Sagaing Division, 1908
This article has been extracted from THE IMPERIAL GAZETTEER OF INDIA , 1908. OXFORD, AT THE CLARENDON PRESS. |
Note: National, provincial and district boundaries have changed considerably since 1908. Typically, old states, ‘divisions’ and districts have been broken into smaller units, and many tahsils upgraded to districts. Some units have since been renamed. Therefore, this article is being posted mainly for its historical value.
Sagaing Division
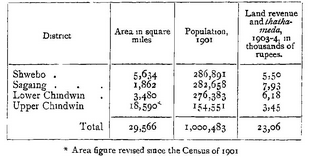
North-western Division of Upper Burma, lying between 21 29' and 26 22' N. and 93 58' and 96 20' E. It comprises four Districts the UPPER and LOWER CHINDWIN, bestriding the Chindwin ; and SAGAING and SHWEBO, extending from that river across the Mu valley to the Iirawaddy. It is bounded on the north by the unadministered Hukawng valley ; on the east by the Mandalay Division on the south by Mymgyan District of the Meiktila Division ; and on the west by Manipur and the Chin Hills. The population was 821,769 in 1891 and 1,000,483 in 1901, but the former figure did not include the population of two Shan States in the Upper Chindwin District which were enumerated in 1901. tion is given in the following table ; The distiibution of population
There are 4,864 villages and 4 towns : SAGAING (population, 9,643), SHWEBO (9,626), MONYWA, and KIND AT, the first three of which aie trade and industrial centres of some importance. The administrative head-quarters are at Sagamg, which is conveniently situated at the south-eastern corner of the Division, the District head-quarters of the Shwebo and Lower Chindwin Districts being accessible by rail, and that of the Upper Chindwin District by rail and river steamer. The majority of the population are Burmans, the numbei of Burmans in 1901 being no less than 915,204 The only other indigenous race strongly represented is the Shans (68,077), nearly all of whom inhabit the northern townships of the Uppei Chindwin District. An appreciable portion of the population is foreign, but most of the 7,704 Musalmans and 4,538 Hindus enumerated m 1901 were either military policemen or indigenous Zairbadis. A few Chins are found in the hills along the western border of the Upper Chindwin District, and a few China- men at the mam trade centres The people, being Burman or Shan for the most part, aie nearly all Buddhists. The aggregate of the adherents of the Buddhist faith in 1901 was 981,369, while Christians numbered 3,773, and Amrmsts (piactically all Chins) 2,289.