Electronic goods: India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
Exports
2020, 2021
From: February 5, 2022: The Times of India
See graphic:
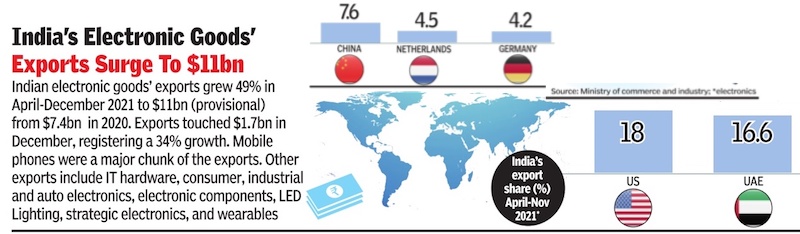
The Export of Electronic goods from India in 2020, 2021
Manufacturing
2016 – 23
From: August 1, 2023: The Times of India
See graphic:
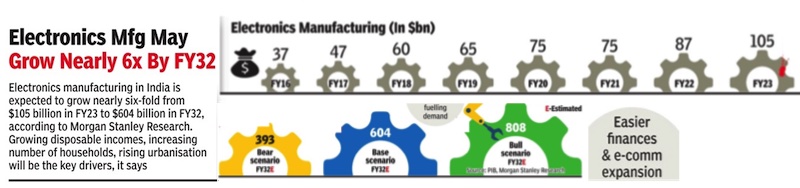
Electronics Manufacturing in India, 2016 – 23
Production/ imports
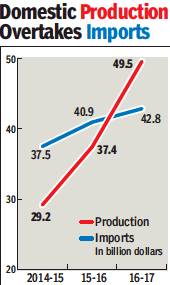
2016-17: Domestic electronics production higher than imports
From: Pankaj Doval, In a first, e-goods made in India pull ahead of imports, December 30, 2017: The Times of India
From: Pankaj Doval, In a first, e-goods made in India pull ahead of imports, December 30, 2017: The Times of India
The Centre’s efforts to promote local manufacturing through the ‘Make in India’ programme seem to be reaping dividends with the domestic production of electronics — one of the key reasons behind foreign currency spends after oil — moving ahead of imports for the first time in 2016-17.
Official sources told TOI domestic electronics production in 2016-17 stood at $49.5 billion, higher than the nearly $43 billion spent on imports. The government has taken a number of steps to boost manufacturing of electronics, particularly of smartphones, appliances, set-top boxes and televisions. A majority of imports in many of these areas are coming from neighbouring China, something India is now trying to counter through fiscal incentives and other measures.
The local benefits were reinforced recently when the customs duty on import of a variety of products was raised earlier this month. This was for products such as mobile phones, set-top boxes, microwave ovens, and LED lamps.
Govt plans a major push for digital initiatives
Many units have also availed benefits over the past two years under the Modified Special Incentive Package Scheme (MSIPS) and theelectronics manufacturing clusters (EMC) programme.
The growth in local manufacturing has been strong over the past three financial years as imports are moderating. In 2015-16, the local production was $37.4 billion against imports of $41 billion, while in 2014-15, electronics goods worth around $30 billion were made in India against $37.5 billion sourced from overseas. The government plans to give a massive push to digital activities and achieve a turnover of $1 trillion by 2022. Manufacturing of electronicsisseen as a major contributor towards meeting this target. Information technology minister Ravi Shankar Prasad has already held two rounds of meetings with top CEOs of the IT and electronicsindustry and those linked to the promotion of digital services.
“The policy initiatives of the Modi government have resulted in accelerating local manufacturing in electronics. We are confident that the momentum will be sustained over the coming years,” Prasad told TOI. “The plan is to ensure that we make in India not only to meet the domestic requirement, but also to cater to the world markets.”
The overall demand for electronics (sourced locally and through imports) in 2016-17 has been to the tune of $86.4 billion ($60.5 billion in 2014-15), and the government expects this to more than double by 2020 and stay between $171 billion and $228 billion. “The overall projection by 2023-24 is $400 billion,” an official source said.
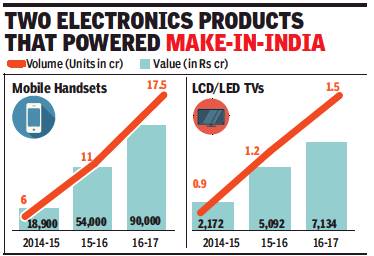
What is heartening for the government in this growth is the impetus it has provided to local production and jobs. While 6 crore handsets were manufactured in the country in 2014-15, this has grown nearly threefold in just two years to 17.5 crore in 2016-17. The value of phones made in India has moved up from Rs 19,000 crore in 2014-15 to as much as Rs 90,000 crore in 2016-17.
A similar spurt has been seen in the production of televisions. “The production of LCD/LED TVs grew from nearly 90 lakh units in 2014-15 to1.5 crore units in 2016-17. In terms of turnover, LED production grew from Rs 2,172 crore in 2014-15 to over Rs 7,100 crore in 2016-17,” the source said. The duty incentives for local manufacturing have already prompted a variety of companies to manufacture in India, or source from contract suppliers such as Taiwanese Foxconn and Wistron (which are investing/expanding in India) or homegrown ones like Dixon and Optiemus.
Those now sourcing locally include Chinese Xiaomi, Oppo, Vivo, Huawei and Gionee. Even American electronics giant Apple has started a modest assembly operation in Bengaluru. In the television arena, companies such as Sony and Panasonic are sourcing in India.
The growth in local manufacturing is also leading to significant employmentcreation in the market, estimated to be in excess of 1 lakh direct jobs and 2 lakh indirectly. “A new electronics manufacturing policy is on the anvil, and we are confident of achieving the earmarked targets for local manufacturing,” Prasad said.