Dowry prohibition laws: India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Are all demands by husband/ in laws dowry?
SC: Yes
The Times of India Mar 01 2015
Amit Choudhary
Any demand by hubby, in-laws is dowry: SC
Putting an end to the judicial tendency to interpret dowry in a narrow sense, the Supreme Court has said any demand made by the husband or his relatives before or after the marriage would come within the definition of dowry. Expanding the ambit of dowry, the court overruled its earlier verdicts in which it had said demand for money for meeting some urgent domestic expenses could not be termed as dowry demand.
A bench of Justices T S Thakur, R F Nariman and Prafulla C Pant said dowry must be given a pragmatic interpretation to fulfill the objectives of the Dowry Prohibition Act. “Any money or property or valuable security demanded by any of the persons mentioned in Section 2 of the Dowry Prohibition Act, at or before or at any time after the marriage which is reasonably connected to the death of a married woman, would necessarily be in connection with or in relation to the marriage unless, the facts of a given case clearly and unequivocally point otherwise,” it said.
SC 2022: Yes, again
Amit Anand Choudhary, January 12, 2022: The Times of India
NEW DELHI: The Supreme Court said the word "dowry" ought to be given a wider interpretation to include any demand made on a woman, whether in respect of a property or a valuable security of any nature, and held that demand for money for constructing a house comes within the ambit of dowry.
A bench of Justices N V Ramana, A S Bopanna and Hima Kohli said interpretation of a provision of law that will defeat the very intention of the legislature must be shunned in favour of an interpretation that will promote the object sought to be achieved through the legislation meant to uproot a social evil like dowry.
"In this context the word 'dowry' ought to be ascribed an expansive meaning so as to encompass any demand made on a woman, whether in respect of a property or a valuable security of any nature. When dealing with cases under IPC Section 304-B, a provision legislated to act as a deterrent in society and curb the heinous crime of dowry demands, the shift in the approach of the courts ought to be from strict to liberal, from constricted to dilated. Any rigid meaning would tend to bring to naught the real object of the provision. Therefore, a push in the right direction is required to accomplish the task of eradicating this evil which has become deeply entrenched in our society, " said Justice Kohli, who penned the judgment for the bench.
The court set aside a verdict of the Madhya Pradesh high court which had acquitted a husband and father-in-law for a dowry death on the ground that the victim had herself asked her family members to contribute money to construct a house, which cannot be treated as a dowry demand.
The top court said that the demand made by the deceased herself had to be seen and understood in the correct perspective as she was being tortured to bring money from her family. It said the order of the trial court convicting both of them for the dowry death was correct. In this case, the deceased, who was five months pregnant, immolated herself in her matrimonial home.
"We are of the opinion that the trial court has correctly interpreted the demand for money raised by the respondents on the deceased for construction of a house as falling within the definition of the word dowry. It cannot be lost sight of that the respondents had been constantly tormenting the deceased and asking her to approach her family members for money to build a house and it was only on their persistence and insistence that she was compelled to ask them to contribute some amount for constructing a house," it said.
The court said the evidence brought on the record shows that the deceased was pressured to make such a request for money to her mother and uncle. "It was not a case of complicity but a case of sheer helplessness faced by the deceased in such adverse circumstances," the court said while convicting both husband and his father under Section 304-B and Section 498-A IPC and awarded seven years’ rigorous imprisonment, which is the minimum sentence prescribed for an offence under Section 304-B IPC.
"The above glaring circumstances, when viewed together, can hardly mitigate the offence of the respondents or take the case out of the purview of Section 304-B IPC, when all the four prerequisites for invoking the said provision stand satisfied, namely, that the death of Geeta Bai took place at her matrimonial home within seven years of her marriage; that the said death took place in abnormal circumstances on account of burning and that too when she was five months pregnant; that she had been subjected to cruelty and harassment by the respondents before her death and such cruelty/harassment was in connection with demand for dowry," the court said.
Court judgements
‘Dowry plaint after husband’s divorce plea not vendetta” HC
May 16, 2024: The Times of India
Bhopal/Jabalpur : If a woman remained quiet about dowry harassment to save her marriage and lodged a complaint after her husband filed for divorce, it cannot be construed as an act of vendetta, Madhya Pradesh high court has said while refusing to quash an FIR filed against the husband and in-laws, reports Ashutosh Shukla.
The husband had filed a petition seeking quashing of the FIR, arguing that his wife lodged an FIR for dowry harassment in retaliation to his divorce petition.
Quoting Supreme Court orders on what forms a “counter blast” to an action, like filing of divorce by a husband, Justice G S Ahluwalia said: “If the wife had maintained silence in order to save her marital life and did not lodge the report, then her silence for the noble cause should not be considered against her by holding that the FIR was lodged by way of counter blast to the divorce petition.”
No complaint by bride isn’t abnormal conduct: HCC
Ajay Sura, January 9, 2023: The Times of India
CHANDIGARH: The Punjab and Haryana high court has held that if a matter related to the demand of dowry by a man or his family members was not reported to the police or panchayat by the wife or her parents, then as per the mindset of our society, it cannot be termed as abnormal conduct.
“Generally, the girl herself and her parents make best efforts for settlement and adjustment with the husband and his family, and they do not want to spoil things by washing (dirty) linen in public,” said a division bench of Justice M S Ramachandra Rao and Justice Sukhvinder Kaur.
The judges dismissed an appeal filed by Captain Sandeep Tomar, a former officer of Bihar Regiment and a UP native, who was awarded life imprisonment by a court in Fazilka, Punjab, in July 2014 for poisoning his wife Shweta to death and trying to pass it off as suicide.
On July 9, 2013, local police received information that an Army officer’s wife had committed suicide by hanging herself inside the Abohar cantonment. The Abohar police filed a case against Captain Tomar and his family members on the complaint of his father-in-law Ram Naresh Singh, an employee of Hindustan Aeronautics Limited and a resident of Uttar Pradesh. According to the complainant, he spent a great deal of money to arrange the wedding of his daughter Shweta and Captain Tomar on February 12, 2013. But Captain Tomar and his family used to harass her for dowry. During the investigation, it was also found that the deceased was taunted by her husband for her physical appearance after which she had to undergo an operation for breast enlargement. It was also found that the accused’s family had accepted a draft of Rs 10 lakh at the time of marriage.
In his appeal against conviction, the accused claimed that there is nothing on record that he had harassed the deceased for dowry because her family never complained about this earlier. After hearing all the parties and examining the record, the HC noticed that the appellant had initially claimed that his wife died by hanging herself with a ceiling fan but later said that he found her unconscious after she had consumed some poisonous substance. On this, the HC observed that the burden to prove the guilt of an accused is upon the prosecution, but there may be certain facts pertaining to a crime that can be known only to the accused or are virtually impossible for the prosecution to prove.
“These facts need to be explained by the accused and if he does not do so, then it is a strong circumstance pointing to his guilt based on those facts,” held the HC in its detailed order released in the last week of December. While dismissing the appeal, the HC held that the conspectus of the events which have been noticed goes to show that the deceased was being treated with cruelty and harassed by her husband for more dowry and was ultimately murdered by him for the lust of dowry.
Dowry prohibition laws: misuse of
Tools to harass
‘Dowry law can’t be tool to harass’
New Delhi: A court here has observed that dowry prohibition law cannot be allowed to become a tool for harassment. Granting relief to a man, who was booked in a dowry harassment case by his wife, the court ordered investigation against the complainant for filing a false case.
The man's wife in July 2012 filed an FIR againsthim in a south Delhi police station, alleging that he demanded dowry and subjected her to cruelty, which resulted in her miscarriage. Police investigated the complaint and filed a cancellation report, giving a clean chit to the accused.
Metropolitan Magistrate Ms Shivani Chauhan, accepting the cancellation report of Delhi Police, said, "Under no circumstances can it be permitted to become a tool for harassment of innocent persons."
During the investigation it was revealed that it was the woman's second marriage and there was no evidence of dissolution of the first. The woman alleged cruelty by the man which had resulted in her miscarriage. But the court noted that the investigation report showed she had voluntarily got the medical termination of her pregnancy. AGENCIES
Weapons of vengeance: India Today's 2010 study
Subhash Mishra | Law: Weapon of vengeance | June 19, 2010 | India Today
False cases under the Dowry Prohibition Act are not only filling up jails with innocent people but are also driving warring families to social and financial ruin.
Marriage, dowry, relationships, family, marital discord: it's a potent mix of human emotions and failings and nowhere is this more in evidence than in the misuse of the Dowry Prohibition Act (DPA).
Extreme Decision
Pushkar Singh, 34
Vineeta, 30 Mumbai
Singh, a teacher, committed suicide after his wife allegedly implicated him in a false case for which he had to spend four months in jail. He hanged himself after his release, blaming his in-laws for his plight. He leaves behind a minor child and his ailing, aged mother.
All in the Family
Brijesh Awasthi, 34
Sunita Awasthi, 33, Mumbai
Brijesh claims that his brother-in-law borrowed money which he did not want to repay and in turn told his sister that Awasthi was planning to remarry secretly. Sunita committed suicide and his in-laws charged him with dowry killing. He is now bringing up his two daughters.
An incredible 9,000 husbands and their relatives (10 per cent of the total jail population) are languishing in Uttar Pradesh prisons under the provisions of the Act. Parents of estranged brides are increasingly lodging cases against their in-laws under the Act to "punish the husbands" and to also conceal the actual cause of the dispute between the couple.
"After murder cases, if there is any other crime sending the greatest number of people to jail, it is the Dowry Prohibition Act," says senior IPS officer and Inspector General of UP Jails Sulkhan Singh. What that proves is that an Act meant to protect victims of dowry has become a weapon of vengeance and a mockery of the judicial system.
Indraneil Bhattacharya, a senior executive in a Lucknow-based private company, was married to Mausami Chatterji in 2002 and within five months their relations deteriorated. But they sustained their togetherness and had two children by 2008. "I requested her not to spend too much money on herself but she refused and finally filed a case under DPA as revenge," says Indraneil.
"We have lost all our money in courts and police stations. Mausami and her kin have driven us out of our house. My parents, who had built the house with their hard-earned money, are now living in a rented house," recalls Indraneil, who is now socially ostracised and economically broken.
The Act has caused so much trauma that Pushkar Singh, a teacher, even ended his life. Implicated under the Act, Singh was sent to jail for four months. He came back, wrote a letter blaming his wife and in-laws for implicating him in a false case of dowry and ruining his life. "I cannot face the society so I am ending my life" were his last words as Singh hanged himself. He left behind his aged and ailing mother and a child.
Another victim, Vikas Parihar, says his wife was a journalist who had illicit relations with the owner of a magazine, and when he protested she filed a case under the DPA. "I have lost my job, my money, my status in society and my family. My day ends running after police personnel and advocates. I have no money now. If I don't contest the case, I would be convicted and sent to jail for a crime that I did not commit. But if I challenge it, I lose everything and may soon turn a beggar. What is the use of such a life?" says an emotional Parihar.
In an unusual case in Barabanki district, Saroj of Belia village was married to Ram Saran of Bhaisupur in 2006. One morning she was found missing from her in-laws house. Her father charged Ram Saran and his family with killing his daughter for dowry and disposing of her body.
The sessions court pronounced rigorous life imprisonment for Ram Saran and his family. But during the high court proceedings, the "dead" Saroj presented herself before the court, saying that she had eloped with her paramour and her father had out of vendetta filed a case against her husband and in-laws under the dpa.
There are, however, larger social and judicial issues here. Between 2000 and 2007, 795 minor girls and 1,300 minor boys were also booked under the Act. "In most cases the bride's family lodges a complaint under the dpa against the husband and his family.
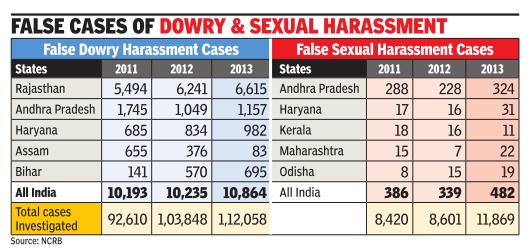
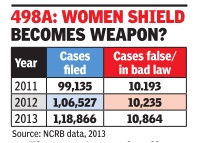
2011-13: false cases
Mar 22 2015
10% of dowry cases false, govt plans changes in law
Deeptiman Tiwary
New Delhi:
Every year more than 10,000 complaints of dowry harassment are found to be false. Given that close to 90,000 to 1 lakh cases are investigated every year, the figure makes it one of the most abused laws in the country . The Centre is now working on a proposal to make Section 498A of the IPC, that deals with offences of dowry demand and cruelty by husband and in-laws, compoundable.So, the law, if amended, would have the provision of settlement between the warring couple if the court allows it.
As the law stands now, the offence is non-compoundable and non-bailable. This leads to immediate arrest of hus band and in-laws with onus on them to prove their innocence. It also rules out any effort at reconciliation.
Sources in home ministry said that a draft note was sent to the law ministry for drawing up a draft bill for the Union cabinet to amend Section 498A. Making dowry law compoundable was also recommended by the law commission and Justice Malimath Committee.
The new law would have penalty provisions of Rs 15,000 instead of Rs 1,000 now if the case is found to be false, said sources. However, it would not be easy to get such an amendment through as women's rights activists have opposed such moves in the past. The argument against any dilution of the law is that it is the strength that several economically dependent and helpless women have against dowry harassment. A dilution effected due to over 10% false cases will affect millions whose cases may be genuine.
Arguments in favour have stressed that those who are really in need hardly approach the police against in-laws due to various societal pressures and it's only those looking to `exact revenge' and having robust economic strength who reach the courts. In a recent order, the Supreme Court had said Section 498A had “dubious place of pride amongst the provisions that are used as weapons rather than shield by disgruntled wives“. An effort by National Commission for Women to amend Dowry Prohibition Act came a cropper after government rejected the recommendation last year. Women and child development minister Maneka Gandhi had in December, 2014 informed Lok Sabha, “The NCW had recommended certain amendments in Dowry Prohibition Act. However, the ministry has taken a considered view on the matter and decided to drop the amendment after taking into account the comments of the high-level committee on the status of women and the ministry of home affairs.”
Govt rejected NCW's bid to amend Dowry Act
Mar 22 2015
Every year more than 10,000 complaints of dowry harassment are found to be false. Given that close to 90,000 to 1 lakh cases are investigated every year, the figure makes it one of the most abused laws in the country . The Centre is now working on a proposal to make Section 498A of the IPC, that deals with offences of dowry demand and cruelty by husband and in-laws, compoundable.So, the law, if amended, would have the provision of settlement between the warring couple if the court allows it.
As the law stands now, the offence is non-compoundable and non-bailable. This leads to immediate arrest of hus band and in-laws with onus on them to prove their innocence. It also rules out any effort at reconciliation.
Sources in home ministry said that a draft note was sent to the law ministry for drawing up a draft bill for the Union cabinet to amend Section 498A. Making dowry law compoundable was also recommended by the law commission and Justice Malimath Committee.
The new law would have penalty provisions of Rs 15,000 instead of Rs 1,000 now if the case is found to be false, said sources. However, it would not be easy to get such an amendment through as women's rights activists have opposed such moves in the past. The argument against any dilution of the law is that it is the strength that several economically dependent and helpless women have against dowry harassment. A dilution effected due to over 10% false cases will affect millions whose cases may be genuine.
Arguments in favour have stressed that those who are really in need hardly approach the police against in-laws due to various societal pressures and it's only those looking to `exact revenge' and having robust economic strength who reach the courts. In a recent order, the Supreme Court had said Section 498A had “dubious place of pride amongst the provisions that are used as weapons rather than shield by disgruntled wives“. An effort by National Commission for Women to amend Dowry Prohibition Act came a cropper after government rejected the recommendation last year. Women and child development minister Maneka Gandhi had in December, 2014 informed Lok Sabha, “The NCW had recommended certain amendments in Dowry Prohibition Act. However, the ministry has taken a considered view on the matter and decided to drop the amendment after taking into account the comments of the high-level committee on the status of women and the ministry of home affairs.“
2015: frequency of misuse
The Times of India, November 8, 2015
Flipside to anti-dowry law: Men cry abuse
Businessman Rajesh Varkharia thought he was waging a lonely legal battle till a chance meeting with two other dowry accused at the Bangalore trial court. “I was totally in the dark. I would just sign where the lawyer asked me to,“ he says, describing his five days in prison as an accused under IPC's Section 498A, the dowry harassment act. Varkharia and three others started Save Indian Family Foundation (SIFF) in 2005 to offer legal advice and assistance to men who say they have been falsely accused of demanding dowry. A decade later, the four-member NGO has over 50 chapters across the country , with 30 members adding to the strength every week, many of whom are between 32 and 35 years of age.
The fact that men are suffering from the “misuse“ of 498A is gaining traction, so much so, that the courts and the government are sitting up and taking notice. Earlier this year, the home ministry proposed amendments in the anti-dowry act on the grounds that false cases were as high as 9%. The move is to make offences of dowry demand and cruelty by husband and in-laws compoundable. (But, in Parliament, minister of state for home affairs Haribhai Parthibhai Chadhary has also added that “there is no direct evidence or study available to suggest that this (section 498A of IPC) is one of the most abused laws in the country“.) The Supreme Court too, in successive judgments, has sought to dull the provision for the immediate arrest of the husband's family . In 2005, the SC described the section as “legal terrorism.“ And in a controversial June 2014 judgment, the SC restrained the police from mechanically arresting the husband and his relatives on the mere lodging of a complaint under Section 498A of the IPC.
Citing very low conviction rate, the SC directed the state governments to instruct police “to satisfy themselves about the necessity for arrest under the parameters (check list) provided under Section 41 of criminal procedure code“. Both the law commission and the Justice Malimath Committee on Criminal Justice Reform have held that the section should be made compoundable and bailable.
Men rights groups like SIFF argue that law doesn't really protect women as it claims. “Is it just the wife who needs protection?
What about the mother-in-law, sister-in law or women relatives of the husband? Why must they suffer?“ asks Vakharia.
However, women rights lawyers say that the focus should not be the law but its implementation. “Every law is misused and there is a section of society that will misuse every kind of legal provision. Should we revoke the whole lot of them,“ asks a lawyer.
They also underline the need for police reforms. “Women are often unaware of the provisions of laws that protect them against dowry harassment or domestic violence; it is the police that might mislead them,“ says an activist.
2018: SC wants protective measures against misuse of Section 498A
The Supreme Court said if Parliament had enacted Section 498A IPC in 1983 to protect women from cruelty in matrimonial homes, it was now obliged to frame protective measures to curb harassment of husbands and their relatives from misuse and prevent a “war between two sexes”.
A bench of CJI Dipak Misra and Justices A M Khanwilkar and D Y Chandrachud said the perception of persecution under Section 498A because of “super sensitivity” and overzealousness by police to arrest husbands could bring about social disaster with the “potential to vertically divide society”.
The SC said it was obligatory on the part of the legislature to enact protective measures against misuse of Section 498A and for courts to carefully scrutinise genuineness of complaints while establishing from evidence the requirement of keeping those arrested in custody rather than enlarging them on bail.
Writing the judgment for the bench, CJI Misra said the SC could not lose sight of growing abuse of the provision. “When implementation of the law (arrest) is abused by law enforcing agency, the legislature introduces a protective provision as regards arrest. Needless to say, the courts have ample power to grant anticipatory bail, and even to quash criminal proceedings totally to stabilise lawful balance because no court of law remotely conceives a war between two sexes,” the bench said.
Friday’s judgment removed a few safeguards against arrest of husbands and their relatives introduced by a two-judge SC bench last year in its decision in the Rajesh Sharma case. The SC did away with the stipulation that genuineness of Section 498A complaints would first be verified by a district level committee and that no arrest would me made till it gave its final report.
While removing the safeguard, which was hailed by ‘harassed husbands’, the bench showed that it was alive to concerns over immediate arrest after lodging of an FIR under Section 498A. Parliament had introduced Section 498A in IPC in 1983 to deal with increasing number of dowry deaths while categorising the offence as cognisable and non-bailable.
Supreme Court on the misuse of the dowry law
SC's 2013 judgement
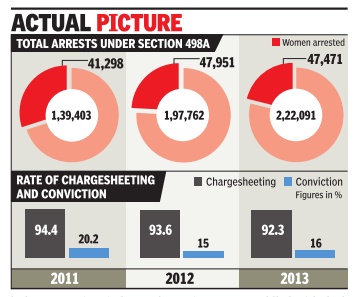
Jump in dowry arrests, not many convicted
Abhinav Garg New Delhi:
TNN
The Times of India Jul 07 2014
The Supreme Court judgment on the misuse of the anti-dowry law comes close on the heels of the latest National Crime Records Bureau figures that show a jump of 12.3% in arrests under Section 498A of Indian Penal Code since 2012.
The data in the 2013 NCRB crime statistics report vindicate the court's concerns that the penal provision meant to combat the menace of harassment of women by husband or in-laws is often being used as a “weapon rather than shield by disgruntled wives“. IPC 498A being a cognizable and nonbailable offence only worsens the plight of the accused.
Section 41 of Criminal Procedure Code lays down a ninepoint check list for police to weigh the need to arrest after examining the conduct of the accused, including possibility of absconding.
An analysis of NCRB reports of last three years show disturbing trends that obviously played on SC's mind when it came out with the recent guidelines. For one, more and more women are being arrested and charged under the section that is meant to protect women. Nearly 21-22% of those arrested by police for cruelty against a wife happen to be women themselves--they are either the husband's mother, sister or other female relatives. Misuse of the law by some estranged wives
Misuse of the provision is also evident from the fact that the rate of chargesheeting by police hovers around 93-94% for all the three years while conviction rate by courts is a dismal low of 15-20%.
TOI spoke to lawyers and judges in Delhi who welcomed the apex court verdict terming it as a much needed safeguard against arbitrary arrest under IPC 498A. They also underlined that the SC judgment would have far-reaching consequences only if police and in vestigative agencies adhere to it instead of sidestepping the norms. The apex court has noted that police have “not come out of its colonial image. Despite six decades of Independence, it is largely considered as a tool of harassment, oppression and surely not considered a friend of public“.
A serving judge highlighted how a Delhi high court ruling that the DCP's nod is a must before arresting in-laws of a woman in a case of marital cruelty has been negated by police. “We have observed a trend where police have actively aided misuse of dowryand cruelty-related marital provisions.
Despite HC directives, certain police stations include 354 (outraging modesty) or causing injuries as additional sections in the FIR. Police then immediately lodge the FIR saying since it is not a simple case of 498A or 406 IPC, permission of DCP is not required.“
Advocate Prabhjit Jauhar said the SC verdict must be celebrated in today's scenario.
“On a daily basis I come across cases where estranged wives take recourse to filing FIRs under 498A. Since the courts have now become liberal in giving bail under this section, the new trend is to insert allegations of rape or attempt to rape to get FIRs registered under 376 IPC. Wives don't even hesitate in levelling allegations against the father-inlaw for sexual misconduct when there is no direct proof of the same. In these circumstances getting bail becomes very difficult and innocent persons have to undergo incarceration for 20 days to 4 months till they are granted regular bail. Courts are saddled with dockets of anticipatory or regular bails in these cases,“ he pointed out.
However, advocate Arvind Jain disagreed with the SC verdict. He drew attention to the overall conviction rate of roughly 26% and wondered on what basis the apex court could single out arrests under 498A as problematic.
“If law is a weapon, everybody is using it. You need to appreciate that all these dowryrelated crimes are committed within four walls of the house and seldom do women have sufficient evidence to prove in court. One needs to see the complete reality that law has not been able to prevent dowry harassment and deaths. The interpretation coming from SC appears to be insensitive towards women.“
2022: Omnibus dowry allegations don’t merit prosecution: SC
AmitAnand Choudhary, February 9, 2022: The Times of India
New Delhi: Citing misuse of penal provisions for dowry harassment to settle personal scores by dragging in-laws and other relatives into criminal proceedings, the Supreme Court on Tuesday held that general and omnibus allegations cannot be a ground for prosecution and asked courts to be careful and cautious in dealing with such complaints. A bench of Justices S Abdul Nazeer and Krishna Murari said the SC in its numerous judgments had expressed concern and warned courts not to proceed against relatives of the husband when no prima facie case is made out against them. The court passed the order while quashing criminal proceedings lodged by a woman in Bihar against her husband and in-laws. As the husband, who was also made an accused did not challenge the FIR, the court refrained from dealing with the allegations against him and granted relief to his five relatives.
“. . . . This court has at numerous instances expressed concern over the misuse of section 498A of IPC and the increased tendency of implicating relatives of the husband in matrimonial disputes, without analysing the long term ramifications of a trial on the complainant as well as the accused. It is further manifest from the said judgments that false implication by way of general omnibus allegations made in the course of matrimonial dispute, if left unchecked, would result in misuse of the process of law. Therefore, this court by way of its judgments has warned the courts from proceeding against the relatives and in-laws when no prima facie case is made out against them,” it said.
While granting relief to the petitioner, the court noted that there was no specific allegation against the in-laws and the woman’s allegations were general in nature, which was not sufficient enough to hold trial.
“Upon a perusal of the contents of the FIR, it is revealed that general allegations are levelled against the appellants. The complainant alleged that ‘all accused harassed her mentally and threatened her of terminating her pregnancy’. Furthermore, no specific and distinct allegations have been made against either of the appellants herein, i. e. , none of the appellants have been attributed any specific role in furtherance of the general allegations made against them. This simply leads to a situation wherein one fails to ascertain the role played by each accused in furtherance of the offence,” the bench said.
The bench said that facing trial leaves a person with a after getting acquitted and holding trial in such cases should be discouraged.
Stop automatic arrests: SC
SC: Dowry law misused, stop automatic arrests
Dhananjay Mahapatra New Delhi: TNN
The Times of India Jul 03 2014
The Supreme Court on Wednesday said women were increasingly using the anti-dowry law to harass in-laws and restrained police from mechanically arresting the husband and his relatives on the mere lodging of a complaint under Section 498A of the Indian Penal Code.
Citing very low conviction rate in such cases, it directed state governments to instruct police “not to automatically arrest when a case under Section 498A of IPC is registered but to satisfy themselves about the necessity for arrest under the parameters (check list) provided under Section 41 of Criminal Procedure Code”. Section 41 lays down a nine-point check list for police to weigh the need to arrest after examining the conduct of the accused, including possibility of absconding.
If police arrested the accused, “the magistrate, while authorizing detention of the accused shall peruse the report furnished by the police officer in terms of Section 41 and only after recording its satisfaction...will authorize detention,” the bench of Justices C K Prasad and P C Ghose said.
I t also said that this check list for arrest and deten tion would apply to all offences, which are punished with a prison term less than 7 years. Punishment under Section 498A is a maximum of three years but it had been made a cognizable and nonbailable offence, which made grant of bail to the accused a rarity in courts.
But the court singled out the dowry harassment cases as the most abused and misused provision, though the legislature had enacted it with the laudable object to prevent harassment of women in matrimonial homes.
Writing the judgment for the bench, Justice Prasad said there had been a phenomenal increase in dowry harass ment cases in India in the last few years. “The fact that Section 498A is a cognizable and non-bailable offence has lent it a dubious place of pride amongst the provisions that are used as weapons rather than shield by disgruntled wives,” he said.
“The simplest way to harass is to get the husband and his relatives arrested under this provision. In a quite number of cases, bed-ridden grand-fathers and grandmothers of the husbands, their sisters living abroad for decades are arrested,“ he said.
The Times of India’s View For long now, concerns have been expressed about stringent anti-dowry laws being misused by some women to harass or blackmail their in-laws. These apprehensions have not only been expressed by courts, women's activists too have acknowledged that such misuse is not unknown. It was, therefore, necessary for the law to take this reality into account.
The apex court's order does just that. Automatic arrest was one of the provisions that lent itself most to abuse and making it mandatory for a magistrate to sanction arrest should help curb this abuse of law. Beyond that, there's a lesson for all of us ¬ social ills can't be eliminated just by enacting laws, as India tends to do. Society as a whole needs to join the movement against them.
Supreme Court’s guidelines for arrests in dowry cases/ 2014
SC enforces guidelines for arrests in dowry cases
The Times of India Jul 04 2014
Cops Face Action If They Fail To Follow `Dos & Don'ts' List
The Supreme Court has warned the police of departmental action and contempt proceedings if they do not follow the checklist in the Criminal Procedure Code mandating them to weigh the need to arrest a person accused of dowry harassment.
A bench of Justices CK Prasad and PC Ghose said police must follow the `Dos and Don'ts' prescribed under Section 41 of CrPC before arresting a person in an offence punishable with less than seven years of imprisonment on being found guilty.
The checklist mandates that a person accused of such an offence can be arrested if the police officer is satisfied that it was necessary:
to prevent such person from committing any further offence for proper investigation of the case
to prevent the accused from causing disappearance of evidence
to prevent the accused from tampering with evidence
to prevent the person from inducing, threatening or luring the witness
to dissuade him/her from disclosing facts to police officer or the court
to prevent the accused from absconding
to secure his presence before the court during the hearing
The bench said the law mandated the police officer to record reasons in writing why he came to the conclusion that arrest was necessary and that he had satisfied himself with each and every provision of the checklist. Justice Prasad, writing the judgment, said: “In pith and core, the police officer before arrest must put a question to himself, why arrest?
Is it really required? What purpose it will serve/What object will it achieve?
“Before arrest, first the police officers should have reason to believe on the basis of information and material that the accused has committed the offence. Apart from this, the police officer has to be satisfied further that the arrest is necessary for one or the more purposes envisaged under Section 41.“ If the police arrest and produce a person before a magistrate, and if he finds the arrest was in breach of the checklist, then he “is duty-bound not to authorize further detention and release the accused“, the bench said.
The court said the legislature had inserted Section 41 in CrPC to “avoid unnecessary arrest or threat of arrest looming large on accused“. This provision asks police to issue a notice to the accused specifying the time and date for his appearance for purpose of investigation. If the accused complies and cooperates with the investigation, he would not be arrested.
Sc said if cops scrupulously adhered to the Section 41 mandate, then “the wrong committed by police officers intentionally or unwittingly would be reversed and the number of cases which come to the court for grant of anticipatory bail will substantially reduce“.
SC, 2025: ‘No dowry case arrest till 2 mths of complaint’
23 Jul. 25 The Times of India
SC on Tuesday adopted Allahabad HC’s two-year-old guidelines directing cops not to arrest a husband or his kin for two months from the date of his wife lodging a dowry harassment case under IPC section 498A while asking an IPS woman officer to apologise through newspaper ads the harassment she inflicted on her estranged husband and his relatives, reports Dhananjay Mahapatra .
While exercising its powers under Article 142 to dissolve the marriage, a bench of CJI B R Gavai and Justice A G Masih said, “The guidelines framed by Allahabad HC… for safeguards regarding misuse of section 498A, IPC, shall remain in effect and be implemented by appropriate authorities.”
Dhananjay.Mahapatra@timesofindia.com
New Delhi : In an important decision, Supreme Court adopted Allahabad HC’s two-year-old guidelines directing police not to arrest a husband or his relatives for two months from the date of his wife lodging a dowry harassment case under section 498A of the IPC while asking an IPS woman officer to apologise through newspaper publications the harassment she inflicted on her estranged husband and his relatives.
A bench of CJI B R Gavai and Justice A G Masih gave this ruling while drawing up an amicable settlement between 2022-batch IPS officer Shivangi Bansal nee Goel and her husband in exercise of its exclusive powers under Article 142 of the Constitution to dissolve their marriage.
While drawing up the settlement, SC said, “The guidelines framed by Allahabad HC in impugned judgment dated June 13, 2022, in Criminal Revision No. 1126 of 2022 vide paras 32 to 38, with regard to constitution of family welfare committees for safeguards regarding misuse of section 498A, IPC, shall remain in effect and be implemented by the appropriate authorities.”
SC said the apology was needed because of the cases filed by her “...the husband remained in jail for a period of 109 days and his father for 103 days, and the entire family suffered physical and mental trauma and harassment. What they have suffered cannot be resituated or compensated in any manner”. However, “It shall not ever be used against Shivangi Bansal/Shivangi Goel before any court of law, administrative/regulatory/quasi judicial body/tribunal against her interests now or in the future, ” it added.
No arrest in dowry cases till charges are verified: SC
`Set Up Panels In Every District For Initial Probe
Expressing con cern over disgruntled wives misusing the anti-dowry law against their husbands and in-laws, the Supreme Court on Thursday directed that no arrest or coercive action should be taken on such complaints without ascertaining the veracity of allegations.
Acknowledging a growing trend among women involved in marital discord to abuse Section 498A of IPC to rope in their husbands' relatives -including parents, minor children, siblings and grandparents -in criminal cases, a bench of Justices A K Goel and U U Lalit said it was high time such frivolous cases which violated the human rights of the innocent was checked.
This is a shift from the dominant judicial conception of women as victims who would silently suffer injustice rather than bring disrepute to their family by taking domestic conflict outside the four walls of the home. Going by the po pular portrait, it is only the worst victim of abuse among women who approach the court for redress. On Thursday , the court broke away from the reigning perception to rule that in dowry cases, the account of the alleged victim need not be taken at face value. Undercutting the innocence law enforcement agencies had so far assigned to complainants in dowry harassment cases, the Supreme Court on Thursday directed all states to set up family welfare committee (FWC) in each district and tasked them with testing the veracity of every complaint.
“It is a matter of serious concern that large number of cases continue to be filed under Section 498A alleging harassment of married women...Many such complaints are not bona fide. At the time of filing of the complaint, implications and consequences are not visualised. At times, such complaints lead to uncalled for harassment not only to the ac cused but also to the complainant. Uncalled for arrest may ruin the chances of settlement,“ the bench said.
“We are conscious of the object for which the provision was brought into the statute.At the same time, violation of human rights of innocent cannot be brushed aside,“ it added. The bench ruled that all such complaints received by the police or the magistrate must be referred to the family welfare committee and no action should be taken against the husband and the in-laws till the committee gave its report after interacting with the parties.
“Report of such committee be given to the authority by whom the complaint is referred to, latest within one month from the date of receipt of complaint,“ the court said. The court also said bail applications of hus band and in-laws should be decided expeditiously by trial courts, preferably the same day it is filed.
The court further said impounding of passports or issuance of Red Corner Notice against person living abroad should be avoided and personal appearance of husband's family members should not be insisted upon by trial courts in dowry harassment cases. It also directed that a designated police officer should be appointed to deal with complaints under Section 498A.
Cash demand to meet domestic spend is not dowry
In an order, a magistrate court while acquitting a man and his family of dowry and cruelty charges, has observed that a demand for money on account of financial stringency or for meeting some urgent domestic expenses or for purchasing manure cannot be termed as a demand for dowry .
While dismissing the wife's case due to lack of evidence, a Borivli magistrate court held, “Even if the accused had demanded an amount of Rs 5 lakh for purchase of household articles, then that does not ipso facto amount to unlawful demand under Indian Penal Code Section 498 A (husband or relative of husband of a woman subjecting her to cruelty).“
The court also pointed out that the FIR was registered two years after the alleged cruelty first started and the delay was not explained.
The court said the definition of dowry under the Dowry Prohibition Act meant any property or valuable security that should be given or agreed to be given either directly or indirectly , at or before or any time after the marriage and in connection with the marriage.
“The evidence adduced by the prosecution does not, therefore, show that any demand for `dowry' as defined in Section 2 of the Dowry Prohibition Act was made by the appellants (accused) as what was allegedly asked for was some money for meeting domestic expenses and for purchasing manure.“
2017/ SC restores `immediate arrest'
`Abuse Of Sec 498A Can't Be Reason To Curtail Ambit Of Law'
A three-judge Supreme Court bench headed by Chief Justice Dipak Misra disagreed with the court's July 27 judgment which diluted the rigour of Section 498A of IPC which warrants immediate arrest of a husband and his relatives in a dowry-linked complaint of cruelty .
In the July 27 judgment, a bench of Justices Adarsh Kumar Goel and U U Lalit had cited data from the National Crime Records Bureau which indicated widespread misuse of Section 498A by women to get husbands and their relatives arrested and harassed for years. But on Friday , the SC decided that abuse of Section 498A should not amount to curtailing the ambit of the law.
The two-judge bench had ordered setting up of family welfare panels in every district to examine the veracity of each complaint under Section 498A. It had said no arrest would be made till the committee gave a report endorsing prima facie authenticity of the complaint.
The earlier order had said there would be a designated police officer to probe Section 498A complaints and advised trial courts not to insist on personal appearance of all family members of the husband, especially those living elsewhere, and permit appearance through video conferencing.
In a case relating to protection of persons from arrest by police without warrant, as it happens in Section 498A complaints, the three-judge bench of Justices Misra, A M Khanwilkar and D Y Chandrachud went far beyond the scope of the petition and said, “At this stage, we are obligated to say that we are not in agreement with the judgment in Rajesh Sharma vs UP case (pronounced on July 27). Abuse of Section 498A (by women) would not make this court curtail the ambit and scope of the section enacted to protect women from cruelty in matrimonial homes.“
The bench faulted the exercise undertaken by the two-judge bench in laying down elaborate guidelines as an exercise reserved solely for the legislature. It issued notice to the Centre and appointed senior advocate V Shekhar as amicus curiae while posting detailed deliberations for October 29.
Husband will not inherit stridhan if wife dies ‘mysteriously’ within 7years: SC
The Times of India, Jan 20 2016
AmitAnand Choudhary
7-year hitch: Hubby can't be heir
The Supreme Court has held that a man would not be entitled to claim property and stridhan gifted to his wife if she dies under mysterious circumstances within seven years of marriage, bringing the case within the ambit of dowry death. A bench of Chief Justice T S Thakur, Justices A K Sikri and R Bhanumathi clarified that in case of natural death, the heirs of the woman would be entitled to claim the properties but in case the woman dies under mysterious circumstances within seven years of her marriage, the properties would be handed over to her children or her parents in case the couple has no children.
Enumerating Section 6 of the Dowry Prohibition Act, the bench said the dowry articles must be handed over to the woman within three months after the marriage and the husband or inlaws could be prosecuted for not giving back the movable and immovable properties within the stipulated time.
“If the dowry amount or articles of the married woman was placed in the custody of her husband or in-laws, they would be deemed to be trustees of the same. The person receiving dowry articles or the person who has dominion over the same, as per Section 6 of the Dowry Prohibition Act, is bound to return the same within three months after the date of marriage to the woman in connection with whose marriage it is given,“ the bench said.
The bench said the husband and in-laws would be guilty of a dowry offence punishable up to a two-year jail term if they refuse to hand over the dowry property and the Act also laid down that even after conviction they would have to return the property. It passed the order on a plea filed by a man and his kin facing prosecution for returning the dowry article to parents of his wife who died under suspicious circumstances 15 months after marriage.
Naming husband’s relatives does not make them accused: SC
Merely naming distant relatives not enough to make them accused in dowry cases: SC
Satya Prakash, Hindustan Times New Delhi, September 17, 2014
Merely naming the husband’s distant relations is not enough to summon them as accused in dowry cases, the Supreme Court has ruled.
A bench of Justice V Gopala Gowda and Justice Adarsh Kumar Goel said courts cannot summon distant relations of a man in dowry cases in absence of any specific role attributed to them and material to support the allegations. Courts have to be careful in such cases, it emphasised.
“Only the husband, his parents or at best close family members may be expected to demand dowry or to harass the wife but not distant relations, unless there is tangible material to support allegations made against such distant relations,” the bench said quashing the charges against distant relations of a woman’s husband in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh.
The verdict comes barely two-and-a-half-month after the top court put an end to the practice of automatic arrest under the anti-dowry law, expressing concern over the misuse of Section 498A of IPC by “disgruntled wives” against in-laws and husbands. It had asked state governments to ensure that the police didn’t go on an arresting spree -- as was the practice -- in dowry harassment cases.
The attitude to arrest first and then proceed with the rest was "despicable" and must be curbed, it had said, adding police must give reasons and proof to magistrate before making an arrest under Section 498A of IPC, the SC had said in July.
In the instant case, the woman in question had names distant relations of her husband along with her husband and in-laws under Section 406 of IPC (criminal breach of trust) and Section 6 of the Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961 after the husband filed a petition for divorce in 2010. Those names in the FIR included the grandson of the brother of her husband’s grandfather and and some others whose names were added in a subsequent complaint without any specific allegations against them.
The Allahabad HC had refused to quash the charges against them. But terming it a clear abuse of process of the court, the SC quashed all charges against the accused – who were all distant relations of the complainant woman.
Concerned over its abuse, the Law Commission and Parliament’s standing committee on home affairs had recommended that offences under Section 498A IPC be made compoundable i.e. husband and wife should be allowed to settle the dispute between themselves.
Loophole in IPC Section 304B plugged by SC
Dhananjay Mahapatra, May 29, 2021: The Times of India
The SC plugged a much-exploited legal loophole in IPC Section 304B that aided acquittals in dowry death cases while expressing anguish that the law had failed to serve as a deterrent, reports Dhananjay Mahapatra.
The court said, “The phrase ‘soon before’ as appearing in Sec 304B cannot be construed to mean ‘immediately before’. The prosecution must establish the existence of ‘proximate and live link’ between the dowry death and cruelty or harassment for dowry demand by the husband or his relatives.” It advised trial courts not to take a pigeon-hole approach to Section 304B in categorising death as homicidal or suicidal or accidental.
Wife’s ancestral property is not dowry: SC
FROM THE ARCHIVES OF ‘‘THE TIMES OF INDIA’’: 2008
Dhananjay Mahapatra | TNN
Seeking share in wife’s ancestral property is not dowry, says SC
In a legal regime which takes a very strong view of dowry deaths, there appears to be a small respite for husbands. For, the Supreme Court on Monday ruled that asking for the wife’s share in ancestral property from in-laws would not come under the definition of “dowry”. This judgment could become a small but significant breather for husbands, on whom the courts virtually impose the onus of coming clean on dowry death charges if their wives die an unnatural death within seven years of marriage and there had been past allegations of harassment.
“Demanding her share in the ancestral property will not amount to a dowry demand,” said a bench comprising Justices Arijit Pasayat and Harjit Singh Bedi while dismissing a man’s appeal seeking acquittal in a dowry death case. However, it reduced the sentence from 10 years to 7 years prison term. Baldev Singh had moved the apex court challenging a Punjab and Haryana high court verdict convicting him for abetting the suicide of his wife. The court had acquitted his mother and sister of dowry harassment charges.
Rejecting his plea for acquittal like his mother and sister, the bench said unnatural death of a woman in her matrimonial home within seven years of marriage raises a presumption of dowry harassment against the husband.
It clarified that Section 304-B of the IPC and Section 113-B of the Evidence Act provided that the onus would be on the husband to prove his innocence if there had been allegations of dowry harassment proximate to the unnatural death.
“There must be existence of a proximate and live link between the effect of cruelty based on dowry demand and the concerned death. If alleged incident of cruelty is remote in time and has become stale enough not to disturb mental equilibrium of the woman concerned (to take extreme step), it would be of no consequence,” said Justice Pasayat, writing the judgment for the bench.
Dowry laws
They apply: HC/ 2024
Oct 8, 2024: The Times of India
Dowry laws apply to live-in couples too, says HC:
Allahabad high court has held that for an offence of dowry demand or a dowry death to be made out, it is sufficient to show the victim and the accused man lived as husband and wife, regardless of whether she was a legally wedded wife. HC laid down the position while upholding a Prayagraj sessions court’s rejection of a plea in April this year to discharge an accused, Adarsh Yadav, over his live-in partner’s death.
See also
Dowry and dowry-related crimes: India <> Dowry: Pakistan <> Dowry prohibition laws: India