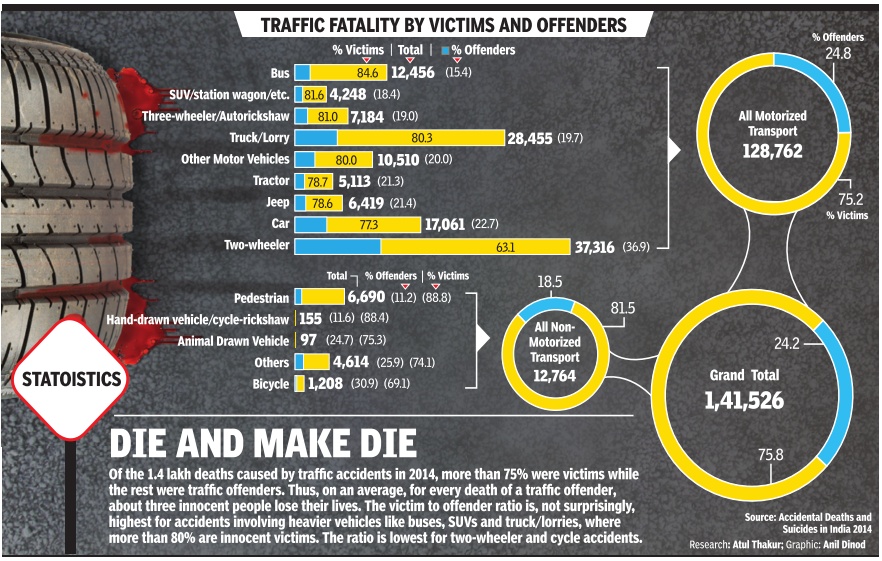
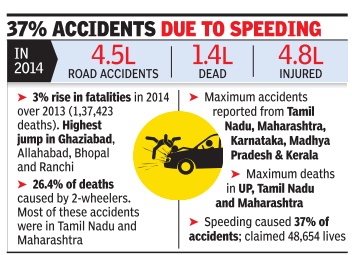
Indian roads were at their deadliest in 2014 claiming more than 16 lives every hour on an average.Over 1.41 lakh people died in accidents, 3% more than the number of fatalities in 2013.The numbers of crashes and of people left injured -at 4.5 lakh and 4.8 lakh -were also at the highest levels since the recording of such data started in India. According to the latest data released by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), speeding and danger ous driving were the biggest reasons for road fatalities. Accidents involving two-wheelers and lorries accounted for nearly half of the lives lost in road crashes.
Among 53 mega cities, Delhi registered the highest number of fatalities at 2,199. It was followed by Chennai (1,046), Bhopal (1,015) and Jaipur (844).
While 13,787 two-wheeler drivers were killed in crashes, 23,529 other people were killed in accidents involving these vehicles, while close to 1.4 lakh people were left injured. Speeding accounted for about 1.7 lakh crashes and nearly 49,000 deaths. Dangerouscareless driving or overtaking claimed another 42,000-plus lives in 1.4 lakh crashes.
Most deaths in UP, P 18 Over four times more paramilitary personnel die in road accidents than fighting terrorists or Maoists. New National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data show that of 1,232 central armed police force (CAPF) deaths in 2014, 32% were due to road accidents while only 7% were due to operations against terrorists. As many 175 committed suicide while 12 died in fratricide.
According to the data, 32.1%, 8.4% and 7.2% casualties in CAPFs were due to roadrailways accidents, natural calamities and killed in action operationencounteretc. respectively .
This is the first time government has specifically collected data on deaths of paramilitary personnel and assigned them various causes.The forces include BSF, CRPF, SSB, NSG, ITBP , CISF and As sam Rifles which have a cumulative strength of 9.27 lakh.
There have been forcespecific studies done earlier but never a comprehensive one. For example, in 2014 home ministry put out data that showed more CRPF men died due to diseases than fighting Maoists.
According to that data, in 2014, while 50 CRPF men died in Maoist attacks, 95 died due to various diseases. Of these 27 fell to malaria, while 35 died due to heart attack. Most paramilitary personnel died in roadrail accidents in Telangana.
With 111 of 194 deaths in the state belonging to this category, it makes up for 66.7% of all CAPF deaths in the state. There are three other states that have more than 50% CAPF deaths due to roadrail accidents. These include Jammu & Kashmir (27 out of 43), Arunachal Pradesh (17 out of 24), and West Bengal (5 out of 8). Interest ingly , there is not a single operation-related death in Jammu and Kashmir, indicating increased normalcy .
The data, however, put maximum CAPF deaths in the undefined “unnatural deaths“ category. Excluding roadrail accidents, this accounts for 51.3% of total CAPF deaths due to causes other than natural death.
Not surprisingly , Chhattisgarh which has seen the worst of Maoist violence over the years, has recorded maximum casualties in operations. Chhattisgarh accounted for 31 out of 89 deaths in operations.
Curiously Uttar Pradesh, which has been comparatively much quieter as far as Maoist violence is concerned and does not share borders with any hostile country , comes a close second accounting 30 operational deaths. They together make up for over 68% deaths in operations.
Jammu & Kashmir has accounted for 66.7% of total fratricide incidents (8 out of 12), pointing at some level stressful conditions in which jawans function there.