Information Technology Act: India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
Section 66A
2015: SC judgement
The Times of India Mar 25 2015
Amit Choudhury & Dhananjay Mahapatra
`Section 66A is ambiguous & prone to misuse'
The Supreme Court fortified the right to freedom of speech and liberty by striking down as unconstitutional Section 66A of the Information Technology Act, which police had used indiscriminately to arrest persons for posting criticism of government and political leaders. “Section 66A is so widely cast that virtually any opinion on any subject would be covered by it, as any serious opinion dissenting with the mores of the day would be caught within its net. Such is the reach of the section and i it is to withstand the test of constitutionality, the chilling effect on free speech would be total,“ the court said.
Justices J Chelameswar and R F Nariman said the law was ambiguously worded prone to misuse and, there fore, stretches far beyond the “reasonable restrictions“ criterion laid down under Ar ticle 19(2) of the Constitution They brushed aside the government's promise not to misuse the law, saying tha what is unconstitutiona should not be on the statute book at all. “Governments may come and governments may go but Section 66A goes on forever. An assurance from the present government even if carried out faithfully would not bind any successor government,“ the court said.
However, despite the SC judgment, citizens still need to be careful while posting comments online as provisions similar to Section 66A exist in Indian Penal Code's Sections 153 and 505. But the ruling could act as a deterrent against arrest. Referring to as many as 20 judgments of the US Supreme Court, the bench also said restriction on free speech by Section 66A, brought into force by the UPA government in 2009 by amending the I-T Act and defended in the apex court by the NDA government, far exceeded“ reasonable restrictions “provided under Article 19(2) of the Constitution. Writing a 123page judgement for the bench, Justice Nariman said: “It cannot be over emphasized that when it comes to democracy , liberty of thought and expression is a cardinal value that is of paramount significance under our constitutional scheme.“ Section 66A purports to authorize the imposi tion of restrictions on the fundamental right contained in Article 19(1)(a) (guaranteeing right to freedom of speech and expression) in language wide enough to cover restriction both within and without limits of constitutionally permissible legislative action,“ says the 123-page judgment. The court also struck down Section 118 of Kerala Police Act, which was on the lines similar to Section 66A.
Law student Shreya Singhal had moved the Supreme Court, challenging the constitutionality of Section 66A, after two Maharashtra girls were arrested for their social media posts criticizing the bandh called by Shiva Sena on the day Bal Thackeray was cremated.
However, the court upheld the constitutional validity of Section 69-A of the I-T Act, which empowered authorities to issue directions for blocking for public access of any information through any computer resource if the authorities felt that it was necessary to do so in the interest of “sovereignty and integrity of India, defence of India, security of the state, friendly relation with other countries and disturb public order or incite an offence.
The Supreme Court said it was upholding the validity of the provision because there was an elaborate procedure provided under the law for deciding blocking of websites and that it demanded the authorities to record in writing the reasons behind the decision to block.
The bench also watered down the power provided to internet service providers under Section 79 to take down posts on mere request of others who find it offensive. It said posts could be taken down only on the orders of a court.
'A bad law will not stand the test of judicial scrutiny'
India Today, March 27, 2015
P. Rajeev
The scrapping of Section 66A proves that a bad law will not stand the test of judicial scrutiny
Few provisions of law have attracted as much criticism from the entire spectrum of Indian citizenry as Section 66A. Although the legislative intent was primarily to tackle internet spam, it quickly became clear that this provision of law was susceptible to wanton abuse.
The Lok Sabha had passed this amendment bill along with six other enactments without any discussion in a span of just seven minutes on December 23, 2008; the Rajya Sabha also passed it the next day. Parliament did not get an opportunity to discuss it in detail.
In a democracy, passing bills in Parliament amid din is always objectionable. It is true that the Constitution bestows upon the judiciary the power of review, but Parliament should ensure that the legislations it enacts should not be ultra vires, i.e. beyond its legal power or authority. But in this case, Parliament failed to do so. I tried twice to rectify this by moving a statutory motion and private members' resolution. I moved the first annulment motion in the history of Parliament to scrap the Information Technology (Intermediaries Guidelines) Rules. There was a debate in Parliament on this issue and then IT minister Kapil Sibal assured the House of making changes after consultations with all stakeholders. But the government failed to keep the assurance.
The second occasion was during the discussion on a private members' resolution which urged the government to amend Section 66A in accordance with Article 19(2) of the Constitution. I recall Sibal's intervention: "The limits of exercise of freedom of expression in the social media can't be constitutionally prescribed because when the Constitution was framed, there was no social media. There was only the print media." Now, the Supreme Court has correctly ruled that even though the internet may be treated separately from other media and there could be separate laws, these laws still have to pass the test of "reasonable restrictions" on free speech allowed by Article 19(2) of the Constitution.
When we raised concerns on the vagueness of the terms used in the act, Sibal had said, "Please don't ask us to define that cannot be defined. What annoys you may not annoy me." This argument has been torpedoed by the apex court in its judgment in para 74: "If one looks at Section 294, the annoyance that is spoken of is clearly defined-that is, it has to be caused by obscene utterances or acts. Equally, under Section 510, the annoyance that is caused to a person must only be by another person who is in a state of intoxication and who annoys such person only in a public place or in a place for which it is a trespass for him to enter. Such narrowly and closely defined contours of offences made out under the Penal Code are conspicuous by their absence in Section 66A which in stark contrast uses completely open ended, undefined and vague language."
By striking down a provision of law that lent itself to blatant abuse often at the behest of vested political interests, the court has demonstrated once again that bad law will not stand the test of judicial scrutiny and liberty of expression are accorded the highest levels of constitutional protection.
Free speech recognises one's right to dissent and protest. Although the judiciary had come up with judgments putting heavy restrictions on the freedom to protest of late, this judgment can be viewed as a milestone in recognising freedom of dissent as an integral part of free speech. In a civilised state, internet regulation is essential but that doesn't mean it should be completely controlled. There must be freedom with reasonable constitutional restrictions.
Citizens can still be arrested for online posts
Citizens can still be arrested for online posts

Mar 25 2015
Dhananjay Mahapatra & Amit Choudhury
The SC decision to strike down Section 66A of I-T Act may infuse social media addicts with a sense of unrestricted freedom of expression, but indiscrete postings or tweets could still result in arrest under similar IPC provisions. In most cases slapped against people for posting offensive views on social media, police invariably invoked Sections 153 and 505 (IPC) with Section 66A of I-T Act, which is bailable. It is the invoking of additional IPC sections that allowed law enforcers to arrest people for offensive posts.
Sections 153 and 153A allow registration of a case against a person giving a statement, written or oral, that incites riots or provokes communal tension and enmity between communities.It's punishable with imprisonment from 6 months to one year with fine. Section 505 punishes those who spread rumours to cause public disorder with imprisonment up to 3 years.
Section 66A was not part of the original I-T Act enacted during the NDA government in 2000. The UPA amended it in 2009 and brought Section 66A into force on October 27, 2009. Veerappa Moily was law minister then and A Raja was IT minister. Kapil Sibal succeeded Raja as IT minister.
After the uproar over the arrest of two girls in Palghar, Sibal issued an advisory to states that no arrest under Section 66A could be made by police unless the SP concerned issued an order in writing.
TOI spoke to Moily, who said: “I welcome the SC judgment. It empowers people to have freedom of expression.“ He refused to be drawn into a blame game over enacting Section 66A.Law, he said, should be dynamic and evolve with time to meet exigencies peculiar to a particular time.
Sibal too welcomed the judgment. He sounded a caution. “Section 66A is not the culprit as it is bailable. Police used to invoke IPC provisions to arrest. So, one should be well advised to exercise restraint while exercising free speech on social network sites.“
He said pure free speech ideally shouldn't attract IPC provisions even if it's severest criticism of politicians.But, if free speech has an intention to cause public disorder, communal disharmony and inimically affects national integrity and friendly relations with other countries, then rigour of IPC provisions kick in.
“The challenge before the country now is the discretion provided to police in registering a case under IPC provisions branding a statement offensive under IPC Sections 153 and 505. The distinction between a pure free speech from offensive statements by the police is the challenge. It's this discretion with police that is often misused,“ he said.
Though struck down in 2015, police continues to use it in 2019
Himanshi Dhawan, May 19, 2019: The Times of India
Four years ago, free speech got a boost as the Supreme Court declared a draconian provision — Section 66A of the Information Technology Act, 2000 — unconstitutional. The case — Shreya Singhal vs Union of India — was expected to stop misuse of this law to scotch dissent and contrary views. But police stations in the country seem to have missed the memo.
On May 15, BJP activist Priyanka Sharma was released after five days in prison. Her “crime”: Posting a meme of West Bengal CM Mamata Banerjee. The state police had booked her under the outdated Section 66A.
Sharma is not the only one. If ever there was evidence that law enforcement is caught in a time warp, it is here. A 2018 research paper by lawyers Abhinav Sekhri and Apar Gupta from the Internet Freedom Foundation found 45 cases under 66A pending before the country’s high courts between January-September 2018, and 21 cases pending before the SC between March 2015 and September 2018. The research was based on online searches and did not cover FIRs or lower courts. In fact, NCRB has even stopped collecting data on the 66A FIRs. The two lawyers took the issue up with the SC who demanded that all police stations be updated about the SC 2015 ruling. Gupta describes the use of the section as illegal and an affront to rule of law. “Section 66A was found to suffer from legal defects since its inception. Yet it continues to be used by those in authority against those who are economically and socially disempowered. When victims protest, the police conveniently drop the ‘A’ in this zombie law.”
and in Jan 2021, too
Anam Ajmal , January 17, 2021: The Times of India

From: Anam Ajmal , January 17, 2021: The Times of India
At least 799 cases are still pending against people under the scrapped Section 66A of the Information Technology (IT) Act, according to digital advocacy group Internet Freedom Foundation (IFF). The Supreme Court struck down Section 66A in 2015.
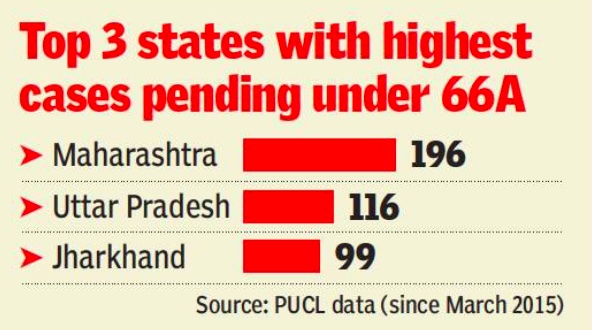
The findings were published by IFF, in collaboration with Civic Data Lab (CDL), and have been presented through a website zombietracker.in. The website has details of the total cases registered, pending cases and those disposed by the courts in 11 states of the country. The highest number of pending cases under 66A comes from Maharashtra (320), followed by Uttar Pradesh (131) and Jharkhand (118).
“We plan to widen our research and include data from other states in the website soon,” said CDL member Abhinav Sekhri. The data for the website was sourced from district courts, Sekhri added.
According to the tracker, 1,988 cases were registered under Section 66A of IT Act across 11 states. Out of this, 1,189 cases were disposed, including 236 with verdicts.
[In July 2021,] Appearing for PUCL, advocate Sanjay Parikh said Maharashtra, which had registered 349 cases prior to the judgment, registered 381 more FIRs invoking Section 66A. UP had registered just 22 cases before 2015, but its police went on to file 245 more cases after the judgment. Jharkhand had just 43 FIRs prior to the judgment but went on to register 291 FIRs after March 2015.
…and in July 2021 as well
Himanshi Dhawan, July 18, 2021: The Times of India
From: Himanshi Dhawan, July 18, 2021: The Times of India
It’s been over a year since his Facebook post invited the ire of an unruly mob and his subsequent arrest, and Souradeep Sengupta’s world has completely changed. He has all but quit social media, resigned from his job as lecturer at a Silchar college and moved cities. “It was no longer safe for me to stay there,” he says.
The 27-year-old — who spent three days in prison in March 2020 for a post against PM Narendra Modi — is among the 745 cases pending before courts across the country where the accused had been charged under Section 66A of the Information Technology act, a ‘zombie law,’ struck down in 2015. This week the Supreme Court expressed shock at its continued use to prosecute people.
Following the apex court’s intervention, the Union home ministry issued orders not to register any more cases under 66A and withdraw the ones that have been lodged at police stations. It had earlier sent similar missives in 2019. It is no wonder that Sengupta is less than hopeful. “There is a gap between these orders and what is happening on the ground. The section had already been struck down when I was charged with it in March last year but yet my cases are ongoing. It is very frustrating,” he says.
A morphed picture, a WhatsApp forward, sometimes even a ‘like’ became an excuse to slap the dead law on people. For the people it was used against, the process became the punishment. In May 2019 Kolkata resident Priyanka Sharma, was arrested for morphing a picture of West Bengal CM Mamata Banerjee on one of actor Priyanka Chopra, while in May 2017, 22-year-old Rahat Khan, was arrested in Dankaur by the Greater Noida police for posting a morphed picture of the UP CM.
Muzaffarnagar’s Zakir Ali Tyagi, who posted a comment on Facebook questioning the Uttarakhand High Court orders on the Ganga river being a living entity, was detained for 42 days in prison in April 2017. “The police dropped the 66A provision in my case and put charges of sedition after they were questioned on its validity. I only understood later I had suffered in prison because of a law that did not exist,” he says.
Hyderabad resident PM Sai Prasad too was charged with 66A for posting videos alleging that the local legislator had falsified personal information in his election affidavit and had encroached on land. Busy watching a latenight show of the Rajinikanth-starrer Petta in January 2019, Prasad was hauled to prison and remained in custody for three days. He continues to fight the case of defamation and criminal conspiracy though 66A was dropped by the police as an afterthought. Later, the Telangana High Court sought an explanation from the police on the use of the act.
Prasad, who is a BJP youth wing officebearer, has plans to pursue the matter legally till he is exonerated. “I have the privilege of legal and financial support but this law that does not exist continues to be used against people who are far less fortunate,” he says.
And though he has parted ways with many friends and relatives, Sengupta has not been cowed down. “I regret that my family and friends have been dragged into a battle they did not pick. But in taking a stand, I know that I am not an isolated case,” he says.
A petition by People’s Union for Civil Liberties (PUCL) raising an alarm over such cases is pending before the SC. A 2018 research paper by lawyers Abhinav Sekhri and Apar Gupta found that despite the 2015 (Shreya Singhal) judgment police and trial courts continued to use the law due to a lack of an effective mechanism to communicate the illegality of the law. “The only effective way to ensure implementation of the order is long-term monitoring with the support of the court,” says Gupta.
Offences under the IT Act
’Liking’ a post is not an offence HC
Rajesh Kumar Pandey, TNN, April 21, 2025: The Times of India
Prayagraj : The Allahabad high court has ruled that liking a social media post is different from sharing it and will not attract Section 67 of the IT Act, which deals with obscene and objectionable material.
Justice Saurabh Srivastava, while quashing a case against Imran Khan, noted that the applicant had merely liked a message published by another person and there was no offensive post in his Facebook and WhatsApp accounts. The verdict was delivered on April 17.
“The applicant has liked the post of one Farhan Usman for unlawful assembly,” Justice Srivastava said. Usman’s post referred to a protest gathering near the collectorate to hand over a memorandum to the President of India.
The court said, liking a post does not amount to publishing or transmitting it. A post or message can be said to be published when it is posted, and a post or message can be said to be transmitted when it is shared or retweeted, Justice Srivastava-observed.
The court was dealing with an application filed under Section 482 (inherent powers of high court) of CrPC petition seeking quashing of the case against Khan. He was booked for “provocative messages on social media, which resulted in the assembly of about 600-700 people belonging to the Muslim community for arranging procession without permission”.
‘FB stalking case can’t rest on conjecture’
Allegations against a person for stalking and sexually harassing minor girls on social media can’t be based on “surmise and conjecture,” said a Kolkata Pocso court held. It acquitted a man booked eight years ago for allegedly stalking his school junior on Facebook by morphing her face over nude photos to avenge her rejection. It said police “couldn’t fix who was actual offender. The complainant, out of suspicion, took accused’s name in court but in FIR she didn’t mention his name.” The court said it’s difficult to rely on her identification of accused “as the allegation was only based on surmise and conjecture,” and was therefore, “doubtful”. TNN
Other sections, rules, clauses
HC stays 2 clauses that might rob media of independence
Sureshkumar k, Sep 17, 2021: The Times of India
The Madras high court stayed the operation of the oversight mechanism brought in through the new Information Technology Act Rules by the Centre, saying it may rob the media of its independence.
The HC said this while passing an interim order staying the operation of Rule 9 (1) and (3) of the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021.
Pointing out that a similar order has also been passed by the Bombay high court, the Madras HC said: “Indeed, there may have been no need to pass an independent order. However, it is submitted on behalf of the petitioners that notwithstanding the order passed by the Bombay high court, which ought to have a pan India effect, notices have been issued to the petitioners subsequently requiring them to adhere to the rules”.
The issue pertains to two separate pleas moved by vocalist T M Krishna and Digital News Publishers Association (DNPA) challenging the rules.
Petitioner says IT rules offend his right as artist, affect right to privacy
Rule 9 (1) of the new IT rules states a publisher shall observe and adhere to the code of ethics and norms of conduct for journalists under the Press Council guidelines and Cable TV Code. Rule 9 (3) relates to a threetier structure to deal with complaints against publishers. Level III of this structure is an oversight mechanism by the Centre, while level I and II are self-regulation by publishers and self-regulating bodies of publishers.
Petitioner TM Krishna contended that the rule is ultra vires the parent Act – the IT Act — besides imposing arbitrary, vague and unreasonable restrictions on digital news media and social media intermediaries. “The code of ethics contained in Part II of the rules is likely to create a chilling effect on speech, where creators of content will self-censor themselves and produce art that is acceptable to the state, rather than art which, otherwise legitimate, pushes the boundaries of societal, religious, political and cultural norms,” Krishna said. He added the rules offend his right as an artist and a cultural/political commentator by imposing a chilling effect on free speech and by impinging on his right to privacy. Another petitioner DNPA said two provisions of the rules offended the association. It particularly questioned the legality of Rule 16, which is an omnibus provision giving power to the secretary of the Union ministry of information and broadcasting to block public access to any digital information.
Prima facie there is substance that the oversight mechanism to control media by govt may rob it of its independence and the fourth pillar of democracy may not be there at all. By way of abundant caution, sub-rules 1 and 3 of Rule 9 of the said IT rules of 2021 will remain stayed — MADRAS HC
Fact check unit
Bombay calls it unconstitutional, strikes it down
Swati Deshpande, Sep 21, 2024: The Times of India
Mumbai : Describing it as an infringement on the right to equality and freedom of speech, Bombay high court on Friday quashed the amended Information Technology rules enabling the Centre to set up its own fact check unit (FCU) and flag social media content about its functioning as ‘fake, false or misleading’.
Holding the FCU to be unconstitutional, Justice A S Chandurkar of the Bombay high court – who served as ‘tie-breaker judge’ after a division bench in Jan 2024 deli- vered a split verdict – described the expression, ‘fake, false and misleading’ as ‘vague and overbroad’.
“The FCU in a sense is an arbiter in its own cause,” said Justice Chandurkar, echoing the view of Justice Patel who had on Jan 31, 2024, struck down the rule as unconstitutional for its vagueness and disproportionality. Justice Patel had differed with Justice Neela Gokhale, on the twojudge bench that heard the matter and arrived at a split verdict, thus bringing it before a third judge.
Justice Chandurkar said the FCU rule would have “a chilling effect” on individuals as well as intermediaries; the new rule could have led to loss of ‘safe harbour’ against legal action for social media platforms if FCU-flagged content was not acted upon. The FCU rule is sans safeguards to prevent its abuse, said Justice Chandurkar, rejecting the Centre’s stand that making the FCU’s findings subject to a legal challenge was a safeguard.
Punitive action taken
URLs blocked: 2016> 19
Anam Ajmal, Nov 21, 2019: The Times of India
There has been a 442% rise in the number of URLs blocked in India in 2019, compared to three years ago, a reply by ministry of information and technology in the Lok Sabha showed.
The government also clarified that there is no proposal to link Aadhaar with social media accounts. The linkage is a contentious subject currently heard in the Supreme Court. According to the reply, while the government had blocked 633 URLs in 2016, the number climbed up to 3,433 in 2019 (till October 31), a jump of 442%.
The question was raised by Congress MP Jothimani S from Tamil Nadu who had also asked IT minister Ravi Shankar Prasad details of the removal of “objectionable online content posted on social media.”
In his reply, Prasad wrote that section 69A of the IT Act 2000 empowers government to “block any information generated, transmitted, received, stored or hosted in any computer resource under certain conditions, including in the interest of sovereignty and integrity of India, defence of India, security of the state and public order.” Replying to the question on “privacy concerns about biometric data stored by UIDAI and leakages of personal information,” Prasad said the “core biometrics is encrypted at the time of enrolment/updation. It is never kept unencrypted and is never shared.”
“For security of Aadhaar data, UIDAI has a well-designed, multi-layer robust security system in place and the same is being constantly upgraded to maintain highest level of data security and integrity,” the reply stated, adding that security audits are conducted on regular basis to strengthen security and privacy of data.
