Direct taxes: India
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
In its latest report, CAG has said that over the last six years, Central Board of Direct Taxes alone had made refunds of close to Rs 41,000 crore, without obtaining legislative approval. A similar practice is also followed on the indirect taxes front, although on a smaller scale. According to CAG's estimates, over the past four years, refund of indirect taxes added up to nearly Rs 45 crore. | In its latest report, CAG has said that over the last six years, Central Board of Direct Taxes alone had made refunds of close to Rs 41,000 crore, without obtaining legislative approval. A similar practice is also followed on the indirect taxes front, although on a smaller scale. According to CAG's estimates, over the past four years, refund of indirect taxes added up to nearly Rs 45 crore. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Share of direct taxes in total tax revenue, on an increase= | ||
| + | [[File: direct and indirect taxes collected by the central government.jpg|Direct and Indirect taxes collected by the central government: 1985-2014; Graphic courtesy: [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com//Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=STATOISTICS-NOT-SO-DIRECT-22042015008035 ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com//Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=STATOISTICS-NOT-SO-DIRECT-22042015008035 ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Apr 22 2015 | ||
| + | |||
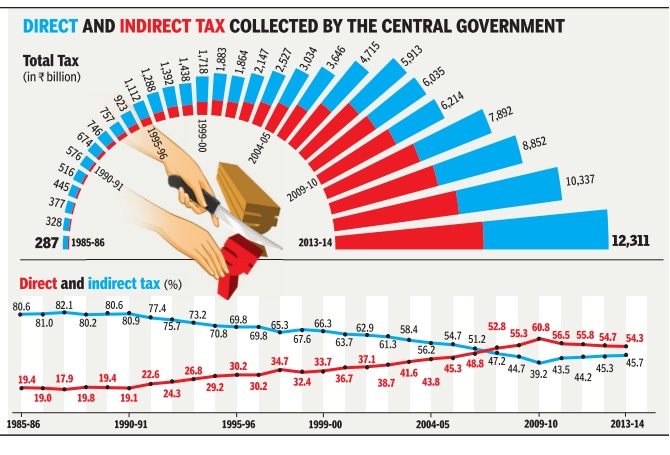
| + | Unlike direct taxes like income tax which are paid only by the relatively well-off, whether an individual or a company, indirect taxes like sales tax, VAT, service tax are paid by everyone irrespective of their income levels. This is why higher collections of direct taxes are seen as a sign of a `progressive' tax regime. Data on the central government's tax revenues shows that from 1990-91 to 2009-10, the share of direct taxes in total tax revenue witnessed a steady increase. Since 2009-10, however, this share has been declining largely due to service tax emerging as a major source of revenue Research: Atul Thakur; Graphic: Sunil Singh; Source: Reserve Bank of India 1 | ||
| + | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
[[Direct taxes: India]] | [[Direct taxes: India]] | ||
Revision as of 00:09, 8 June 2015
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content.
|
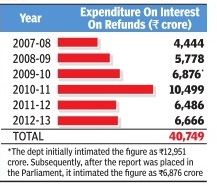
Interest liability on tax refunds
CAG pulls up finmin on tax refunds
New Delhi: TIMES NEWS NETWORK
The Times of India Aug 05 2014
Auditor Says I-T Department Refunded Rs6,700Cr Without House Nod
The finance ministry has been pulled up by the Comptroller & Auditor General (CAG) for making tax refunds of close to Rs 6,700 crore without Parliamentary authorization.
In its latest report, tabled in Parliament last week, CAG said, the Public Accounts Committee too had concurred with it and pointed out that “there was no valid ground as to why the department (of revenue) could not make broad estimates of expenditure on interest liability on tax refunds based on the studied trends of the past“.
It also said that the revenue department itself had admitted that in terms of Article 266 of the Constitution, it had no legal authority to withdraw the ‘interest' on excess tax collected and make refunds without getting it approved by Parliament.
Apart from CAG, even experts have argued that in the interest of transparency , the government should not hold back tax refunds and explicitly provide for it in the Budget.
But the finance ministry has refused to heed to this plea. has refused to heed to this plea. Typically, to meet the stiff tax targets set by the finance minister, tax officials push companies to cough up higher taxes, which are then refunded. The department also goes slow on refunds to ensure that the overall tax collection number looks healthy. Usually, the government has refunds of around Rs 1 lakh crore at the start of the financial year.
In fact, last year, the issue was also referred to the attorney general G E Vahanvati, who initially suggested that the CAG was right but later gave a different opinion when more facts were presented to him. Vahanvati and Sumit facts were presented to him. Vahanvati and Sumit Bose, then revenue secretary , had been summoned to the PAC for what it believed were “mutually contradictory opinions“ on the expenditure that the government incurred in paying interest on tax refunds.
In its latest report, CAG has said that over the last six years, Central Board of Direct Taxes alone had made refunds of close to Rs 41,000 crore, without obtaining legislative approval. A similar practice is also followed on the indirect taxes front, although on a smaller scale. According to CAG's estimates, over the past four years, refund of indirect taxes added up to nearly Rs 45 crore.
Apr 22 2015
Unlike direct taxes like income tax which are paid only by the relatively well-off, whether an individual or a company, indirect taxes like sales tax, VAT, service tax are paid by everyone irrespective of their income levels. This is why higher collections of direct taxes are seen as a sign of a `progressive' tax regime. Data on the central government's tax revenues shows that from 1990-91 to 2009-10, the share of direct taxes in total tax revenue witnessed a steady increase. Since 2009-10, however, this share has been declining largely due to service tax emerging as a major source of revenue Research: Atul Thakur; Graphic: Sunil Singh; Source: Reserve Bank of India 1
See also
Direct taxes: India Income Tax India: Expert advice Income Tax India: Laws Income Tax India: NRIs Wealth tax: India