Energy: India
What Is the Difference Between Power and Energy? The Staff of QUEST explains:
The word “energy” is used to describe many different things—how we heat and cool our homes, how we fuel cars. Energy isn’t something that can be seen or felt, but you can see and feel the effects when energy is transferred from one place to another.
Energy is what makes change happen and can be transferred form one object to another. Energy can also be transformed from one form to another.
Power is the rate at which energy is transferred. It is not energy but is often confused with energy. The watt is the most commonly used unit of measure for power. It measures the rate of energy transfer.
A watt equals a joule per second. If a smart phone uses five joules of energy every second, then the power of the phone is five joules per second, or five watts.
Indpaedia has separate pages on
Energy: India and
Power: India, 1/ Power: India, 2 (ministry data)
This article has been sourced from an authoritative, official readers who wish to update or add further details can do so on a ‘Part II’ of this article. |
Contents |
The source of this article
INDIA 2012
A REFERENCE ANNUAL
Compiled by
RESEARCH, REFERENCE AND TRAINING DIVISION
PUBLICATIONS DIVISION
MINISTRY OF INFORMATION AND BROADCASTING
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
Significance

Why India's giant leap in green energy is still a small step
The Times of India Oct 20 2016 : WHY INDIA'S GIANT LEAP IN GREEN ENERGY IS STILL A SMALL STEP
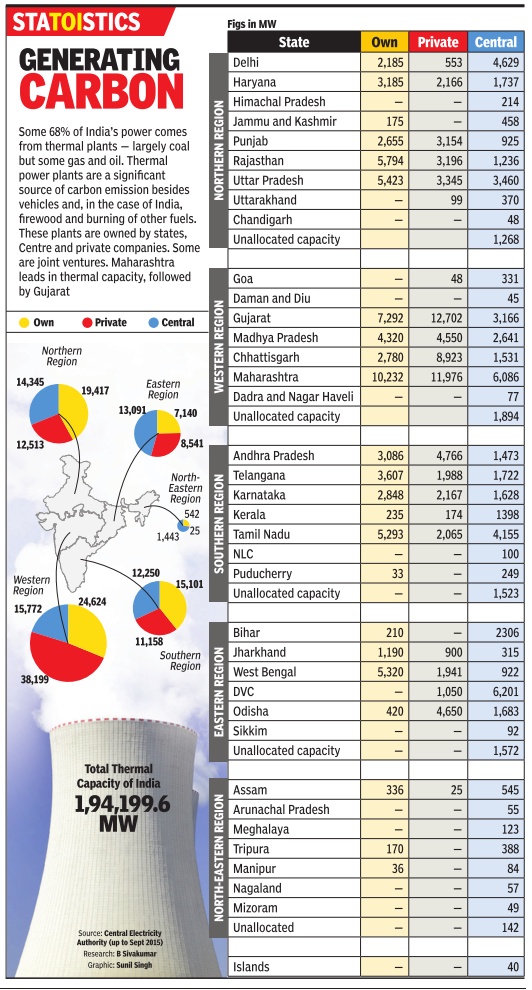
ENERGY is an essential input for economic development and improving the quality of life. Development of conventional forms of energy for meeting the growing energy needs of society at a reasonable cost is the responsibility of the Government. Development and promotion of non-conventional/alternate/new and renewable sources of energy such as solar, wind and bio-energy, etc., are also getting sustained attention. Nuclear energy development is being geared up to contribute significantly to the overall energy availability in the country.
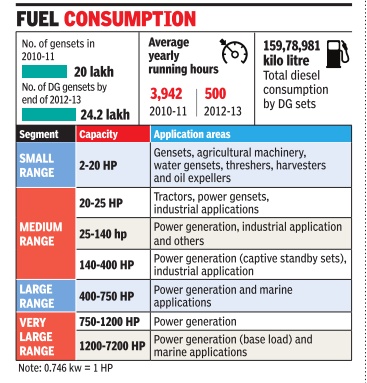
Diesel generators
Jan 02 2015
Sanjay Dutta
Diesel gensets lose power as reforms start paying off
Diesel-fired gensets appear to be losing power as the mainstay of energy for commercial establishments and other large consumers as the Centre's thrust on raising generation capacity and other reforms in the last few years begin to pay off by way of improved supply from the mains. The average running period for DG sets of all sizes has dropped to 500 hours in a year from 3,942 hours in 201011, a power ministry note says, quoting two separate reports prepared by Petroleum Conservation and Research Association and Bureau of Energy Efficiency .
In terms of average perday operation, gensets are being run for an average 1.37 hours against an average 10.8 hours operated some twothree years back.
This by no means is an end of the road for diesel gensets, which have recorded a growth of roughly 10% in annual sales. “Even though the number of DG sets have grown over the last two years... Basically, the DG sets are being used (installed) as stand-by source of supply ,“ says the note.
The note, thus, gives an in dication of shape of things to come against the backdrop of the Modi government taking steps to ensure 24X7 power supply in the next two-three years.
There are an estimated 24 lakh diesel gensets operating across the country , up from 20 lakh pegged around 2010-11.The report reckons the aggregate capacity of gensets of all sizes operating in the country by the end of 2012-13 to be 105,512 mw. This is roughly 20 times more than Delhi's daily demand for power. Gensets are known as a major contributor to pollution and a fall in their running hours has a positive bearing on the environment.
Consumption, energy
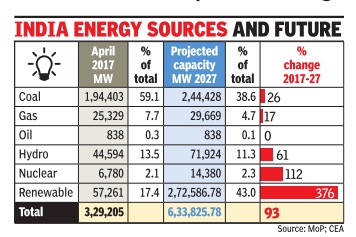
India's total energy mix: 1991-2017

See graphic:: India coal consumption growth, 1991-2017
Boom In the Renewable Sector: Report
Coal will continue to have a prime place in India's total energy mix for the next many years but data shows that the country's coal boom may have been over a couple of years ago, much earlier than expected.
Over the past two years, the country's coal use has increased by an average of just 2.2%, a sharp fall from the previous 10 years when average annual growth was over 6%.
The findings, published by Greenpeace's Energydesk on Wednesday , are significant because India, the world's third largest CO2 emitter after China and the US, is seen as the next big coal frontier. Though the country's per capita carbon emission is much less than these top two emitters, the decline in overall use of coal will help India achieve its goal under Paris climate accord. India has committed to produce 40% of its electricity from non-fossil sources of energy by 2030 under the deal.It, therefore, has planned to scale up targets for renewable energy capacity from 30GW by 2016-17 to 175 GW by 2021-22.
The report shows that the renewable sector is certainly booming in India due to increasingly cost-competitiveness of solar and wind energy installations. “India's demand for the carbon-heavy fuel is not sky-rocketing and the country's energy needs will do nothing to arrest coal's global decline,“ said Ashish Fernandes of Greenpeace energy .
The Greenpeace, however, said there were a number of new coal-based power plants in the pipeline. It said the coal industry has experienced troubles, with many plants running less than half the time due to an over-capacity crunch. It also noted that the slowdown in coal consumption growth was largely due to the cement, iron and industrial power generation sectors burning less.
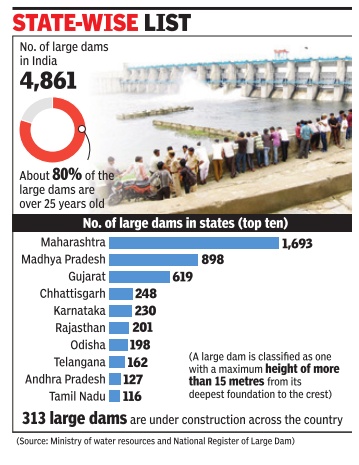
Domestic power consumption in India, 2011-14, state-wise
The Times of India Sep 22 2014
See graphic: Domestic power consumption in the various states of India

STATE OF POWER
Domestic power consumption in various states is not uniform and depends on their economic growth. The uneven electrification of households in the country is also responsible for this
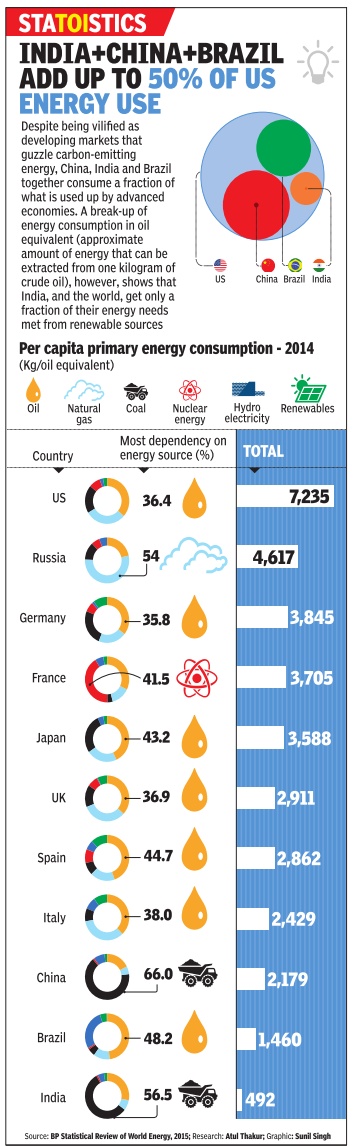
Energy consumption and energy efficiency: 2014
See graphic: Energy consumption and energy efficiency: in India, compared with other countries
The Times of India, December 07 2014
As per December,2014, India is the fourth largest energy consumer in the world, trailing the US, China, and Russia. Currently, India is not able to consistently meet domestic energy demands, which makes securing energy sources one of the top priorities and the largest energy source is coal.
Per capita consumption
2014: India a low no. 105 among 143 countries
See graphic: Production and consumption of electricity, per capita, and a comparison with BRICS countries, 2014

Showing a significant increase in electricity generation, India is now the third highest producer in the world. Generation alone, however, is a misleading indicator of quality of life because when it comes to per capita consumption of electricity, India ranks 105 among 143 countries for which data is available
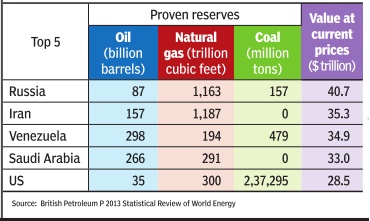
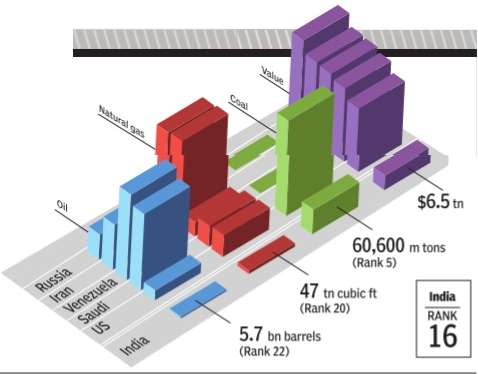
Reserves, energy
2017: Energy reserves
See graphic.
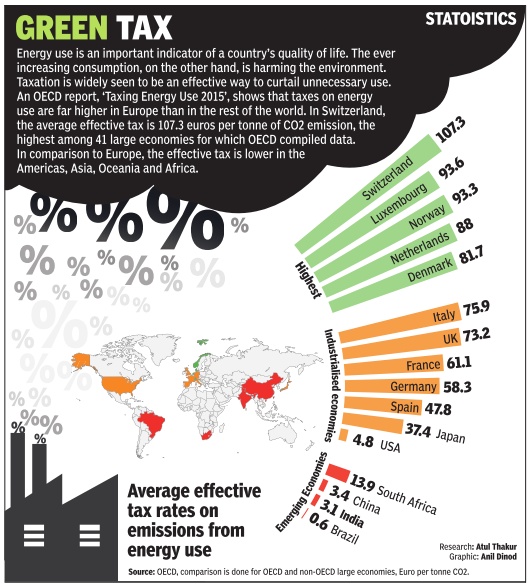
Taxation
Taxing energy use, India and the world: 2015
See graphic: India and the world: Tax rates on emissions from energy use: 2015
See also
Power: India, 2 (ministry data)
New And Renewable Energy: India