Defence production, India: 2 (ministry data)
This article has been sourced from an authoritative, official readers who wish to update or add further details can do so on a ‘Part 3’ of this article. |
The source of this article
INDIA 2012
A REFERENCE ANNUAL
Compiled by
RESEARCH, REFERENCE AND TRAINING DIVISION
PUBLICATIONS DIVISION
MINISTRY OF INFORMATION AND BROADCASTING
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
Defence Production: India
The Department of Defence Production was set up in November 1962 with the objective of developing a comprehensive production infrastructure for the defence of the nation. Over the years, the Department has established wide ranging production facilities for various defence equipment through the ordnance Factories and Defence PSUs. The products manufactured include arms and ammunition, tanks, armoured vehicles, heavy vehicles, fighter aircraft and helicopters, warships, submarines, missiles, ammunition, electronic equipment, earth moving equipment, special alloys and special purpose steels.
Ordnance Factories
The Ordnance Factory Board has 39 factories with two more being set up at Nalanda and Korwa. The organization has over the years progressed from labour intensive manual operations to Highly Automated Computer Based manufacturing systems and the emphasis has shifted from production of basic and intermediate inputs to production of finished stores and the organization has emerged as the system integrator.
Ordnance Factories are divided into 5 operating groups (i) Ammunition and Explosive, (ii) Weapons, Vehicles and Equipments, (iii) Materials and Components, (iv) Armoured Vehicles and (v) Clothing and equipments, each headed by Additional DGOF.
Defence Undertakings
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) is a Navaratna company and the largest DPSU under the Department of Defence Production, Ministry of Defence. It has positioned itself as a comprehensive solution provider to the Indian Defence Services in aviation, spanning fighter aircraft, trainer aircraft and light helicopters. Around 90% of the sales of HAL is to the Indian Defence Services. The company is producing the following types of aircraft for the Air Force, Army, Navy and civilian requirements: SU-30MKI multirole fighter, Hawk - Advanced Jet Trainer, Light Combat Aircraft (LCA), Intermediate Jet Trainer (IJT), Dornier 228 - Light Transport Aircraft, Dhruv (Advanced Light Helicopter) and Cheetal/Chetak helicopters. Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), a Navaratna PSU, was established at Bangalore in the year 1954. BEL ranks 62nd among top 100 companies worldwide in defence revenues, as published by Defence News, USA. BEL has nine operating units spread all over the country. The company has core competencies in areas of Radars, Weapon systems, Fonars, Communication, Electronic Warfare Systems,
Network Centric Systems, Electro Optics, Tank Electronics and Homeland Security systems. About 80% turnover of the company comes from these business segments. Apart from these areas, BEL manufactures specialised products like Electronic Voting Machines and large variety of Components like electron tubes, semiconductor devices, solar cells etc. BEL has strong R&D base that has enabled the organisation to maintain technological edge. Around 75% of the turnover is achieved from indigenous technology.
Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers Ltd. (GRSE), a Mini Ratna Category I Public Sector Company, has kept pace with India’s expanding maritime interests and is recognised as a leading Shipbuilding Yard and manufacturer of high-value, high-technology, complex engineering items. Over the years, GRSE has gained expertise in construction of Warships for the Indian Navy, Ships and Hovercrafts. Apart from shipbuilding and ship repair, GRSE is one of the very few versatile shipyards having its own Engineering and Engine Division.
Goa Shipyard Ltd. (GSL) is the youngest and smallest of Defence shipyards. Over the years, GSL has designed and built a wide range of vessels for the defence and commercial sectors, with special expertise in designing and building modern Patrol Vessels of Steel and Aluminium hull. The product range includes Offshore Patrol Vessels, Special Purpose Warships, Survey Vessels, Fast Attack Craft, Sail training Ships, Offshore Supply Vessels, Ferries and Tugs. Other products and services include Damage Control Simulators, Safety at Sea Training facilities, repair and modernization of vessels, and GRP boats. The seven Fast Patrol Vessels (FPVs) currently in service with the Indian Coast Guard are an in-house product of GSL.
Hindustan Shipyard Limited (HSL) has so far built 163 ships, including 11 offshore structures, and repaired nearly 1850 ships of various types. The shipyard has also built Offshore Patrol Vessels and Inshore Patrol Vessels for Indian Navy and Drill Ship, Offishore Platform and support vessels for the oil sector. In order to modernize the shipyard and prepare HSL to undertake the construction of highly sophisticated Naval vessels such as landing platform decks, conventional submarines and state-of-the-art special vessels for the Indian Navy, a massive programme is being prepared by the Department of Defence Production in consultation with Indian Navy and DRDO.
Mazagon Dock Limited (MDL) is a leading defence shipyard involved in the construction of frontline warships and submarines for the Indian Navy and Coast Guard. The yard is presently constructing state-of-the-art stealth frigates, missile destroyers and Scorpene submarines, and is striding forward in attaining self-reliance goals in the construction of warships and submarines. MDL’s production efforts resulted in the launch of a missile destroyer at Chennai on April 1, 2010 and a multi-support vessel being built for export on June 5, 2010.
BEML Limited (BEML Bharat Earth Movers Limited), established in 1964, is a Mini-Ratna (Category-I) multi-location, multi product company engaged in the design, manufacturing, marketing and after sales service of a wide range of Defence products, Mining & Construction equipment, and Rail and Metro-rail products. The Company primarily operates in the three distinct business segments, i.e., Defence Business, Mining & Construction Business and Rail & Metro Business. The major activities of R&D of BEML include design and development of new products and aggregates for products such as Dozers, Dumpers, Excavators, Loaders and other Defence and Railway
Products, Technology absorption, Indigenization, Company standardization activities etc.
Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL), a Mini-Ratna Category - I company, was incorporated in the year 1970. A pioneer in the manufacture of Anti-Tank Guided Missiles, BDL is now manufacturing ATGMs of later generations, surface-to-air weapon systems, strategic weapons, launchers, under water weapons, decoys and test equipment. Besides producing indigenously developed Prithvi Missile (Surface to Surface) and Akash (Long Range Surface to Air) Missiles, BDL is engaged in the production of Konkurs - M and Invar (3UBK-20) Anti Tank Guided Missiles (ATGMs) in collaboration with KBP, Tula (Russia) and Rosoboron export (Russia) respectively and Milan-2T with MBDA, France. In-house developed CMDS (Counter Measure Despising System) has already been accepted by the Indian Air Force for Jaguar and LCA. BDL is presently working on adoption of the system to a variety of Aircraft Platforms and also developing Radio Frequency controlled ATGM.
Mishra Dhatu Nigam Limited (MIDHANI), a Mini-Ratna Category-I company, was established in November 1973 to achieve self-reliance in the manufacture of a wide range of super alloys, titanium alloys, special purpose steels etc., primarily for defence and strategic sectors. It has made significant contributions during the last three decades in developing, productionising and supplying highperformance metals and alloys for programmes of national importance in defence, space and atomic energy. High-technology materials needed in light combat aircraft, and MIG aircraft engines, rocket-motor casing for space applications, missile programmes and special steels for nuclear reactors are provided by MIDHANI.
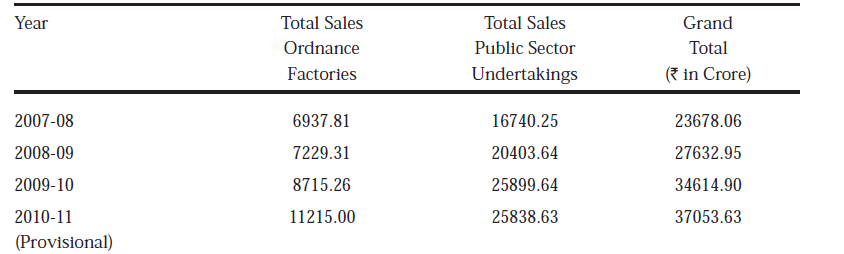
PRODUCTION & TURNOVER OF OFB & DPSUS
The production and turnover of Ordnance Factories and Defence PSUs have been increasing steadily, in response to the increasing requirements of armed forces as well as the nation’s security and strategic concerns. Details of turnover for the last three years are given below :
For achieving self-reliance in defence production, it is also essential to develop a wide production base in the private sector, apart from developing the public sector industries. Defence PSUs and Ordnance Factories have, as a policy, been outsourcing many of their requirements and have, over the years, developed a wide vendor base which includes a large number of medium and small scale enterprises, apart from large scale industries.
PRIVATE SECTOR PARTICIPATION IN DEFENCE PRODUCTION
In May 2001, the Government of India had decided to allow private sector participation in defence industry which was till then reserved for the public sector. Under the guidelines issued by the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP), 100% investment by private sector is allowed in the sector and foreign direct investment upto 26% is allowed, subject to licensing.
Applications for licensing are considered by a Standing Committee in the Department of Defence Production and appropriate recommendations are given to the DIPP. As on 21.07.2011, DIPP has issued 169 Letters of Intent (LOI)/Industrial Licenses to private Indian companies for setting up defence industrial units. A number of joint ventures have also been formed between Indian and foreign companies.
In 2006, the Ministry of Defence had made a major change in the Defence Procurement Procedure, under which offsets have been provided for in respect of all contracts of Rs. 300 crores or more. Specified goods or services worth 30% of the value of such contracts, have to be procured by supplies from Indian industry. Since a large number of major procurements are on the anvil in connection with the modernization of the armed forces, the Indian defence industry will have several opportunities for participation in offset contracts.
DEFENCE PRODUCTION POLICY
The Government has recently brought out a Defence Production Policy with the following objectives :-
(i) To achieve substantive self reliance in the design, development and production of equipment/weapon systems/platforms required for defence in as early a time frame as possible;
(ii) To create conditions conducive for the private industry to take an active role in this endeavour; and
(iii) To enhance the potential of SMEs in indigenization and to broaden the defence R&D base of the country.
To achieve the above objectives, it has been decided that preference will be given to indigenous design, development and manufacture. For building a robust defence industrial base, it has been decided to encourage larger involvement of the Indian private sector industry in the design and development of defence equipment. In order to synergise and enhance the national capabilities introducing state-of-theart Defence equipment, formation of consortia, joint ventures and public private partnerships etc. will be encouraged. The Academia, Research and Development Institutions as well as Technical and Scientific Organizations will also be involved in the process.
DIRECTORATE GENERAL OF QUALITY ASSURANCE (DGQA)
Directorate General of Quality Assurance (DGQA) is an Inter-Service Organisation under the Department of Defence Production that is responsible for quality assurance of all defence equipment and stores for the Army and Navy (excluding Naval Armaments) as well as common use items for the Air Force. DGQA provides technical guidance to manufacturers and users and is also responsible for technical evaluation and final acceptance of specified products. The organization also acts as the Authority Holding Sealed Particulars (AHSP) and provides technical assistance to the Armed Forces in several areas such as formulation of GSQR and RFPs, technical evaluation of tenders, conduct of defect investigations, assessment of users' satisfaction etc.
The Organization consists of 10 technical directorates, each of which is responsible for a specified range of equipment. Each directorate has three functional tiers at the Headquarters, Controllerates and Quality Assurance Establishments in the field. In addition, DGQA also operates proof establishments for armament for carrying out proof firing of weapons and ammunition. The details of stores for which quality assurance services were provided by DGQA during the last three years are given below:
DIRECTORATE GENERAL OF AERONAUTICAL QUALITY ASSURANCE (DGAQA)
The Directorate General of Aeronautical Quality Assurance (DGAQA) is an organisation under the Department of Defence Production that is responsible for quality assurance and final acceptance of military aircraft, accessories and other aeronautical stores. The organization provides technical guidance to ensure quality assurance during all stages such as design, development, production, overhaul and repairs.
DGAQA also plays an important role in providing technical guidance to the Service Headquarters and manufacturers during various stages of procurement of aeeronautical stores. The organisation has put in place quality management systems to ensure that the stores procured meet the required specifications and performance parameters.
The Headquarters of the organisation is in New Delhi and there are 34 field establishments in different parts of the country. The total value of stores, for which quality assurance coverage was provided during 2009-2010, was Rs. 12546 Crore. A number of quality audits were also conducted on critical products and accessories for ensuring compliance with the specifications. The organization is also taking part in a number of investigations and joint studies with the Service Headquarters for improving the quality and reliability or aeronautical stores.
DIRECTORATE OF STANDARDISATION (DOS)
The primary objective of the Directorate of Standardisation is to establish commonality in equipment and components among the three Services so that the overall inventory of the Defence Services is reduced to the minimum. The objective is sought to be achieved through:
(a) Preparation of various Standardisation documents;
(b) Codification of Defence Inventory; and
(c) Entry Control.
The achievements vis-a-vis targets of these three major activities are given below:
(a) Standardisation: The target set for the year 2010-11 is 792 for standard documents, against which 710 have been prepared till November 30, 2010. 4,784 Standardisation documents have been formulated till November 30,2010.
(b) Codification: Codification target for the year 2010-11 is 60,096, against which 43,350 items have been codified till November 30, 2010 thereby making the total number of items codified till date to be 4, 49,179.
(c) Updation: Updation target for the year 2010-11 is 25,215 against which 7914 items have been updated till November 30,2010.
Provision of Foreign Standards: The mandate of this Directorate is to be the central repository for all National and International Standards. This Directorae has received a number of requets for foreign standards from various Departments/organisations under the Ministry of Defence.
It has been decided to procure the highest demanded foreign standards like ASTM, ISO and BS from the concerned Standards Developing Organisations (SDOs). These standards will be dispensed to Defence users free of cost.
DIRECTORATE OF PLANNING & COORDINATION
The Directorate of Planning & Coordination was set up in 1964 with the primary objective of preparing overall plans for the production of defence equipment in the country. The Directorate functions as an attached office of the Department of Defence Production.
The Directorate also deals with major production programmes for armoured vehicles, arms, ammunition, shipbuilding and communication, as well as international cooperation and offsets.
=DEFENCE EXHIBITION ORGANISATION (DEO=)
The main function of DEO is to organise and co-ordinate Defence exhibitions in India and abroad, primarily with a view to promote the export potential of defence oriented products and services, developed and manufactured by the Indian Defence Industry.
DEO maintains a permanent Defence Exhibition at the Defence Pavilion, Pragati Maidan, New Delhi. Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs), Ordnance Factory Board (OFB), Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Directorate General of Quality Assurance (DGQA) and Directorate General of Aeronautical Quality Assurance (DGAQA) have displayed their products, innovations and services in this Exhibition.
India International Trade Fair (IITF): The Defence Pavilion also participates in the India International Trade Fair (IITF) held every year at Pragati Maidan, New Delhi during November 14-27. The Defence Pavilion has been awarded 8 Gold, 4 Silver, 3 Bronze and one Special Appreciation during the last 26 years. International Exhibitions in India: To provide a platform for the Indian Defence industry to showcase its capabilities, DEO organises two biennial international exhibitions in India, namely, the Aero India and the Defexpo India. While Aero India is dedicated to aerospace and aviation industry, the focus of Defexpo India is on land and naval systems.
Aero India: Aero India, first begun in 1996, has already carved a niche for itself as a premier aerospace and aviation exhibition in the international arena.
The Eighth edition of Aero India was organised from February 9 to 13, 2011 at the Air Force Station, Yelahanka, Bengaluru and has shown a growth of 40% in net area used by exhibitors over its previous edition with a participation of record number of 660 companies including 360 foreign companies.
Defexpo India: Conceived as a complementary exposition to Aero India, the Defexpo India was launched in 1999. The sixth edition of Defexpo India was held from February 15-18, 2010 at Pragati Maidan, New Delhi. 31 countries with more than 300 foreign companies and 350 domestic companies had participated. International Exhibitions Abroad: With a view to provide an impetus to export potential of Indian Defence Industry, DEO organizes "India Pavilion" for major defence products manufactured by them in the international exhibitions abroad. During the year, India participated in the Berlin Air Show-2010 to promote Aero India-2011. India participated in the Africa Aerospace & Defence exhibition (AAD- 2010) which was held from September 21-25, 2010 at Cape Town, South Africa. Participation in AAD-2010 overall was a great success.
National Institute for Research and Development in Defence Shipbuilding (NIRDESH)
Modern Naval platforms are complex and technology intensive and hence it is imperative that the country has the technological base and skill sets within, to design and develop them.
The Government has, therefore, set up the National Institute for Research and Development in Defence Shipbuilding (NIRDESH) to take the country towards selfreliance in this crucial area of defence technology. NIRDESH has been established as a Society under the Societies Registration Act and will be a part of the Department of Defence Production. NIRDESH will be funded by the Ministry of Defence and all the Defence Shipyards in the country.
Raksha Mantri (Defence Minister) laid the foundation stone on January 4, 2011 for NIRDESH at Chaliyam, near Kozhikode (Calicut), Kerala.
Raksha Mantri (Defence Minister) will head the Board of Governors as the President, with representations from the Ministry of Defence, Indian Navy, Coast Guard and Chairmen of Defence Shipyards as members.
RESETTLEMENT OF EX-SERVICEMEN
The Department of Ex-Servicemen Welfare (ESW) formulates various policies and programmes for the welfare and resettlement of Ex-Servicemen (ESM) in the country. The Department has two Divisions, viz., the Resettlement and the Pension, and it has 3 attached offices, namely, Secretariat of Kendriya Sainik Board (KSB), Directorate General (Resettlement) (DGR) and Central Organisation, Ex-servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS).
The KSB is responsible for the welfare of Ex-servicemen and their dependents and also for the administration of welfare funds; the office of Directorate General of Resettlement implements various policies/ schemes/ programmes like pre and post retirement training, re-employment, self employment etc. ECHS takes care of the health and medical needs of Ex-Servicemen and their dependents.
The main thrust of the Department of Ex-Servicemen Welfare is on resettlement/rehabilitation of Ex-Servicemen and their dependents. This is sought to be achieved through:
(a) Equipping Ex-Servicemen for suitable employment by imparting necessary training.
(b) Facilitating re-employment of the ESM in the Corporate/Government/Quasi Government Sectors and Public Sector Undertakings and also through Self Employment ventures.
Officers’ Training: DGR organizes short term courses of one to three months duration and a few courses up to six months duration for Ex-Servicemen Officers. Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs)/ Other Ranks (ORs) Equivalent Training: Resettlement Training Programmes for Junior Commissioned Officer Ranks are conducted in diversified fields for varying duration in government, semigovernment and private institutes spread all over the country.
Ex-Servicemen (ESM) Training: The scheme for Ex-Servicemen training is meant for those Ex-Servicemen who could not avail the facility of resettlement training while in service. It is also extended to the widow/ one dependent of an Ex- Servicemen.
RE-EMPLOYMENT OF EX-SERVICEMEN
The Central and State Governments provide a number of concessions to exservicemen for their re-employment in Central/ State Government Departments. These include reservation of posts/ relaxation in age and educational qualifications, exemption from payment of application/ examination fees and priority in employment to the disabled Ex-Servicemen and dependants of deceased service personnel on compassionate grounds.
Reservation in Government Jobs: The Central Government has provided for the following reservation for ESM:
(a) 10% in Group ‘C’ posts,
(b) 14.5% in Group ‘C’ and 24.5% in Group ‘D’ posts in Public Sector Undertakings and Nationalized Banks.
(c) 10% posts of Assistant Commandants in paramilitary forces.
(d) 100% in Defence Security Corps.
PLACEMENT
Persistent efforts of the Department for increasing awareness amongst the Corporate Sector on the availability of trained Ex-Servicemen have borne fruit and now major demands are coming from the Corporate Sector/PSUs. During the year 2010-11 (upto December 31, 2010), 52,271 ESM have gained employment.
SCHEMES FOR SELF-EMPLOYMENT
The Government has formulated several self-employment ventures for rehabilitation and resettlement of Ex-Servicemen and their families. The details of some schemes are given in the following paragraphs.
Allotment of Army Surplus Vehicles: Ex-Servicemen and widows of defence personnel, who died while in service, are eligible to apply for allotment of Army Surplus Class V-B vehicles.
Coal Transportation Scheme: This is a popular scheme in vogue for the last 30 years. At present, 89 Ex-Servicemen Coal Transporation Companies are in operation and through them, 267 Ex-Servicemen officers and approximately 3000 retired PBORs have benefited.
Coal Tipper Scheme: This is a welfare scheme for widows/disabled soldiers linked to the coal transportation Scheme.
Allotment of Oil Product Agency: Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas has reserved 8% of Oil Product Agencies, (i.e, LPG Distributorship, Petrol Pumps and Superior Kerosene Oil Distributorship etc.) for the defence category applicants who comprise of war/peace-time widows and disabled soldiers.
Mother Dairy Milk Booths and Fruit & Vegetable (Safal) shops: This is a time tested remunerative self-employment scheme for Ex-Servicemen PBORs. DGR sponsors eligible Ex-servicemen for this purpose to Mother Dairy. The scheme has now been extended to other cities of NCR, viz., Gurgaon, NOIDA, Faridabad and Ghaziabad. COCO retail outlets of IOC and BPCL: Employment is being provided by these two States-owned petroleum companies to Ex-Servicemen officers for managing their retail outlets under COCO scheme.
Management of CNG Station by ESM (Officers) in NCR: This scheme was operative only in the National Capital Territory of Delhi earlier which has now been extended to cover entire NCR including NOIDA, Faridabad and Gurgaon.
WELFARE
Raksha Mantri (Defence Minister) Discretionary Fund (RMDF): A portion of the earnings of Armed Forces Flag Day Fund is set apart as RMDF, which is used to provide financial assistance to needy Ex-Servicemen, widows and their wards for various purposes. Prime Minister's Scholarship Scheme: The aim of the scholarship is to encourage the wards of Ex-Servicemen / Widows to go for higher technical/professional education. Wards of Coast Guard personnel are also eligible. The scholarship is provided for the entire duration of the course Rs Rs. 1250 per month for boys and Rs 1500 for girls, paid annually.
See also
Defence production, India: 2 (ministry data)