Nuclear weapons testing: India
(→Pokhran-II) |
(→Pokhran I/ 1974) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
=Pokhran I/ 1974= | =Pokhran I/ 1974= | ||
==The events== | ==The events== | ||
| − | [https://www.indiatoday.in/education-today/gk-current-affairs/story/pokharan-i-324141-2016-05-18 Pokhran I: India's first ever hands-on with nuclear technology, May | + | [https://www.indiatoday.in/education-today/gk-current-affairs/story/pokharan-i-324141-2016-05-18 Pokhran I: India's first ever hands-on with nuclear technology, May 18, 2016: ''India Today''] |
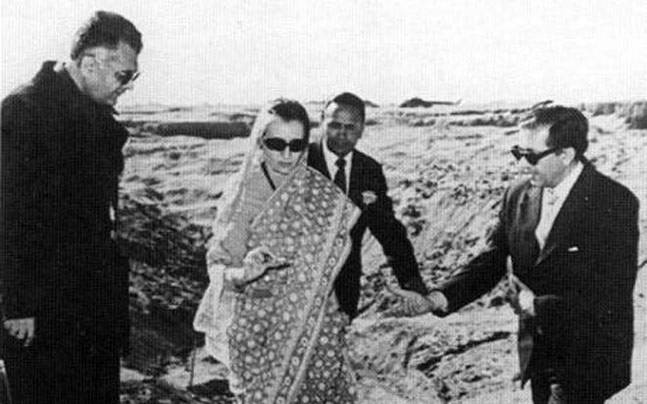
| − | [[File: Mrs. Indira Gandhi, the then Prime Minister overseeing the status (Pokhran- I).jpg|Mrs. Indira Gandhi, the then Prime Minister overseeing the status (Pokhran- I) <br/> From: [https://www.indiatoday.in/education-today/gk-current-affairs/story/pokharan-i-324141-2016-05-18 Pokhran I: India's first ever hands-on with nuclear technology, May | + | [[File: Mrs. Indira Gandhi, the then Prime Minister overseeing the status (Pokhran- I).jpg|Mrs. Indira Gandhi, the then Prime Minister overseeing the status (Pokhran- I) <br/> From: [https://www.indiatoday.in/education-today/gk-current-affairs/story/pokharan-i-324141-2016-05-18 Pokhran I: India's first ever hands-on with nuclear technology, May 18, 2016: ''India Today'']|frame|500px]] |
[[File: Pokhran-I, the test.jpg|Pokhran-I, the test <br/> From: [https://www.indiatoday.in/education-today/gk-current-affairs/story/pokharan-i-324141-2016-05-18 Pokhran I: India's first ever hands-on with nuclear technology, May 12, 2018: ''India Today'']|frame|500px]] | [[File: Pokhran-I, the test.jpg|Pokhran-I, the test <br/> From: [https://www.indiatoday.in/education-today/gk-current-affairs/story/pokharan-i-324141-2016-05-18 Pokhran I: India's first ever hands-on with nuclear technology, May 12, 2018: ''India Today'']|frame|500px]] | ||
Revision as of 19:32, 13 May 2018
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
From the archives of The Times of India
April 10, 2013
They are hostile neighbours widely seen by many as competing to have a bigger nuclear arsenal. However, after its first nuclear test in 1974, India offered to share nuclear technology with Pakistan. In her statement to Parliament after the tests on July 22, then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi said she had told her Pakistani counterpart, Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto, that New Delhi would be ready to share the relevant technology with Islamabad. Quoting her statement, the US embassy reported, as revealed by Wikileaks, “I have explained in my letter to Prime Minister Bhutto the peaceful nature and the economic purposes of this experiment and have also stated that India is willing to share her nuclear technology with Pakistan in the same way she is willing to share it with other countries, provided proper conditions for understanding and trust are created. I once again repeat this assurance.”
Sanjay, Rajiv vied to bag IAF deals
Rajiv and Sanjay Gandhi may have, during the Emergency, vied with each other as representatives in at least one of the most rewarding IAF contracts, US Embassy cables released by WikiLeaks suggest. While Maruti, controlled by Sanjay, was negotiating for British Aircraft Corporation to land two IAF contracts, Rajiv was working for Saab-Scania, whose Viggen aircraft was in the fray with Jaguar for one of the two projects.
Gandhi was bemused by int’l fallout after Pokhran
Indira Gandhi’s offer to share nuclear technology with Pakistan was extraordinary in its audacity, but equally in its foresight. The Indian offer came as her Pakistani counterpart Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto termed as insufficient Gandhi’s assurance that tests were not meant to harm Pakistan. In his response to Gandhi, Bhutto said, many past assurances from India “regrettably remain unhonored”. Testing a nuclear device is no different from detonation of a nuclear weapon, he wrote.
Pakistan first tested a nuclear weapon in May 1998 — a fortnight after India conducted its second nuclear test. But Gandhi’s offer to share nuclear technology with Pakistan was not the move of a potential nuclear proliferator. Instead, it showed the confidence of a leader who probably believed that India, after the test, could seamlessly become part of the international nuclear system, where New Delhi could become a legitimate nuclear supplier. Gandhi’s confidence, as it turned out, was misplaced. India was immediately placed under a tough technology denial regime. In fact, the Nuclear Suppliers Group was created as a result of the test precisely to keep countries like India beyond the pale. It took a hard-fought nuclear deal with the US to open that door for India in 2008.
But on July 22, 1974, Gandhi was looking ahead, and wanted to ensure that the craters formed by nuclear explosions could be used for strategic storage of oil and gas or even shale oil extraction. In her statement to Parliament, she seemed bemused by the international reaction to the first Pokharan test. “It was emphasized that activities in the field of peaceful nuclear explosion are essentially research and development programmes. Against this background, the government of India fails to understand why India is being criticized on the ground that the technology necessary for the peaceful nuclear explosion is no different from that necessary for weapons programme. No technology is evil in itself: it is the use that nations make of technology which determines its character. India does not accept the principle of apartheid in any matter and technology is no exception.”
Pokhran I/ 1974
The events
Pokhran I: India's first ever hands-on with nuclear technology, May 18, 2016: India Today

From: Pokhran I: India's first ever hands-on with nuclear technology, May 18, 2016: India Today

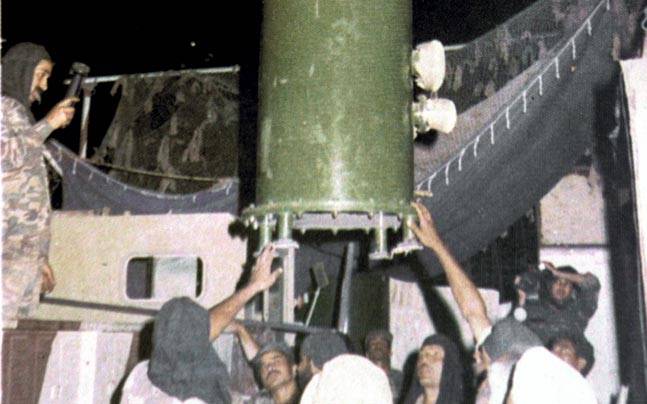
From: Pokhran I: India's first ever hands-on with nuclear technology, May 12, 2018: India Today
The day was May 18 in the year 1974. On this day, the Indian government conducted its first nuclear test in the deserts of Pokhran, Rajasthan making it a peaceful nuclear explosion. Smiling Buddha (MEA designation: Pokhran-I) was the assigned code name of India's first successful nuclear bomb test.
With the Smiling Buddha, India became the world's sixth nuclear power after the United States, Soviet Union, Britain, France and China to successfully test out a nuclear bomb.
Here is the history and aftermath of the nuclear test:
India started its own nuclear program in 1944
Physicist Raja Ramanna expanded and supervised scientific research on nuclear weapons and was the first directing officer of a small team of scientists that supervised and carried out the tests The name Pokhran came from the place it was tested which is a city of the same name located in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan.
A team of 75 scientists and engineers, led by Raja Ramanna, PK Iyengar, Rajagopala Chidambaram and others had worked on it from 1967 to 1974 The test was a success but the aftermath of the nuclear test was not an encouraging one
The test became the center of attention as there was widespread outrage and concern over the move since this nuclear bomb was tested by the country, which was outside the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council, and the experiments took place without any warning to the international community
As a result, the US took offense to India barging into the nuclear society without any warning and then, blocked aid to India and imposed numerous sanctions
The device tested was a fission device and there had been no release of radioactivity in the atmosphere Although, India has still not joined the 1970 nuclear non-proliferation treaty, claiming that the nuclear tests were for peaceful reasons, the nuclear deal between India and the United States showed that India's status as a responsible nuclear power has been accepted by the rest of the world.
Interested in General Knowledge and Current Affairs? Click here to stay informed and know what is happening around the world with our G.K. and Current Affairs section.
To get more updates on Current Affairs, send in your query by mail to education.intoday@gmail.com
Pokhran-II
The events
India Today.in , Building up a nuclear muscle “India Today” 15/12/2016
1998
Pokhran-II
On May 13, 1998, Prime Minister Atal Behari Vajpayee announced India's new status as the world's sixth nuclear weapons armed power. Two days before the prime minister's announcement, on May 11, 'Operation Shakti' had been initiated. India had stunned-and somewhat alarmed-the world community with a series of five nuclear weapons tests. The weapons were of three different kinds-one fusion or thermonuclear weapon, two fission devices and two sub-kiloton devices-which indicated the flexibility and range of India's nuclear arsenal, slowly built up over the years. Pokhran-II was the first Indian test of a nuclear weapon since 1974. Post-1974, bomb technology had been placed on the backburner, until Pakistan came close to acquiring a nuclear weapon with Chinese assistance. Faced with the twin threats of a Chinese and Pakistani nuclear weapons arsenal and a closing global window-the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty was opened for signatures in 1996-the strategic community was left with no other option but to hit the test button.
2017/ number of nuclear weapons tested
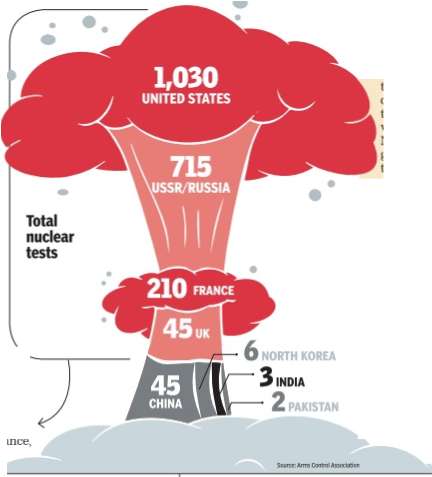
From: November 6, 2017: The Times of India
See graphic:
Nuclear weapons tested by India, Pakistan and other countries, till Nov 2017
See also
Pakistan- India economic relations
Pakistan- India: Cease-fire and its violations
Nuclear weapons testing: India- Pakistan
Nuclear arsenals: India, Pakistan
and many more articles, especially about the 1965 and 1971 wars, The Kargil war of 1999, 1947...
