Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
1980- April 2017: milestones
See graphic:
Bhartiya Janata Party, a brief timeline, 1980 onwards...

1984- 2014: seats in the Lok Sabha
See graphic, ' The Bharatiya Janata Party: seats in the Lok Sabha: 1984-2014 '

1984-2004: Growth across the nation


BJP rides wave to make inroads into new states
The Times of India May 17 2014
BJP's stunning breakthroughs, despite organizational weaknesses and geographical limits, in states like Haryana, Assam, West Bengal and Tamil Nadu speak of the strength of the Modi “lehar“ and provide an opportunity for future consolidation.
BJP leaders were themselves surprised by the response to Narendra Modi in these states where the party has had minimal presence or had atrophied over the years due to organizational neglect.
In Haryana, such was the voter anger against the Hooda government in the state and the Congres regime at the Centre that BJP won 7 seats and 33% of the vote despite some poor candidate selection.
BJP did not go for an alliance with Om Prakash Chautala's INLD due to cases pending against the Jat leader and its pact with Kuldeep Bishnoi's Hayana Janhit Party did not, on paper, command a wide social base. But despite the BJP-Bishnoi pact lacking Jat support, the community voted in large numbers for a `Modi sarkar' ignoring competing claims of Chautala and Hooda.
In fact, the impressive response to Modi's first rally in Rewari after being named BJP's PM candidate set the tone and BJP pulled in votes from almost all sections.
In Assam, as in Haryana with regard to INLD, BJP's decision to avoid an alliance with AGP paid off handsomely . Modi clearly struck a rich vein when he articulated a deep groundswell of resentment against illegal migration and simmering ethno-religious tensions as the seven seats and a 36% vote share indicate.
BJP and its ally PMK won a seat each in Tamil Nadu, riding on its status as the frontrunner. Modi's rallies, despite the language barrier, were well attended and it was the first time since Rajiv Gandhi that a leader from the north became a talking point.
The decision to take on Mamata Banerjee by slamming her “poriborton“ as a sham and raking up the illegal migrants issue was an inspired one as it pitched Modi into the centre of the discourse in West Berngal. The two seats BJP won in the state seem modest, but represent a breakthrough with almost 18% of the votes.
1990-16: BJP emerges all across India

1999: Pawar, BSP voted against the Vajpayee government
The Times of India, Dec 13 2015
Pawar advised Maya to vote against BJP govt in 1999
It is well known that the vote cast by five MPs of Bahujan Samaj Party brought down the Vajpayee government in 1999. But all these years, there has been speculation about the reason the Dalit outfit voted against the man widely credited with making Mayawati the CM of UP for the first time after the State Guest House assault case.
Sharad Pawar has now said that he was the trigger, having persuaded the Dalit czarina that a vote against the government would benefit her politically . He has made the revelation in his just-released autobiography “On My Terms“.
A confidence vote was brought in Lok Sabha after AIADMK withdrew its support to the BJP-led government in April 1999. As the Speaker called for a division of votes, the parliamentary staff took some time to close the doors and activate the voting system, enough for Pawar to have a quick chat with Mayawati. The Vajpayee government lost by one vote.“Those who had noticed me talking to Mayawati before the voting pressed me to clarify,“ he says.
The NCP boss says he is still asked about that brief chat ahead of the voting. “Let me put it this way: I just impressed upon her that the BSP's interests in UP would be served better if she voted against the Vajpayee govern ment,“ he has revealed.
Importantly , Pawar has confirmed that PM Narasim ha Rao rejected a proposal for conducting a nuclear test in view of possible global reac tion. Pawar, as defence minis ter in 1991-92, was told by ad visors to the ministry tha the country was fully equipped to conduct nuke tests to establish it as a nucle ar power. As they pressed for tests, he took the file to Rao for a decision. “After going through the file, he rejected the advice, which I though was the correct decision in the circumstances that pre vailed then,“ Pawar notes.
He says the national econ omy was in a shambles when Congress government took over and Rao did not wan any global reaction to impede the reforms.
2012 and 2017
How the BJP won state assemblies

From December 19, 2017:The Times of India
See graphic:
How the BJP won state assemblies between 2012 and 2017
Performance in state assembly elections
See graphic, ‘How BJP's seats and vote share in 2017 compare with 2012 seats’

2014 Lok Sabha elections : BJP crosses four electoral boundaries with landslide
Milan Vaishnav
The Times of India| May 17, 2014
The 2014 elections have only just ended but analysts are already struggling to comprehend how the BJP's stunning electoral success, deemed unlikely just one year ago, came to pass. The results of India's sixteenth general election challenge our common understanding of contemporary Indian electoral politics in at least four ways.
BJP can't go beyond its traditional strongholds
First, the conventional wisdom was that the BJP was trapped by its traditional political and geographic boundaries, deemed insurmountable thanks to the party's Hindutva agenda. Yet, the BJP has garnered an estimated one-third of the all-India vote, a massive improvement from 19% in 2009 and its all-time best of 26% in 1998. This improvement was driven by sizeable vote swings in critical Hindi heartland states as well as smaller but significant gains in the South and East, neither an area of traditional strength. These gains were possible thanks to Modi's persistent focus — in the national theatre of politics — on development and economic mobility. This message aligned perfectly with the issues vexing most Indian voters; a post-poll conducted by CSDS found that in every state surveyed, voters identified development, inflation or corruption as their most important election issue. To be clear, the BJP's saffron agenda has not vanished; recent campaign rhetoric and the party's manifesto confirm this. Yet, going forward, deviation from the focus on governance and development could imperil these newfound gains.
It can't stitch up alliances better than Congres
A second assumption that was upturned in this election was that Congres, not the BJP, had the advantage in alliance formation. Despite all the talk about its off-key "India Shining" mantra sinking the BJP in 2004, their loss was more about the BJP's inability to forge the right alliances. This fed doubts about whether the BJP could construct effective alliances in 2014, especially with Modi at the helm. Yet it was a Modi-led BJP that struck key deals over the past several months while the Congres, in contrast, was viewed as a sinking ship. Many observers dismissed the BJP's alliance with the Lok Jan Shakti Party in Bihar, the Telugu Desam Party in Andhra Pradesh, and the Haryana Janhit Congres as trivial. But such criticism overlooked the importance of small shifts in vote share in a fragmented, first-past-the-post electoral system.
Support for regional parties is growing
A third assumption underpinning Indian elections since 1989 has been the growth of regional parties. Between 1996 and 2009, the non-Congres, non-BJP share of the vote has hovered around 50%, rising to a record 53% in 2009. The 2014 election, though, saw a decline in regional party support; their nation-wide vote share dipped to roughly 47%, reversing the prevailing trend. Two players merit special attention here. The first is the evisceration of the BSP. Mayawati may draw a blank in Uttar Pradesh while the hard-fought inroads she made in other Hindi heartland states simply evaporated. The second is the weakening of the Left. At a time of rising inequality and concerns over crony capitalism, the conditions would seem propitious for a Leftist revival; instead we are witnessing their collapse.
Lok Sabha polls are a sum of state verdicts
A fourth assumption has been that national elections are best understood as an aggregation of state verdicts. The 2014 election outcome, however, is a partial reversal of "derivative" national elections. Not only was this election marked by presidential overtones, but the animating issues—namely, the slumping economy—have also been pan-Indian. Despite this apparent shift, there are two caveats to the "nationalization" thesis.
First, states still remain the most important tier of government for ordinary Indians. This is reflected in the fact that, notwithstanding the record voter turnout in these Lok Sabha polls, turnout for state elections is still 4.5% higher, on average, in any given state. Second, much of the south remained resistant to the BJP's charms. Although the BJP picked up new seats in Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu, its advances were limited and much smaller than in the north.
(The writer is an associate with the South Asia programme at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace in Washington, DC)
2015
The Times of India, November 11, 2015
Saffron group also lost big chunk of its own base
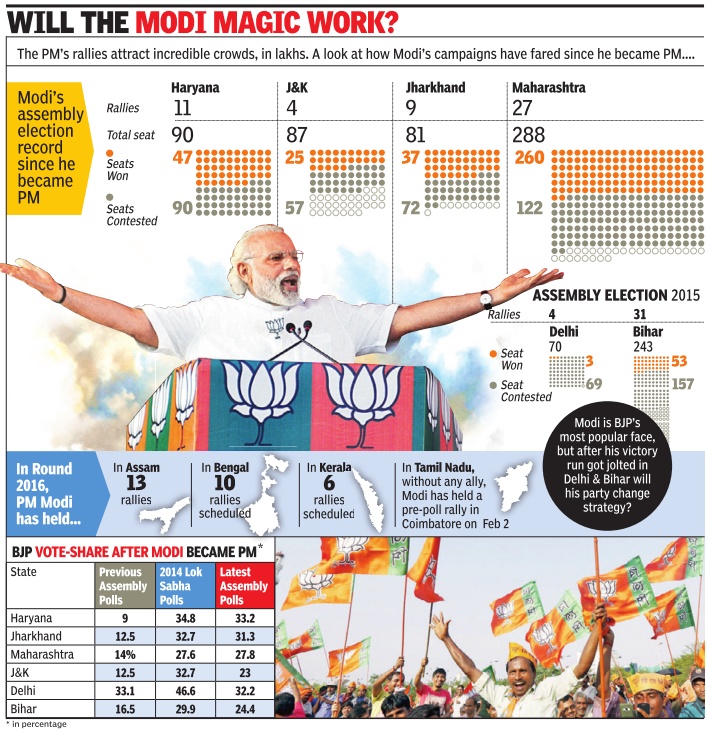
BJP's analysis of its de feat in Bihar, accord ing to what finance minister and senior partyman Arun Jaitley told the media on Monday , is that the Maha Gathbandhan's arithmetic beat NDA's chemistry. The data shows that while the first part of that analysis is correct, the second part is not and that NDA flunked the chemistry paper as well. That's revealed by the sizeable fall in NDA's vote share from 2014. The arithmetic was simple enough. In 2014, NDA totalled a vote share of 38.8% of all the votes polled in Bihar, including those for NOTA. JD (U) polled 15.8%, RJD 20.1% and Congress 8.4%. Had the three been together, their combined vote share of 44.3% would have been well over NDA's and the results would thus have been quite differ ent. The formation of Maha Gathbandhan manifested the recognition of this reality by the three parties.
Jaitley was referring to the fact that the arithmetic addition of the vote bases of the three parties did happen, contrary to NDA's expectations. He was right.
Maha Gathbandhan's vote share in these polls was 41.9%. Considering that Jitan Ram Manjhi's HAM(S) had broken away from JD(U) between the 2014 and 2015 polls and had won 2.3% of the votes polled, what this meant was that the grand alliance succeeded in keeping the rest of its votes together and transferring them to each other, no mean achievement.
Now for the chemistry. NDA 's vote share in the elections just concluded was 34.1%, or 4.7 percentage points lower than in 2014.
This despite the addition of the HAM(S) votes to its kitty . Exclude the fledgling party and BJP , Paswan's LJP and Upendra Kushwaha's RLSP polled just 31.8% of the votes, a drop of seven percentage points from 2014. That's not down to Maha Gathbandhan arithmetic, it shows a disenchantment with NDA among voters.
BJP's vote share was itself five percentage points lower than in 2014. The party could legitimately point out that this is an unfair comparison because it contested 182 of the assembly segments in the Lok Sabha elections and only 157 this time. So, we looked at only those segments in which it was in the contest in both 2014 and 2015 and the analysis still shows a significant drop in vote share for BJP .
There were 129 assembly constituencies in which BJP was in the contest in both elections. Its share of votes in these segments in 2014 was 39.9%. This time round, it was 37.7%, a swing of over two percentage points away from the party . Remember also that unlike in 2014, supporters of Manjhi should also have voted for BJP candidates in these seats thereby boosting its share beyond 40% if it had held on to its own votes.
Actually , BJP polled even in absolute terms nearly 87,000 fewer votes in these 129 seats than it did in 2014. This at a time when the total votes polled in these seats rose by almost 11.1 lakh. In short, while the votes polled rose on average by over 8,500 per seat, BJP's votes fell by about 700 per seat.
That points to a failure of its own chemistry , not just a success of Maha Gathbandhan arithmetic. What made matters worse was that its allies lost their chemistry even more drastically .
2015, Bihar elections: performance in Union ministers’ strongholds
The Times of India, Nov 10 2015
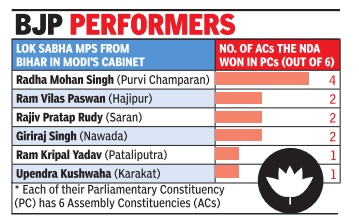
Vishwa Mohan
NDA fares poorly in stronghold of Union ministers from Bihar
BJP and its allies found the going tough in the Lok Sabha seats represented by their Union ministers with only agriculture minister Radha Mohan Singh's constituency Purvi Champaran returning a decent number of MLAs. In Purvi Champaran, the NDA won four out of six assembly segments. Three -Motihari, Kalyanpur and Pipra -of these were won by BJP while Govindganj went in favour of ally LJP .
Purvi Champaran also emerged as the best performing district for the BJP-led alliance in Bihar. The NDA won eight out of 12 assembly seats in the district. Singh, a veteran BJP member from the state, has been in the Mo di Cabinet since May 2014.
Upendra Kushwaha and Ram Kripal Yadav turned out to be the worst performers, winning only one seat each rom their respective constituencies of Karakat and Pataliputra. Kushwaha, minister of state for HRD, is the chief of the Rashtriya Lok Samata Party , which had fielded 23 candidates across the state.The party was victorious on only two of these seats.
Yadav, a former RJD member, joined BJP before the 2014 parliamentary elections. He represents Pataliputra in the Lok Sabha and is minister of state for drinking water and sanitation in the Modi Cabinet. Except for Danapur assembly segment in his parliamentary constituency , all five went in favour of the Grand Alliance.
Besides these three, Ram Vilas Paswan, Rajiv Pratap Rudy and Giriraj Singh are the other Lok Sabha MPs in the Union Cabinet. Though there are two more ministers from Bihar (Ravi Shankar Prasad and Dharmendra Pradhan), these two represent the state in the Rajya Sabha.Pradhan, petroleum minister, is from Odisha but represents Bihar in the upper House.
Rudy , MP from Saran and minister of state (independent charge) for skill development and parliamentary affairs, could win only two out of six seats for the NDA. Similarly, Hajipur MP Paswan and Nawada MP Giriraj Singh won two seats each for the BJP-led alliance.
2016: Assam, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Wesr Bengal