Petroleum, diesel, natural gas, India, II (ministry data)
(→2011-12: Use of kerosene in Indian households) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 8: | Line 4: | ||
This article has been sourced from an authoritative, <br/>official publication. Therefore, it has been ‘locked’ and will <br/> never be thrown open to readers to edit or comment on.<br/> | This article has been sourced from an authoritative, <br/>official publication. Therefore, it has been ‘locked’ and will <br/> never be thrown open to readers to edit or comment on.<br/> | ||
| − | After the formal launch of their online archival encyclopædia, <br/> readers who wish to update or add further details can do so on <br/> a ‘Part | + | After the formal launch of their online archival encyclopædia, <br/> readers who wish to update or add further details can do so on <br/> a ‘Part III’ of this article. </div> |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
[[File: Average price of crude oil in India, 2001-15.jpg| Average price of crude oil in India, 2001-15; Graphic courtesy: [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Gallery.aspx?id=09_12_2015_027_015_012&type=P&artUrl=Indian-basket-of-crude-hits-11-yr-low-09122015027015&eid=31808 ''The Times of India''], December 9, 2015|frame|500px]] | [[File: Average price of crude oil in India, 2001-15.jpg| Average price of crude oil in India, 2001-15; Graphic courtesy: [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Gallery.aspx?id=09_12_2015_027_015_012&type=P&artUrl=Indian-basket-of-crude-hits-11-yr-low-09122015027015&eid=31808 ''The Times of India''], December 9, 2015|frame|500px]] | ||
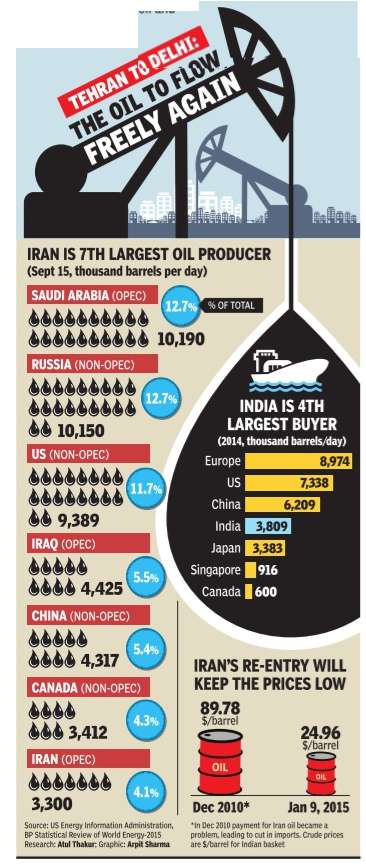
[[File: Oil production in Iran vis-à-vis other producers; countries, including India, that purchase oil from Iran, as in 2014.jpg| Oil production in Iran vis-à-vis other producers; countries, including India, that purchase oil from Iran, as in 2014; Graphic courtesy: [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Gallery.aspx?id=20_01_2016_010_014_005&type=P&artUrl=STATOISTICS-TEHRAN-TO-DELHI-THE-OIL-TO-FLOW-20012016010014&eid=31808 ''The Times of India''], January 20, 2016|frame|500px]] | [[File: Oil production in Iran vis-à-vis other producers; countries, including India, that purchase oil from Iran, as in 2014.jpg| Oil production in Iran vis-à-vis other producers; countries, including India, that purchase oil from Iran, as in 2014; Graphic courtesy: [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Gallery.aspx?id=20_01_2016_010_014_005&type=P&artUrl=STATOISTICS-TEHRAN-TO-DELHI-THE-OIL-TO-FLOW-20012016010014&eid=31808 ''The Times of India''], January 20, 2016|frame|500px]] | ||
| − | =The source of | + | =Part I= |
| + | =The source of Part I= | ||
''' INDIA 2012 ''' | ''' INDIA 2012 ''' | ||
| Line 30: | Line 27: | ||
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA | GOVERNMENT OF INDIA | ||
| + | |||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
'''PETROLEUM AND NATURAL GAS''' | '''PETROLEUM AND NATURAL GAS''' | ||
| Line 190: | Line 188: | ||
of all State capitals and cities with population of more than 1 crore will be emphasized | of all State capitals and cities with population of more than 1 crore will be emphasized | ||
for extension of BS-IV auto fuels. | for extension of BS-IV auto fuels. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===BS IV=== | ||
| + | ====Launched in 2017==== | ||
| + | See graphic. | ||
| + | |||
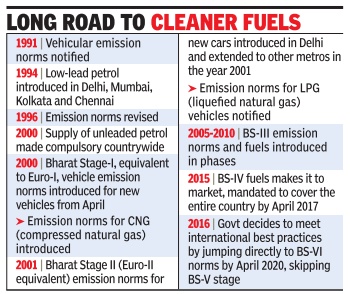
| + | [[File: Vehicular emission, a timeline, 1991-2016.jpg|Vehicular emission norms, a timeline, 1991-2016; [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Gallery.aspx?id=02_04_2017_011_029_010&type=P&artUrl=One-nation-one-fuel-India-keeps-BS-IV-02042017011029&eid=31808 April 2, 2017: The Times of India] |frame|500px]] | ||
==Pricing of Petroleum Products== | ==Pricing of Petroleum Products== | ||
| Line 365: | Line 369: | ||
is working in close association with Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) for | is working in close association with Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) for | ||
popularizing labelling programmes for equipment using petro based fuels. | popularizing labelling programmes for equipment using petro based fuels. | ||
| − | = | + | =See also= |
| − | + | [[Automobile industry: India]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | See | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[ | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Petroleum, diesel, kerosene, India: I]] | |
| − | + | [[Petroleum, diesel, natural gas, India, II (ministry data)]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|P | |
| + | PETROLEUM, DIESEL, NATURAL GAS, INDIA, II (MINISTRY DATA)]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|P | ||
| + | PETROLEUM, DIESEL, NATURAL GAS, INDIA, II (MINISTRY DATA)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:07, 21 September 2020
This article has been sourced from an authoritative, readers who wish to update or add further details can do so on a ‘Part III’ of this article. |

[edit] Part I
[edit] The source of Part I
INDIA 2012
A REFERENCE ANNUAL
Compiled by
RESEARCH, REFERENCE AND TRAINING DIVISION
PUBLICATIONS DIVISION
MINISTRY OF INFORMATION AND BROADCASTING
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
[edit] Introduction
PETROLEUM AND NATURAL GAS
The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas is entrusted with the responsibility of exploration and production of oil and natural gas including import of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), and the refining, marketing, distribution, import, export and conservation of petroleum products.
[edit] CRUDE OIL AND NATURAL GAS PRODUCTION
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) and Oil India Limited (OIL), private and joint venture companies are engaged in the exploration and production of oil and natural gas in the country.
Government of India approved the New Exploration Licensing Policy (NELP) in 1997 and it became effective in February 1999. Since then, licences for exploration are being awarded only through a competitive bidding system and National Oil Companies (NOCs) are required to compete on an equal footing with other Indian and foreign companies to secure Petroleum Exploration Licences (PELs).
Eight rounds of bids have so far been held under NELP, and 235 exploration blocks have been awarded. Under NELP, 97 oil and gas discoveries in 29 blocks have already been made. Further, ninth bid round of New Exploration Licensing Policy (NELPIX) was launched on 15.10.2010. Bids were opened on 28.3.2011. 74 bids have been received for 33 blocks, out of 34 blocks offered under NELP-IX.
[edit] ONGC VIDESH LIMITED
ONGC Videsh Limited (OVL), a wholly-owned subsidiary of ONGC, was incorporated as Hydrocarbons India Limited on 5 March 1965 with an initial authorised capital of Rs 5 lakh, for the business of international exploration and production. Its name was changed to ONGC Videsh Limited on 15th June 1989. The Authorised and Paid-up Share Capital of OVL as on 31st March 2011 is Rs 1,000 crore. The primary business of the company is to prospect for oil and gas acreages abroad. These include acquisition of oil and gas fields in foreign countries as well as exploration, production, transportation and sale of oil and gas.
OVL currently has participation in 33 projects in 15 countries namely, Vietnam (2 projects), Russia (2 projects), North Sudan (2 projects), South Sudan (1 project) Iran (1 project), Iraq (1 project), Libya (1 project), Myanmar (2 projects), Syria (2 projects), Cuba (2 projects), Brazil (6 projects), Nigeria (2 projects), Colombia (6 projects), Venezuela (2 project) and Kazakhstan (1 project). OVL's share of crude oil and natural gas production is currently from 9 projects in eight countries, viz., Russia, North & South Sudan, Vietnam, Syria, Colombia, Venezuela and Brazil. OVL's share of the crude oil and natural gas production in 2010-11 was 9.448 Million Metric Tonne of Oil & Oil equivalent gas including 2.692 BCM of natural gas. The other 23 projects being implemented by OVL are at various stages of exploration and appraisal and development. One Pipeline Project was completed in Sudan in 2005.
The gross revenue of OVL was Rs 18,683 crore during the financial year 2010-11 with net profit of Rs 2691 crore. Further, OVL is pursuing acquisition of various oil and gas exploration and production opportunities in Russia, Central Asia, Latin America, Africa, and Middle East, which are at different stages.
[edit] OIL INDIA LIMITED
Oil India Limited (OIL), is a National Oil Company engaged in the exploration, production and transportation of crude oil and natural gas in the country. OIL was incorporated in 1959 as a company with a two-third share of Burmah Oil Company and one-third share of Government of India. In 1961, OIL became a joint venture Company with equal share of Government of India and Burmah Oil company. On 14th October 1981, OIL became a Government of India enterprise, a wholly-owned Public Sector Undertaking. OIL has operational areas in the States of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Orissa, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Rajasthan.
The Company currently produces around 3.90 MMTPA of crude oil and around 7.00 MMSCMD of natural gas and more than 45,000 tonnes of LPG annually. The entire crude oil, LPG production and major share of the Natural Gas production come from its traditionally rich oil and gas fields concentrated in the North East region. To increase its production potential and chart a steady growth, the company has taken a very structured approach towards intensification and integration of geo-scientific studies to find new oil.
Since most of the crude oil and gas produced by OIL is from its matured and aging fields, it has initiated fit for purpose EOR/ IOR initiatives for revitalization of matured fields and taken up steps to explore the locked up potential. New technologies and methods viz. Infill/Horizontal/J-Bend/ Sub-Thrust drilling are being deployed to augment exploration and development efforts. The Company is also focusing on exploration in frontier areas and NELP blocks which have good prospects.
[edit] GAIL INDIA LIMITED
The setting up of GAIL (India) Limited, formerly known as Gas Authority of India Limited in August 1984 heralded a new era of natural gas in the country. GAIL is now completing 27 glorious years of service to the nation. Starting with a natural gas transmission company, it is today an integrated energy company along the Natural Gas value chain with global footprints. Having started as a gas transmission company during the late eighties, it grew organically over the years by building a large network of Natural Gas Trunk Pipelines covering a length of over 8700 km. Today, GAIL has interests in the business of Natural Gas, LPG, Liquid Hydrocarbons and Petrochemicals, the latter being value-added products.
The Company has also entered in telecom sector by leasing bandwidth available through the OFC which is laid along the gas pipelines for their operation and maintenance. GAIL has also diversified into Exploration and Production, City Gas Distribution and is steadily developing an overseas presence.
The GAIL has a turnover of Rs. 32,459 crore (US $ 7.2 billion approx.)and Profit After Tax (PAT) of Rs. 3,561 crore (US $ 790 million approx.) in the year 2010-11. GAIL has recently acquired its first Shale Gas asset in the USA through its wholly owned US subsidiary GAIL Global (USA) Inc.. The subsidiary company has executed definitive agreements with Carrizo Oil & Gas Inc. based in Houston, Texas, to enter into an unincorporated joint venture, under which GAIL Global (USA) Inc. will acquire a 20% interest in Carrizo's Eagle Ford Shale acreage position. The Joint Venture will have 20,200 gross acres, out of which GAIL subsidiary would have 4,040 net acres spread over four counties in Texas.
Leveraging on its pipeline network, GAIL has built up a strong 12,200 km. Optical Fibre Cable (OFC) network for leasing of bandwidth as a carriers' carrier. GAIL's telecom business unit - 'GAILTEL' offers highly dependable bandwidth for telecom service providers across 175 locations in ten states.
[edit] Exploration and Production
In a move towards integration along the energy chain and for sourcing supply, GAIL has entered into the area of exploration and production. Currently, the company is involved in oil and gas exploration activities over an acreage of 1,64,637 sq. km. GAIL now holds a participating interest between 10 to 80 per cent in 27 oil and gas exploration blocks. Of these, 9 are on-land blocks and 18 are offshore blocks. In India, there are 24 blocks which are in Basins such as Mahanadi, Bengal, Gujarat - Saurashtra, Mumbai, Cambay, Assam-Akaran and Cauvery. Furthermore, GAIL has also got stake in the A-1 and A-3 blocks in Myanmar and Block No. 56 in Oman. GAIL consortium has participating interest in three CBM blocks in the country in collaboration with Arrow Energy of Australia, EIG Energy Infrastructure Group and Tata Power.
[edit] Overseas Presence
Apart from its equity participation in three retail gas companies in Egypt and in China Gas Holdings in China, participating interest in offshore blocks in Myanmar and one onland block in Oman, GAIL is pursuing business opportunities in regions such as South/South-East Asia, West Asia, Russia and Central Asian Republics and African continent in the areas of exploration and production, gas transmission, CNG and city gas distribution, LNG and petrochemicals. GAIL has set up a whollyowned subsidiary company viz. GAIL Gobal (Singapore) Pvt. Ltd in Singapore.
[edit] REFINING
The present refining capacity in the country as on 1st June 2011 was 193.386 Million Metric Tonnes Per Annum (MMTPA). Out of 21 refineries operating in the country, 17 are in public sector, 3 are in private sector and 1 is in JV (Joint venture) of Public Sector. Out of 17 Public Sector refineries, 8 are owned by Indian Oil Corporation Ltd. (IOCL), 2 each by Chennai Petroleum Corporation Limited (a subsidiary of IOCL), Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL), Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL) and Oil & Natural Gas Corporation Limited (ONGC). Numaligarh Refinery Limited (a subsidiary of BPCL) and Mangalore Refinery & Petrochemicals Limited have one each. The Joint Venture Refinery belongs to Bhart Petroleum Corporation Limited. The capacity-wise details of the refineries are given below:
[edit] IMPLEMENTATION OF BS-III/IV FUELS IN THE COUNTRY
The Auto Fuel Policy, approved by the Government, laid down a roadmap for upgradation of the quality of auto fuels (Petrol and Diesel) to Bharat Stage (BS) IV in 13 identified cities and BS-III in the rest of the country. As per the roadmap, supply of BS-IV Petrol and Diesel commenced in all 13 identified cities from 1 April 2010.
The oil Industry has successfully completed the introduction of BS-III fuels in the entire country with the last phase completed on 22nd September, 2010. Oil sector PSUs have invested an amount of Rs 32,760 crore in upgration of refining technology and creation of facilities for production of BS-IV/III auto fuels.
Efforts are being made to progressively expand coverage of BS-IV fuels with introduction of these fuels in 50 more cities by 2015. The additional cities will be identified considering the pollution levels and the vehicle population and inclusion of all State capitals and cities with population of more than 1 crore will be emphasized for extension of BS-IV auto fuels.
[edit] BS IV
[edit] Launched in 2017
See graphic.
[edit] Pricing of Petroleum Products
The Administered Pricing Mechanisam (APM) or Cost Plus Pricing for petroleum products which was introduced in 1976 was abolished with the effect from 1 April 2002, consequent to the de-regulation of the oil sector in India. Vide Gazettee Notification dated 28 April 2002, Government notified that pricing of all petroleum products except PDS Kerosene and Domestic LPG, would be market determined.
In line with this policy, the Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) carried out 23 price revisions up to January 2004, on the principle of Import Parity Pricing (IPP). However, with the sustained rise in international oil prices from 2004, the Government found it necessary to modulate the retail prices of the four sensitive petroleum products, viz., Petrol, Diesel, PDS Kerosene and Domestic LPG. In June 2006, based on the recommendations of the Rangarajan Committee, the Government changed the pricing mechanism for Petrol and Diesel from Import Parity to Trade Parity (Trade Parity being the weighted average of Import Parity and Export Parity prices in the ratio of 80:20) while the pricing of PDS Kerosene and Domestic LPG continues on Import Parity basis.
To arrive at a viable and sustainable system of pricing of petroleum products, Government had set up an Expert Group under the chairmanship of Dr. Kirit Parikh. In the light of Government's budgetary constraints and the growing imperative for fiscal consolidation, and the need for allocating more funds to social sector schemes for the common man, the Government has, with effect from 26 June, 2010, made the pricing of Petrol and Diesel both at refinery gate and the retail level marketdetermined. In case of a high rise and volatility in international oil prices,
Government will suitably intervene in the pricing of Petrol and Diesel.
The Government is committed to make available the essential fuels, particularly the cooking fuels to the common man at affordable prices. Accordingly, it has been decided to continue subsidising PDS Kerosene and Domestic LPG.
[edit] Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL)
Indian Oil Corporation is India's flagship national oil company with business interests encompassing the entire hydrocarbon value chain - from refining, pipeline transportation and marketing of petroleum products to exploration & production of crude oil & gas, marketing of natural gas, petrochemicals, renewable energy and now into Nuclear. The authorised and paid-up share capital of IOCL as on 31st March 2011 is Rs. 6,000 crore and Rs. 2427.95 crore respectively.
Over the years, Indian Oil Corporation has grown by expanding its own operations, bringing independent refineries like Chennai Petroleum (CPCL) and Bongaigaon Refineries (BRPL) under its fold, by merging of Assam Oil Company (AOC) and IBP with it and thus IOC has synergized its refining as well as marketing operations.
Indian Oil Corporation supplies precious petroleum products through an unmatched countrywide network of above 35,000 touch points, which correspond to about 55% of the industry infrastructure. IOC operates the largest and most extensive network of retail outlets, numbering more than 19,000. It reaches Indane cooking gas to the doorsteps of about 61 million households through about 5290 Indane distributors. These efforts are backed by supplies from 140 terminals & depots, 96 aviation fuel stations and 89 Indane bottling plants. About 7,726 bulk consumer pumps are also in the operation for the convenience of large consumers, ensuring product and inventory at their doorstep. The company is the leader in refining, marketing and pipeline transportation in the country.
It entered into a new era of gas transportation business during the financial year 2010-11 by commissioning a gas pipeline from Dadri to Panipat to supply Regassified - LNG for its Panipat petro-chemical complex. Indian Oil's cross-country network of pipelines, spanning over 10,899 KM with total capacity of 75.26 MMTPA of crude and finished products and 10 MMSCMD of gas being the largest in the country, helps in meeting the vital energy needs of the consumers in an efficient, economical and environment-friendly manner.
Today, Indian Oil is the country's largest commercial enterprise with Maharatna status and India's highest ranked company in the prestigious Fortune Global 500 listing of the world's largest Corporates.
[edit] Exploration and Production
Indian Oil has been making continued efforts to expand its E&P portfolio domestically as well as overseas. Presently, it has assets in India and seven other countries in association with experienced domestic and foreign upstream companies. While gas discoveries have been made in 3 blocks, production is yet to start from any of these blocks. In all, the E&P portfolio includes 23 blocks, comprising 13 domestic and 10 overseas. These overseas assets are located in Iran, Libya, Nigeria, Goban, Yemen, Timor-Leste and Venezuela.
[edit] Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL)
HPCL is an integrated oil Company in India, with Navratna status. It has two refineries producting a wide variety of petroleum products fuels, lubricants and specialty products; one in Mumbai (West Coast) having a capacity of 6.5 MMTPA and the other in Visakhapatnam (East Coast) with a capacity of 8.3 MMTPA. The Corporation holds equity stake of 16.95% in Mangalore Refinery & Petrochemicals Limited, a state-of-the-art refinery at Mangalore with a capacity of 9.69 MMTPA.
HPCL, in collaboration with M/s Mittal Energy Investment Pvt. Ltd, is also setting up a state-of-the-art 9 MMTPA capacity Green Field Refinery at Bathinda in Punjab. HPCL owns and operates the largest Lube Refinery in the country producing Lube Base Oils, having a capacity of 3,35,000 Metric Tones, contributing over 40% of the country's total Lube Base Oil production. Besides, the Corporation owns six Lube Blending Plants (2 in Mumbai and 1 each at Budge Budge, Ramnagar, Chennai & Silvassa) and a Lube oil pipeline for evacuation of base oil from Mumbai Refinery. Presently, HPCL is producing over 300 grades of lubes, specialties and greases.
The marketing network of HPCL consists of 13 Zonal offices in major cities and 101 Regional offices facilitated by a Supply & Distribution infrastructure comprising terminals, aviation services facilities, LPG bottling Plants, Lube filling plants, Inland Relay Depots, Retail Outlets (Petrol Pumps) and LPG & Lube Distributorships. HPCL has state-of-art information technology infrastructure to support its core business. The data center is located at Hitech city in Hyderabad. HPCL has, over the years, moved from strength in keeping with the national priorities. The ambitious plans include furthering the synergies and participating in the oil industry's growth by vertically integrating in the upstream and downstream sectors. The policy initiatives undertaken also include growth and diversification ventures in different sectors.
[edit] Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL)
BPCL is an integrated oil company with Navratna status in the downsteam sector engaged in refining of crude oil and marketing of petroleum products. it has also diversified into production and marketing of petrochemical feedstock. BPCL has refineries at Mumbai and Kochi with a combined refining capacity of 21.5 MMTPA. The Refineries are certified for ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and OHSAS 18001 reflecting the continuing commitment towards quality, environment, health and safety.
The Authorized Share Capital and Paid up Capital of the company as on 31.12.2010 was Rs 450 crore and Rs 361.54 crore respectively. BPCL has a robust distribution network comprising of 120 storage depots, 12 major installations, 48 LPG bottling plants, 1676 KM cross-country pipeline (including 292 KM pipeline set up by its joint venture company) and 2 lubricant blending plants.
During April-December 2010, 298 new Retail Outlets have been commissioned and 254 more are expected to be commissioned during the period January-March 2011 and total number of retail outlets as on 31.3.2011 is estimated at 9220. During April-December 2010, 106 LPG distributorships have been commissioned. In addition, 25 more LPG Distributorships are expected to be commissioned during the balance period of the year 2010-11. The total number of distributorships as on 31.3.2011 is estimated at 2356.
[edit] Renewable Energy
BPCL has taken steps to develop non conventional / renewable resources of energy and has undertaken various initiatives in tapping non-conventional energy sources like bio diesel, wind energy, solar energy and fuel cells in order to develop such alternate sources of energy.
[edit] Exploration and Production
Since incorporation of Bharat Petro Resources Limited (BPRL), a wholly owned subsidiary company of Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL), in October 2006, for carrying out the upstream oil & gas business of BPCL, BPRL and its subsidiaries/joint ventures have been making investments in the various exploration blocks in India and abroad. The company was incorporated with an Authorized Share Capital of Rs. 1000 crore which has been now increased to Rs 3000 crore. The Subscribed Share Capital of BPRL as on 30.11.2010 is Rs. 1079.80 crore. The paid up share capital as on 31st March 2010 was Rs. 702.55 crore. BPRL currently has participating interests in 26 Blocks spread across 7 countries in 15 geological basins. Out of these blocks, 9 Blocks are located in India which was acquired under different bidding rounds of New Exploration Licensing Policy (NELP). Most of the blocks are in an advanced stage of exploration. BPRl's acreage in all these blocks is about 81,000 sq km, of which 73,000 sq km (or approx 90%) is offshore acreage.
[edit] Conservation of Petroleum Products
After coal, petroleum products remain the primary energy source in India, with their consumption increasing at a very steep rate. For faster development, the role of energy sector is of paramount importance. India is at present one of the least energy efficient countries in the world with an identified scope of reducing energy consumption by 20-30 percent in all major sectors through conservation measures.
The spiralling prices of crude oil in the recent past have made all the developing economies to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious utilization of the already strained resources. The Petroleum Conservation Research Association (PCRA) set up as a registered society under the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas in 1978 has been given the mandate to promote conservation of petroleum products in the major sectors of economy like transport, industry, households and agriculture through direct technical assistance, R&D, educational and training programmes, and mass awareness campaigns.
PCRA's activities cover conservation of all energy sources, development, evaluation and commercialization of efficient equipment and additives, popularizing petro-crop cultivation and production of bio-fuels, environment protection, etc. PCRA has been conducting public awareness campaigns for promoting energy conservation in petroleum sector on a regular basis which included various educational and practical sessions to variety of consumer sectors. PCRA has also launched media campaigns to promote efforts of conservation and is working in close association with Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) for popularizing labelling programmes for equipment using petro based fuels.
[edit] See also
Petroleum, diesel, kerosene, India: I
Petroleum, diesel, natural gas, India, II (ministry data)
