Income Tax India: Laws
(→See also) |
(→=Education loans to study abroad) |
||
| Line 170: | Line 170: | ||
= Reliefs on tax= | = Reliefs on tax= | ||
| − | ==Education loans to study abroad= | + | ==Education loans to study abroad== |
[http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Tax-relief-valid-on-edu-loans-to-study-02122015001062 ''The Times of India''], Dec 02 2015 | [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=Tax-relief-valid-on-edu-loans-to-study-02122015001062 ''The Times of India''], Dec 02 2015 | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 23 July 2016


This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content.
|
Contents |
Foreign tax credit (FTC)
The Times of India, Jul 01, 2016
Lubna Kably
In a bid to reduce litigation, the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) has made it easier for Indian-resident taxpayers, including large Indian companies having overseas operations, to claim credit for the taxes borne by them abroad. Credit of foreign taxes (referred to as foreign tax credit, or FTC) were allowed under tax treaties with other countries and the Income Tax Act, but the absence of specific rules often led to litigation.Denial of FTC by tax authorities also resulted in double taxation on the same income in the hands of Indian-resident taxpayers.
FTC rules issued by the CBDT provide that credit for foreign taxes can be claimed against taxes paid in India, like income tax (be it personal or corporate), cess and surcharge. Further, Indian companies can also claim FTC against Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT). Taxpayers have to submit proof of the tax paid or deducted at source in the foreign country to claim FTC.
The earlier draft rules, issued in April, had excluded disputed foreign taxes from the ambit of FTC. Now credit can be claimed in respect of disputed foreign taxes, subject to meeting compliance requirements.
Indian-resident taxpayers pay taxes on their global income in India, including on foreign source income which has already been subject to tax overseas (see graphic). FTC eliminates double taxation on the same income. To illustrate: A parent company headquartered in India earns interest on debt given to its Sri Lankan (SL) subsidiary and is subject to a 10% withholding tax. The Indian company will pay tax in India on its global income (including the foreign source interest income). The new rules will make it easier for it to claim an FTC for the 10% tax with held in Sri Lanka.
According to RBI data, India Inc's overseas investments by way of debt and equity amounted to $750 million in May . FTC rules will help Indian companies with global operations get benefit of credits for foreign taxes. The rules will also help high net worth individuals who make overseas investments and bear foreign taxes on their dividend or interest income. “Clarity on grant of FTC against the MAT liability is a big positive as is the move to provide credit for `disputed foreign taxes' upon final settlement of dispute. However, the modus operandi for allowing such credit -especially when the assessments are time-barred -needs to be prescribed,“ says Girish Vanvari, tax leader at KPMG India.
Some hiccups remain.Gautam Nayak, tax partner, CNK & Associates, says, “The rules provide clarity about the extent of FTC available and documents to be submitted for that. However, difficulties faced by certain taxpayers have not been addressed.FTC would not be available for taxes not covered by the relevant tax treaty , such as state taxes paid in the US or branch profits' taxes paid overseas.Besides, the tax credit would be restricted to the rate of tax payable under the tax treaty , even if the actual tax paid as well as the Indian tax payable is higher. So, if excess taxes have been withheld by the foreign payer out of abundant precaution, or on account of their local laws, tax credit would be available only for tax payable under the treaty terms. For example, the US levies a higher rate of withholding of 30% if a foreign entity (say an Indian company) does not have a tax identification number. In such cases, credit in India would be available only to the extent of applicable rate prescribed under the tax treaty.“
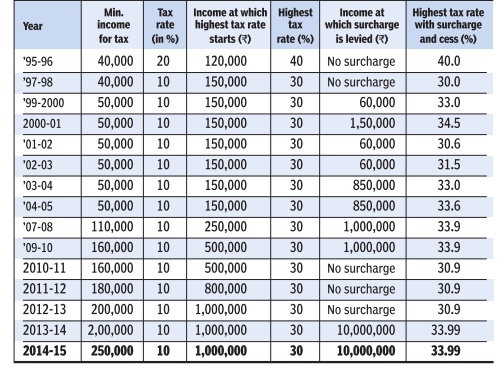
Income tax rates in India: 1995-2015
See the chart on this page
Indian income tax laws: ten things...
...that you should know Adapted from EconomicTimes March 2014
1) The interest earned on a bank fixed deposit is...Interest on FDs is fully taxable as income at the rate applicable to the taxpayer.
2) Travel insurance policies are not tax deductible for salaried individuals.
3) An individual won't get tax deduction for... employer's contribution to PF.
4) Gifts worth over Rs 50,000 in a year are taxed as income of recipient.
5) Any income of a minor child will be clubbed with that of the parent. HRA is not tax-exempt if you pay rent to... Your minor child.
6) A disabled dependant gets you a deduction under Section 80DD. This is an additional tax benefit
7) f you have a second house lying vacant, you have to...
a. Pay tax on rent not received. b. Include in wealth tax. c. Pay property tax on it. All the three conditions apply on a second house lying vacant.
8) If one earns rent on property, how much of it is taxable? Rental income is eligible for 30% standard deduction.
9) Only those with income below the basic exemption are exempt from filing tax returns.
10) The RGESS deduction is available only to first-time investors in equities.
Income Tax returns
Who has to file income tax returns
Salaried persons earning up to Rs 5 lakh annually
Salaried persons earning up to Rs 5 lakh annually will have to file income tax returns: Central Board of Direct Taxes
PTI | Jul 22, 2013
The CBDT had exempted salaried employees having a total income of up to Rs 5 lakh including income from other sources up to Rs 10,000 from the requirement of filing income tax return for assessment year 2011-12 and 2012-13, respectively.
However, for the assessment year 2013-14 and thereafter, salaried persons earning up to Rs 5 lakh annually will have to file income tax returns, Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) said on Monday.
Earlier in May 2013, the CBDT had made E-filing of income tax return compulsory for the assessment year 2013-14 for persons having total assessable income exceeding Rs 5 lakh.
The CBDT said that the exemption has been not been extended as the facility for online filing of returns has been made "user-friendly with the advantage of pre-filled return forms".
These e-filed forms also get electronically processed at the central processing centre in a speedy manner, it said.
For filing returns, an assessee can transmit the data in the return electronically by downloading ITRs, or by online filing.
Thereafter the assessee had to submit the verification of the return from ITR-V for acknowledgement after signature to Central Processing Centre.
Not filing I-T returns?Imprisonment,fine
Not filed I-T returns? You face jail & fine
TNN | Aug 17, 2013-
MUMBAI: Those defaulting in filing income tax returns are liable to prosecution, the I-T department has said.
If the tax evaded exceeds Rs 25 lakh, the defaulter can be sentenced to a minimum imprisonment of six months and maximum of seven years, besides being asked to pay a fine. If the tax evasion amount is less than Rs 25 lakh, the imprisonment could range between three months to two years in addition to fine.
Recently, the additional chief metropolitan magistrate, New Delhi, sentenced a taxpayer to six months' imprisonment in one assessment year and one year imprisonment in subsequent assessment year for repeating the offence of not filing income tax returns.
Income tax: fashion designers
‘Fashion designers are artists, eligible for I-T exemption’ Shibu Thomas
Mumbai: A fashion designer is an artist, the Bombay High Court has said and ruled that they are eligible for incometax exemptions available under the category. Ten years after the income-tax department first objected to tax benefits claimed by one of India’s leading fashion designers, Tarun Tahiliani, a division bench of Justice Dhananjay Chandrachud and Justice J P Devadhar on Monday said the designer should get tax privileges extended to the artists.
Tahiliani opened the country’s first fashion boutique, Ensemble, and is credited with being one of the designers who have brought high couture to India. Tahiliani’s IT woes began in October 2000 when he sought tax exemption for his income of Rs 83.90 lakh. Under Section 80 RR of the Income-Tax Act, a resident of India, who is an an author, playwright, artist, musician, actor or sports person can claim exemption of 75% of his income earned from foreign assignments. Tahiliani said that applying the exemptions, his taxable income for that year would be Rs 53.24 lakh.
The tax department, however, refused to accept that the fashion designer was an artist. It also contested deductions sought by sought by Tahiliani on his taxable income for 1999-2000 and 2001-2002. The income-tax appellate tribunal ruled in Tahiliani’s favour, upholding his claim that he was a creative artist. The IT department challenged the order before the high court.
The department’s lawyer contended that a fashion designer didn’t belong to the creative profession as the vocation was classified under applied arts and not fine arts. The IT department said that the benefit of exemption was granted to aid the artists, who represent Indian culture abroad.
The HC dismissed the IT department’s petition and held that fashion designers were entitled to tax exemptions meant for artists.
In a relief to global energy and petrochemical giant Shell, the Bombay high court on Tuesday ruled that the firm is not liable to pay tax in a transfer pricing case of 2009-10. The potential tax demand on Shell by the I-T authorities was $240 million. The ruling comes after Vodafone’s recent win in the HC in a similar case. The I-T authorities in Mumbai had alleged that there was underpricing of shares which the company had issued to an overseas group entity Shell Gas BV in March 2009.
The company said it had issued 87 crore shares at Rs 10 per share, but the I-T department assessed the value at Rs 180 per share and said there was thus a Rs 15,000-crore under pricing in the transaction, an amount on which tax could be levied. The Bombay HC has now held that these share premiums are not taxable. In case of Vodafone, the HC had then held that issuance of shares in a capital financial transaction did not amount to taxable income. The cellular service major had challenged an order of Income Tax authority in a transfer pricing case.
Several global giants are involved in transfer pricing litigation with the government, whose stand has been criticized.
Investors have been critical of the way the tax department went about slapping notices over the past few years.
“We welcome the High Court decision. Shell has always maintained that equity infusion by a foreign parent company into an Indian subsidiary cannot be taxed as income,’’ said a Shell spokesperson after the verdict was pronounced. “ This is a positive outcome which should provide a further boost to the Indian government’s initiatives to improve the country’s investment climate”.
Permanent account number (PAN)
2016: PAN mandatory for…
The Times of India Jan 04 2016
Mandatory PAN requirements
1 With effect from January 1, 2016, it has become mandatory to quote the permanent account number (PAN) for all transactions above `2 lakh for all modes of payment.
2 Only bank accounts opened under the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana have been exempted. But all other bank accounts and all kinds of deposits will have to quote PAN.
3 PAN will be mandatory for purchase of prepaid cards worth `50,000 or more in a year. Pur chase of gold jewellery worth above `2 lakh (`5 lakh current limit) would also need PAN.
4 The limit for quoting PAN for sale or purchase of real estate property has been raised to `10 lakh from `5 lakh.
5 PAN needs to be quoted only for a cash payment for a hotel or restaurant bill and foreign travel or purchase of forex of `50,000 (current limit `25,000).
2016: Required for transactions above Rs 2 lakh
The Times of India, Jun 22 2016
John Sarkar
New PAN rule hurts sale of luxury goods
Mails are flying thick and fast at most luxury stores across the country as harried sales staff face a tough time trying to coax people to part with their permanent account number (PAN) details. By the looks of it, they are not accomplishing much, resulting in poor sales of luxury goods. Furnishing of PAN details has been made mandatory by the government for any transaction above Rs 2 lakh in a bid to weed out black money .
However, the move has deterred many wealthy shoppers from spending lakhs of rupees on luxury products such as handbags, watches and writing instruments. “Our bags start at Rs 2 lakh.Sales at our store have been hit badly because our regular customers have stopped coming,“ said a senior executive of a French luxury brand. Earlier, most of them would pay in cash. But now, instead of giving their PAN details, they are opting to shop abroad.“
Most people in the luxury industry TOI spoke to complained about similar issues.For instance, at a store selling high fashion French leather goods in the capital, executives are tearing their well-groomed hair out to convince customers to reveal their PAN card number.
“We have taken a hit of several lakhs of rupees over the last few days but have not been able to figure out a way around the problem,“ said an executive at the store.“The other day , a lady who had come to buy a bag said she wouldn't risk getting her husband into trouble by furnishing his PAN card details.Eventually , she walked out without buying anything.“
Nikhil Mehra, CEO of Genesis Group that has marketing and distribution arrangements for several luxury brands such as Jimmy Choo, Giorgio Armani, Em porio Armani and Tumi among others and is the JV partner for Canali, Burberry and Villeroy and Boch in India, said consumer sentiment here has been affected by this ruling. “However, for most of our brands it is not a challenge because prices are within the Rs 2 lakh limit,“ he said.
The Indian luxury market has been pegged at Rs 16,300 crore in 2015 by market research firm Euromonitor and is expected to touch Rs 39,000 crore by 2020, with an annual growth rate of 19%.
Reliefs on tax
Education loans to study abroad
The Times of India, Dec 02 2015
Lubna Kably
Tax relief valid on edu loans to study abroad
In good news for parents whose children study overseas or plan to do so, the Pune income-tax appellate tribunal has held that higher education abroad is no bar for claiming tax relief on educational loans. A deduction for interest paid on such loans will be allowed from the taxable income of a parent, who has taken the loan and is paying interest, even if the child is studying overseas.
However, such a loan must be taken from either financial institutions, banks or from government-approved charitable institutions. Though Section 80E of the I-T Act states a parent is eligible for claiming tax relief on such loans, it has often been a ground for dispute during tax assessment. The term `higher education' has been defined in Section 80E of the I-T Act as: “Any course of study pursued after passing the senior secondary examination (SSE) or its equivalent from any school, board or university recognised by the central government, state government, local authority or any recognised authority .“
“This section does not specify that higher education must be undertaken by the student in India or that the overseas course must be approved by authorities in India. The only requirement is that such higher education should be undertaken by the student after passing SSE or its equivalent from a recognised institution in India,“ says Parizad Sirwalla, tax partner, KPMG.
Even in this case of Nitin Shantilal Muthiyan, which came for hearing before the Pune tribunal, the tax officer had held that deduction under Section 80E is allowable only in cases of higher education pursued in India. He, thus, disallowed the claim of interest of Rs 73,125 made by the taxpayer whose son, who had completed his BE in Electronics from Pune University, was pursuing a course at George Washington University , US. At the first stage of appeal, the commissioner of I-T (appeals) also upheld the action of the tax officer.
The taxpayer then filed an appeal with the income-tax appellate tribunal (ITAT) and obtained a favourable order. The ITAT in its order observed: “Provisions of Section 80E do not contain any stipulation that the higher education should be pursued only in India. If the intent of the legislation was that education should be pursued in India, in order to avail of the interest deduction, it would have stated so. Further, the taxpayer's son had completed SSE or its equivalent, as is required by this section, before pursuing studies overseas.“ Thus, the ITAT allowed the interest deduction claim made by the father during financial year 2008-09.
“The ITAT's decision is welcome, particularly in light of the spiralling cost of overseas education, and more and more Indian students opting for higher studies overseas. In terms of applicability of the decision, an ITAT's decision is binding within its jurisdiction, but carries precedent value in similar disputes for other jurisdictions, which are outside its purview,“ adds Sirwalla.
TDS (tax deducted at source)
Online rectification in ITR simplified, 2015
The Times of India, Dec 10, 2015
I-T Dept simplifies online rectification of TDS in ITR
The finance ministry said a new facility has been provided for pre-filling of TDS schedule
Aimed at making life easier for tax payers, the I-T department today said it has simplified the process of online rectification of incorrect details of tax deducted at source (TDS) filed in the income tax return (ITR).
Earlier, taxpayers were required to fill in complete details of the entire TDS schedule while applying for rectification on the e-filing portal of the I-T Department.
To avoid this, the finance ministry said a new facility has been provided for pre-filling of TDS schedule while submitting online rectification request on the e-filing portal to facilitate easy correction or updating of TDS details. "This is expected to considerably ease the burden of compliance on the taxpayers seeking rectification due to TDS mismatch," an official statement said. Errors due to incomplete TDS details in rectification applications were leading to delays in processing of such applications, thereby causing hardships to taxpayers, it added.
See also
Income Tax India: Expert advice /
Income Tax India: Laws /