National Capital Region (India): Power Sector
This article has been sourced from an authoritative, official readers who wish to update or add further details can do so on a ‘Part II’ of this article. |
Contents |
The source of this article
Draft Revised Regional Plan 2021: National Capital Region
July, 2013
National Capital Region Planning Board, Ministry of Urban Development, Govt. of India, Core-4B, First Floor, India Habitat Centre, Lodhi Road, New Delhi-110003
National Capital Region Planning Board
National Capital Region (India): Power Sector
BACKGROUND
Electricity is one of the critical infrastructure on which the socio-economic development of the country or a region depends. The liberalization of the economy has led to an increased tempo in industrial and commercial activities leading to higher electricity demand in all sectors of the economy. Electricity is essential for all facets of our life. It has now become a basic human need. The commitment to inclusive growth also requires access to affordable, reliable and quality power to all households. The power supply in the National Capital Region (NCR) has not kept pace with the increasing population and the growth of economic activities in the region. There is an overall shortage of power in the northern grid from where the region draws its power and hence power cuts have become a routine affair, disturbing daily life as well as affecting economic productivity. Augmentation of power generating capacity and improvement/augmentation in transmission and distribution system is essentially required to be taken up for the balanced and harmonized development of the National Capital Region.
EXISTING SITUATION AND ISSUES
7.2.1 Existing Power Supply Situation
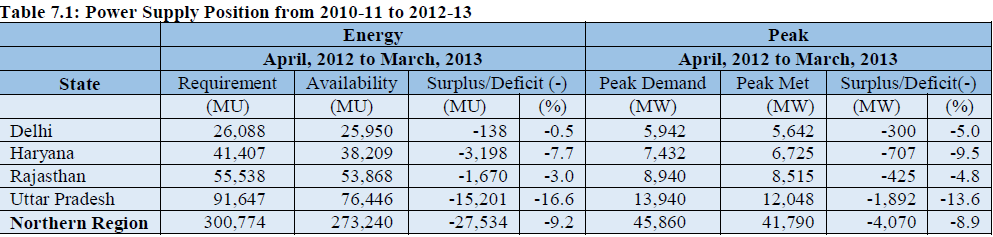
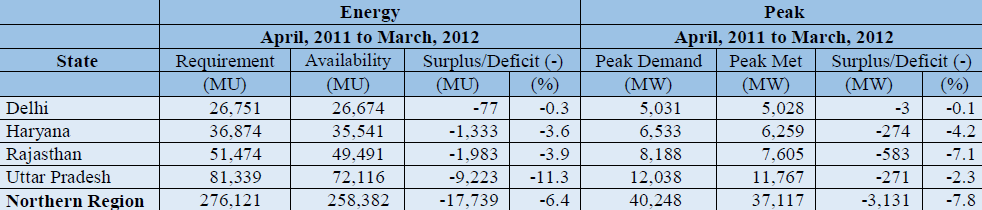
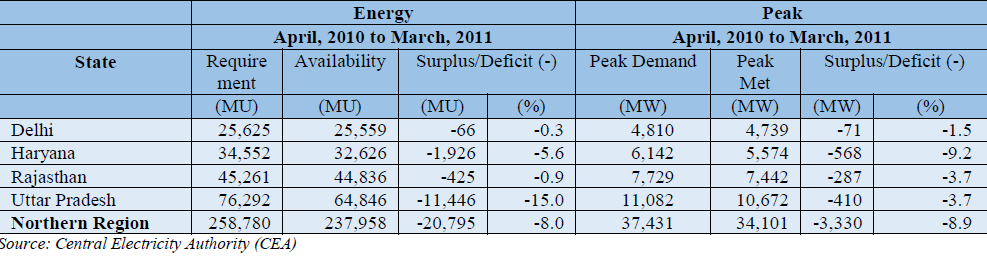
The power supply position during the period 2010-11 to 2012-13 for NCT-Delhi and the constituent states of NCR is given in Table 7.1. During the year 2012-13, the peak deficit in NCT-Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh was 5.0%, 9.5%, 4.8% and 13.6% respectively. The energy shortage in this period in NCT-Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh was 0.5%, 7.7%, 3% and 16.6% respectively.
7.2.2 Aggregate Technical & Commercial (AT&C) Losses
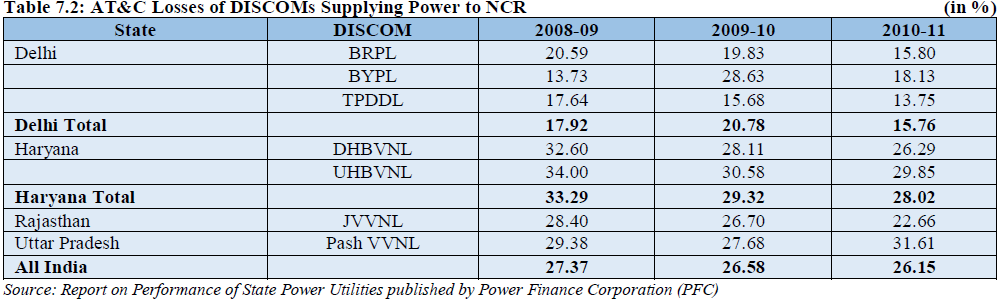
The AT&C losses in respect of DISCOMs supplying power to NCR for the period 2008-09, 2009-10 and 2010-11 is given in Table 7.2. Although, AT&C losses in case of DISCOMs of Delhi have come down during the last few years, a lot has to be done by the concerned DISCOMSs of Uttar Pradesh, Haryana and Rajasthan to reduce their AT&C losses.
The main factors contributing for high technical losses are overloading of existing lines and substation equipments, non up gradation of old lines and equipment, low HT:LT ratio and poor maintenance of equipments. The main factors contributing to high commercial losses are theft, pilferage and tampering of meters, absence of energy accounting and auditing through IT intervention, low accountability of employees etc.
7.2.3 NCR as Sub-Grid of Northern Grid The power system of NCT-Delhi and the NCR sub-region of Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh form part of the northern grid. In the constituent states of NCR, State Load Dispatch Centres (SLDCs) are responsible for real time grid operation as well as scheduling and dispatch of generators in the respective states.
The generation, procurement and supply of electricity within the constituent states of NCR is primarily the responsibility of the respective state governments, which carry out these functions through different corporations/IPPs. Central government supplements the efforts of state governments in improving the availability of power by way of generation capacity addition through CPSUs and allocating firm/unallocated power from the central generating stations to the states, including the NCR states, which distribute the same to different DISCOMs within the States. Thus, the requirement of power of NCR needs to be taken care of by the concerned NCR states in their respective area of NCR. In view of above, a meeting was taken by Secretary (Power) in January, 2005, wherein the issue of formation of Unified Power Authority for NCR/creation of separate NCR sub-grid out of Northern Grid was discussed. In this meeting a consensus emerged that formation of such authority for NCR would be a difficult proposition due to administrative and legal problems. In view of this, no further action was taken up in this regard.
Northern Region Power Committee (NRPC) facilitates the integrated operation of the power system in
Northern Region. NRPC may from time to time, agree on matters concerning the stability and smooth
operation of the integrated grid and economy and efficiency in the operation of the power system in
Northern Region, of which NCR is a part. Members of NRPC include the State Generating Company,
State Transmission Utility (STU), State Load Dispatch Centre (SLDC), one of the State owned
distribution companies as nominated by the State Government from each of the States in the region and
one distribution company by alphabetical rotation out of the private distribution companies functioning in
the region. Thus, in NRPC, there is representation from each field in power sector which enables better
inter-agency coordination. NRPC can deliberate and agree by consensus on any operational issue of power
sector in Northern Region, which facilitates development of integrated system and its smooth operation.
7.3.2 Future Augmentation of Power Generation in NCR
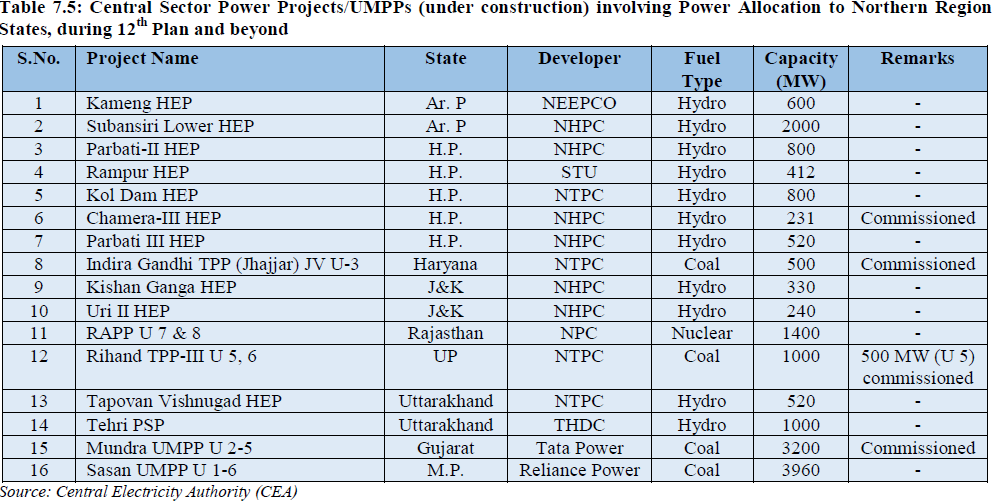
List of under implementation Central Sector Projects/UMPPs for likely benefit during 12th Plan and beyond from which NCT-Delhi and other States of Northern Region may get allocation of Power is given in Table 7.5:
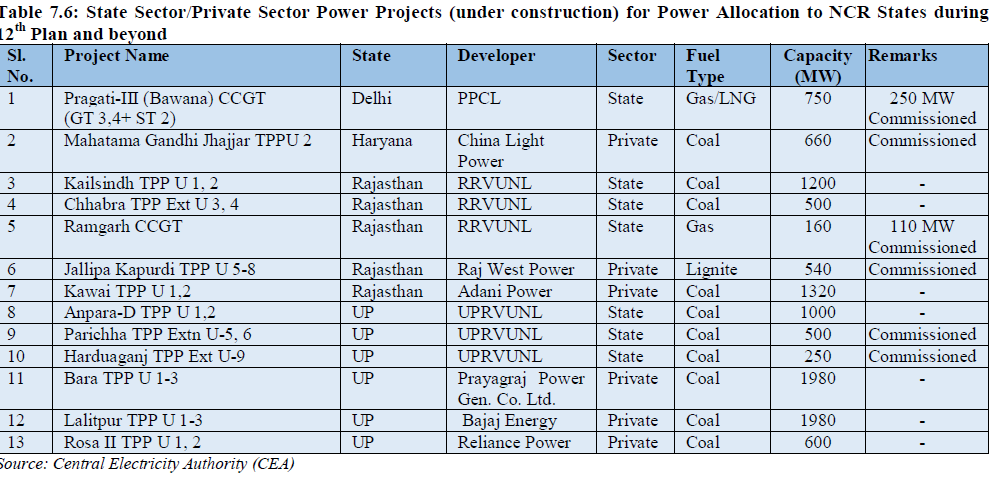
List of generation projects under implementation in State/Private Sector for likely benefits during 12th Plan and beyond to Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh which may improve power situation in NCR is given below:-
There is need to plan for additional power generating capacity of 15,625 MW for the region by the year
2021-22 and recommendations for the same are as follows:
(i) State Governments to allocate power to their respective sub-region from their upcoming state
sector projects.
(ii) State Governments to allocate power to their respective sub-region from the present
allocation/generation of power.
(iii) The respective DISCOMs to procure power through competitive bidding to meet the demand.
7.3.3 Planned ISTS (Inter State Transmission System) Network in NCR Area
The power evacuation systems for upcoming ISGS (Inter State Generating Stations) /IPP projects in NCR area have been finalized. Further, for state sector generation projects, the power evacuation system is planned and implemented by respective State Transmission Utilities (STUs). For the generation projects which have sought connectivity and long term access from CTU (Central Transmission Utility), the necessary additional transmission system/ strengthening of existing transmission system have also been planned and approved.